Diabetes - Special topics
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
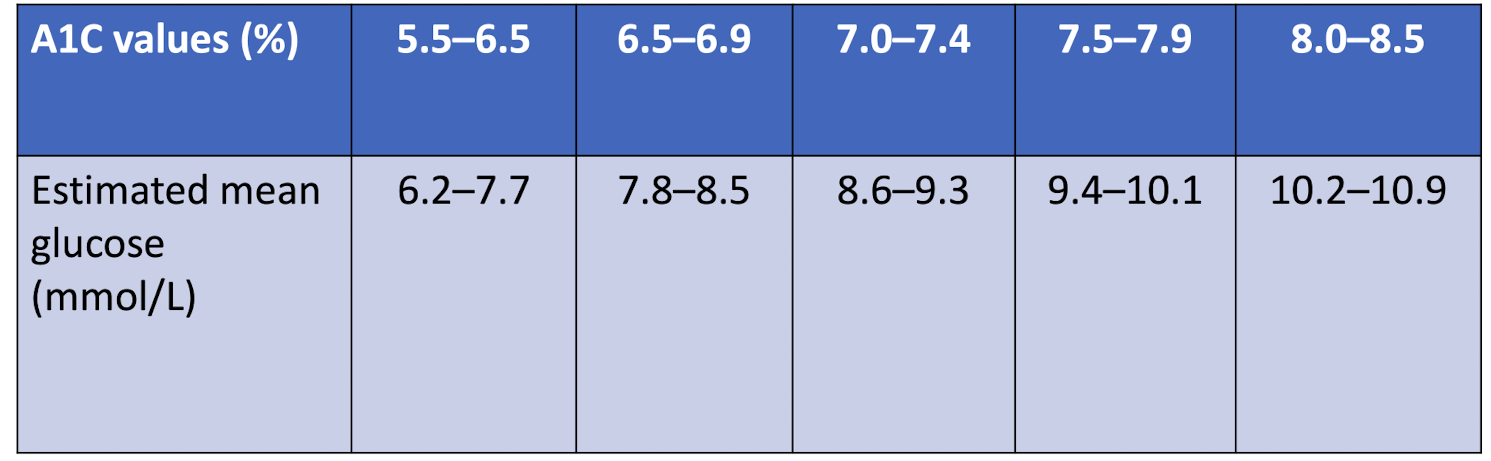
How does the estimated mean glucose level compare to A1c values?
Glucose levels are usually slightly higher than what the A1c % is
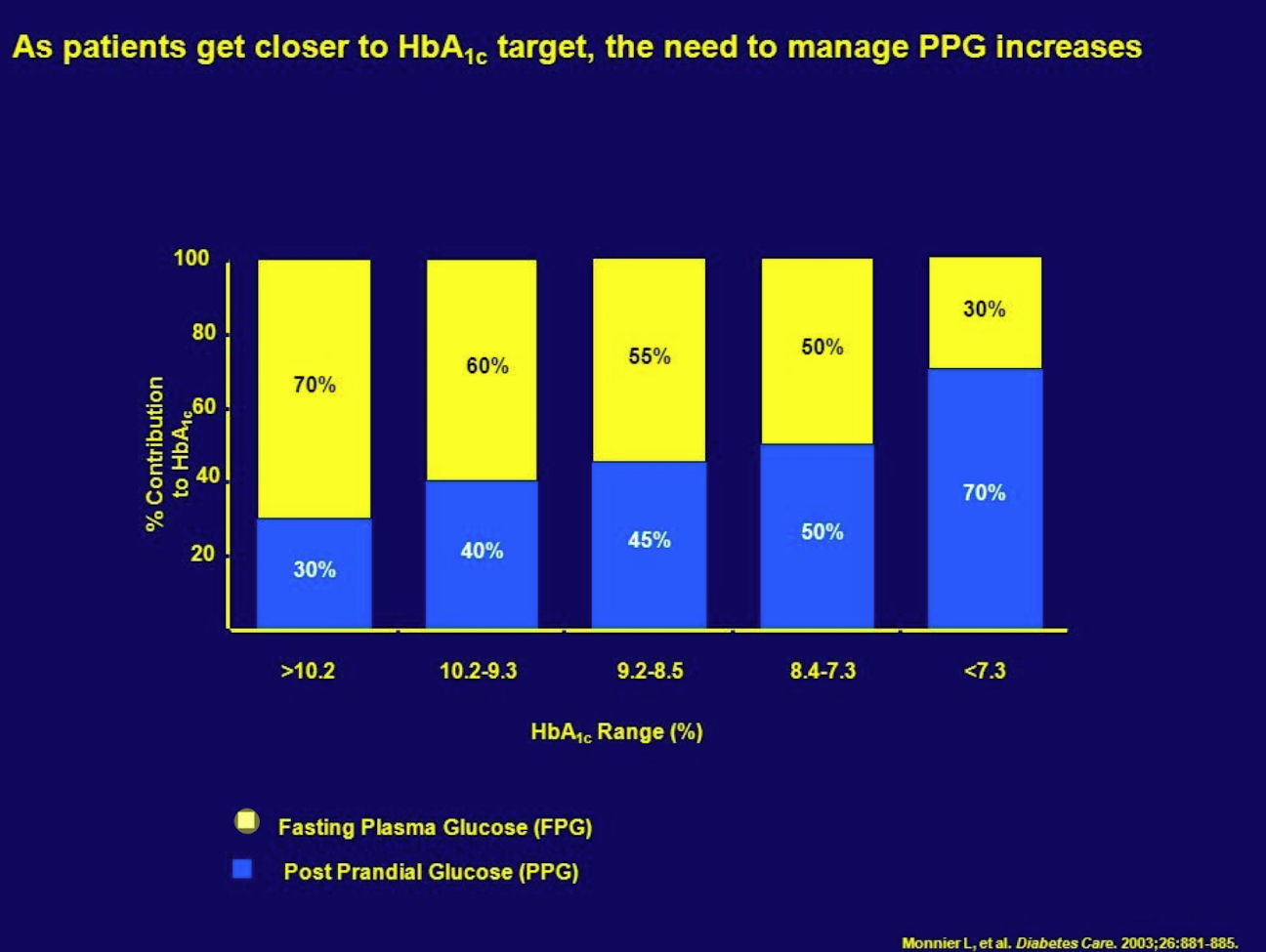
What happens to PPG as patients get closer to their A1c target?
PPG becomes a larger percentage of contributions to the A1c
(so need to manage PPG more)
What does a clinical frailty score of 1-3 indicate?
Functionally independent
What does a clinical frailty score of 4-5 indicate?
Functionally dependent
What does a clinical frailty score of 6-8 indicate?
Frail and/or with dementia
How do FPG and PPG targets change with clinical frailty?
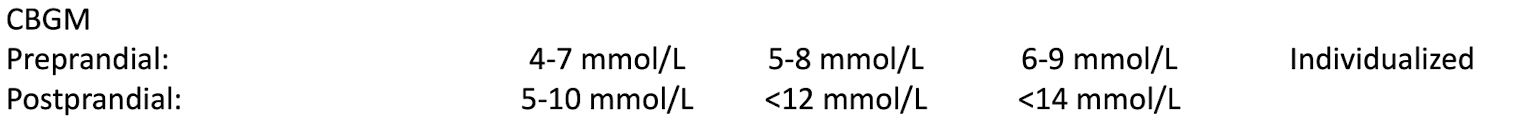
What is the evidence for targeting a low A1c?
Trials show decreased risk of microvascular complications (12% RRR)
(mostly driven by the nephropathy results)
What do the DCCT trials say about targeting a low A1c?
reduction in retinopathy
reduction in nephropathy
reduction in neuropathy
reduction of MACE
reduction in mortality
What risk is involved with targeting a low A1c?
Severe hypoglycemia risk is doubled with intensive targets vs conventional
What does fructosamine testing reflect?
Average glycemic level over the preceding 2-3 wks
When would it be helpful to use fructosamine instead of A1c?
patients when A1c is unreliable
monitoring shorter term control of glucose
Why do we use the fingertip for CBG?
Changes in BG appear most rapidly at this site vs alternate sites
When can additional test strips get covered by ODB in exceptional circumastances?
acute illness
drug interactions
GDM
occupation requiring strict avoidance of hypo
not meeting glycemic target for 3 months or greater
Max amount of test strips covered in 365 days for different scenarios
on insulin - 3000/yr
meds with high risk of hypos - 400/yr
meds with low risk of hypos - 200/yr
managing with non-pharms only - 200/yr
How often should patients verify the accuracy of their glucometer?
Once per year (check right after getting lab FPG and compare results)
Accuracy required for glucometers as per ISO
95% of meter readings must be within ± 0.83 mmol/L of lab results at concentrations lower than 5.6 mmol/L
95% of meter readings must be within ± 15% of lab results at concentrations of 5.5 mmol/L or higher
Target glycemic variability for CGM
36% or less
Target time in range for CGM
>70%
(if older/high risk: >50%)
Examples of benefits of exercise in T2DM
decrease insulin resistance
improve lipids
improve BP
improve glycemic control
What is included in the pre-exercise assessment?
neuropathy
retinopathy
coronary artery disease
peripheral arterial disease
risk of hypo
if BG <5 mmol/L, have 10-20 g CHO before activity
risk of hyper
if BG >16.7 mmol/L, ensure adequate hydration and monitor for signs/sx of dehydration
if BG >16.7 mmol/L AND feels ill, test for ketones - if elevated avoid or delay physical activity
Preconception checklist for women with pre-existing diabetes
use reliable BC until adequate glycemic control
attain preconception A1c of 7% or less
6.5% or lower is safe
can continue metformin and glyburide, otherwise switch to insulin
Assess for and manage any complications of diabetes
folic acid 1mg/d: 3 months pre-conception to 12 wks post-conception
discontinue potential embryopathic meds
ACEi/ARB
Statins
Target BG values for pregnant patient with pre-existing diabetes
Fasting and pre-prandial <5.3
1h postprandial <7.8
2h postprandial <6.7
A1c 6.5% or less (6.1% or less if possible)
Why do we target a lower A1c in pregnancy?
Lower late stillbirth and infant death
Risk factors for GDM
35 yrs or older
high-risk group (African, Arab, Asian, Hispanic, Indigenous, South Asian)
Using corticosteroids
BMI 30 or higher
Prediabetes
previous GDM
given birth to macrosomal infant
1st degree relative with T2DM
PCOS or acenthosis nigricans (darkened patches of skin)
How does pregnancy normally affect glucose?
Insulin resistance occurs and insulin sensitivity decreases
What is the mechanism in GDM
Insufficient insulin secretion to maintain normoglycemia
True or false. Hyperglycemia in pregnancy is often symptomatic.
False - often asymptomatic
GDM implications for mom
Increased risk of:
pre-eclampsia
preterm delivery
c-section
shoulder dystocia
postpartum hemorrhage
GDM implications for baby
Increased risk of:
congenital malformations
macrosomia
neonatal hyperglycemia
NICU admission
jaundice
When does GDM screening occur?
24-28 weeks of gestational age
(first trimester if diabetes risk factors)
GDM glucose targets
fasting and preprandial <5.3
1h postprandial <7.8
2h postprandial <6.7
When is pharmacologic therapy initiated in GDM?
If glycemic targets are not achieved within 1-2 wks
What is considered “in range” for CGM in a T1DM pregnancy?
3.5-7.8
CGM targets for GDM or T2DM pregnancy
Unknown
First line therapy in GDM
Insulin (all rapid-acting have similar outcomes)
What can be used as an alternative to insuilin in GDM?
Metformin
(good safety data in pregnancy)
What has metformin showed evidence of in pregnancy?
less maternal weight gain
less large-for-gestational-age
less neonatal hypoglycemia
What should pregnant patients be made aware of before starting metformin?
Should be informed that it crosses the placenta
What can be added to metformin in GDM?
Glyburide
Post-partum, should patients who had GDM be screened for diabetes?
Yes - lifelong diabetes screening q 1-3 yrs
What is MODY?
Monogenic diabetes
(rare genetic disorder that presents in young people, <25 yrs old)
Are people with MODY insulin-dependent?
No
How is MODY inherited?
Autosomal dominant
Which atypical antipsychotics have the highest incidence of hyperglycemia?
olanzapine
clozapine
Mechanism by which atypical antipsychotics cause hyperglycemia
decreased peripheral insulin sensitivity
decreased insulin secretion
inhibition of beta-cell responsiveness
weight gain
At what doses of thiazide diuretics should you start to worry about hyperglycemia?
>25 mg HCTZ equivalent
Mechanism by which glucocorticoids cause hyperglycemia
increased gluconeogenesis
increased insulin resistance
decreased pancreatic insulin secretion
Mechanism by which statins can cause hyperglycemia
increased insulin resistance
decreased insulin secretion
Why can hyperglycemia occur if someone is sick?
stress
increased hormones (cortisol, catecholamines, glucagon)
(leads to gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis)
Do insulin requirements usually increase or decrease during acute illness?
Usually increase
SADMANS
Sulfonylureas
ACEi
Diuretics, direct renin inhibitors
Metformin
ARBs
NSAIDs
SGLT2i
Reason for holding metformin and sulfonylureas during acute illness
Have reduced clearance and increase risk for AEs
When should patients monitor ketones?
BG 14 mmol/L or higher
during acute illnesss, infections, injuries
Meaning of various blood ketone levels
<0.6 mmol/L is acceptable
0.6-1.5 mmol/L - recheck BG and ketones in 2-4 hrs
1.5-3 mmol/L - may be at risk of DKA
>3 mmol/L - requires immediate medical attention
What should diabetic patients consider when booking surgeries?
Try to book for mornings so that fasting overnight
What should diabetic patients do if they are on a liquid diet when preparing for a procedure?
Replace CHO portion of meals with clear fluids with similar CHO content
(apple juice, white grape juice, regular
Jell-O, regular gingerale, regular sprite)
What should patients on insulin know if getting a procedure done?
bring fast-acting sugar to prepare for treating a hypo
basal insulin may stay the same or need to be reduced by 20-50%
bolus insulin:
dose based on CHO content during clear fluids
hold on day of procedure
resume after procedure once eating meals
Guidelines for SGLT2is prior to a procedure
Stop 2-3 days before procedure (to decrease risk of DKA)
Guidelines for SUs and meglitinides prior to a procedure
Stop when starting clear fluid diet (since it increases risk of hypos)
Guidelines for metformin prior to a procedure
Stop when starting clear fluid diet
Guidelines for GLP-1 RAs prior to a procedure
Stop when starting clear fluid diet or dose prior
Guidelines for DPP-IVs prior to a procedure
No changes necessary
Which antihyperglycemic agents should be held on the day of a procedure?
All
Significance of IV contrast dye usage for medications
If used, metformin must be held for additional 2 days after procedure, and renal function may need to be checked prior to restarting the metformin
At what BG level does driving performance start to deteriorate?
<3.8 mmol/L
After taking fast-acting sugar for a low BG before driving, how long should a person wait before checking their BG again?
At least 40 minutes
After a low BG level, what BG level does someone need to have before driving?
At least 5 mmol/L