ANAT<3
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
two struc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms

DNA structure
two strands that make a helix

RNA structure
single strand of nucleotides, very long
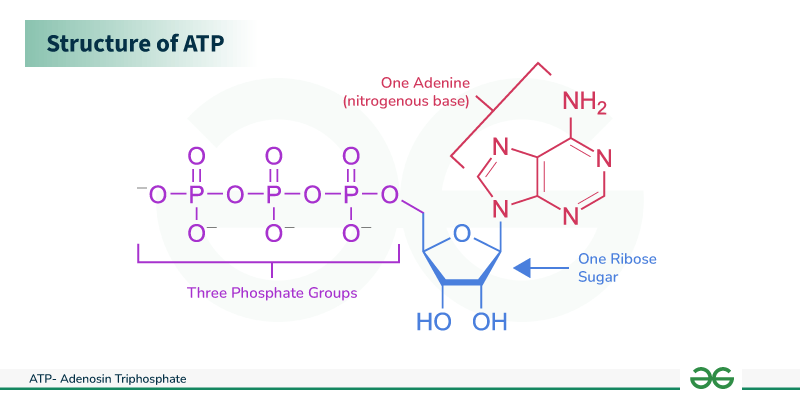
ATP stucture
3 phosphate, Nitrogenous base, RNA nucleotide
Why is ATP called the cells energy currency
it acts as the primary molecule used to store and transfer energy within a cell
sugar molecules; a macronutrient found in food and drinks that provide energy for the body
description of carbohydrates
fatty, waxy, or oily compounds that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in polar solvents such as water; hydrophobic small molecules
description of lipids
essential for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs
description of proteins
large biomolecules, composed of chains of smaller units called nucleotides
description of nucleic acids
the simplest form of sugar, considered the basic building block of carbohydrates, which cannot be further broken down into smaller sugar units
description of monosaccharides
the sugar formed when two monosaccharides are joined by glycosidic linkage
description of disaccharides
a complex carbohydrate molecule composed of long chains of simple sugar units (monosaccharides) linked together by glycosidic bonds
description of polysaccharides
a molecule that consists of two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond
dipeptide
molecules that combine to form proteins
amino acids
link that connects two amino acids together within a protein chain
peptide bond
A substance that contains many amino acids
polypeptide
proteins that help speed up metabolism, or the chemical reactions in our bodies
enzymes
triglycerides has
a glycerol backbone esterified with three fatty acids.
saturated has
a carbon chain with only single bonds between each carbon atom
unsaturated has
one or more double bonds between carbon atoms
Phospholipids has
a phosphate group on one end, called the “head,” and two side-by-side chains of fatty acids that make up the lipid “tails. ”
wax has
esters made up of an alcohol chain and a fatty acid chain
steroids has
a 4 ring structure, found in cell membrane, act as hormones in the body
chemical substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions
chemical element
list the subatomic particles;
describe their relative masses,
charges and positions in the atom
Protons: 1.007, Positively charged, in the nucleus.
Neutrons: 1,008, Neutral particles (no charge), in the nucleus.
Electrons: 5.45 x 10^ -4 Negatively charged, orbit the nucleus
the smallest unit of matter, like a tiny building block, that makes up everything around us, including our bodies
atom
the total weight of an atom, essentially the combined mass of its protons and neutrons
atomic mass
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
isotopes
An unstable form of a chemical element that releases radiation as it breaks down and becomes more stable.
radioisotope
difference between ionic and covalent bonds
If a compound is made from metal and a nonmetal, its bonding will be ionic.
if a compound is made from two nonmetals, its bonding will be covalent.
ionic and covalent bonds contrasted from hydrogen bonds
Ionic bonds are the attraction of two opposite charges. A covalent bond is made of joined hydrogen atoms.
Hydrogen bonds are the attraction between a hydrogen and an electronegative atom.
compare and contrast polar and nonpolar compounds
nonpolar covalent bond is a bond that involves equally shared electrons
polar covalent bonds are asymmetric sharing of electrons.
how are dehydration synthesis reactions and hydrolysis reactions are important in metabolism
primary mechanisms used to build up and break down large biological molecules like proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids
stands for "potential of hydrogen”; measurement of how acidic or basic a solution is, using a scale from 0 to 14, values where below 7 are acidic, 7 is neutral, and values above 7 are basic
explanation of the concept of pH
compare the functional rules of neutral fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes in the body
Neutral fats primarily function as energy storage molecules
phospholipids form the structural backbone of cell membranes
steroids act as signaling molecules and regulate various bodily functions
waxes provide a protective barrier on body surfaces like skin and hair due to their water-repellent properties
contrast structural and functional proteins
Provide structure and support to cells, tissues, and organisms. They include collagen, actin, myosin, and keratin, which help shape hair, skin, nails, and bones.
Perform specific biological functions in the body, such as transporting molecules, storing molecules, and providing immune protection. They include hemoglobin, insulin, and enzymes.
ability to increase the rate of chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy, or energy toll, required for the reaction to occur.
description of the mechanism of enzyme activity
compare and contrast DNA and RNA
DNA is a double-stranded molecule, while RNA is single-stranded. DNA is also much longer than RNA.
consumed for energy in processes including ion transport, muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, substrate phosphorylation, and chemical synthesis; serving as a usable storage form of free energy.
the role of ATP in cell metabolism
It acts as a building material, as a carrier for nutrients and waste products, and as a lubricant and shock absorber.
why we need water
properties of water
high heat capacity-ability to retain heat and regulate body temperature
cushioning-hypodermis provides physical cushioning to any medical trauma
high heat of vaporization-takes a lot of energy to turn water from liquid to gas.
composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; sugar molecules
carbohydrates
large, complex molecules that play many important roles in the body
proteins
the amount of enzyme needed to catalyze a chemical reaction under specific conditions
enzyme activity
a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base, RNA nucleotide, 3 phosphates
ATP
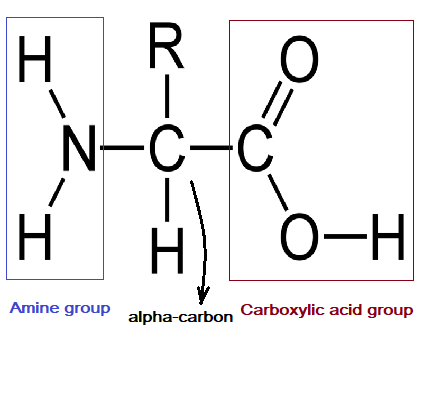
R=CH2-CH2-COOH
H2N-C-COOH
^H
amino acid
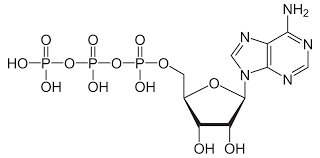
ATP
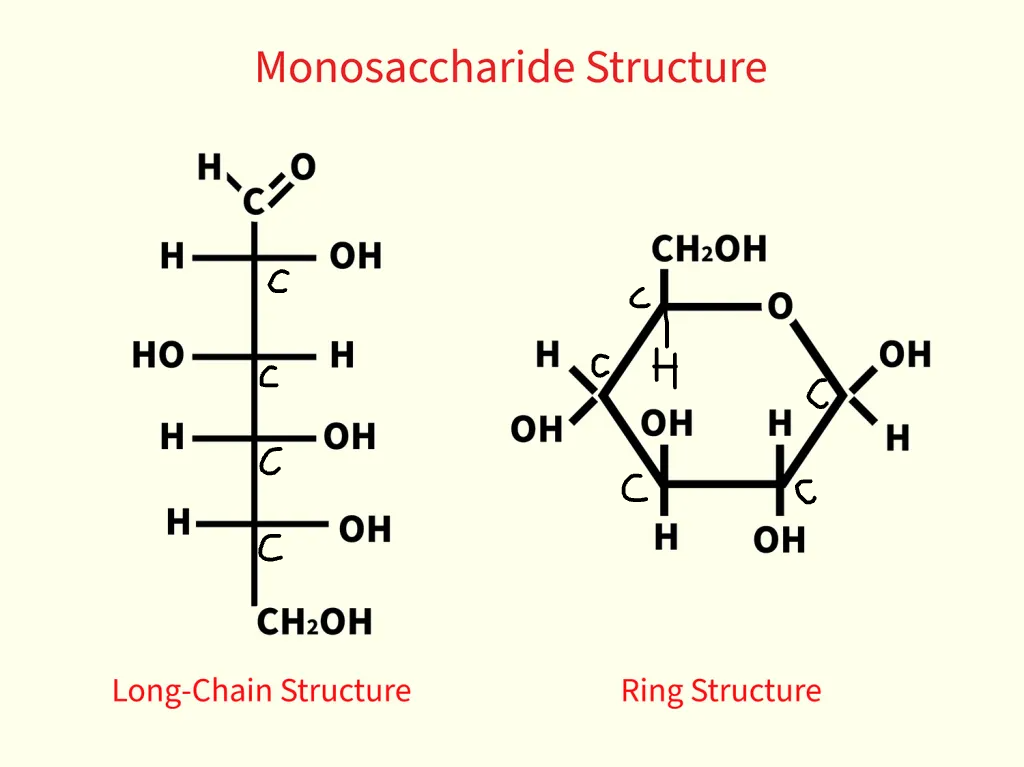
carbohydrate (monosaccharide)
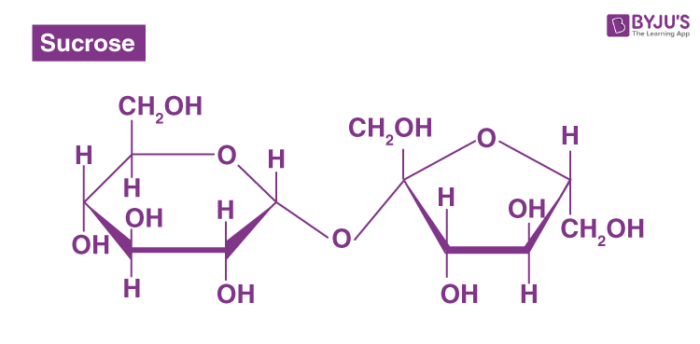
carbohydrate (disaccharide)
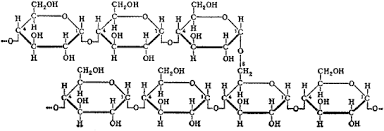
carbohydrate (polysaccharide)
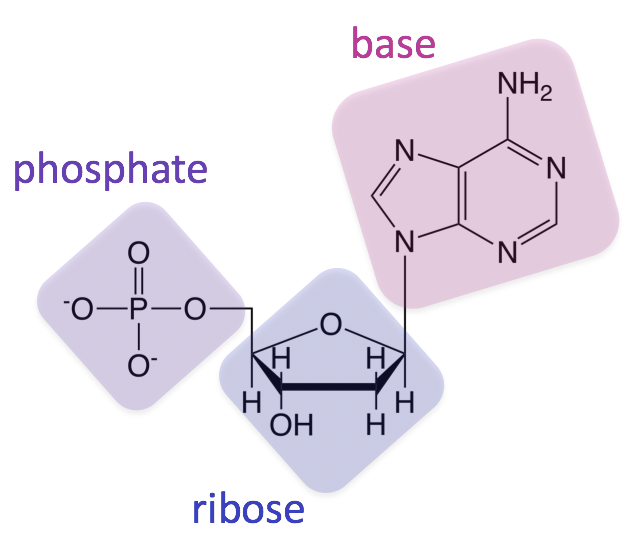
nucleic acid
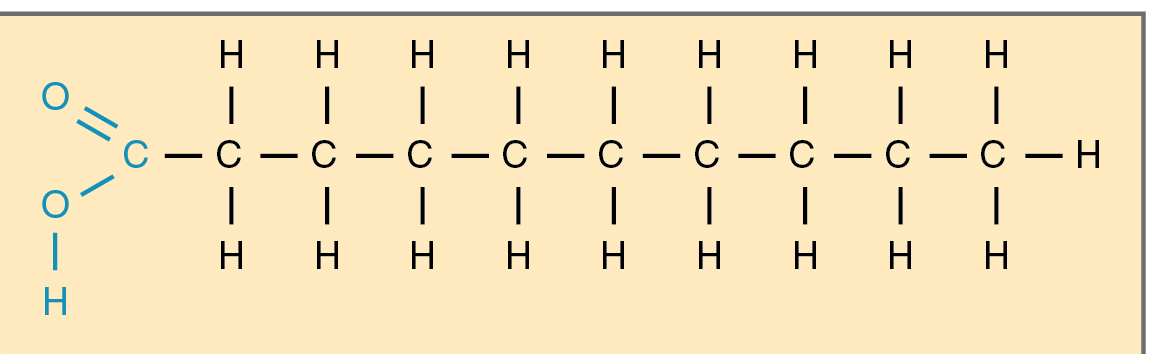
saturated fat
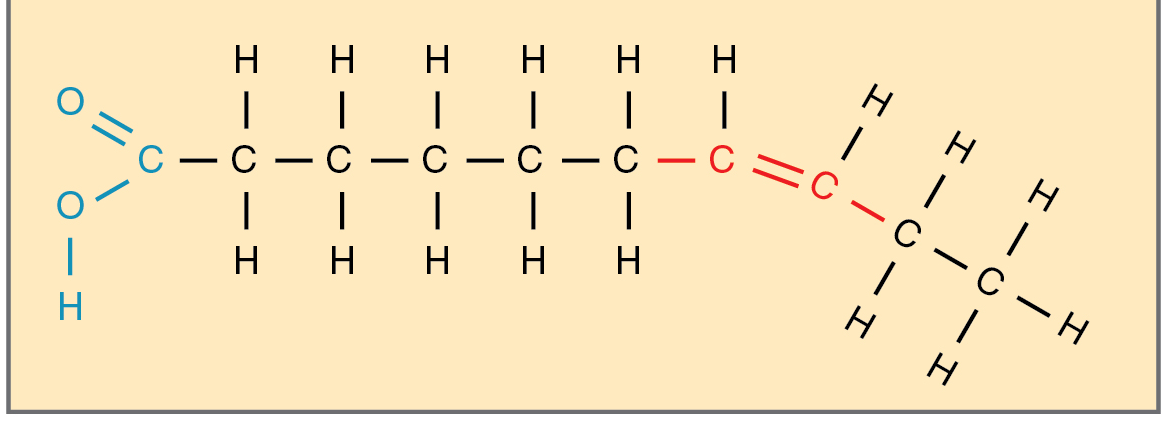
unsaturated fat
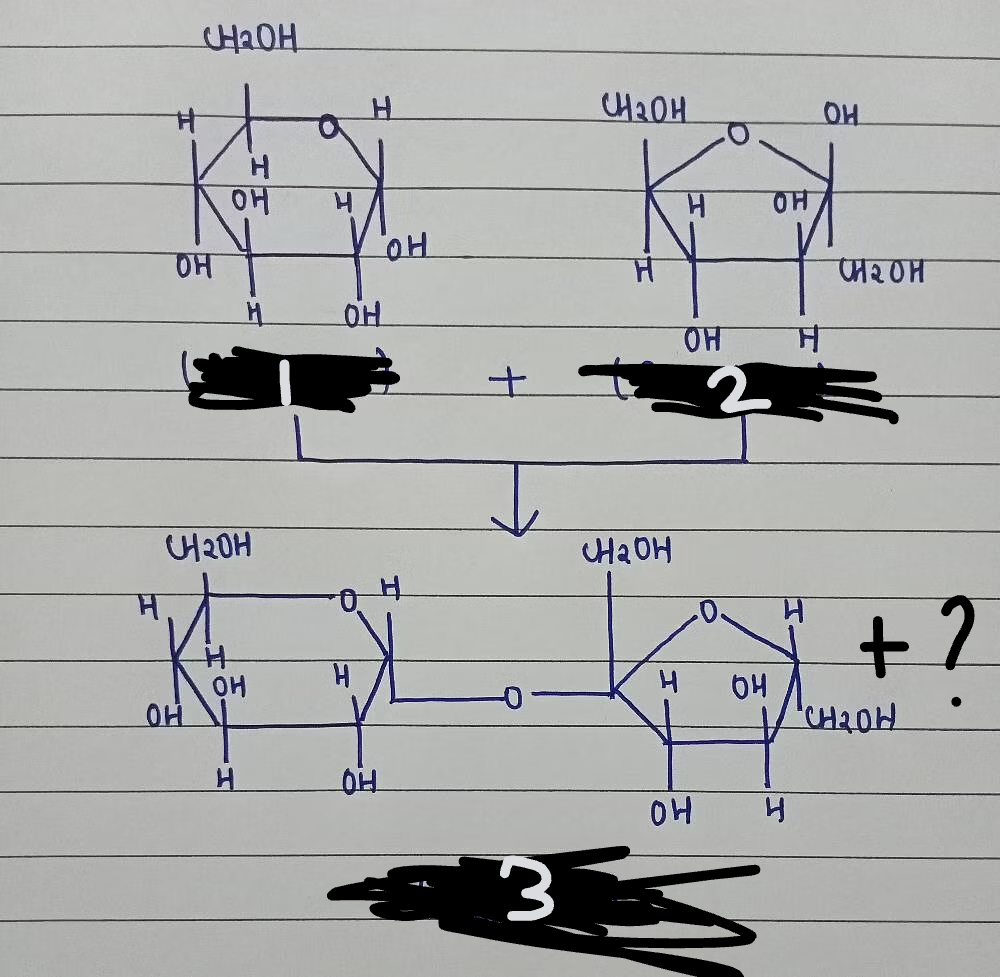
1+2=3+?
glucose + fructose= sucrose + H2O
why study organic compounds
all living things are made up of organic compounds
by joining monomers, or single molecules, together in a long chain
how macromolecules are formed
a process called hydrolysis
how macromolecules are disassembled
what is the relationship between these two terms monosaccharide and polysaccharide
polysaccharides are composed of 3 or more monosaccharides linked together
name and describe two storage polysaccharides
starch, found in plants
glycogen, found in water
name and describe two structural polysaccharides
cellulose, found in plant cell walls
chitin, found in exoskeletons of insects and some cell walls of fungi
every amino acid has four characteristic components list the four parts of an amino acid
a central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and R group
how are enzymes and catalysts different
enzymes are organic in nature; where catalysts are inorganic compounds
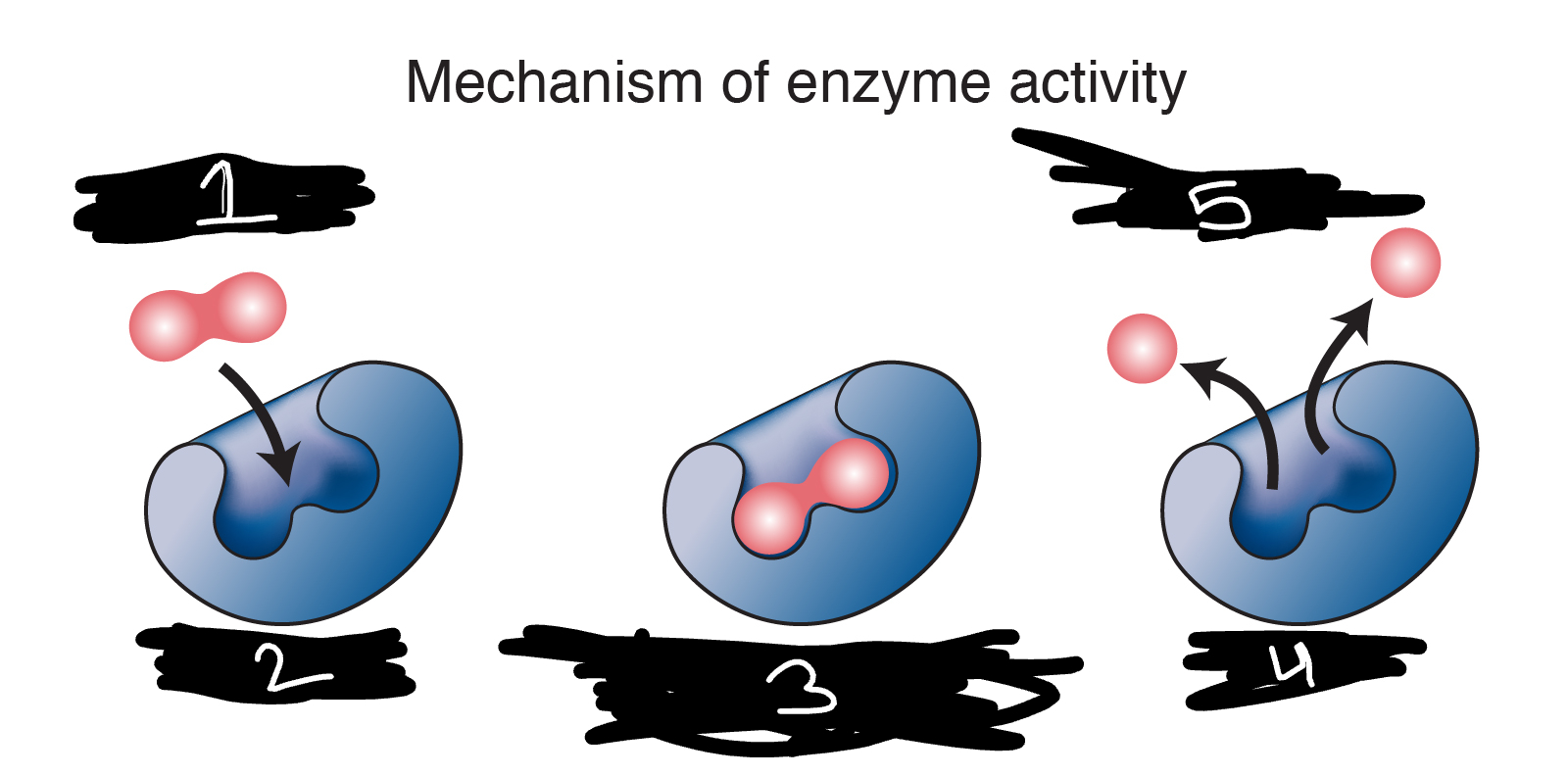
enzyme activity
1 substrates
down arrow substrates enter active site of enzyme
2 enzyme
3 enzyme-substrate complex /enzyme-product complex
4 enzyme
up arrow products leave active site of enzyme
5 products
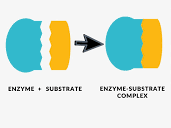
lock and key
blue enzyme
orange substrate
blueorange enzyme-substrate complex
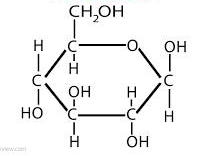
glucose
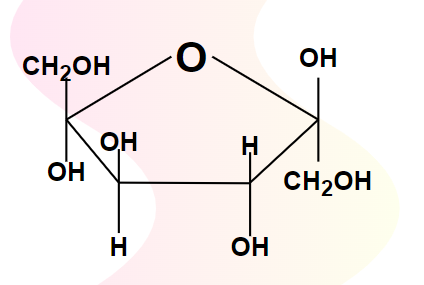
fructose
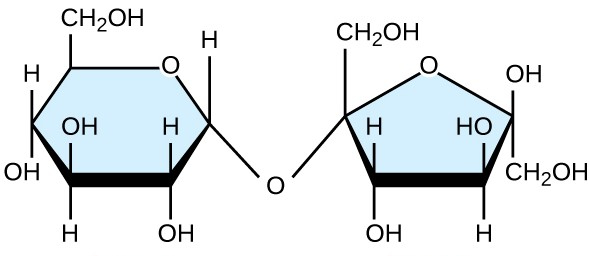
sucrose