A level Bio 1.2 Carbohydrates
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pls leave a 5 star review if you find it helpful :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Molasses is a solution obtained from sugar beet plants. The sugars present in molasses are sucrose, glucose and fructose. Give the number of different types of monosaccharides present in molasses. (1)
2 (1)
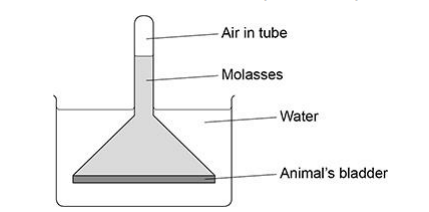
A scientist used the apparatus in below figure to investigate osmosis.
Use your understanding of osmosis to explain why the air pressure in the tube increased. (3)
Water (in beaker) has higher water potential (1)
Water moves in (across) partially/selectively permeable bladder (1)
Increased (molasses/solution) volume (1)
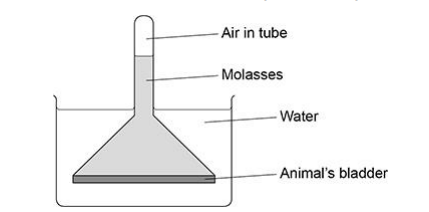
The scientist repeated the investigation, but made one change to the molasses.
The scientist did not change the volume of molasses at the start of the investigation.
The scientist observed that the air pressure inside the tube increased by 160 kPa compared with 800 kPa in the first investigation.
Suggest the change the scientist made to the molasses to cause this smaller increase in air pressure.
Use the air pressure figures in a calculation to support your answer (2)
Decreased (molasses) concentration (1)
(Reduction by) 80%/5 times (1)
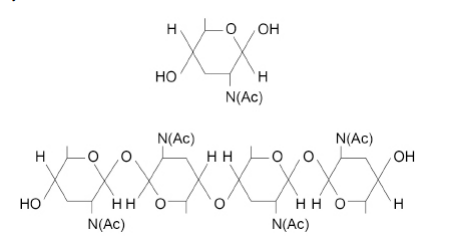
Chitin is a polysaccharide. The chitin monomer is a β-glucose molecule with one OH group replaced by an NHCOCH3 group. NHCOCH3 can be represented by N(Ac).
The figure below shows the monomer that forms chitin and the chitin polymer.
Chitin has a similar structure to cellulose. Use the figure above to describe three ways the structure of chitin is similar to the structure of cellulose.(3)
(Alternate) monomers/glucoses are flipped/upside down (1)
(Joined by ) glycosidic bonds(1)
(forms ) straight/unbranched (chains/molecules) (1)
Lignin is a polymer found in the walls of xylem vessels in plants. Lignin keeps the xylem vessel open as a continuous tube.
Explain the importance of the xylem being kept open as a continuous tube.(3)
(So) no barrier to (water) movement (1)
Cohesion from H between all water molecules (1)
Evaporation/transpiration creates tension (in column) (1)
Iodine solution stains fresh apple tissue black.
When iodine solution is added to apples stored for a week, the stain is less black.
The water potential of apple juice decreases when apples are stored. Suggest why the water potential of apple juice decreases when apples are stored (2)
Starch hydrolysised (1)
Maltose is soluble (1)
Describe the complete digestion of starch by a mammal (5)
Hydrolysis(1)
(Of) glycosidic bonds(1)
(Starch) to maltose by amylase(1)
(Maltose) to glucose by disaccharidase/maltase(1)
Membrane-bound (disaccharidase/maltase) (1)
A precipitate is produced in a positive result for reducing sugar in a Benedict’s test.
A precipitate is solid matter suspended in solution.
A student carried out the Benedict’s test.
Suggest a method, other than using a colorimeter , that this student could use to measure the quantity of reducing sugar in a solution (2)
Filter and dry (the precipitate) (1)
Find mass/weight (1)
Use of a colorimeter in this investigation would improve the repeatability of the student’s results.
Give one reason why.(1)
Colour change is subjective (1)
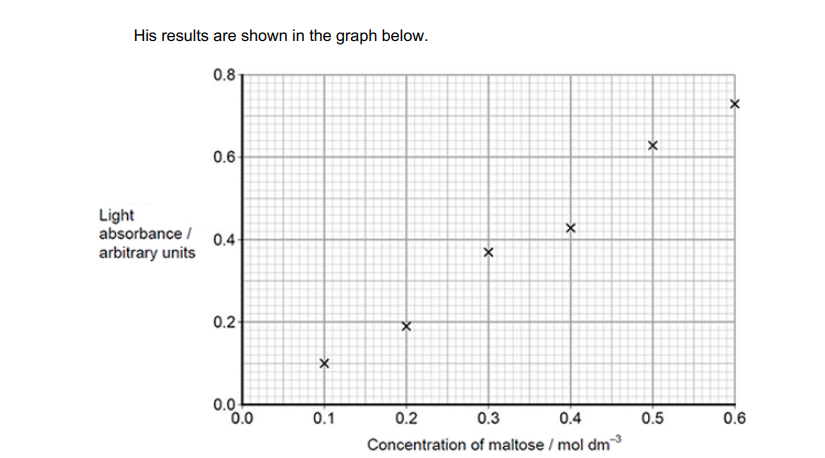
Explain how you would use the graph to determine the maltose concentration with a light absorbance of 0.45 arbitrary units (2)
Line of best fit drawn(1)
Read off value at 0.45(1)
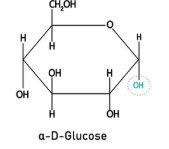
Draw the structure of α glucose (1)
(1)
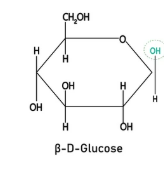
Draw the structure of β glucose (1)
(1)
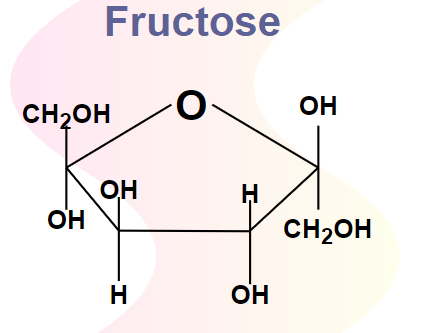
Draw the structure of fructose (1)
(1)
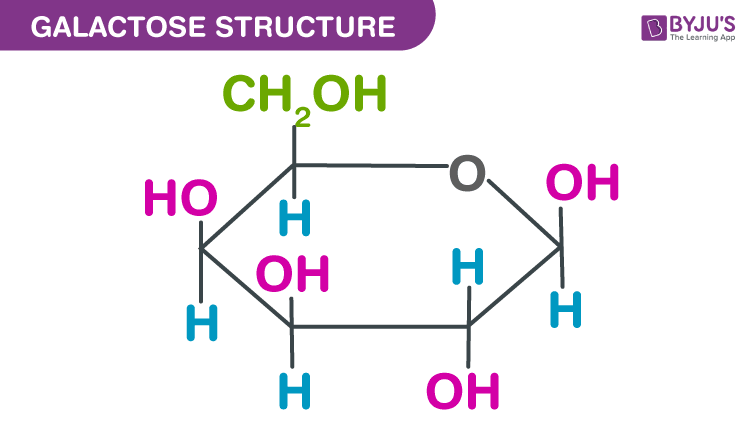
Draw the structure of galactose (1)
(1)
which two monosaccharides is maltose made from (2)
α glucose and α glucose (2)
which two monosaccharides is sucrose made from? (2)
fructose (1)
α glucose (1)
which two monosaccharides is lactose made from? (2)
galactose (1)
α glucose (1)
Describe the biochemical tests of reducing sugars (5)
Grind up the sample using a pestle and mortar in water (1)
Transfer 2 cm3 of the food sample to 2 cm³ of Benedict’s reagent in a test tube and filter (1)
Immerse the test tube in a gentle boiling water bath for 5 minutes (1)
colour change of green, yellow, orange or brick red indicate a positive result (of reducing sugar) (1)
the higher the concentration of reducing sugar , the further the colour change (1)
Describe the biochemical tests of non-reducing sugars (5)
Add 2cm³ of the food sample/solution in a test tube containing 2 cm³ of HCl and place the test tube in a gentle boiling water bath for 5 minutes (1)
Transfer 5 cm³ of sodium hydrogencarbonate solution to the test tube to neutralise the HCl
Heat the solution with 2 cm³ of Benedict’s reagent in a hot water bath for 5 minutes (1)
colour change of green, yellow, orange or brick red indicate a positive result (of non- reducing sugar) (1)
the higher the concentration of reducing sugar , the further the colour change (1)
A student created a method to test the presence of a non-reducing sugar in a solution.
The student :
1) Add 2cm³ of the food sample/solution in a test tube containing 2 cm³ of HCl and place the test tube in a gentle boiling water bath for 5 minutes
2) Transfer 5 cm³ of sodium hydrogencarbonate solution to the test tube
3) Heat the solution with 2 cm³ of Benedict’s reagent in a hot water bath for 5 minutes
Why is hydrochloric acid added to the solution in step 1 ? (1)
The dilute hydrochloric acid will hydrolyse the polysaccharides (1)
A student created a method to test the presence of a non-reducing sugar in a solution.
The student :
1) Add 2cm³ of the food sample/solution in a test tube containing 2 cm³ of HCl and place the test tube in a gentle boiling water bath for 5 minutes
2) Transfer 5 cm³ of sodium hydrogencarbonate solution to the test tube
3) Heat the solution with 2 cm³ of Benedict’s reagent in a hot water bath for 5 minutes
Why is sodium hydrogen carbonate solution added in step 2? (1)
Benedict’s reagent can’t work in acidic solutions (1)
Describe the biochemical test for starch (2)
add two drops of iodine solution into the solution and shake/mix (1)
The colour change from yellow to blue-black indicates a positive result (1)
Describe the structure and bonding of glycogen and how it enables its function to be carried out (6)
Glycogen is a polysaccharide joined by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds between lots of α glucose in a condensation reaction (1)
insoluble so no osmotic potential
can’t diffuse out of cells (1)
Can be readily hydrolysed into α glucose which is used in respiration (1)
as it is highly branched so more enzymes can act simultaneously on these branches(1)
large but compact (1)
maximise the energy it can store (1)
Describe the structure and bonding of amylose and how it enables its function to be carried out (3)
Amylose is a polysaccharide joined α 1,4 glycosidic bonds between lots of α glucose in a condensation reaction (1)
It is unbranched (1)
It is coil and compact so act as energy storage (1)
Describe the structure and bonding of amylopectin and how it enables its function to be carried out (3)
Amylose is a polysaccharide joined α 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds between lots of α glucose in a condensation reaction (1)
Can be readily hydrolysed into α glucose which is used in respiration (1)
as it is highly branched so more enzymes can act simultaneously on these branches(1)
Read the following passage.
Straw consists of three main organic substances – cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin.
Cellulose molecules form chains which pack together into fibres. Hemicellulose is a small molecule formed mainly from five-carbon (pentose) sugar monomers. It acts as a cement holding cellulose fibres together. Like hemicellulose, lignin is a polymer, but it is not a carbohydrates. It covers the cellulose in the cell wall and supplies additional strength. In addition to these three substances, there are small amounts of other biologically important polymers present.
Complete the table to show two ways in which the structure of a hemicellulose molecule differs from the structure of a cellulose molecule. (2)
| Hemicellulose | Cellulose |
| .......................................................... .......................................................... | .......................................................... .......................................................... |
| .......................................................... .......................................................... | .......................................................... .......................................................... |
Hemicellulose is shorter (1)
Hemiglucose is made from pentose monomers, cellulose is made from hexose monomers(1)
The other main component of straw is water. Water content is variable but may be determined by heating a known mass of straw at between 80 and 90°C until it reaches a constant mass. The loss in mass is the water content.
Since straw is plentiful, it is possible that it could be used for the production of a range of organic substances. The first step is the conversion of cellulose to glucose. It has been suggested that an enzyme could be used for this process. There is a difficulty here, however. The lignin which covers the cellulose protects the cellulose from enzyme attack.
Explain why the following steps were necessary in finding the water content of straw:
not heating the straw above 90°C (2)
only water given off below 90 °C (1)
(above 90°C) other substances straw are broken down; and lost as gas (1)
Describe the structure of a cellulose molecule and explain how cellulose is adapted for its function in cells.(6)
made from β-glucose (1)
joined by condensation (1)
1.4 β glycosidic bonds (1)
alternate molecules (1)
long straight chains (1)
cellulose makes cell walls strong which can resist osmotic pressure (1)