BNNS502 Exam 2 Adrenergic & Cholinergic receptors
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
location of B2 adrenergic receptors
smooth muscle of:
lungs
liver
uterus
location of B1 adrenergic receptors
cardiac muscle
The location of a2 adrenergic receptors is
platelets,
smooth muscle in blood vessels,
sweat glands
Name the 4 different adrenergic receptors
alpha 1
alpha 2
beta 1
beta 2
two types of cholinergic receptors
nicotinic and muscarinic
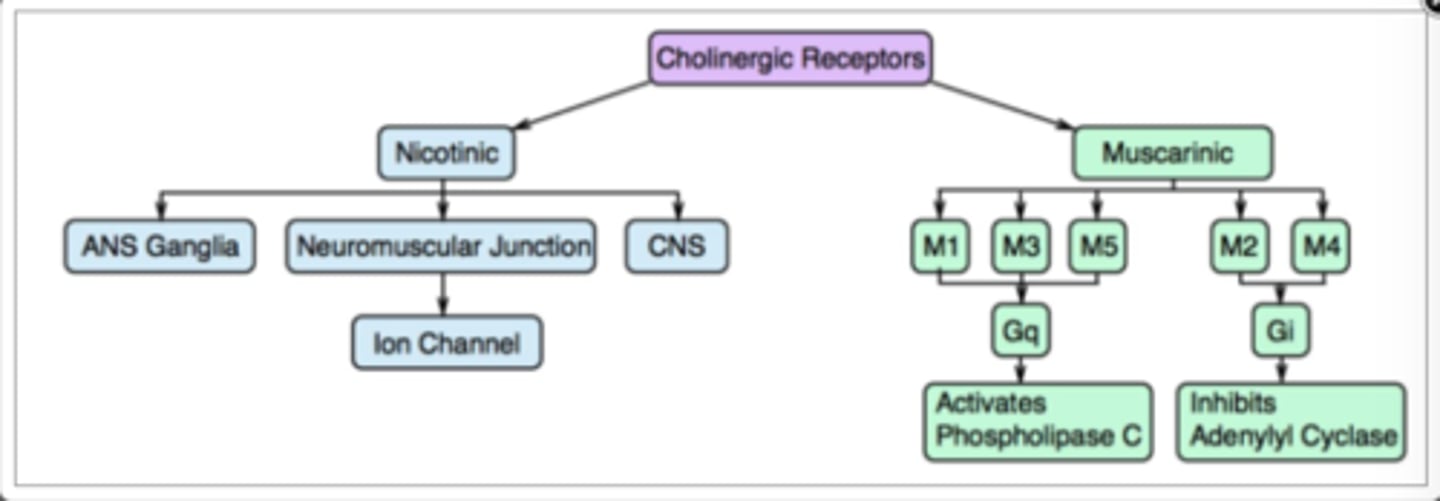
location of muscarinic cholinergic receptors
P.N.S effectors,
Sweat glands,
Skeletal muscle blood vessels
location of nicotinic cholinergic receptors
cells of adrenal medullae (secretion of adrenaline & noradrenaline),
Neuromuscular end plates of Skeletal muscles (contraction)
cholinergic neurotransmitter
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Muscarinic agonists
Stimulate the parasympathetic response
Muscarnic receptor antagonists
block the parasympathetic response
increased heart rate
sympathetic
1 multiple choice option
decreased blood pressure
parasympathetic
1 multiple choice option
bronchodilation
sympathetic
1 multiple choice option
Decreased GI motility
sympathetic
1 multiple choice option
dilated pupils
sympathetic
1 multiple choice option
Increased secretion of adrenaline
S.N.S
1 multiple choice option
urge to urinate
parasympathetic
1 multiple choice option
SLUDD (Parasympathetic responses)
salivation, lacrimation, urination, digestion, defecation
3 decreases of the parasympathetic system
- decreased heart rate
- decreased diameter of airways
- decreased pupil diameter
The neurotransmitter that activates the cells of liver, causing glycogenolysis is
Adrenaline
The receptors located on the cells of the adrenal medulla are
nicotinic
The drug metoprolol is a β1 antagonist. The effect of this medication is to
Decrease BP
The drug salbutamol is a β2 agonist. The effect of this medication is to
Increase bronchodilation
A muscarinic receptor antagonist drug will
block cholinergic receptors.
Nicotinic receptors are located on
adrenal medullae and skeletal muscles
Name the neurotransmitter or hormone involved with Adrenergic receptors
Adrenaline
Noradrenaline
The location of a1 adrenergic receptors is
smooth muscles in blood vessels and iris
Alpha 1 stimulation causes
vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels,
pupil dilation
Alpha 2 stimulation causes:
platelet aggregation, dilation of smooth muscle, increased sweating
Beta 2 stimulation causes
bronchodilation
uterine relaxation
glycogenolysis
Beta 1 stimulation causes
increase heart rate and contractility
Agonist
a molecule that, by binding to a receptor site, stimulates a response
Antagonist
binds to and blocks receptors to prevent a natural neurotransmitter or hormone from stimulating an effect
The effects of a betablocker medication
decreased:
heart rate,
blood pressure,
myocardial contractility,
bronchoconstriction
adrenoreceptor agonist medication
adrenalin
adrenoreceptor agonist effects
enhanced sympathetic activity
increased
adrenalin secretion,
heart rate,
blood pressure,
dilation of
bronchioles
pupils
decreased motility
Would anticholinergic medications be considered agonist or antagonist?
Antagonist
They block receptors for ACh thus inhibiting the effect of ACh
Effects of anticholinergic medications
Decreased skeletal muscle contraction and adrenaline/noradrenaline secretion