Pneumothorax, Pleural effusion
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
pleural space
The space between the parietal pleura and the visceral pleura that allows for the sliding of the lungs during breathing and can be affected by inflammation, infection, or loss of physiologic pressure
-4 mmHg
Normal intrapleural pressure that is require to maintain lung inflation
Pneumothorax
An accumulation of air in the pleural space
Spontaneous primary (no underlying), Spontaneous secondary (Marfan, COPD), Traumatic (GSW, iatrogenic)
What can cause a pneumothorax?
tall, thin males age 10-30, upper lung lobe, increased risk with smoking, lung fibrosis
What are some red flags for spontaneous primary pneumothorax?
diminished breath sounds, decreased tactile fremitus, decreased chest wall movement
What are some clinical findings that are possible with large pneumothoraces?
oxygen supplementation, drainage (one-way valve placement)
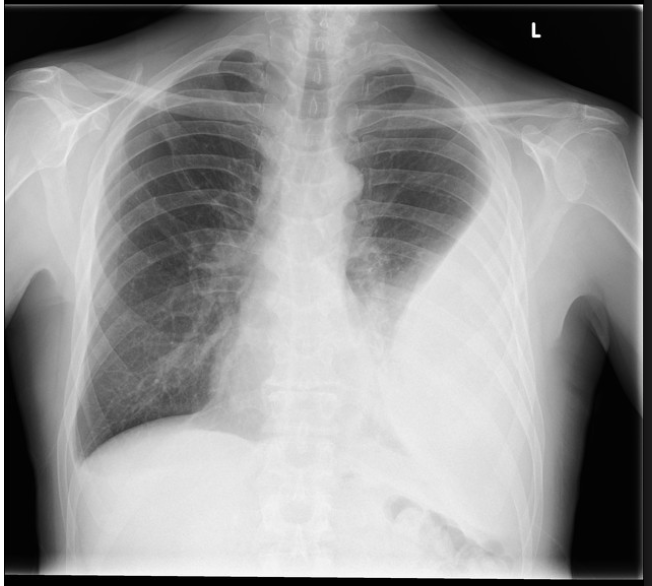
18 y/o male patient presents to the ER with chest pain and shortness of breath. While conducting a physical you note diminished breath sounds on the ENTIRE left side as well as decrease tactile fremtitus. Vitals are stable with the exception of tachycardia. CXR looks like this. What is your treatment plan?
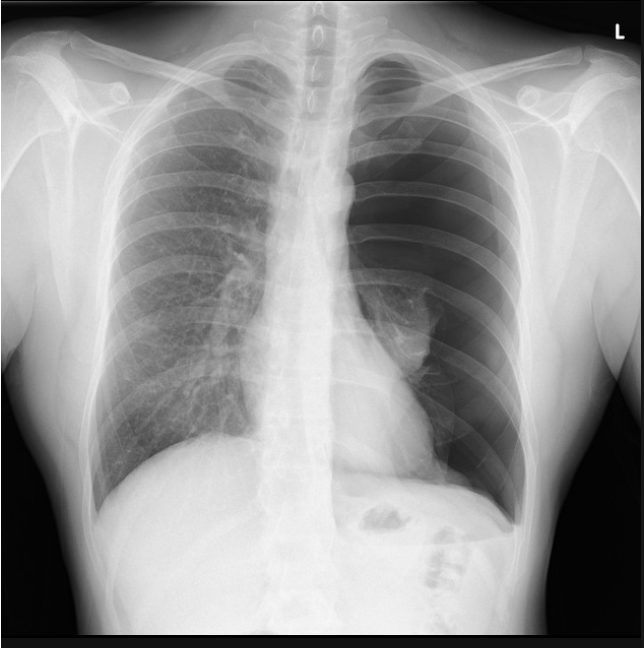
watchful waiting, maybe oxygen supplementation
For a small/stable spontaneous pneumothorax what is our treatment plan?
Surgery to resect blebs and pleurodesis via mechanical abrasion with talc
In the case of recurrent, bilateral, or failure to respond to a chest tube pneumothorax what is our treatment plan?
mid-clavicular, 2nd intercoastal space
Where is a thoracostomy performed for a tension pneumothorax?
clinical instability, tracheal deviation, JVD, absence of breath sounds on the effected side
What are some signs of a tension pneumothorax?
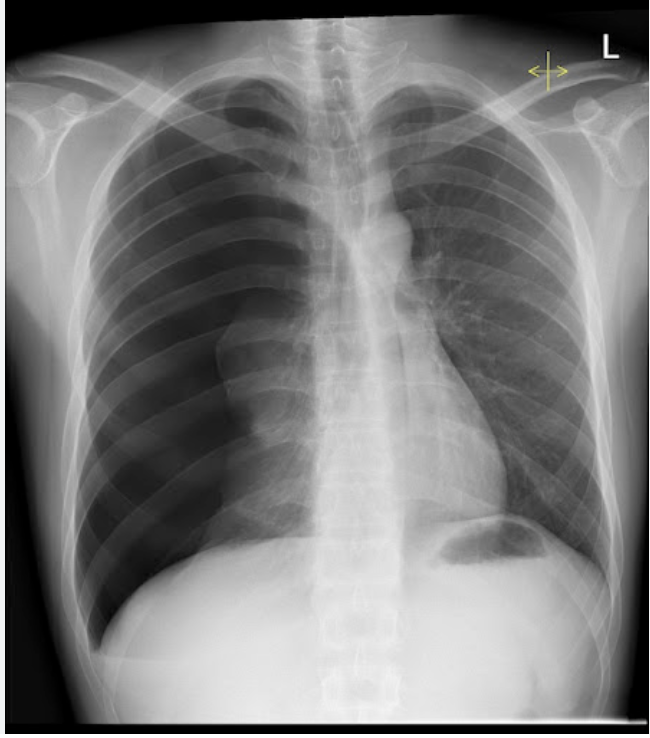
tension pnuemothorax
A continued accumulation of air in the pleural space in which air builds and begins to displace lungs/mediastinum
hemothorax
An accumulation of blood in the pleural space that leads to HYPOresonance and decreased breath sounds
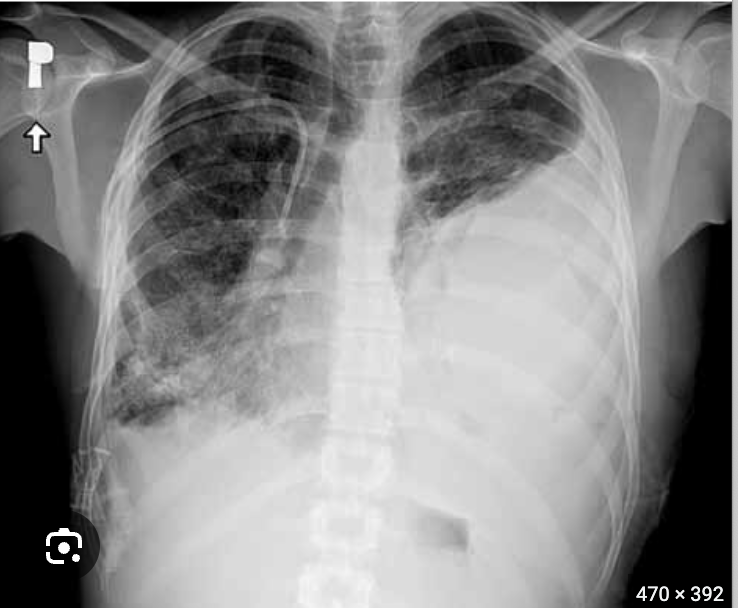
hemopneumothorax
A mixture of blood and air in the pleural space that leads to HYPOresonance over gravity dependent blood and HYPERresonance over superior air filled space that can progress to a tension pnuemo
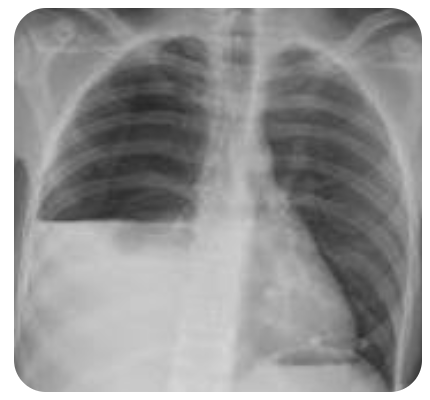
parietal pleura capillaries, interstitial spaces of the lung via the visceral pleura, peritoneal cavity via holes in diaphragm
In a normal state, fluid enters the pleural space from
pleural lymphatics
In a normal state, how is fluid removed from the pleural space
pleuritis
An acute painful, pleural inflammation caused by parietal pleural irritation that is characterized by localized, sharp, and fleeting pain that is exacerbated by coughing, sneezing, deep breathing, and movement - maybe the ipsilateral shoulder hurts
infections (viral/bacterial)
What causes pleuritis in healthy individuals?
effusion, malignancy
What causes pleuritis in ill individuals?
treat underlying, NSAIDs, cough supressants
What is our treatment plan for pleuritis?
pleural effusion
A collection of fluid in the pleural space that is due to input > output
transudative, exudative, empyema, hemothorax
Types of pleural effusions
Transudative
A pleural effusion due to increased hydrostatic or decreased oncotic capillary pressure
exudative
A pleural effusion due an increased production of fluid
empyema
A pleural effusion due an infection leading to lots of pus in the pleural space
hemothorax
A pleural effusion due bleeding into the pleural space
high hydrostatic pressure in vessel, low oncotic intravascular pressure (low albumin, LDH, cholesterol)
What causes a transudative pleural effusion?
HF, nephrotic syndrome (anything with fluid overload)
What conditions are common causes of transudative pleural effusions?
increased permeability of pleural membranes and capillaries so large molecule/serum can pass into pleural space (high protein, high LDH)
What causes an exudative pleural effusion?
bacterial pneumonias (think inflammation)
What conditions are common causes of a type exudative pleural effusions AKA parapnuemonic effusions?
exudative, free following, completely treatable with antibiotics
Characteristics of uncomplicated parapneumonic effusions?
exudative, free flowing that requires a chest tube, can develop adhesions and loculations of fuild
Characteristics of complicated parapneumonic effusions?
empyema
A overt collection of pus that is the end result of a complicated parapneumonic effusion that is not treated properly and occurs in patients that are severely ill and leads to scarring
thoracentesis, pleural fluid gross exam and lab testing
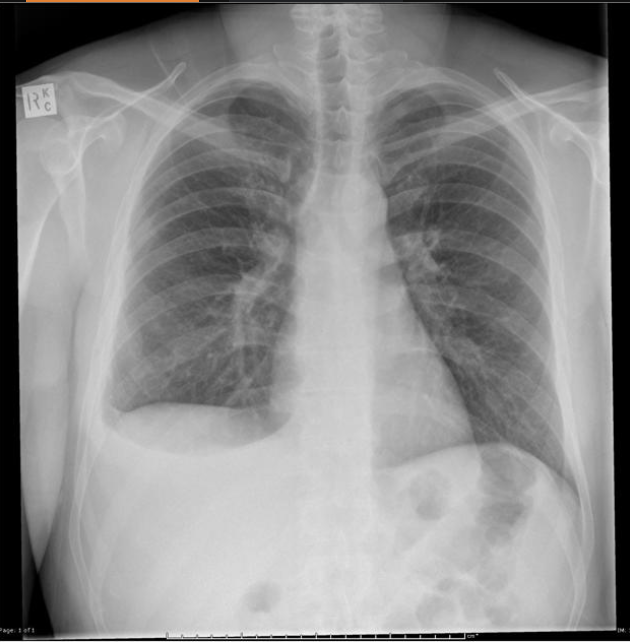
Patient presents to the ER for CP that is exacerbated by breathing. He also reports a cough and dyspnea. On a physical exam you note dullness to percussion and diminished breath sounds over the left lower lung. When you ask the patient to say, E it sounds more like A. CXR shows fluid in dependent lung zones, costophrenic blunting. How can we tell the difference between transudative and exudative
CXR, Chest CT (more sensitive), US (can guide thoracentesis)
What imaging can we use for pleural effusions?
emphyema
A pleural fluid gross exam that shows gross purulence is a
emphyema, chylous effusion
A pleural fluid gross exam that shows white/milky fluid?
hemothorax
A pleural fluid gross exam that shows blood
pleural glucose equals serum, pH is 7.6, low WBC (<1000)
Signs of transudative pleural fluid
pleural protein/serum protein > 0.5, pleural LDH/serum LDH >0.6, pleural LDH is 2/3X serum LDH
What are light’s criteria (AKA signs on exudative effusions) that we must have 1 of?
malignancy (most commonly breast, lung, lymphoma)
Up to 80% of pleural effusions are due to
paramalignant effusion
An effusion that is not a direct result of a neoplasm but is still related to the primary tumor
treat underlying, therapeutic thoracentesis
Treatment plan for transudative and malignant pleural effusions
treat infection
Treatment plan for uncomplicated parapneumonic effusions
treat infection, drain fluid collection, peel fibrous adhesions with bronchoscopy
Treatment plan for complicated parapneumonic effusions
identify the source of bleeding (chest CT with contrast) and stop it, drain the blood
How are we treating a hemothorax