2 Lab Tools of Microbiology
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture Notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
culture
any growth that appears in or on the medium after incubation
standard incubators 37 C
inoculation
introduction of microbes into media for culture
medium
nutrient containing environment in which microbes can multiply
sterile (aseptic technique)
free of microbes; requirement for any instrument used for sampling and inoculation
broth, stab, slant
What are the different physical forms of media? Also known as liquid, semisolid, and solid/ reversible to liquid
general purpose media
Complex media that contains mixture of ingredients that support wide variety of microbial life, grows board spectrum of microbes
Ex: Nutrient, Tryptic Soy Agar, Brain and Heart infusion
enriched media
Contains complex organic substances (blood, serum, hemoglobin, or special growth factors) that fastidious (complex) bacteria require for growth
growth factors: specific vitamins or amino acids
streptococcus
Blood agar media is used for _______ species
Mannitol Salt Agar
This type of enriched media is used for bacteria that are salt tolerant known as halophiles are halo-tolerant bacteria
Include Staphylococcus species & Micrococcus species
Media that contains selective agent sodium chloride
Agar
A complex polysaccharide isolated from red alga Gelidium
solid at room temperature, liquefies at 100C & once liquified doesn’t solidify until it reaches 42C
selective media
A type of media that contains ingredients that encourage a specific type of organism while inhibiting other types of organisms to grow
differential medium
distinguishes between different bacterial species based on their biochemical properties, often leading to visible changes in the medium or colony appearance
allow multiple types of microorganisms but display visible differences between colonies
selective and differential
Mannitol Salt Agar is a ______ and ______ media:
________ because Staphylococcus grows in the presence of salt (and salt inhibits growth of other microbes)
_______ because the bacteria will ferment mannitol & turn it into an acid causing a color change
Blood Agar
A differential but NOT selective media
plate is red, bacteria growth is white/ transparent = bacteria able to lyse the red blood cells
chocolate agar
Differential and non-selective media made of overcooked blood
bacteria that can grow here is enriched & can grow on that media
Mueller tellurite
A medium with selective agent potassium tellurite
used for isolation of Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Enterococcus faecalis broth
Medium that contains sodium azide and tetrazolium
used for isolation of fecal enterococci
phenylethanol agar
Media containing phenylethanol chloride
used for isolation of staphylococci & streptococci
tomato juice agar
Media that contains tomato juice and acid
used for isolation of lactobacilli from saliva
MacConkey agar
Selective and differential media containing bile & crystal violet that inhibits growth of gram positive and encourages growth of gram negative
differential: contains glucose, if bacteria ferments it will change the color of the agar
Salmonella/Shigella agar (SS agar)
Media that contains bile, citrate, and brilliant green
used for isolation of salmonella & shigella
Lowenstein-Jensen
Media that contains the selective agent Malachite green dye
used for isolation & maintenance of Mycobacterium
Sabouraud’s agar
Media that contains selective agent with a pH of 5.6 (acid)
used for isolation of fungi-inhibits growth of bacteria
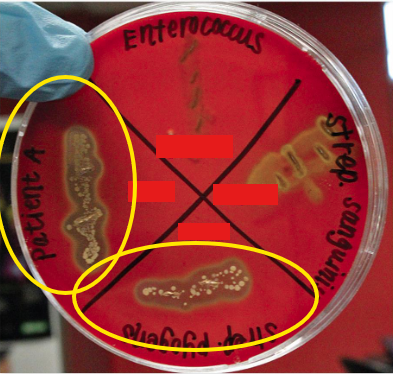
Beta
In blood agar plate, ____ occurs when blood cell was lyse and cleared out
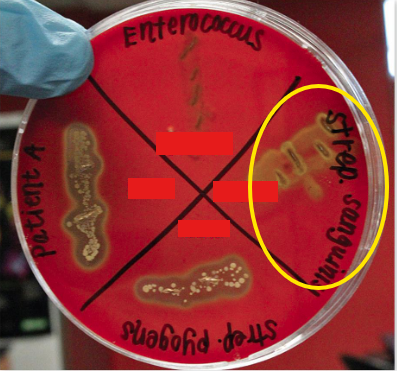
alpha
In blood agar plate, ___ occurs when blood cell is partially lyse
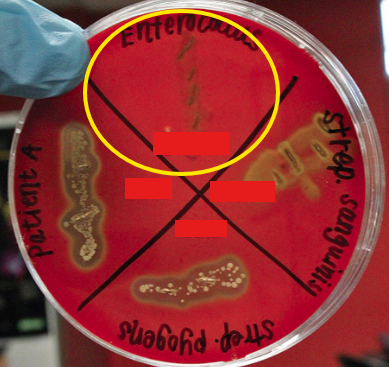
Gamma
In blood agar plate, ____ occurs when the bacteria couldn’t lyse the RBCs and only enjoyed the nutrients that the media provided and grew
Chrom agar
media that is nonselective and differential
ingredients encourage all types of microorganisms and media differentiates organisms by pigments
pink, navy blue, orange, light blue, light pink, white
In Chrom Agar, the agar causes bacteria to turn different colors:
E. coli = _____
Klebsiella = _____ _____
Proteus = _____
Enterococcus = _____ _____
S. Saprophyticus = _____ _____
S. aureus = ______
hydrogen sulfide gas
The photo shows that the inoculated organisms produce _____ _____ ___ producing black pigment at the bottom of the tube

Gas
____ is produced in this tube which disrupts the agar causing it to lift, bubble, or crack

mixed culture
a container that hold two or more identified, easily differentiated species of microorganisms
contaminated culture
a culture that was once pure or mixed that now contains contaminants or unwanted microbes of uncertain identity
inspection
Entails looking under the microscope to discern morphology & any type of arrangement
Looking at growth pattern in a broth or solid
Identification
To name the genus and species which requires biochemical tests that can determine fundamental chemical characteristics:
nutrient requirements
products given off during growth
presence of enzymes
mechanisms for deriving energy
Stain
Dyes that impart colors to cells by becoming affixed to them through a chemical reaction
provides contrast
make inconspicuous features stand out
Cationic and anionic
What are two types of dyes used in microbial staining?
Cationic (basic) dyes
Dyes that has positive charge, attracted to acidic, negatively charged components of bacterial cell walls
Positive staining where the cell is dyed
Several subtypes include: simple stains, differential stains, and special stains
some sort of cell distortion
Anionic (acidic) dyes
Dyes that have a negative charge, repelled by acidic negatively charged components on bacterial cell wall
dyes include Nigrosin & India ink
subtypes of stains include capsule & spore
simple stain
Stain that requires a positively charged dye used to determine size, shape, & arrangement of bacteria
stains include crystal violet, safranin, & fungal red
bacteria must be heat fixed
Differential stain
stain that divides microorganisms into groups based on their staining properties
use two stains to clearly contrast cell types or cell parts
Gram stain
Use crystal violet, iodine, and safranin (counterstain)
used to display gram positive and gram negative bacteria
purple = gram positive
red/ pink = gram negative
Acid fast stain
Used when a cell has a waxy membrane which are harder to penetrate w/t a water based stain
waxy cells appear red (__ ___)
counterstain will appear blue
Capsule stain
Staining a “white halo” bc these structures can’t be stained; use 2 stains
one negative stain which will make the ____ appear white (stains background)
positive stain that stains the bacteria cells
flagellar stain
Stain with an alcohol component which allows flagella to form a precipitate that thickens it
Endospore
a portion of DNA in bacteria covered by many membranes, hard to stain
bacteria produce this when it feels threatened or environment is unfavorable
Vegetative cell
viable cells that are easier to stain & can still make a copy of themselves, if there is an endospore within a ______ ____ it is still viable
once endospore leaves cell, it can no longer replicate
endospore stain
stain used to distinguish endospores from vegetative cells
genera Bacillus & Clostridium
Malachite green, Congo Red
In an endospore stain, the endospore has a greenish color bc of the stain _____ ___ & vegetative cells have a red stain because of _____ ____ (counterstain)
Subterminal
What is the location of this endospore?
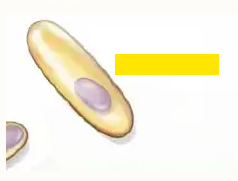
Central
What is the location of this endospore?

terminal
What is the location of this endospore?