C8 Chemical Analysis
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Purity
contains only one compound or element
How does the boiling/ melting point tell you how pure a substance is?
pure substance will boil/melt at a specific temperature
test by measuring bpt and comparing to boiling point of the substance form a data book
closer the value is to the actual value the more purer the substance
impurities will lower the melting point/ increase bpt and increase the melting range
Formulations
useful mixture with a precise purpose made by following a formula
useful mixture of compound and substances that do not react together
produce a useful and desirable characteristics or properties to suit a particular function
medicine- altering the formulation ensures the drug is delivered to the correct part of body at the right concentration
Chromatography
method used to separate mixtures of soluble substances and to identify substances
Mobile Phase
Stationary Phase
where the molecules can move - liquid or gas - solvent (water)
where the molecules cant move- solid or thick liquid chromatography
During Chromatography the substances in the sample ..
The ____ moves through the …
constantly move between mobile and stationary phase to form an equilibrium between the two phases
mobile phase
stationary phase and anything dissolved in the mobile phase moves with it
What determines how quickly a chemical moves in chromatography?
how it’s distributed between the phases - more time in the mobile phase than stationary phase will move further.
Chromatography
where do components normally separate ?
stationary phase
Why might the number of spots change?
different solvents because the distribution of the chemicals will change
pure substance only 1 spot because only one substance
why does the time each molecule spends in each phase depend on?
how soluble they are in the solvent
how attracted to the paper they are
molecules with higher solubility and less attracted to paper will spend more time in mobile phase - further up the paper.
rf value
distance travelled by substance (Baseline to centre of spot) / distance travelled by solvent
Why is chromatography carried out?
to see if a certain substance is present in a mixture
run a pure sample of that substance alongside the unknown mixture . If rf values of the reference and one of the spots in the mixture match the substance may be present
rf value is dependent on the solvent . If the solvent changes so will the rf value
Chromotography required practical
draw a pencil line across the chromatography paper, 1 - 2 cm from the bottom
use a pipette to add small spots of each ink to the line on the paper
place the paper into a container with a suitable solvent in the bottom
allow the solvent to move through the paper, but remove the chromatogram before it reaches the top
allow the chromatogram to dry, then measure the distance travelled by each spot and by the solvent
Calculate Rf value
chlorine
bleaches damp litmus paper turning it white
oxygen
glowing splint relights
Carbon Dioxide
Bubbling Co2 through limewater causes solution to turn cloudy
Hydorgen
lit splint at the open end of a test tube containing hydrogen creates a squeaky pop sound
(hydrogen burning quickly with oxygen)
Carbonates
test
substance containing CO32- ions
add a dilute acid to the sample, which will cause fizzing or effervescence if carbonates are present. Then, bubble the gas produced through limewater; if the limewater turns cloudy, it confirms the presence of carbon dioxide
Test sulfate ions
add hydrochloric acid and 2 drops of Barium chloride solution if present a white precipitate will form
Test Halides
add nitric acid and silver nitrate solution
chloride - white precipitate
bromide - cream precipitate
iodide - yellow precipitate
Flame tests
Lithium ions
Sodium Ions
Potassium ions
calcium ions
Copper ions
crimson yellow lilac orange-red green
Flame test
clean wire loop and dip into a sample of solid compound being tested
Place loop into flame of Bunsen burner set to roaring blue flame
observe colour and record in a table
only works for sample with 1 metal ion
if multiple some colours blocked by the colours of other ions.
metal hydroxides
insoluble and precipitate out of a solution when formed
metal hydroxide test
add a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution to solution
Calcium White
copper blue
ironn2 green
iron 3 brown
aluminium white then redissolves to form a colourless solution
Magnesium white
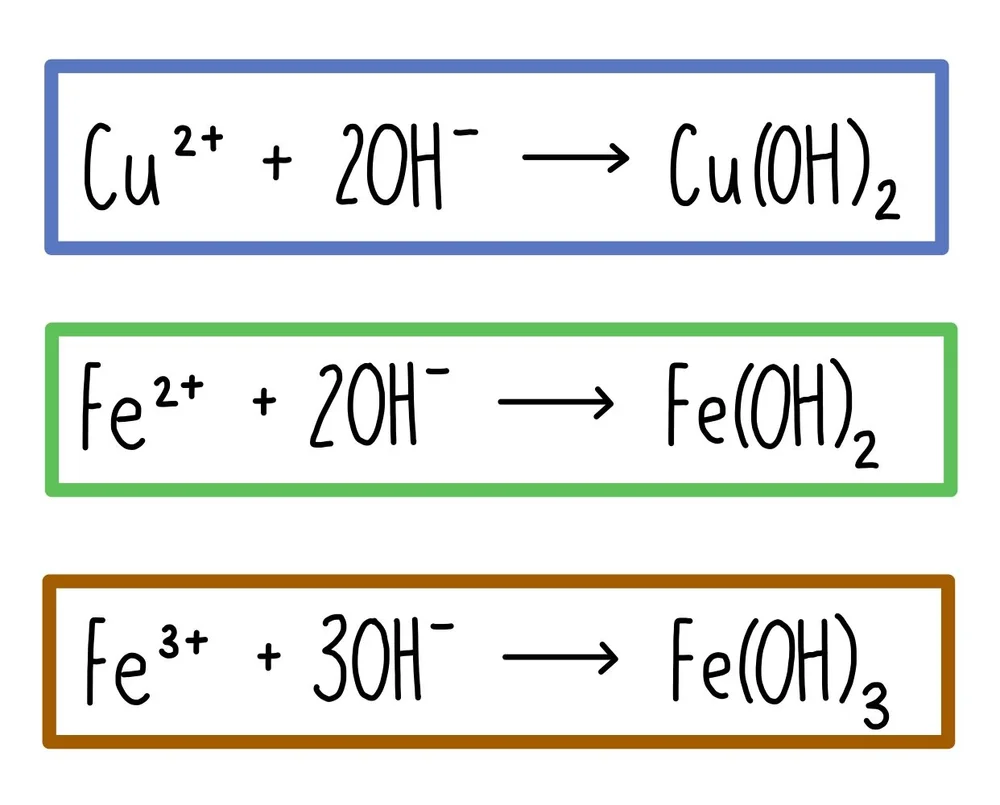
Metal hydroxide ionic equation
only show ions involved in precipitation reaction
do not show sodium or sulfate ions (spectator)
Cu2+ + 2OH- → Cu(OH)2
Fe3+ + 3OH- → Fe(OH)3
flame emission spectroscopy
instrumental method of analysis - identify ions an their concentration.
sample placed in a flame.
As ions heat up their electrons become excited and move to a higher energy level.
When the electrons drop back to their original energy level they transfer energy as light which passes through a spectroscope which can detect wavelengths of light to produce a line spectrum
To identify the metal present the spectrum is compared with reference spectra from known metal ions
what does the combination of wavelengths depend on?
ion charge and electron arrangement
since no 2 ions have the same charge and electron arrangement different ions emit different wavelengths of light so each ion produces a different pattern of wavelengths and different line spectrum.
What does the intensity of the spectrum indicate
concentration of that ion
Why is flame emission spectroscopy more useful than flame tests?
identify different ions in mixtures
flame tests only work for substances containing a single metal ion
Advantages of using a machine
verry sensitive can detect smallest amounts of substances
very fast and tests can be automated
verry accurate