clinical chem 2
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
influence:
\-cellular repair
\-cell maintenance
\-protein biological activity
\-carboxyl group
\-differ by R group
\
nonessential: naturally occuring
\-synthesis of non-protein nitrogen containing compounds
\-energy source
\
\
\
absence of enzyme needed to create cofactor for PAH (have it but can’t make it work)
symptoms and testing
Required test on newborn screening
\-type 1 most severe
\-all enzyme mutations
Low-protein diet \n Medication
\
Turns urine brown/black in presence of oxygen
deposits in cartilage of ears, nose, and tendons of \n extremities \n • Dark blue-black pigmentation (ochronosis)
\
Testing: \n • Modified Guthrie Test \n • Microfluorometric assay
\
type 1: lack enzyme, accumulate ammonia in urine
type 2: mutation in gene for transport protein
color change
\-heparin tube
\-non-hemolyzed
\-deproteinized
\-immediate testing or frozen
\-urine is random on 24hr specimen
\
\
\
\
arginine (Arg)
conversion of ammonia into urea
histidine (his)
precursor to histamine
isoleucine (ilu), leucine (leu), valine (val)
branched chain amino acid
isoleucine
hemoglobin formation
leucine
optimal infant growth
valine
treatment for muscle, mental, and emotional problems
lysine (lys)
basic pH
function:
-antibody production
-triglyceride lower
methionine (met)
innate translation of mRNA
phenylalanine (phe)
promote alertness, mood elevation
threonine (thr)
collagen, elastin, and tooth enamel
tryptophan (trp)
precursor for serotonin,melatonin, and niacin
relaxant
alanine (ala)
-transfer of nitrogens from peripheral tissues to liver
-production of antibodies
-reduction of toxic substance build up
asparagine (asn)
-transport of nitrogen
-conversion of one amino acid into another
aspartic acid (asp)
-precursor for other amino acids
-generation of glucose from non sugar substrates
cysteine (cys)
not to be confused with cystine
-potentially toxic
-structural and functional component of many proteins and enzymes
glutamic acid (glu)
-Glutamate
-net negative charge by pH (polar)
-neurotransmitter
glutamine (gln)
-most abundant in the body
-transport ammonia to liver
proline (pro)
-strengthening of joints,, tendons, and cardiac tissue
-works with vitamin C to promote healthy connective tissue
glycine (gly)
-synthesis of numerous important compounds in the body
-slow muscle degeneration
-improve glycogen storage
serine (ser)
-metabolism of lipids and fatty acids
-protect myelin sheaths
tyrosine (tyr)
-precursor of adrenal hormones (epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine)
protein simple functions
-energy
-colloidal osmotic pressure
-buffers
-protection
-hemostasis
protein functions advanced
-catalyze biochemical reactions (enzymes) for glycolytic pathway and dna replications/polymerase
-transporter (hemoglobin, lactose permease)
-receptors for hormones
-cell structure and support (collagen and keratin)
-immunity (antibodies)
-motion (myosin and actin)
-storage (ferritin)
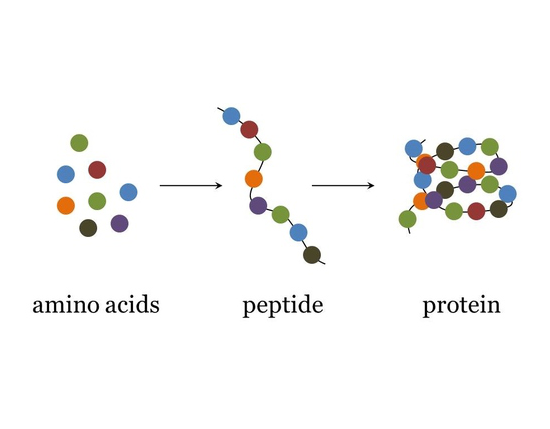
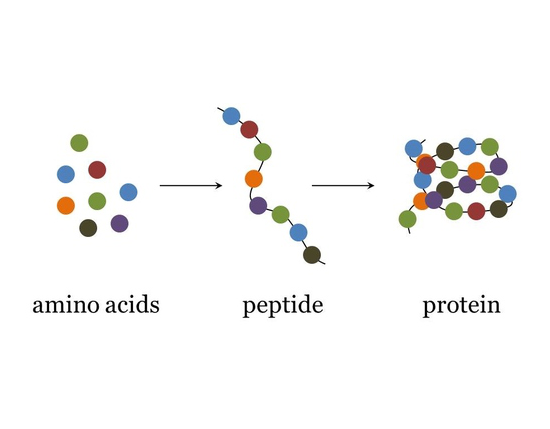
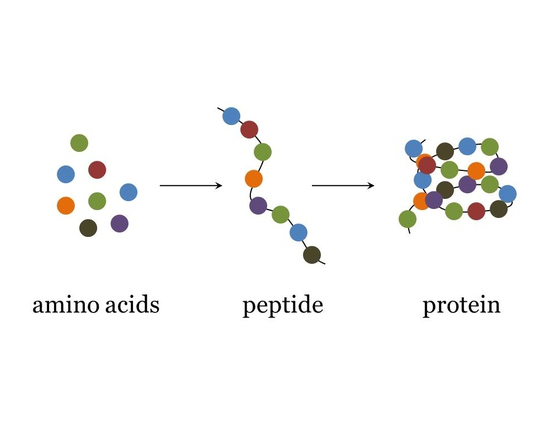
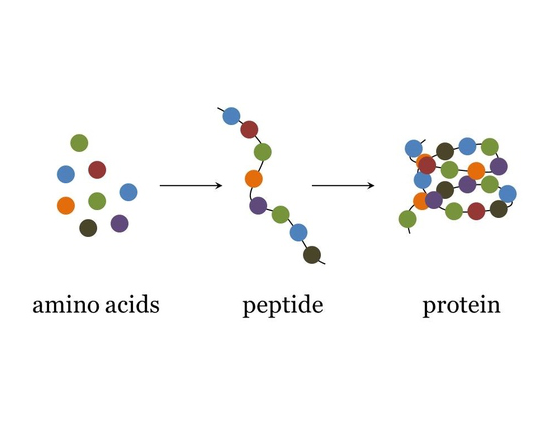
protein consists of
carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen*, and sulfer
polymers made from one or more unbranched chains of amino acids (peptide bonds)- some are small some are big
peptides
small condensation of amino acids
small in comparison to proteins
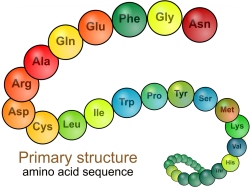
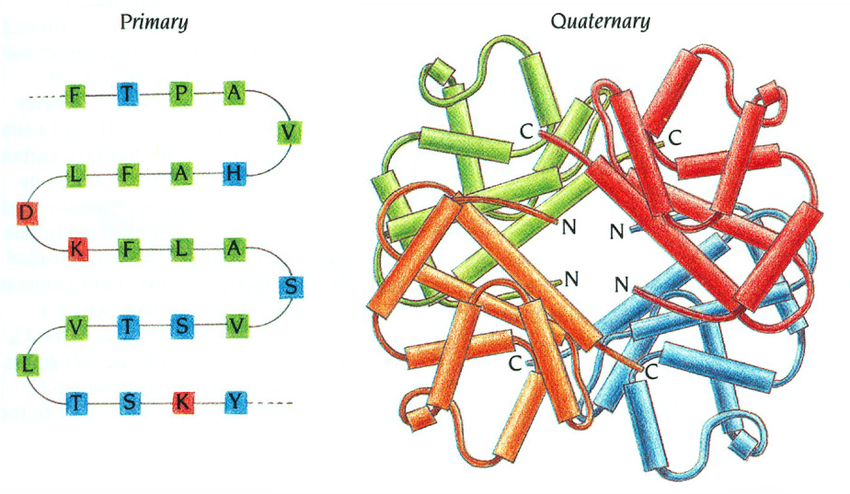
primary
simplest structure cannot be broken down
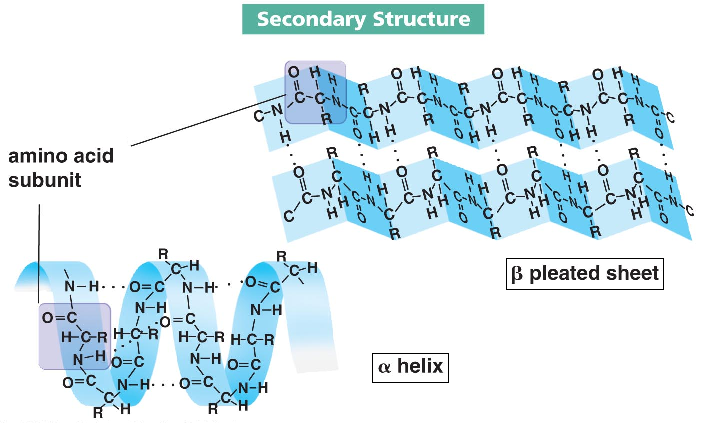
tertiary amino acid

secondary amino acid
quaternary amino acid
denaturation
break down and destruction of molecular aspects
protein synthesis done in the
liver
antibodies made in
plasma cells
protein synthesis is equal to
protein catabolism (protein build up and break down)
diurnal rhythm
increased during day (when eating)
decreased during night (when not eating)
hormones that control protein synthesis
-thyroxine
-growth hormone
-insulin
-testosterone
protein digested in
digestive tract, kidneys, and liver
protein digestions process
hydrolyzed amino acids
nitrogen
nitrogen balance
(N Usage)/(N Intake) = Excretion
negative balance
(N Usage)/(N Intake) < Excretion
positive balance
(N Usage)/(N Intake) > Excretion
protein break down results into
ammonia and ketoacids
protein classification
-simple or conjugated
-function
-composition
-migration in electrical field (electrophoresis)
-centrifuge (density)
-size
-location
simple proteins
yield amino acids
conjugated proteins
simple proteins combined with some nonprotein material in body
apo protein
forms a particular biochemical molecule such as a hormone or enzyme
amphoteric
either acid or base
pH>pi
protein will be negatively charged
pH<pi
protein will be positively charged
proteins least soluble at
isoelectric point
protein is found in all body fluids but the lab is focused on
-serum
-urine
-csf
plasma proteins
most frequently analyzed of all proteins
total protein equation
total protein= albumin + globulins
total nitrogen
measures all chemically bound nitrogen in specimen performed on various sample types
total protein concentration on reference range
concentration lower at birth
reference interval: 6.5-8.3 g/dL
kjeldahl method
sample is digested with acid to convert nitrogen in the protein to ammonium ion
-very accurate and precise
-but time consuming, inconvenient, and impractical for routine use
biuret method
widely used and easily automated
-cupric ions (Cu+2) bind to components in peptide bonds
-in presence of an alkaline medium, and minimum of 2 peptide bonds, a color change from blue to violet occurs
-can be affected slightly by bilirubin or lipemia, and the presence of proline
in biuret method absorbance is is proportional to what bonds
peptides
dye-binding method
-based on the ability of most serum proteins to bind to dyes
-dyes are used to stain the proteins after electrophoresis
-calibration can be difficult to define
-good sensitivity and low interference from small compounds
dye-binding method : coomassie brilliant blue 250 shifts the absorbance maximum of the dye from 465→
595 nm
refractometry
technique that measures how light is refracted when it passes through a given substance
-simple, quick, requires small volume
-not as accurate for nitrogen proteins
refractometer protein range
<3.5 g/dL