Control rods, drives, and switches
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is a Control Rod?
A rod made of a material with a high neutron absorption cross section that prevents neutrons from causing chain reactions to help control the reactivity within the core
What are the names, core locations, motor speeds and worths of each rod (last calculated)
Shim: Pos C9, speed=11 in/min, rod worth = $2.60
Safe: Pos C5, speed=19 in/min, rod worth = $2.19
Reg: Pos E4, speed=21 in/min, rod worth = $1.20
Give rod dimensions and composition.
sealed aluminum tubes containing powdered boron carbide
They are 1.25 in. outer diameter, The upper end of each of the three control rods is a male, threaded 1/2-13 connection, which screws into the extension rod that is connected to the control-rod drive assembly at the top of the reactor tank. All control rods are approximately 20 in. long and have a vertical travel of approximately 15 in.
What are the different parts of the control rods system?
Control rod tube guides:
The tubes are supported from the lower grid plate and are laterally positioned by both grid plates; they extend approximately 10.25 inches (26 cm) above the top grid plate.
The guide-tube assembly is made of anodized aluminum to increase resistance to wear and corrosion.
Rods:
Top of tube is threaded (see dimensions) and attaches to the control rod drive assembly at the top of the reactor tank.
A 3⁄32-inch (0.24 cm) diameter pin, which is inserted through the lower extension rod and into the threaded upper end of the control rod, prevents the parts from working loose.
In a similar fashion, 1⁄4-inch (0.64 cm) diameter pins are used in the connection of the upper and lower extension rods. All control rods are approximately 20 inches (51 cm) long and have a vertical travel of approximately 15 inches (38 cm).
Drives:
The drive assemblies for the control rods are fastened to a mounting plate located on the center channel.
Electrical connectors are provided on the bridge to permit easy disconnection and removal of a rod drive.
Rack-and-pinion drives (Figure 3.8) are used to position the control rods. Each drive consists of an
asynchronous, reversible motor,
a magnet rod-coupler,
a rack-and-pinion-gear system, and
a ten-turn potentiometer which provides an indication of rod position.
When the electromagnet attached to the draw tube is energized, the armature and connecting rod rise with the draw tube, and the control rod is withdrawn from the reactor core. When the reactor is scrammed, the electromagnet is deenergized and the armature is released.
Electrical dynamic braking and static braking on the motors are used to provide fast stops and to limit coasting or over-travel.
Three limit switches on each motor provide information about the position of the motor and the control rod.
How are control rods inspections performed? (List precautions and schedule and prep)
Full staffing required since reactor is not shut down
SRO is inspector because this is tech spec req
Wear water full body water resistant coveralls and gloves while handling, monitor pool for radioactivity
Inspect one at a time and replace in core before next
Fuel must be moved to remove control rod
Don’t let anything fall into pool. Secure things to bridge railings if necessary
Inspect visually 2 years. Typically after fuel inspec and b4 control rod calibrations
get 1 copy SOP 34B and 3 copies SOP 34C
How are control rods inspections performed? (Beginning of day)
Start up checklist per SOP 20 w/out core excess
Perform fuel handling checklist per SOP 35 and mark as done on appendix b
Move 2 elements from b ring and 2 from c ring per 35
Turn off console and mark as done on B
Unplug all 3 console to rod drive motor plugs: J7 (reg), J8(shim), J10 (safe). Mark as done on B
Unplug 36 pin Centronics parallel connector behind north panel of console, mark on B
Checker and SRO sign beginning of day section
How are control rods inspections performed?
Ensure clear communitcation and minimize other talking and noise in bay.
Get full staffing, inspecting SRO in bay, 2 cr handlers, clean person.
Obtain 2 walkie talkies, bucket for fasteners and small tools, 3/32 allen head screwdriver, 2 cresent wrenches, and optional floating pool window
Attatch bucket to bridge railing or place far from pool
Remove rod down actuator cotter pin, nut and actuating washer from pull rod
Unplug position indication for rod being removed at potentiometer at side of motor.
If reg unplug motor supply
Remove small screws, not large bolts from upper edge of base mount.
Lift rod motor off and place on floor.
Make sure operator is at console
Lift the guide barrel up through the base mount, thereby lifting the connecting rod. This is done by reaching inside the barrel from the top and lifting up. As the rod is raised, be sure that someone watches the UPPER part of the rod as it approaches the region of the ceiling lights. Have someone watch the LOWER part of the rod to ensure it doesn’t hit other control rods or the central thimble.
Operator logs cr removed from core
Lift rod high enough to permit removal of top of rod extension via undoing bolts and nuts. Have someone hold lower cr when they are removed and helpful to have someone hold top
rod, pass it down through the control rod opening on the bridge and hand it out under the bridge. This will allow removal of the control rod from the pool (the ceiling is too low to pull it straight out the opening in the bridge).
Monitor area with dose rate meter and place rod on absorbant paper
Inspect for scratches and wear, use caliper to measure diameter at top bottom and center, compare to wear and previous measurements
Take picures of the rod with a sign saying rod and year to put in drive
Replace rod if deteriorated
REverse removal process to reinstall
What type of motor does each of the control rods have? Explain.
All three rod motors are asynchronous (induction) and electrically reversible. The Reg rod is a five phase stepper motor.
Balancing potentiometers to make rod move on set axis without moving side to side, also helps cancel gravity. These motors are the rack and pinion motors
10 turn poteniometer provides rod location
5 phase stepper is what allows us to have autorod

What provides an indication of rod position for each? Explain.
The 10 turn potentiometers when turned 1/10th of their total there’s a thing that inicates how far it turned so that sends a signal to the console that says the rod moved 10%
How do we get Rod Height Indication on the console?
Rod position is indicated by a ten-turn potentiometer that sends motor position indication to the console. Position is indicated in percentage of total travel.
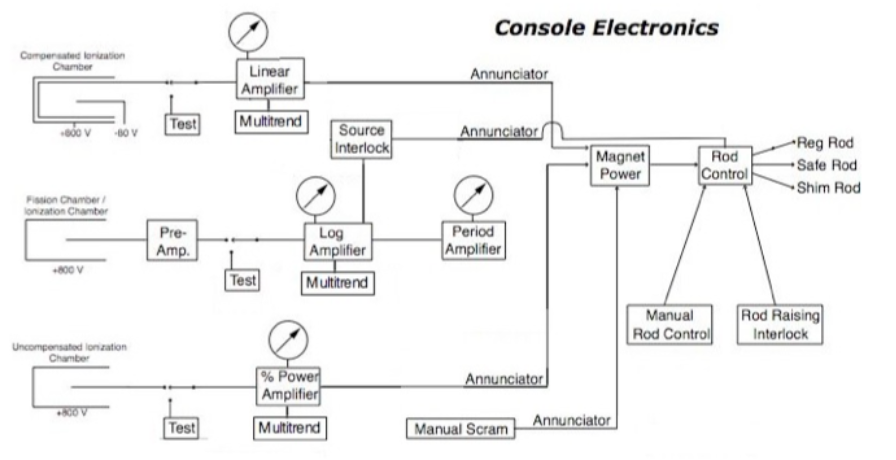
What about Multitrend?
2.5.8 Multitrend The multitrend is a computer system that visually displays current and past readouts of console information, including current and past power channel readouts, rod heights, pool levels, and pool temperatures.
Pool temp via thermocouples, pool level via the pool bat, power channels through their detection pulses/currents, rod height via already discussed
What are limit switches?
communication between console and control rods. These limit switches light the rod control pushbuttons at the motor up and motor down positions and turn off the contact light if the rod down and motor down switches do not agree.
What types of limit switches are there?
Motor up, motor down, rod down
When is each of the limit switches actuated and not actuated?
Up when motor is fully up, down when motor is fully down, down when rod is fully down
What is Dashpot action and why is it important?
Dashpot action is the cushioning effect of the water struggling to escape increasingly smaller holes down the control rod.
Discuss different SCRAMs and what electronic relationships cause them.
High power scram at 99% of range [TS 3.2.3: 275 kW or less] for linear
High power scram at 99% of range [TS 3.2.3: 275 kW or less] for percent
Loss of high voltage scram <0.7 kV [TS 3.2.3] through linear
Manual scram from button on console
Discuss associated Tech Specs [Definitions: Control Rod, Reg Rod and Shim/Safety Rod]
Control Rod: A device fabricated from neutron absorbing material which is used to establish neutron flux changes and to compensate for routine reactivity changes. A control rod may be coupled to its drive unit allowing it to perform a safety function when the coupling is disengaged.
Types of control rods shall include:
Regulating Rod (Reg Rod): The regulating rod is a control rod having an electric motor drive and scram capabilities. Its position may be varied manually or by the servocontroller.
Shim/Safety Rod: A shim/safety rod is a control rod having an electric motor drive and scram capabilities. Its position is varied manually.
Discuss associated Tech Specs [3.2.1,]
Applicability. This specification applies to the function of the control rods.
Objective. The objective is to determine that the control rods are operable.
Specifications. The reactor shall not be operated if any control rod is not operable. Control rods
shall not be considered operable if:
a. Damage is apparent to the rod or rod drive assembly;
b. The scram time exceeds 1 second; or
c. The reactivity addition rate exceeds $0.16 per second.
Tech spec 3.2.3
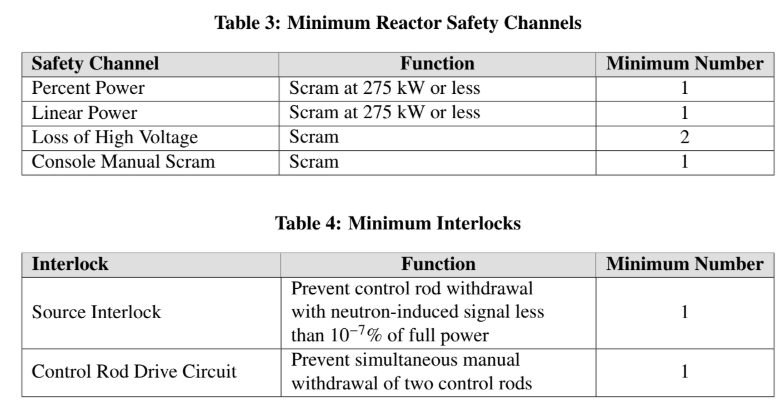
Reactor Safety Systems and Interlocks
Applicability. This specification applies to the reactor safety system channels and interlocks.
Objective. The objective is to specify the minimum number of reactor safety system channels
and interlocks that shall be available to the operator to ensure safe operation of the reactor.
Specifications. The reactor shall not be operated unless the minimum number of safety channels described in Table 3 and interlocks described in Table 4 are operable.
Tech spec 4.2
4.2 Reactor Control and Safety Systems
Applicability. This specification applies to the surveillance requirements of reactor control and
safety systems.
Objective. The objective is to verify performance and operability of those systems and
components that are directly related to reactor safety.
Specifications.
a. The control rod drives shall be visually inspected for damage or deterioration annually.
b. The poison sections of the control rods shall be visually inspected for damage or deterioration biennially.
c. The control rod scram time shall be measured annually.
d. The total reactivity worth and reactivity addition rate of each control rod shall be measured annually or following any significant change (>$0.25) from a reference core.
e. A channel check of each of the reactor power measuring channels in TS 3.2.2, Table 2 shall be performed prior to each operation of the reactor.
f. A channel calibration of the Linear and Percent Power Channels in TS 3.2.2, Table 2, shall be performed annually.
g. A channel test of each item in TS 3.2.3, Tables 3 and 4, shall be performed annually.
Tech spec 5.3.1
5.3.1 Reactor Core
Applicability. This specification applies to the configuration of fuel and in-core experiments.
Objective. The objective is to ensure that provisions are made to restrict the arrangement of fuel
elements and experiments so as to provide assurance that excessive power densities shall not be produced.
Specifications.
a. The core assembly shall consist of stainless steel clad 8.5/20 TRIGA® fuel elements.
b. The fuel shall be arranged in a close-packed configuration except for single element positions occupied by in-core experiments, irradiation facilities, graphite dummies, control rods, startup sources, or central thimble.
c. The reflector, excluding experiments and irradiation facilities, shall be water and graphite.
d. Fuel shall not be removed from or inserted into the core unless the reactor is subcritical by more than the calculated worth of the most reactive fuel element.
e. Control rods shall not be removed manually from the core unless the core has been shown to be subcritical with all control rods fully withdrawn from the core.
Tech spec 5.3.2
Applicability. This specification applies to the control rods used in the reactor core.
Objective. The objective is to ensure that the control rods are of such a design as to permit their use with a high degree of reliability with respect to their physical and nuclear characteristics.
Specifications. The control rods shall have scram capabilities and the poison section shall contain borated graphite, B4C powder, or boron and its compounds in solid form as poison in an aluminum or stainless steel cladding.
What is Core Excess?
Positive reactivity; the amount by which keff >1 when control rods are fully withdrawn. Measured by worth of control rods not yet withdrawn from core when keff=1. Generally core excess at 5W is $1.23
What is Shut-Down Margin (SDM)?
Amount of reactivity by which reactor is subcritical (keff<1) when all control rods are fully inserted/reactor is shut down. By Technical Specifications, shutdown margin is measured with the highest worth control rod not inserted.
Shut down condition is subcrit by at leas 1$
Relation between core excess and shutdown margin
Inverse of each other
What is PNTC?
the prompt negative temperature coefficient.
Reactors use moderators to make fission more efficient because they slow fast neutrons to thermal levels. Our reactor (and other TRIGA reactors) are extra safe because of PNTC ● If the reactor was over moderated, adding heat would decrease the moderator-to-fuel ratio; this would add positive reactivity to the reactor (which can be dangerous) ● In an under moderated reactor like ours, the same change in moderator-to-fuel ratio adds negative reactivity (yay!)
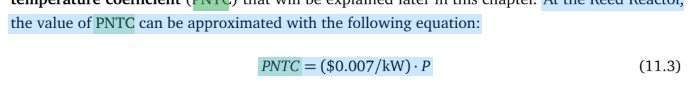
What are the 3 factors of PNTC that are applicable to our reactor?
Define them and explain in which ways they affect our reactor.
1. the cell effect (a ZrH temperature increase ejects neutrons from the fuel to the moderator),
2. Doppler broadening:U-238 absorbs neutrons through resonance (p in the 6FF) ● when fuel heats up, atoms are vibrating, so it takes less energy for U-238 to absorb neutrons ■ U-238 resonance peaks broaden! (a fuel temperature increase produces Doppler broadening affecting resonance escape), and
3. leakage effects/moderator expansion: water expands as it heats which lowers probability of interaction with it (a moderator temperature increase reduces the non-leakage and resonance escape probabilities).
Explain Subcritical Multiplication and the related plots
subcritical multiplication or the multiplication of source neutrons in a subcritical reactor.
Formula found through C= S(1/1-keff) where C is number neutrons produced in each gen and S is neutrons emmitted by source per generation. Rearrange formula for keff. Then it can be seen for criticality 1/M needs to approach 0.
For crit load experiement: add neutron source and detector into core. Add a small amount of fuel and calculate 1/M. Then extend line to x intercept to predict fuel to become critical. Then add about half the remaining fuel till criticality and repeat the process until you have a good estimate of how much fuel to criticality.
Equation only valuable when reactor is subcritical.
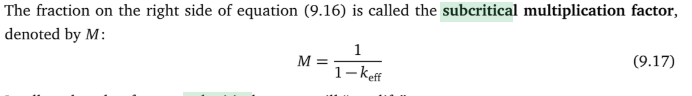
Describe effects of Xenon. How is it produced? Can it be removed from the core and how?
fission products with large neutron absorption cross sections. Decrease reactivity, neturon poison

Describe the effects of Samarium. How is it produced? Can it be removed from the core and how?
