Genetics - quantitative traits and population genetics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are quantitative traits?
Traits that vary continuously - height, weight, etc
What determines the expression of quantitative traits?
Controlled by the effects of multiple genes and alleles
Also affected by environmental influences
What are the three types of polygenic traits?
Metric - continuous scale
Meristic - discrete scale
Threshold - present or absent beyond a certain value
All three are based on the theoretical assumption of an underlying normal distribution
What fields are quantitative traits particularly important in?
Medicine
Agriculture
Conservation
How are quantitative traits important in medicine?
Susceptibility to disease
Complex disorders caused by multiple genetic and environmental factors
Understanding genetic vs environmental causes
Prevention of diseases
Genetic counselling
Genetically tailored treatments
How are quantitative traits important in agriculture?
Economically important traits are quantitative
Quantitative genetics theory and the basis for selective breeding
Environmental variation reduces efficiency of selection
What factors contribute to phenotypic variation?
Vp = Vg + Ve + Vge
Vp - phenotypic variation
Vg - genetic variation
Ve - environmental variation
Vge - genetic + environmental interaction variation
What factors contribute to genetic variance?
Vg = Va + Vd + Vi
Vg - genetic variance
Va - variance due to additive effects
Vd - variance due to dominance
Vi - variance due to epistasis
What is variance due to additive effects (Va) and how does it affect variance?
Portion of genotypic variance that results from the additive effects of alleles where each allele contributes independently
Each allele’s effect on the phenotype does not depend on any other allele within the gene or in another gene
What is variance due to dominance effects (Vd) and what effect does it have on variance?
Portion of genotypic variance that results from the non-additive interaction between alternative alleles in the same gene
Each allele’s effect on the phenotype depends on the other alleles within the gene
What is variance due to epistasis (Vi) and what effect does it have on variance?
Portion of phenotypic variation that results from the non-additive interaction between different genes
Each allele’s effect on phenotype depends on genotype in other genes
How does meiosis change associations between alleles?
Can make it difficult to select for phenotypes that rely on dominance and epistatic effects
Additive genetic effects on the phenotype are independent of other alleles so recombination will not break up favourable allele combinations within and between genes
What are the two types of heritability?
Broad sense heritability
Narrow sense heritability
What does broad sense heritability measure?
Measures the importance of genetic variation relative to total variation in the phenotype
Tells how much is related to genetics and how much to the environment
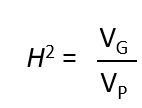
What does narrow sense heritability measure?
Measures the importance of additive genetic variation or variation due to the alleles in the population relative to total variation in phenotypic variation
Tells us how much is additive and how much is environmental
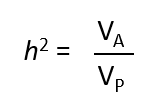
What can heritability be used to predict?
To predict change in the population mean under selection (natural or artificial)
When h² increases the response to selection increases
How can heritability vary?
Changes when a population is moved between environments
Heritability for the same trait can vary between populations even if they are in the same environment
What is the Infinitesimal Model?
Simple model of the inheritance of quantitative traits which assumes an infinite number of unlinked loci with an infinitesimal effect each
Infinite number of genes controlling a phenotypic trait each with a very small effect
What does population genetics theory state?
The frequency of alleles and genotypes in a population will remain constant unless acted upon by mechanisms of evolution
Equilibrium = no evolution
What is the Hardy-Weinberg equation for two alleles?
p + q = 1
p - frequency of one allele (usually dominant)
q - frequency of another allele (usually recessive)
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
p² - proportion of population homozygous for the first allele
2pq - proportion of population that is heterozygous
q² - proportion of population homozygous for the second allele
What are the assumptions of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
Organisms are diploid, mating and have discrete generations
Allele frequencies are the same in each individual
Mendelian segregation occurs
Mating occurs at random
Population size is large so has no genetic drift
No gene flow by immigration or emigration
No mutation
No selection
What is linkage disequilibrium?
Deviations from the expectations of independent segregation and Hardy-Weinberg caused by physical linkage or population demography
eg genetic bottleneck events