Pure Y2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Domain
Set of possible inputs
Range
Set of possible outputs
Function
A mapping such that every element of the domain is mapped to exactly on element of the range
Types of function
Many-to-one, eg. x2
One-to-one, eg. 2x + 1
Inverse function
Does opposite of orig funct
x & y axis swapped, reflected in y = x
Domain and range swapped
Orig funct must be one-to-one, inverse mapping would be one to many which is not a function
y = |f(x)|
All negative values of y become positive
Anything under x-axis flipped above it
y = f(|x|)
All inputted x-values would be positive
So would produce same graph as positive values
So graph produced by positive values of x is flipped onto the negative values of x
Ark lengthin radians
L = rθ
Area in radians
(1/2)θr2
Segment Area in radians
(1/2)r2(θ - sinθ)
Arithmetic nth term
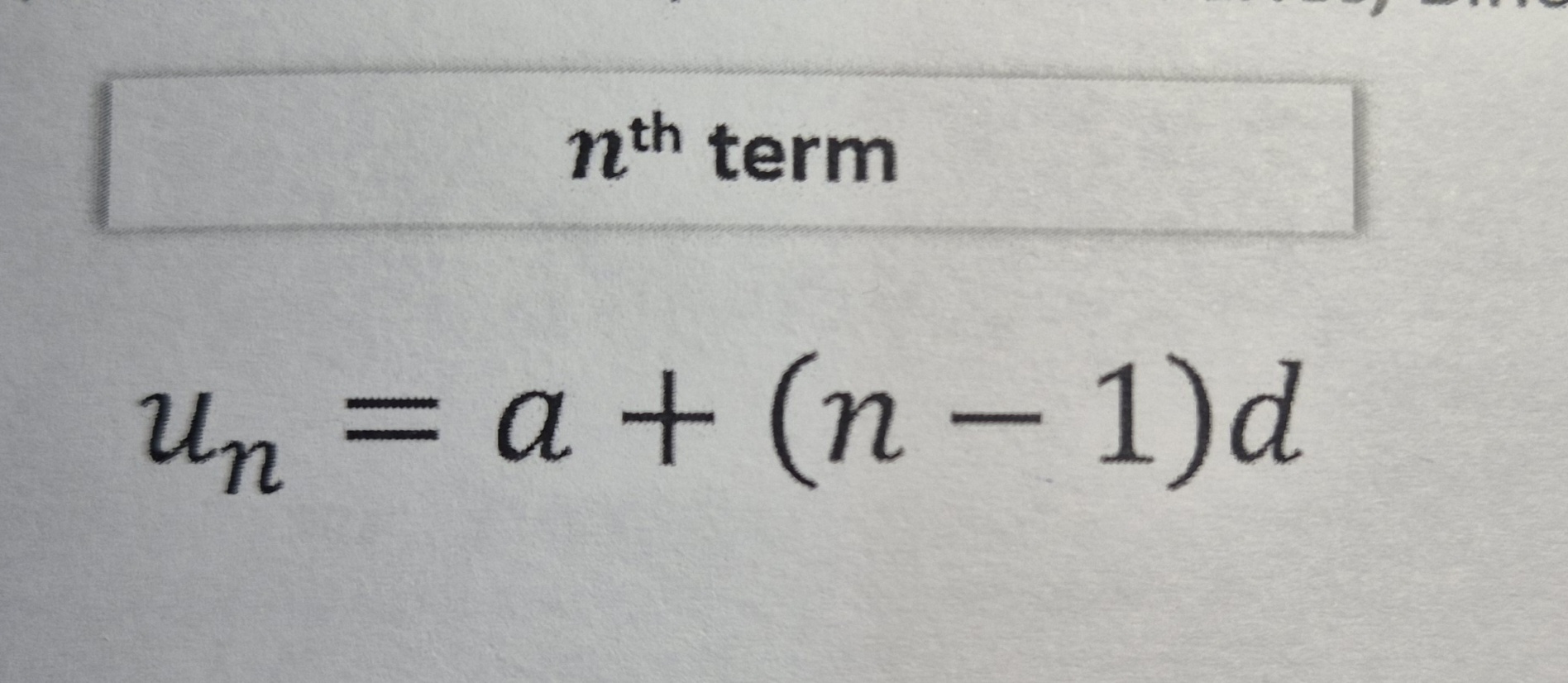
Arithmetic sum
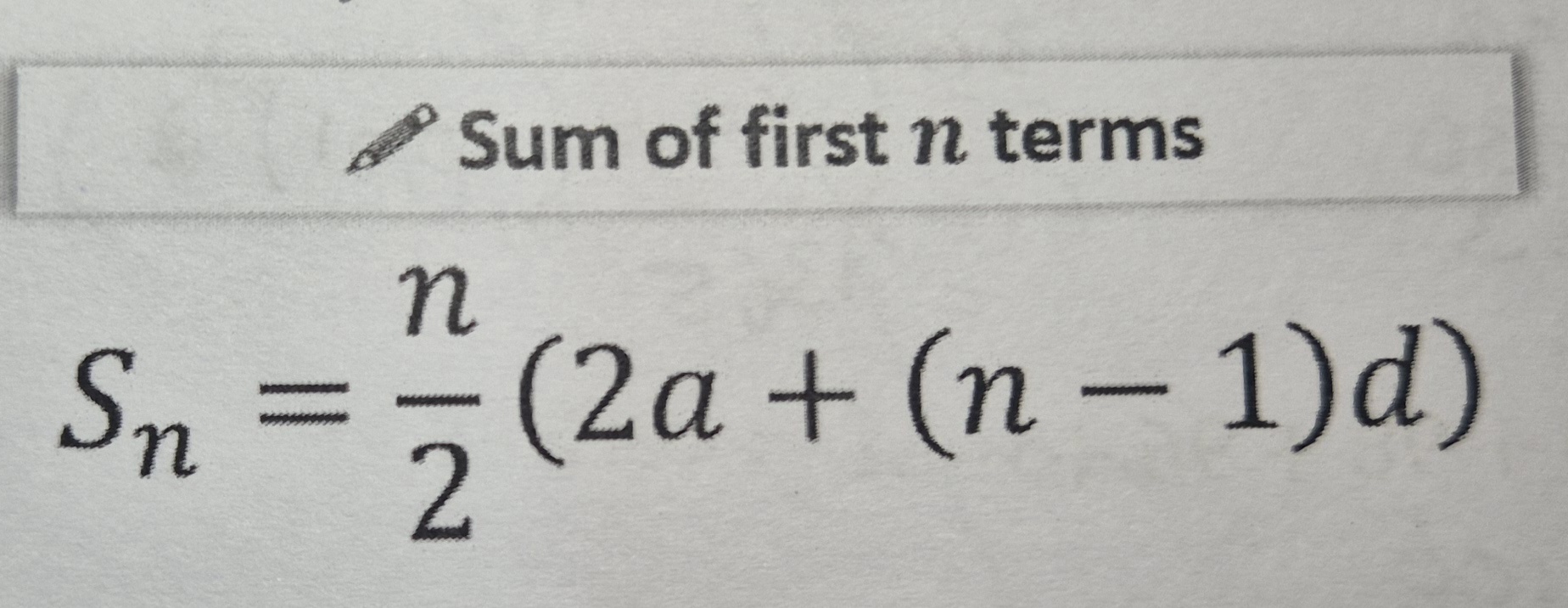
Geometric nth
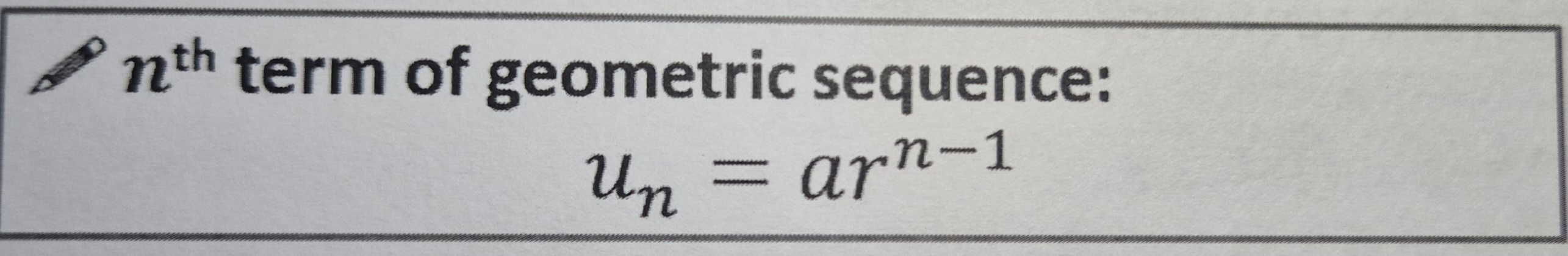
Geometric sum
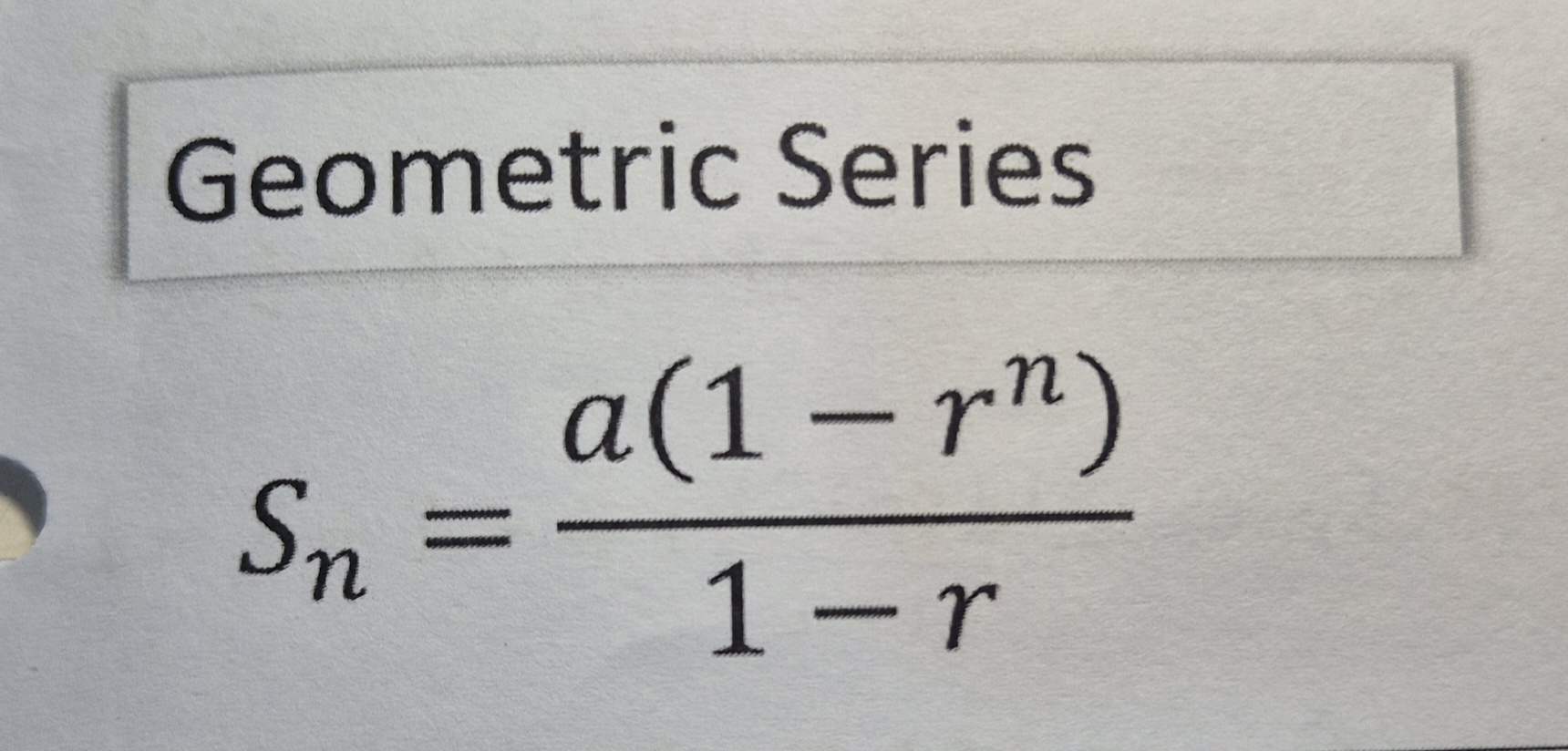
Geometric sum to infinity
For convergent geometric series
When |r| < 1
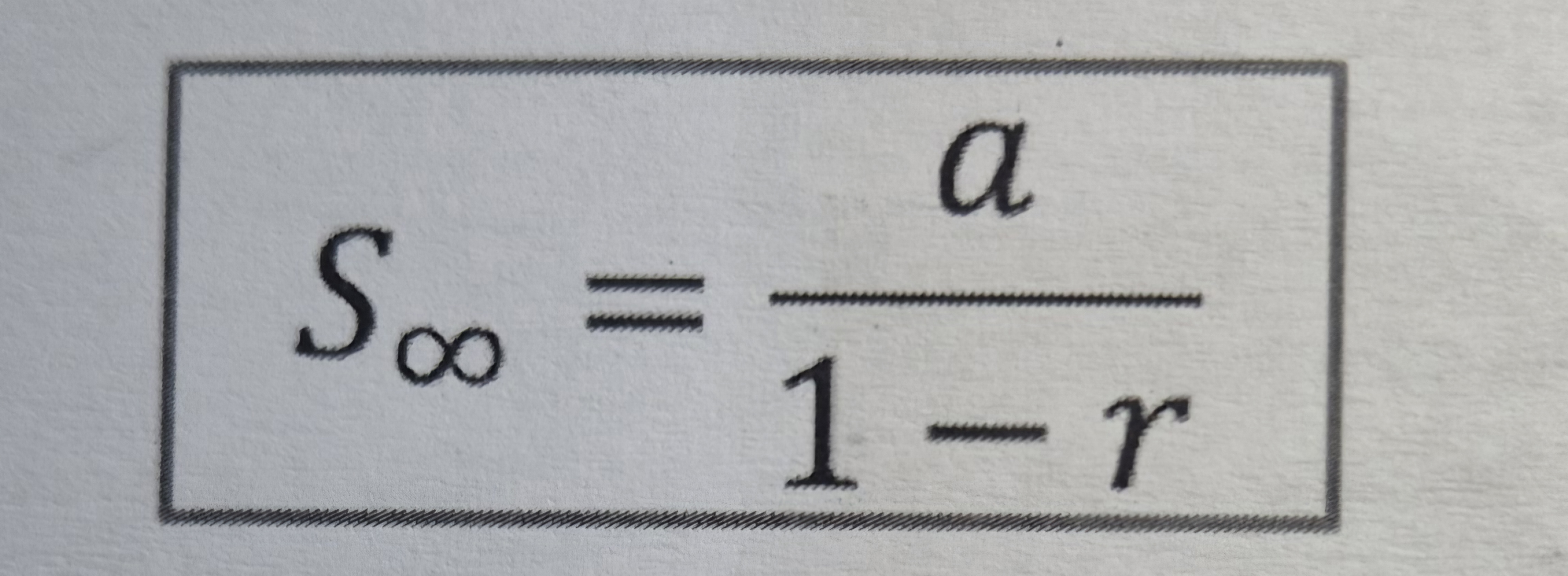
Sigma notation
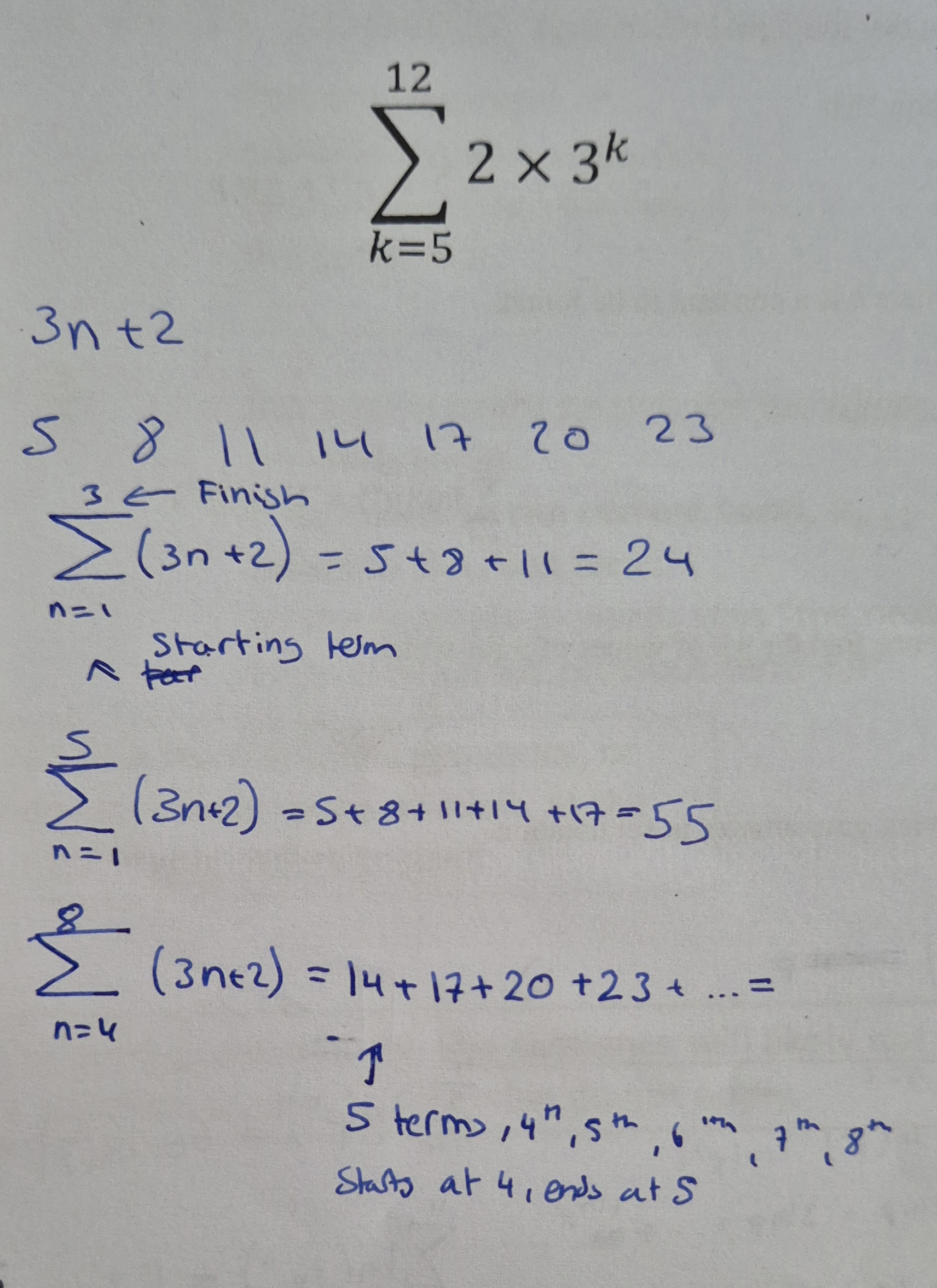
Strictly increasing sequence
Terms are always increasing
Strictly decreasing sequence
Terms are always decreasing
Periodic sequence
Sequence of terms is always repeating
Order k of a sequence is how often it repeats
Binomial expansion formula
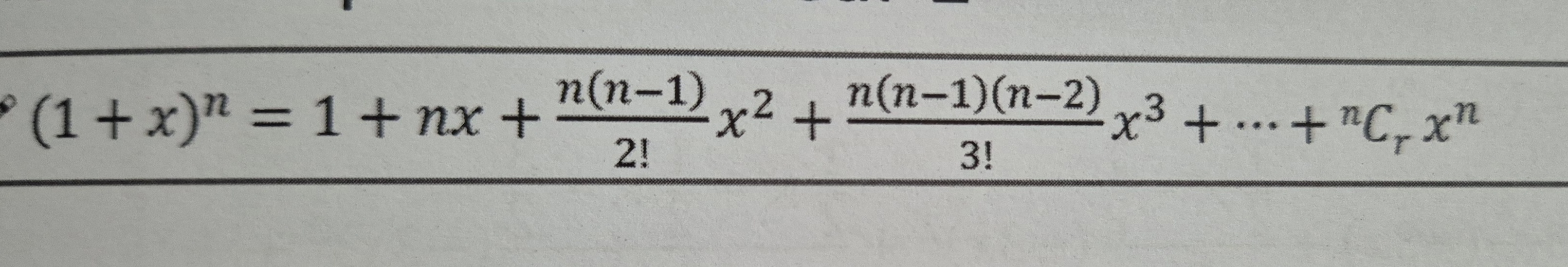
How to tell if expansion is valid
|x| < 1
When would approximations be more vaild
When x is smaller
Double angle formulas

Harmonic Identity

Domain and range of cartesian
Domain is the range of x equation
Range is the range of the y equation
When & how to use Chain Rule
Composite function
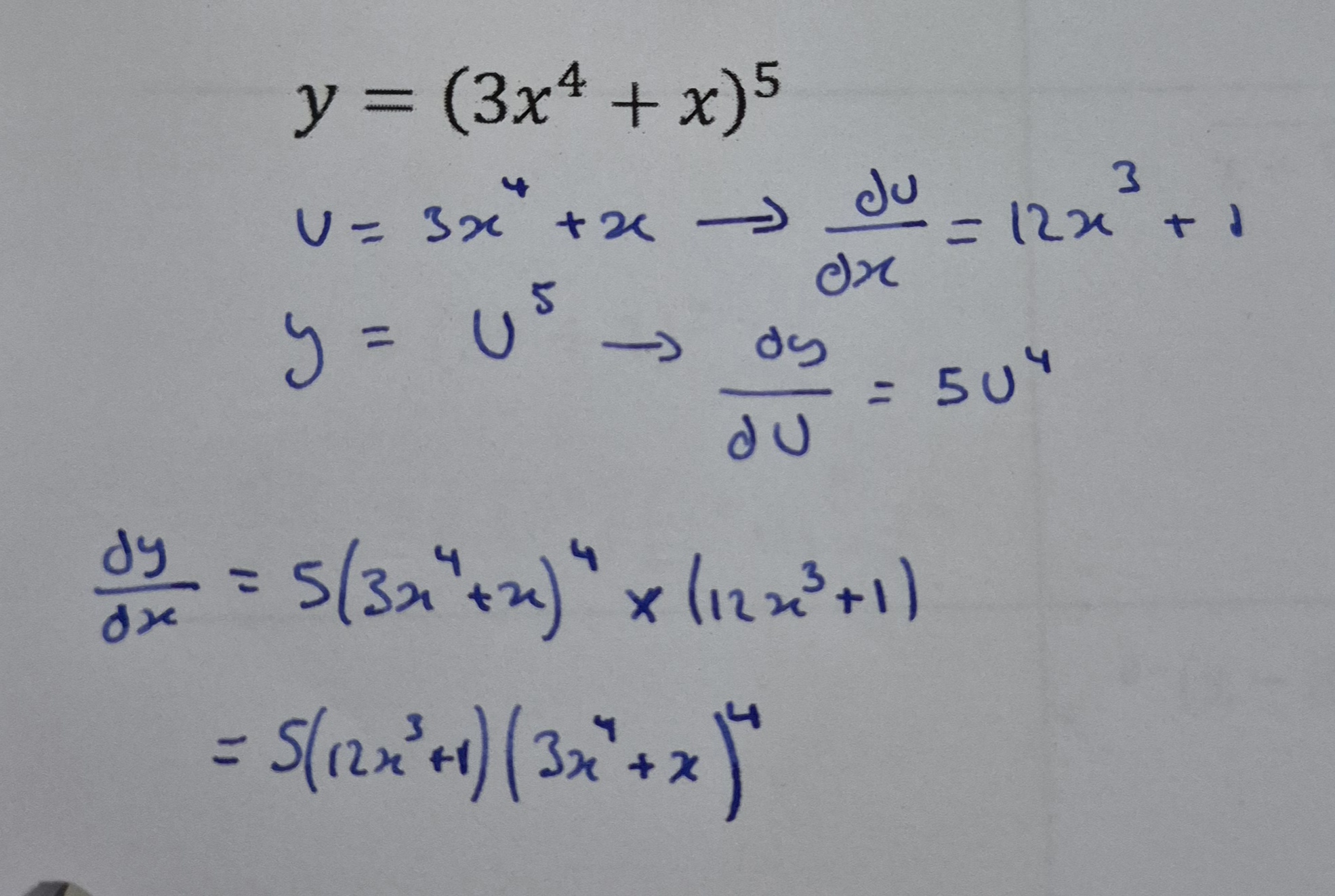
When & how to use Product Rule
Product rule
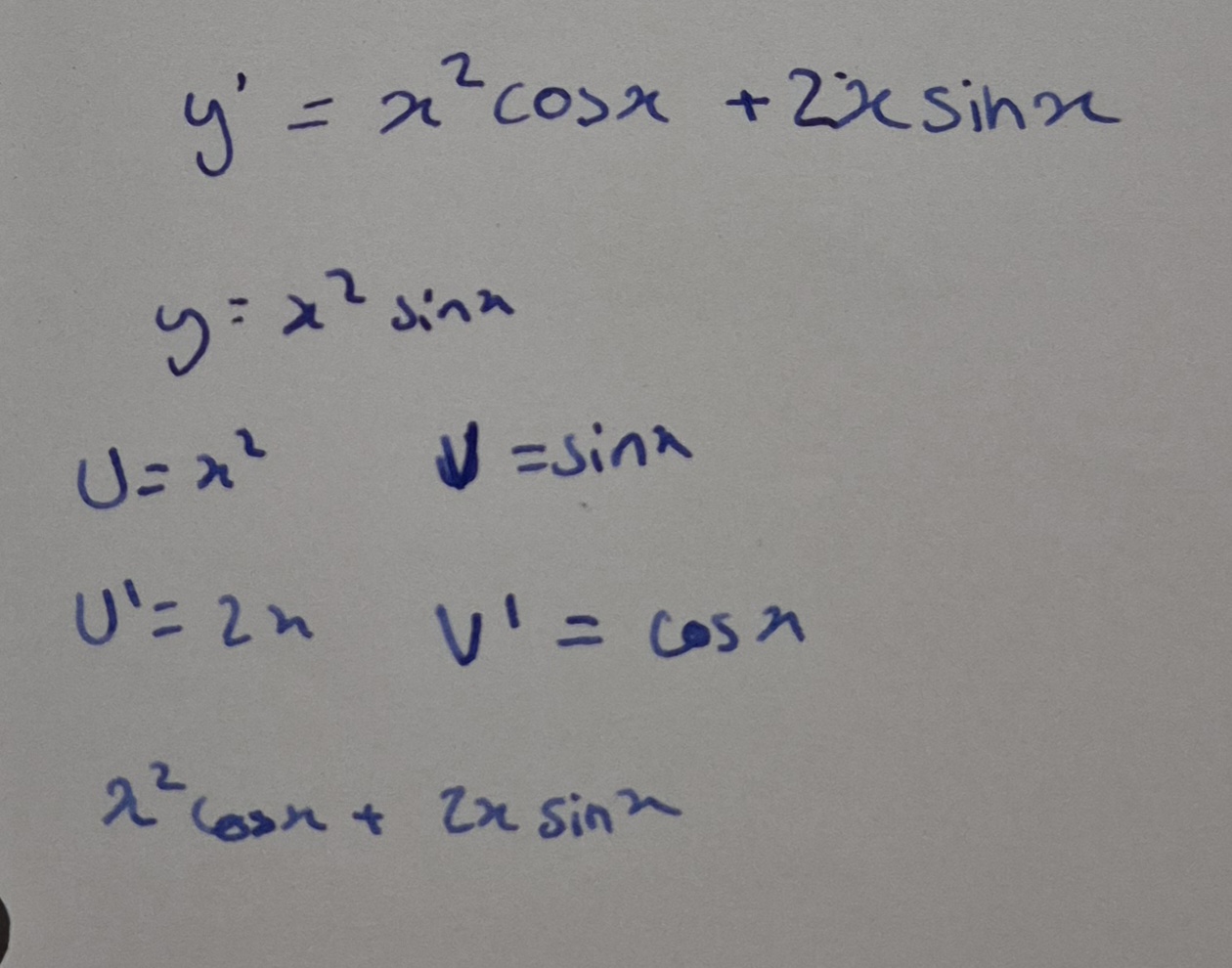
When & how to use Quotient Rule
Division of two functions
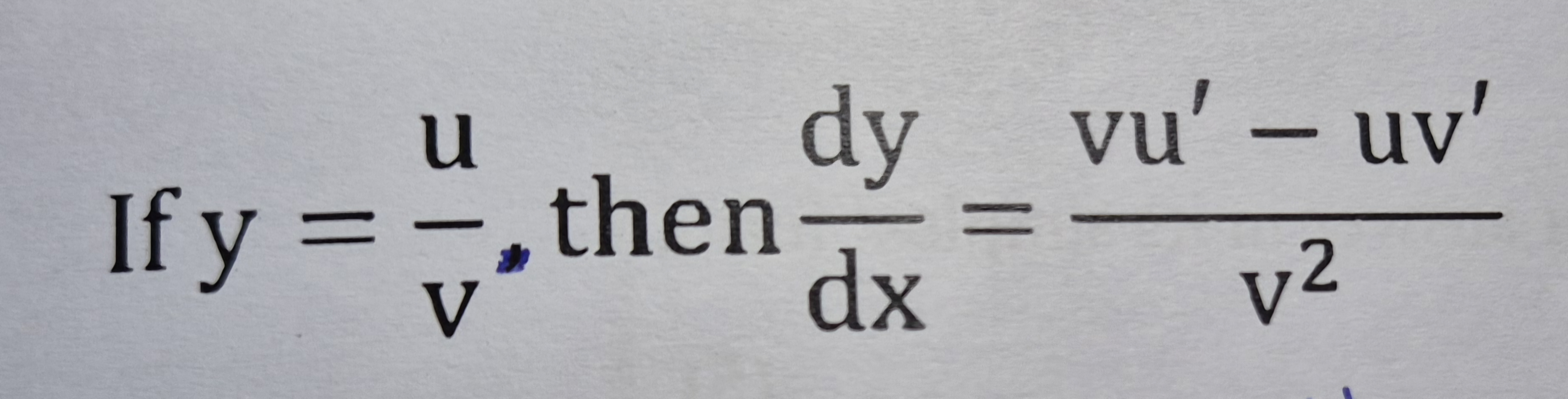
What is an implicit function
When the y is not in terms of x, e.g. x2 + y2 = 25
Implicit differentiation
When differentiating a function of y, but with respect to x, multiply by dy/dx
Concave
f’’(x) <= 0
Swerving right
Point of infleciton
f’’(x) = 0
Gradient doesn’t change
Convex
f’’(x) >= 0
Swerving left