A&P: The Skeletal System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:47 PM on 4/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
270, 206
A human is born with roughly ___ bones. As a person grows, this number decreases to approximately ___.
2
New cards
axial skeleton, appendicular skeleton
Anatomically, the skeletal system is divided into two major divisions: ________________ and ___________________.
3
New cards
bones, cartilages, joints, ligaments
The **skeletal system**, or **skeleton**, is composed of:
4
New cards
20%
The skeleton accounts for ____ of body mass.
5
New cards
80, skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
**Axial skeleton** consists of ___ bones divided into three major regions:
6
New cards
longitudinal axis, head, neck, trunk, brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs
Functions of axial skeleton:
* Form _________________ of body
* Support ______, ______, and ______
* Protect _____, _________, and ______________
* Form _________________ of body
* Support ______, ______, and ______
* Protect _____, _________, and ______________
7
New cards
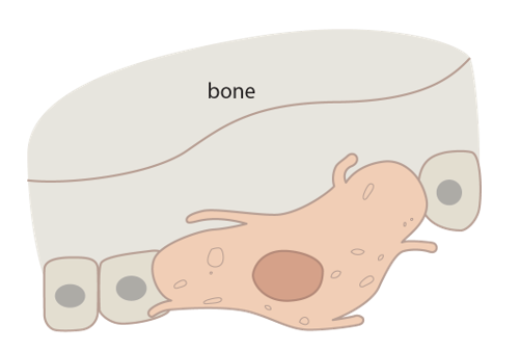
upper and lower extremities, girdles, vertebral column
The **appendicular skeleton** comprises the bones of the _________________ and the associated ______that connect the extremities to the _______________.
8
New cards
pre-sacral vertebrae, 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx
**Twenty-four** of the bones in the **vertebral column** are called the _________________. These consist of ________, _____________, and ____________. The last two bones of the vertebral column are the _______ and ________.
9
New cards
active form
Bone is an _____________ of **connective tissue**.
10
New cards
support, movement, protection, mineral storage, hematopoeisis
Functions of the skeletal system:
11
New cards
body posture, rigid, upright, muscles
**Support:** Bones and cartilage support _________ because both structures are ___. They also allow a person to remain _______ and provide a framework to which soft tissues like _______ and organs can attach.
12
New cards
muscular system, ligaments
**Movement:** Bones of the skeletal system interact with the ____________ to help the body move. Bones themselves cannot move. But when connected to each other by ___________, along with the action of muscles, a human body can move.
13
New cards
external damage, skull, vertebral column, sternum, ribcage
**Protection:** The skeletal system protects vital organs from _____________. The _____ protects the brain, the __________ protects the spinal cord, and the ________ and _________ protect the lungs.
14
New cards
calcium, phosphorus, physiological functions
**Mineral storage:** Bone functions as a storage site for important minerals like _______ and __________. These minerals are used for a variety of _________________ in the body.
15
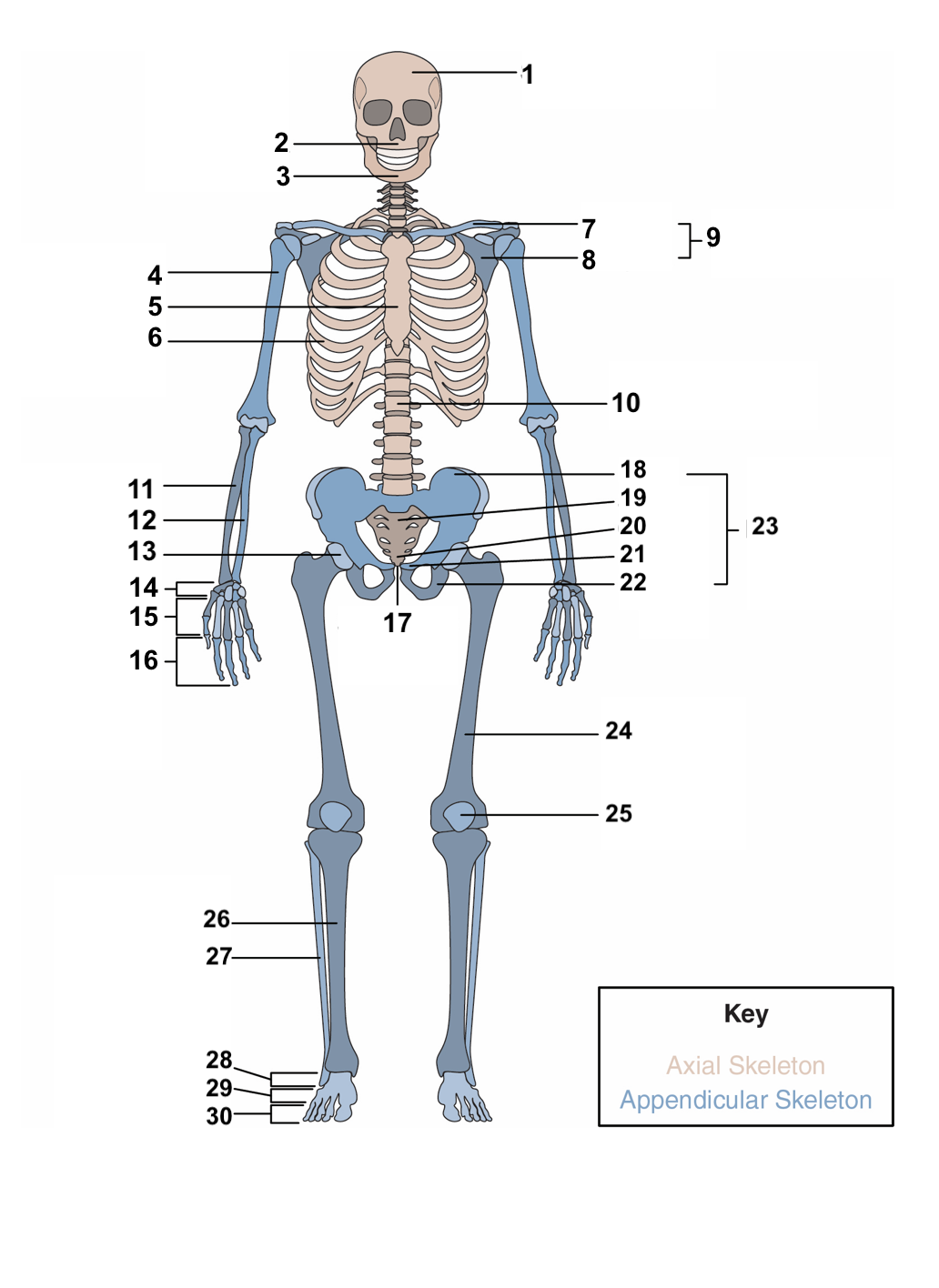
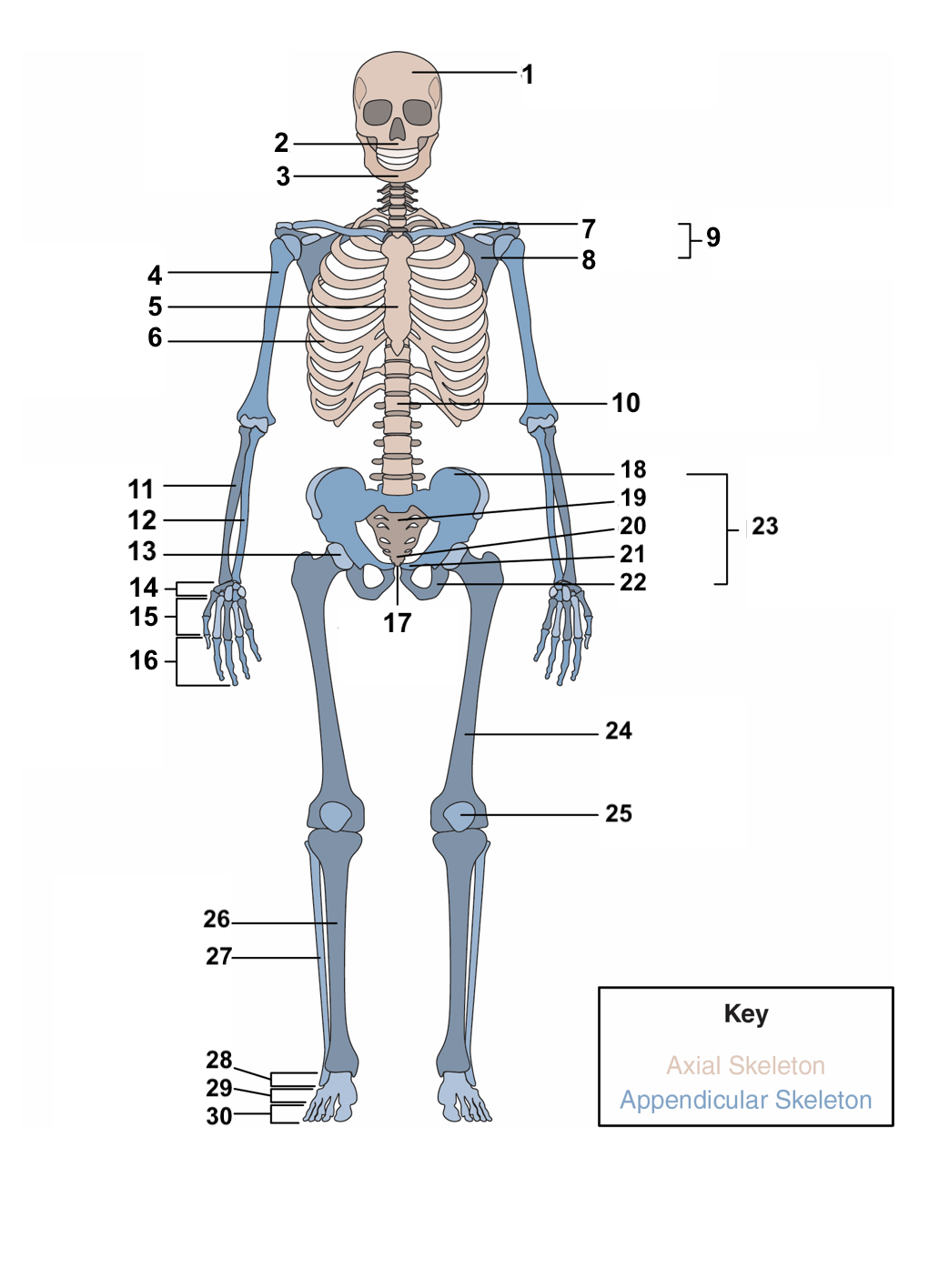
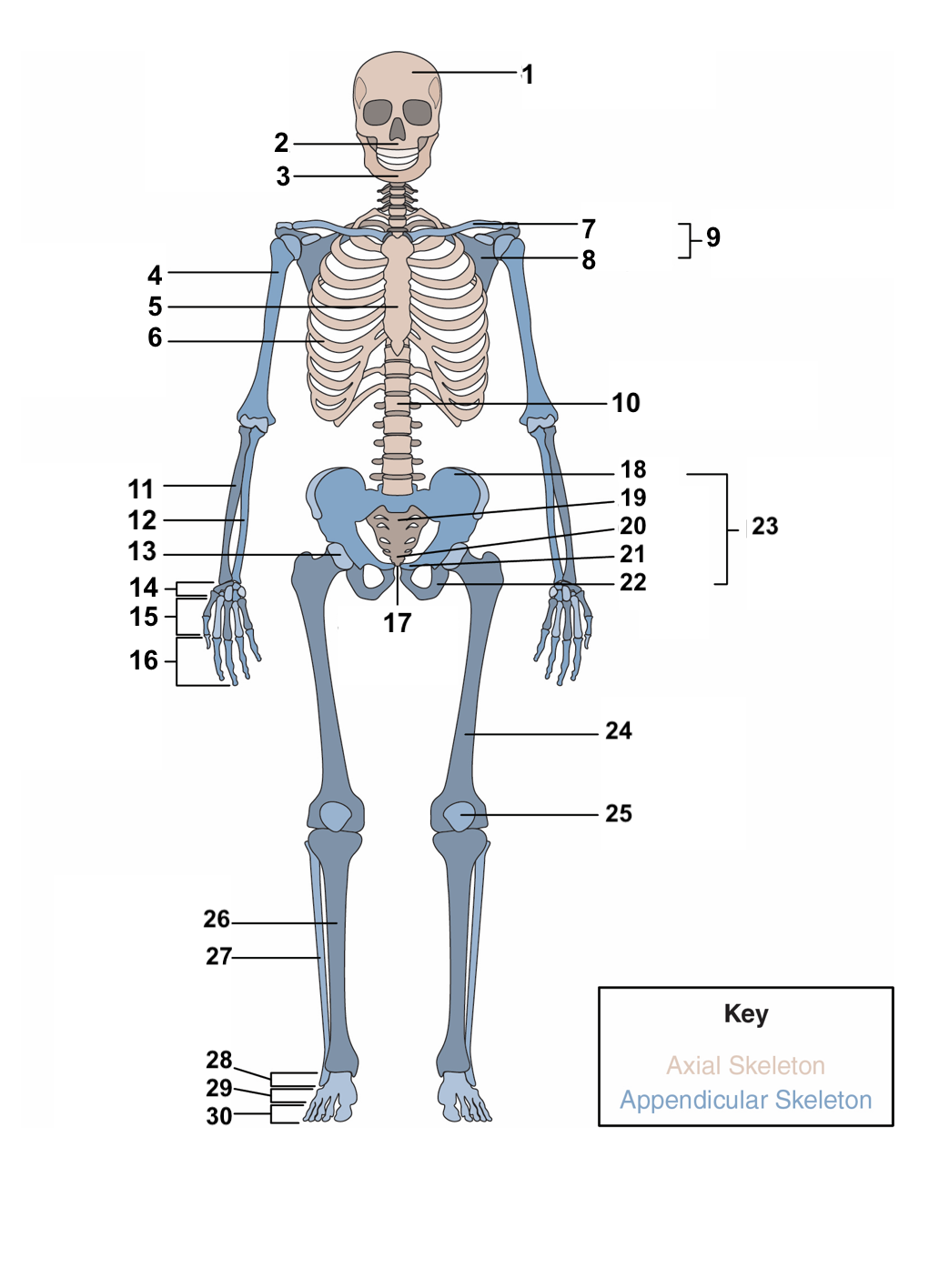
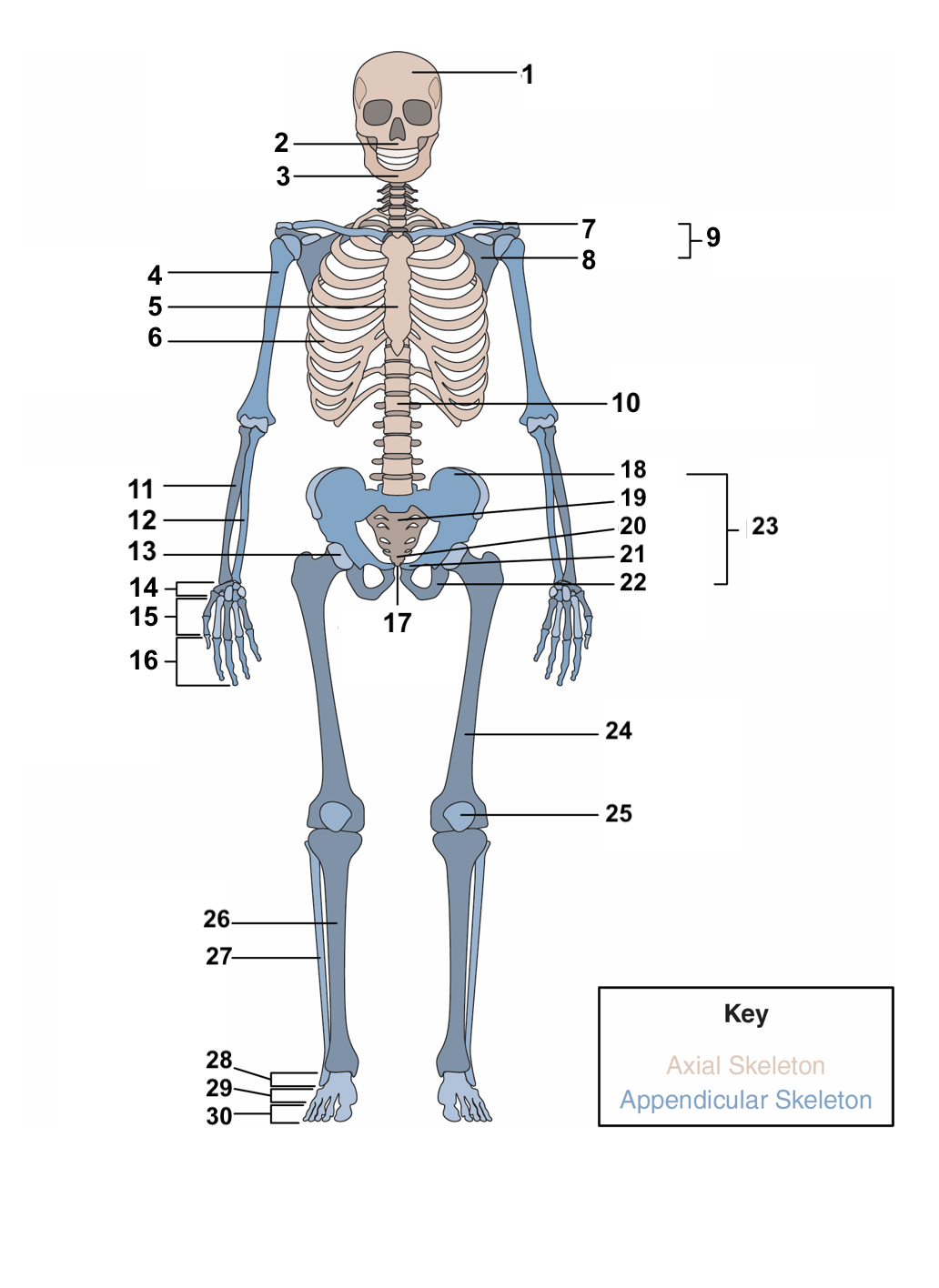
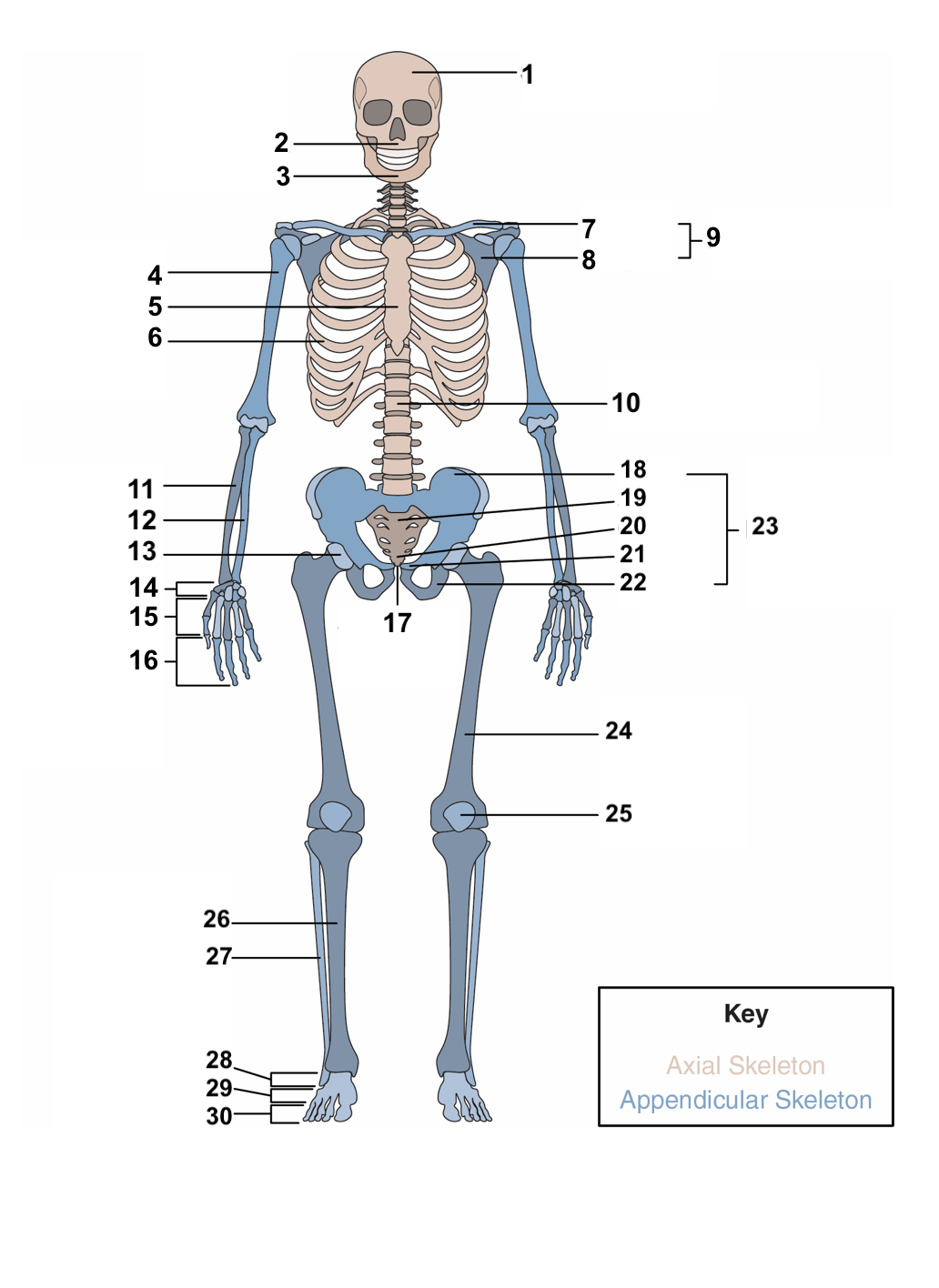
New cards
red blood cells, stem cells
**Hematopoiesis:** This is the process bones use to produce ______________ and ____________, which differentiate to a variety of different cell types in the body.
16
New cards
compact bones, spongy, cancellous bone
The overall structure of bone consists of an outer shell called ________________. It encloses another type of bone tissue that is loosely organized called _______ or _______________.
17
New cards
osteons, cylinders, mineral matrix, living bone cells
**Compact bone** is made of units called ________. These structures look like ________. They contain a _______ and _______________.
18
New cards
Haversian canal, blood vessels, nerve fibers
Each **osteon** also contains a ____________ that houses the bone’s __________ and _____________.
19
New cards
periosteum
Surrounding the compact bone is a fibrous membrane called the ___________.
20
New cards
blood vessels, nerve and lymphatic vessels
The periosteum consists of _________________________ that nourish the compact bone.
21
New cards
long, short, flat, irregular, sesamoid
There are five types of bones in the human body:
22
New cards
Elongated bones; longer than they are wide
Appearance of **long bones**:
23
New cards
Femur, tibia, clavicle, humerus and metacarpals
Examples of **long bones:**
24
New cards
Broad bones that are thin
Appearance of **flat bones:**
25
New cards
Scapula, hip bones (os oxo), sternum, nasal bone, and occipital/parietal/frontal bones of the skull
Example of **flat bones:**
26
New cards
Vertebrae
Example of **irregular bones:**
27
New cards
Small bones
Appearance of **sesamoid bones**:
28
New cards
Patella (kneecap)
Example of **sesamoid bones:**
29
New cards
About same width as length
Appearance of **short bones**:
30
New cards
Carpal and tarsal bones for the wrist and feet
Example of **short bones:**
31
New cards
proximal epiphysis, diaphysis, and distal epiphysis.
The long bone consists of three major sections:
32
New cards
spongy bone, compact bone, bone growth
**Epiphysis:** This is found at each end of the long bone. It consists primarily of ____________ with a thin layer of ______________. _____________ occurs at the epiphysis.
33
New cards
Articular cartilage, frictions
**______________:** This covers the epiphysis. It decreases __________ at the joints.
34
New cards
compact bone
**Diaphysis:** This is the longest part of the long bone. It consists primarily of _______________.
35
New cards
Medullary cavity, red and yellow bone marrow, hematopoiesis, fat cells
**______________:** This is found inside the long bone. It is composed of ___________________. Red marrow is where __________ occurs. Yellow marrow consists primarily of __________.
36
New cards
Ossification, calcium and phosphorus
**_____________** is the process of bone formation that occurs first during embryonic development. This process transforms soft, flexible cartilage to hard bone. It does so by replacing the cartilage with mineral deposits, specifically _______________________.
37
New cards
center, end
Ossification begins in the _____ of bones and spreads toward the ______ of the bones
38
New cards
growth plates
There are **____________** at the end of long bones. This region is also made of cartilage. As the child grows, this area of cartilage at the ____________ experiences ossification to elongate the bone, enabling a person to grow taller.
39
New cards
bone remodeling
Ossification also plays a role in ______________.
40
New cards
bone resorption
Mature bone tissue is constantly being broken down through a process called _________________.
41
New cards
osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts
There are three types of bone cells:
42
New cards
collagen, extracellular matrix
**Osteocytes:** These are bone cells. They produce _________ and other substances that create the __________________ of bone.
43
New cards
bone-forming cells, on the surface
**Osteoblasts:** These are called _______________. They are found __________________ of bone and can be stimulated to differentiate into other type of bone cells called osteocytes.
44
New cards
bone-reabsorbing cells, dissolve
**Osteoclasts:** These are called ______________. They are found on the surface of bone. They _________ the bone.
45
New cards
deposition of new bone
Bone resorption frees calcium and other minerals from bone for use in the body and clears out older pieces of bone. In doing so, this process promotes the __________________.
46
New cards
ilium, ischium, pubis, hipbone
Half of the pelvic bone has three separate bones at birth: the ___, ____, and ___. By adulthood, these bones fuse into one bone called the _______.
47
New cards
pores
As the name implies, spongy bone is lighter and less dense than compact bone. It is spongy because it consists of open sections called ______.
48
New cards
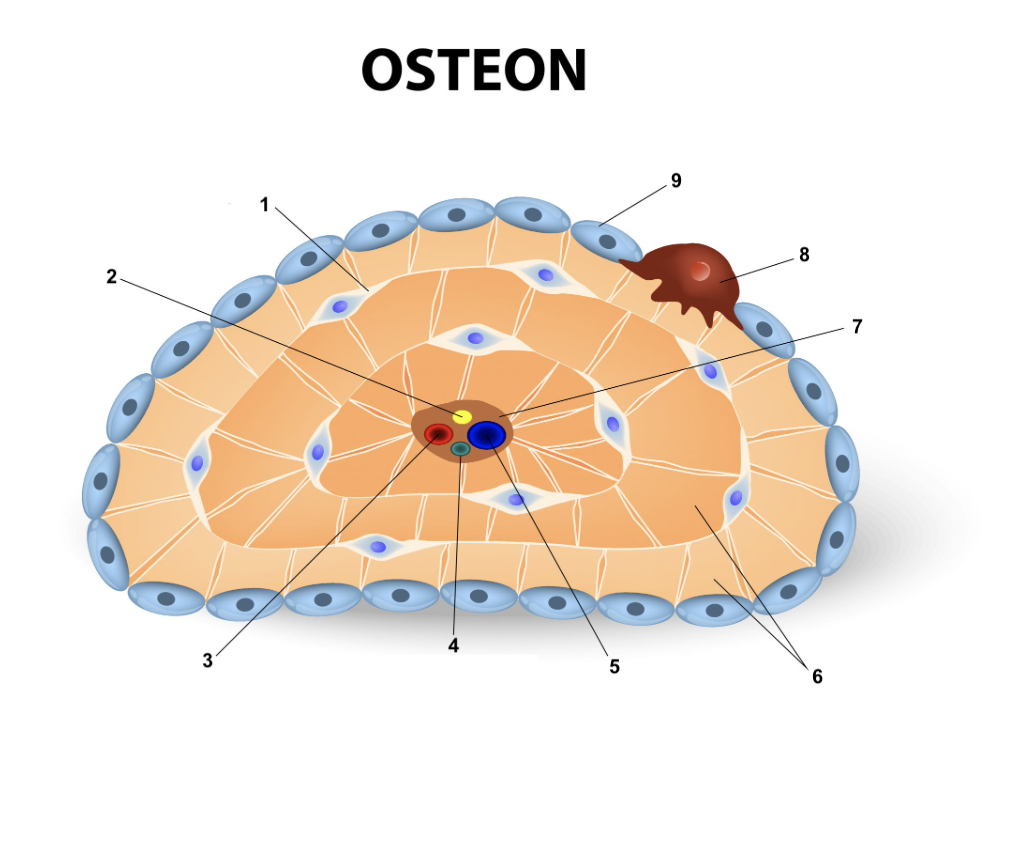
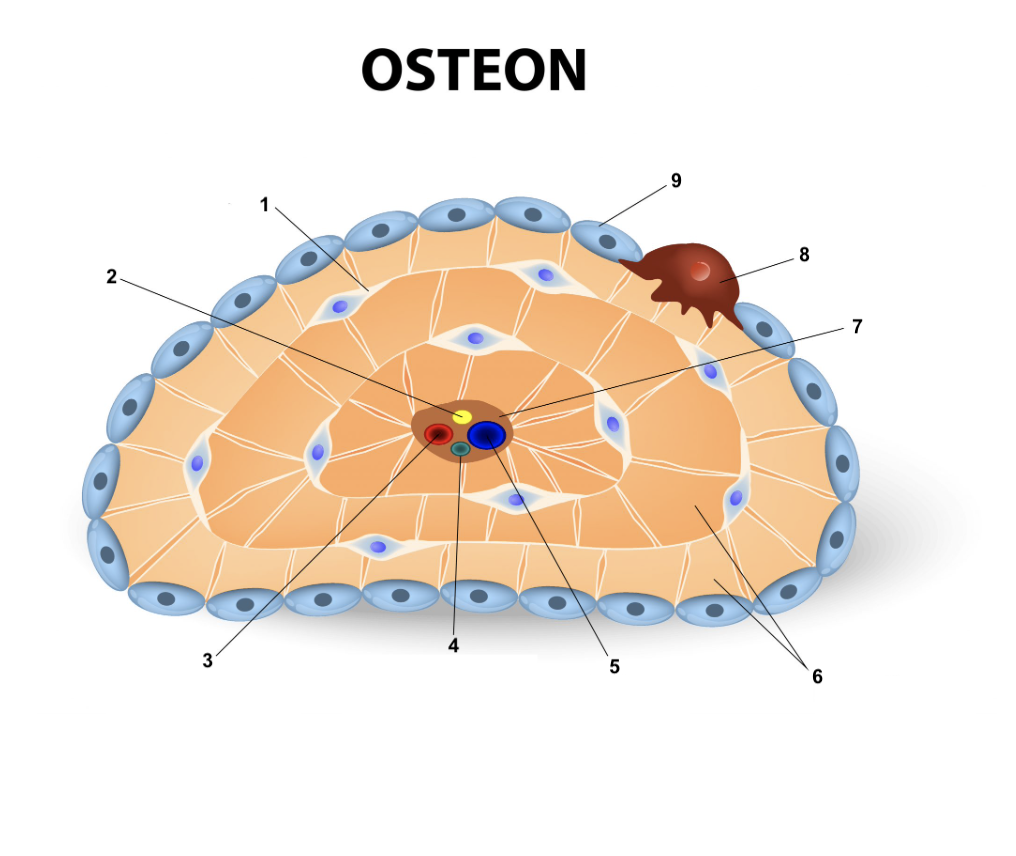
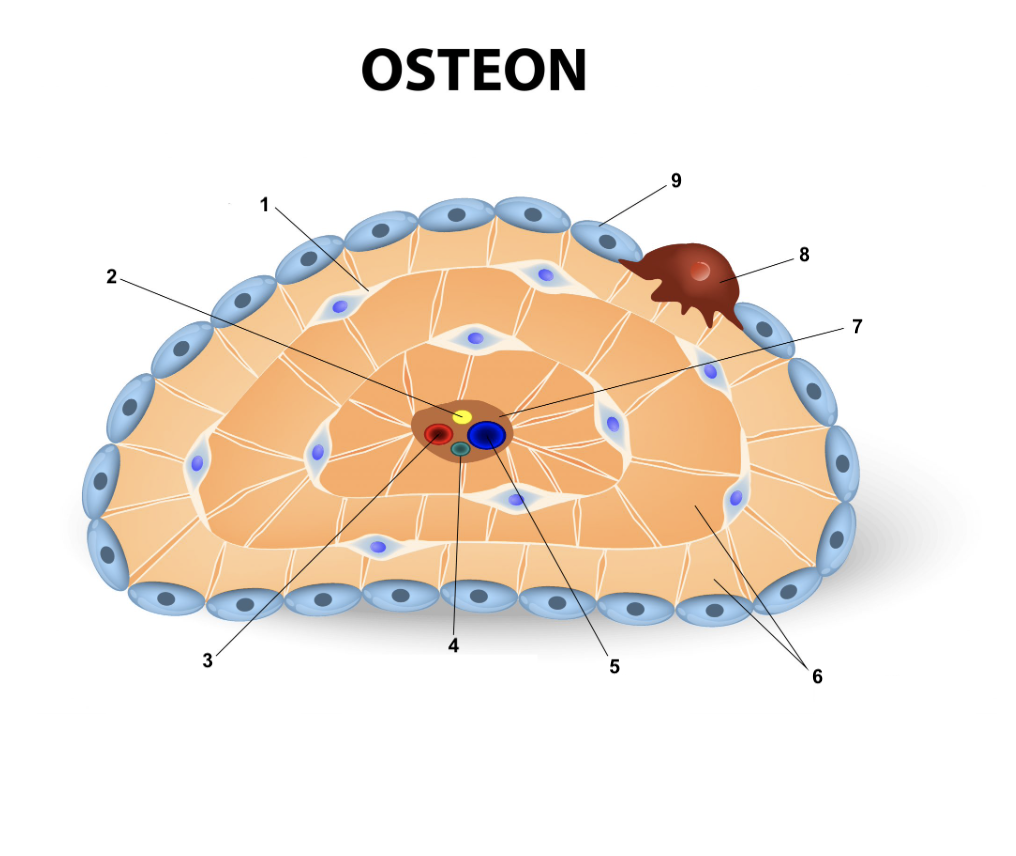
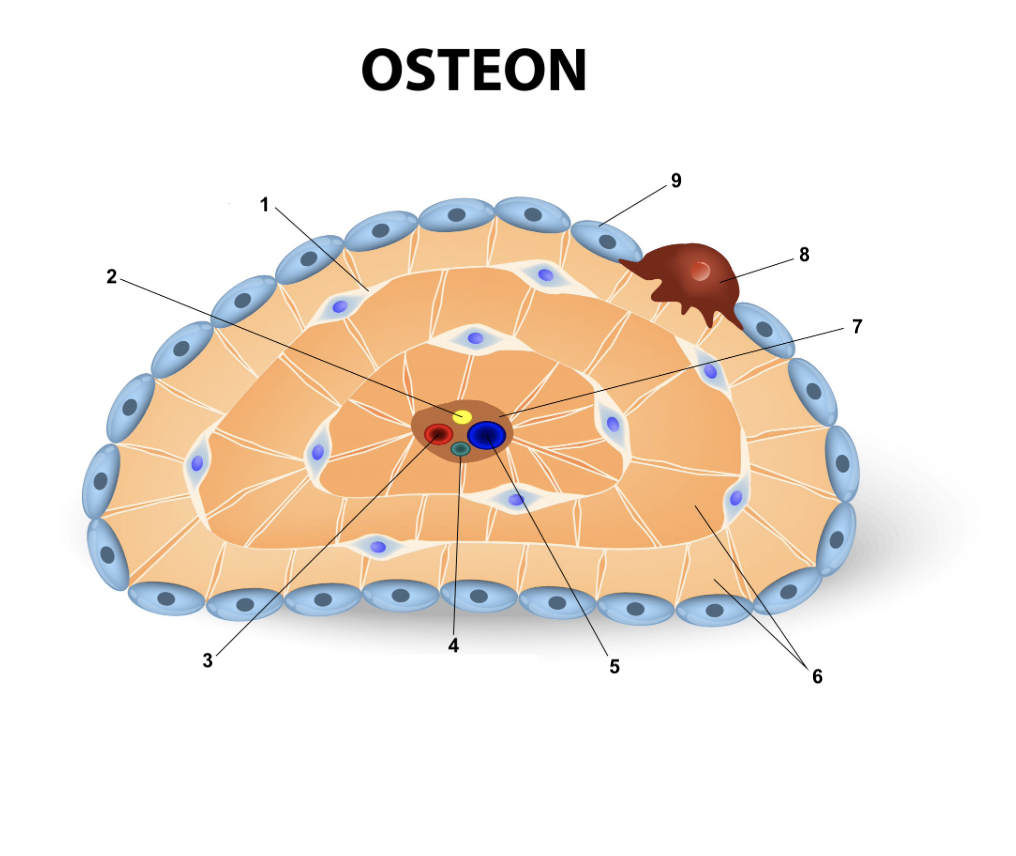
Osteon
1
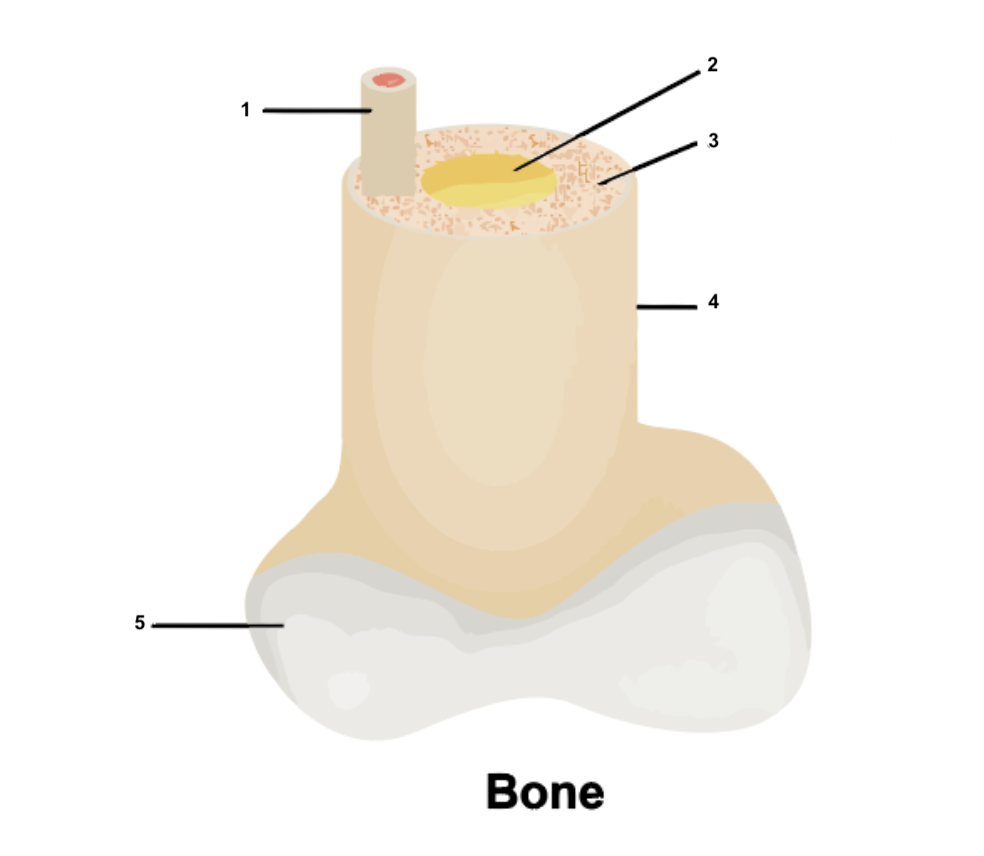
49
New cards
Yellow bone marrow
2
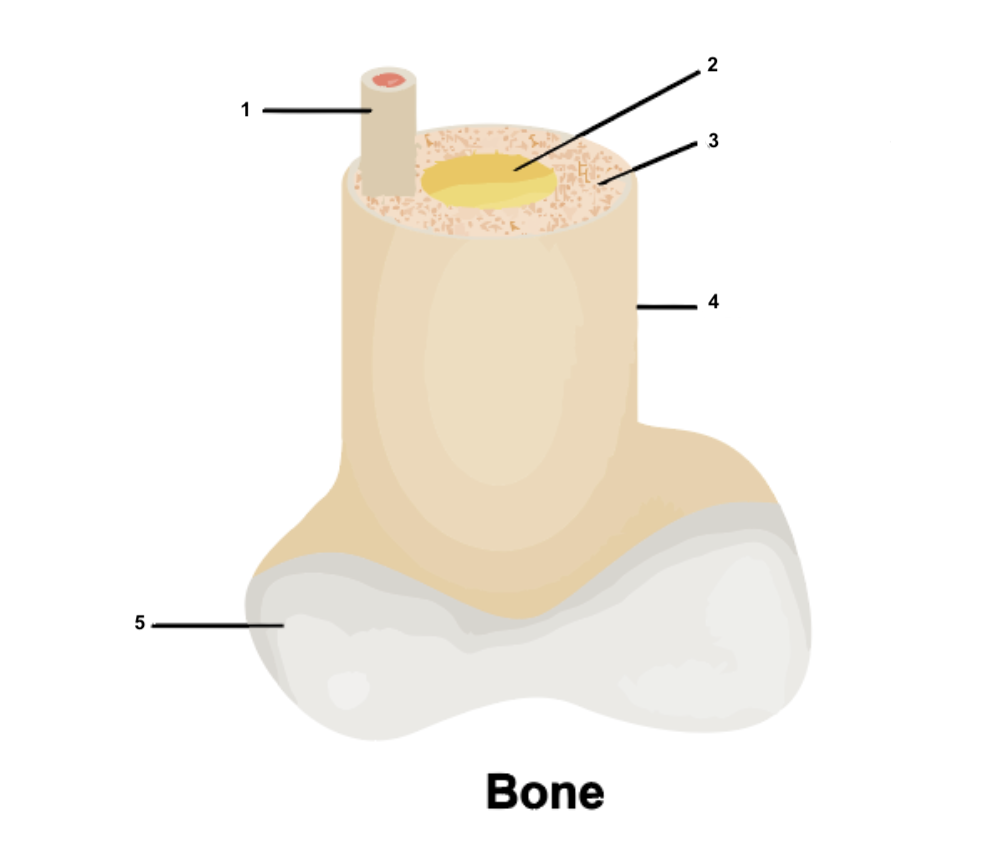
50
New cards
Compact bone
3
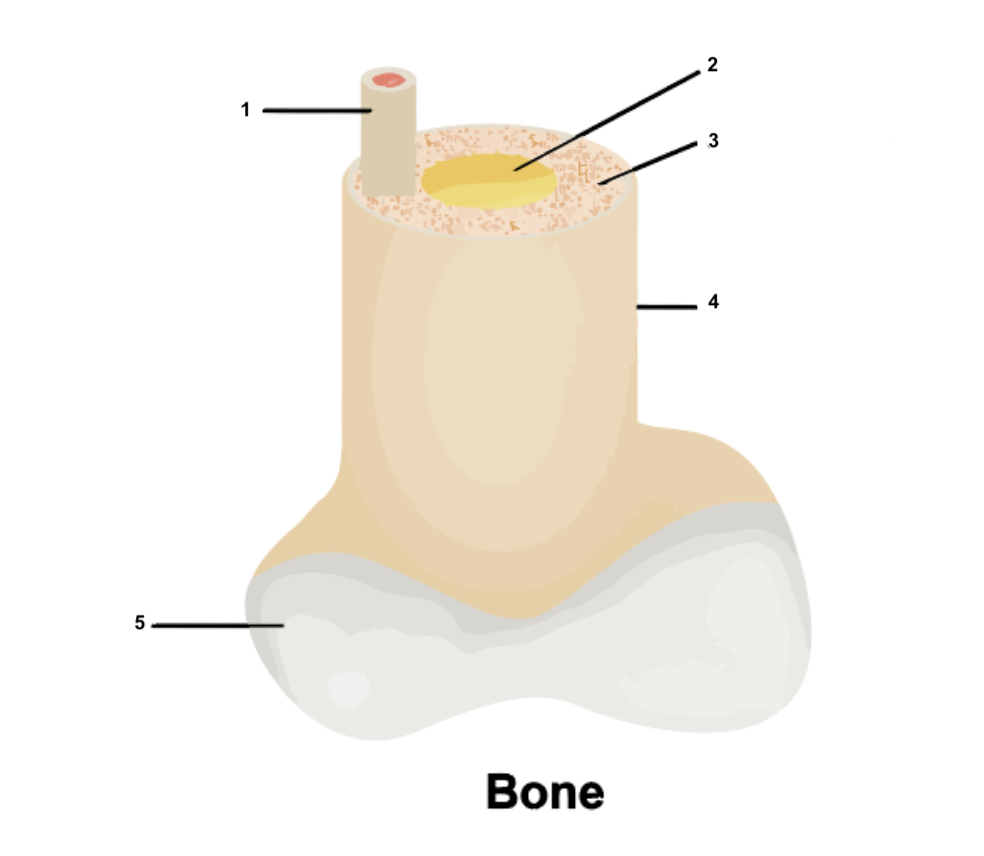
51
New cards
Periosteum
4
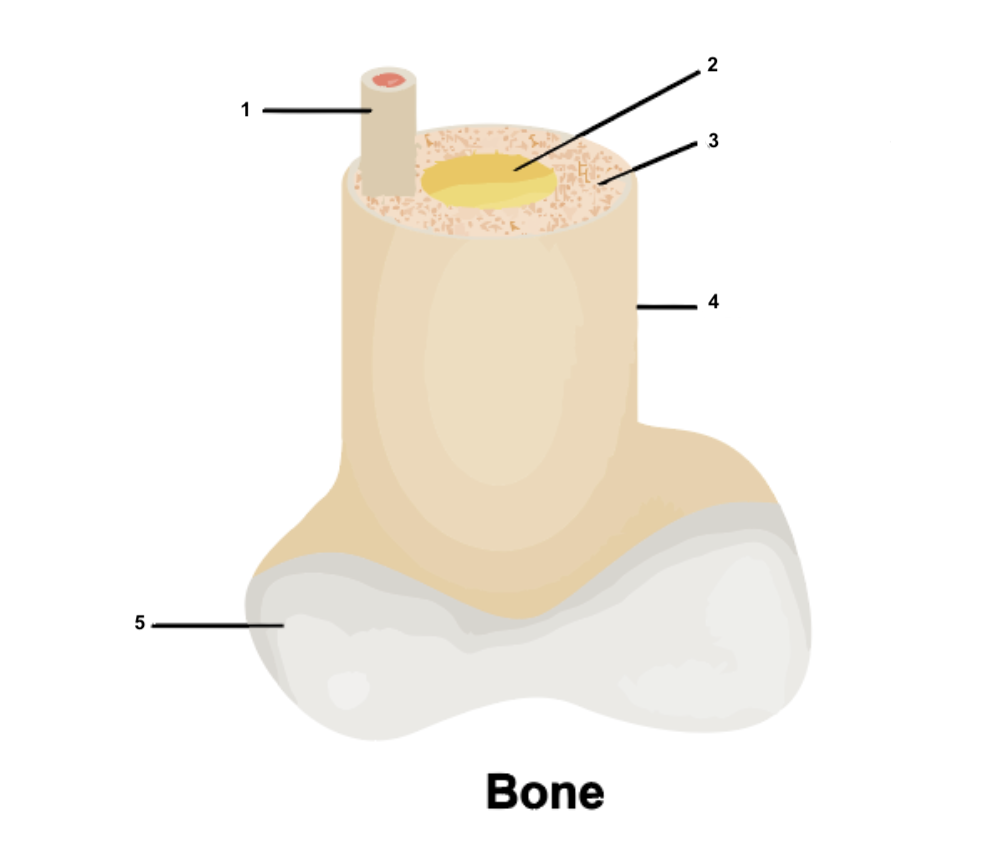
52
New cards
Cartilage
5
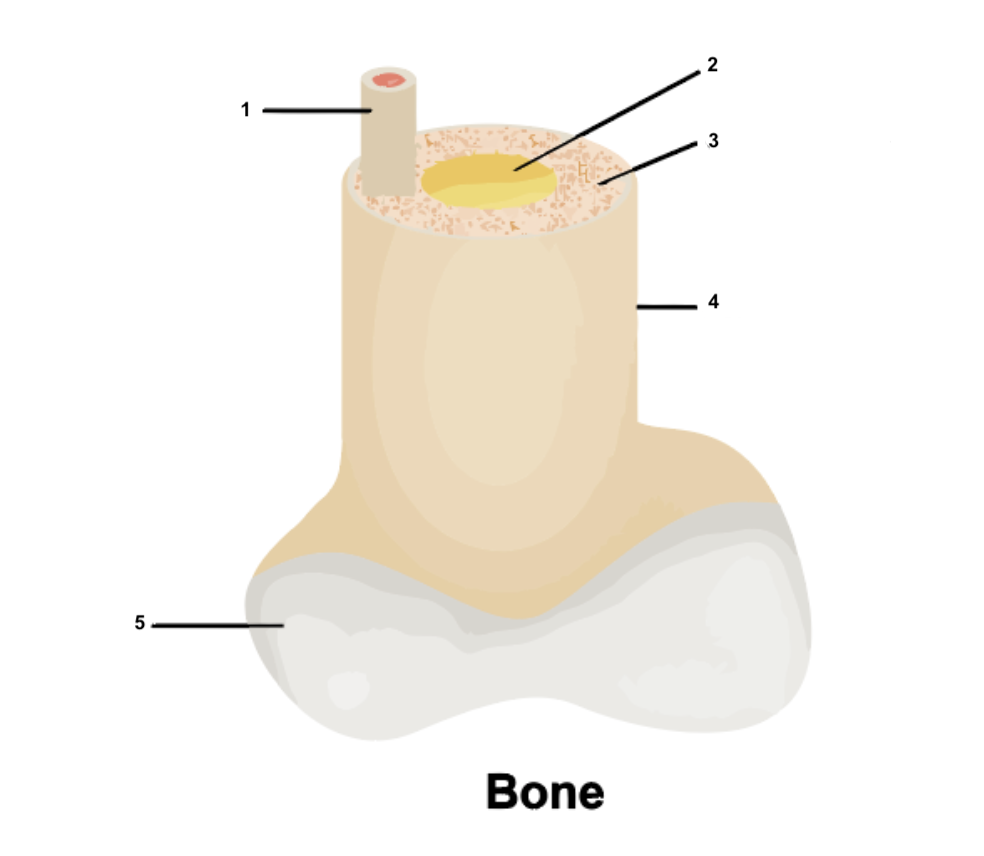
53
New cards
Osteocyte
1
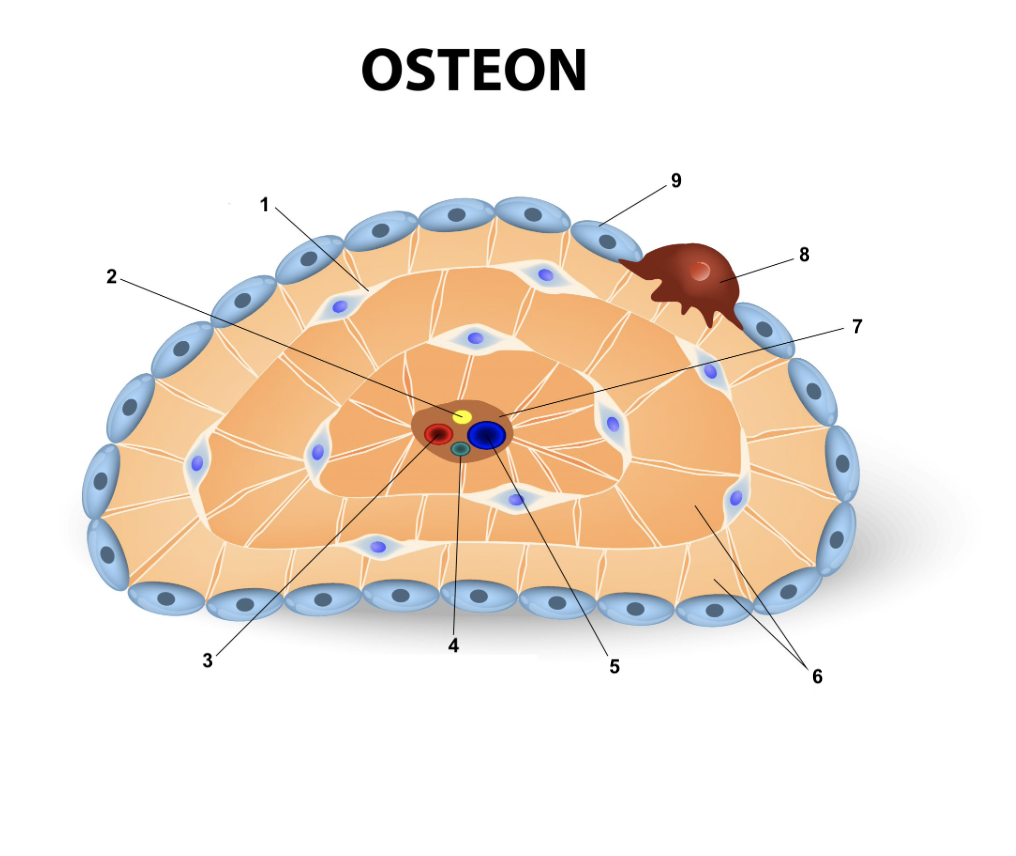
54
New cards
Nerve
2
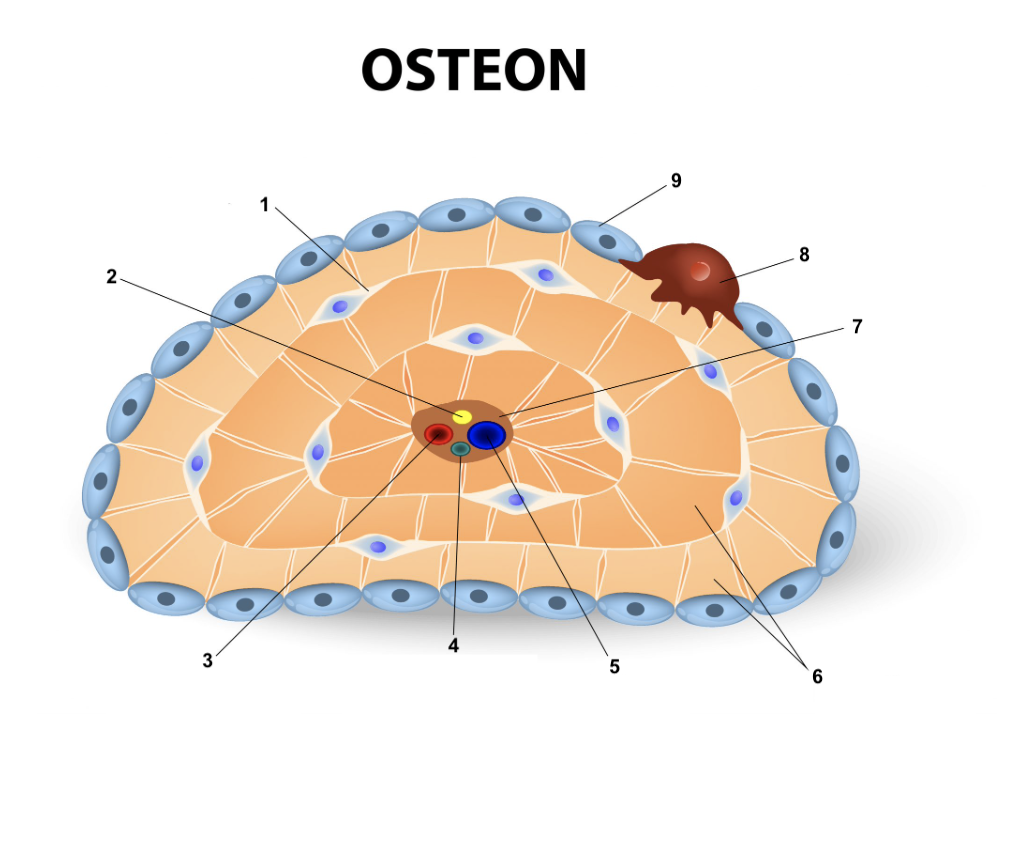
55
New cards
Artery
3
56
New cards
Lymphatic vessel
4
57
New cards
Vein
5
58
New cards
Lamellae
6
59
New cards
Central canal
7
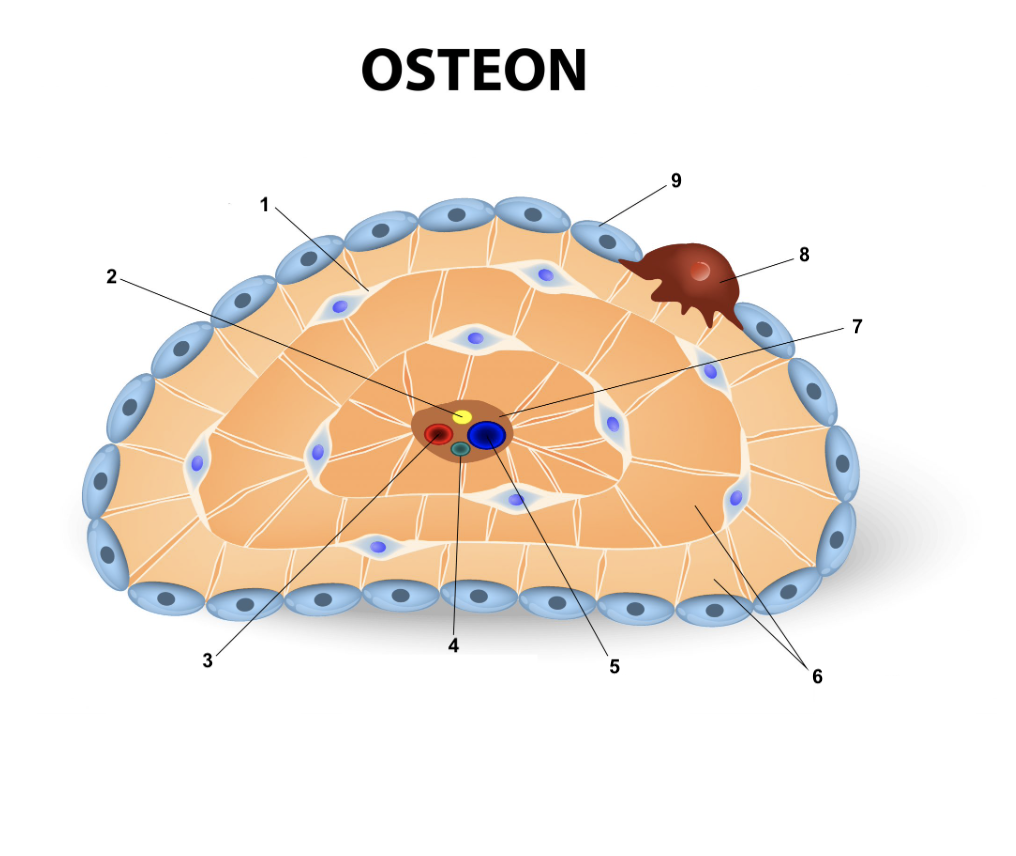
60
New cards
Osteoclast
8
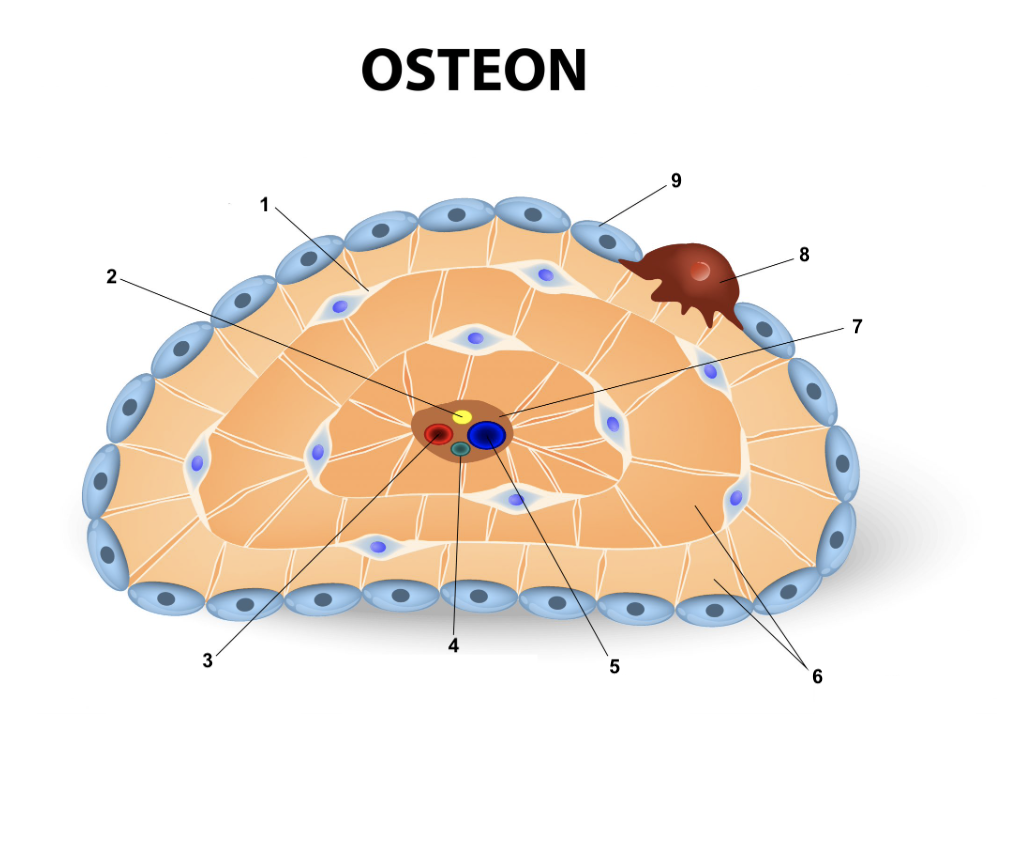
61
New cards
Osteoblast
9
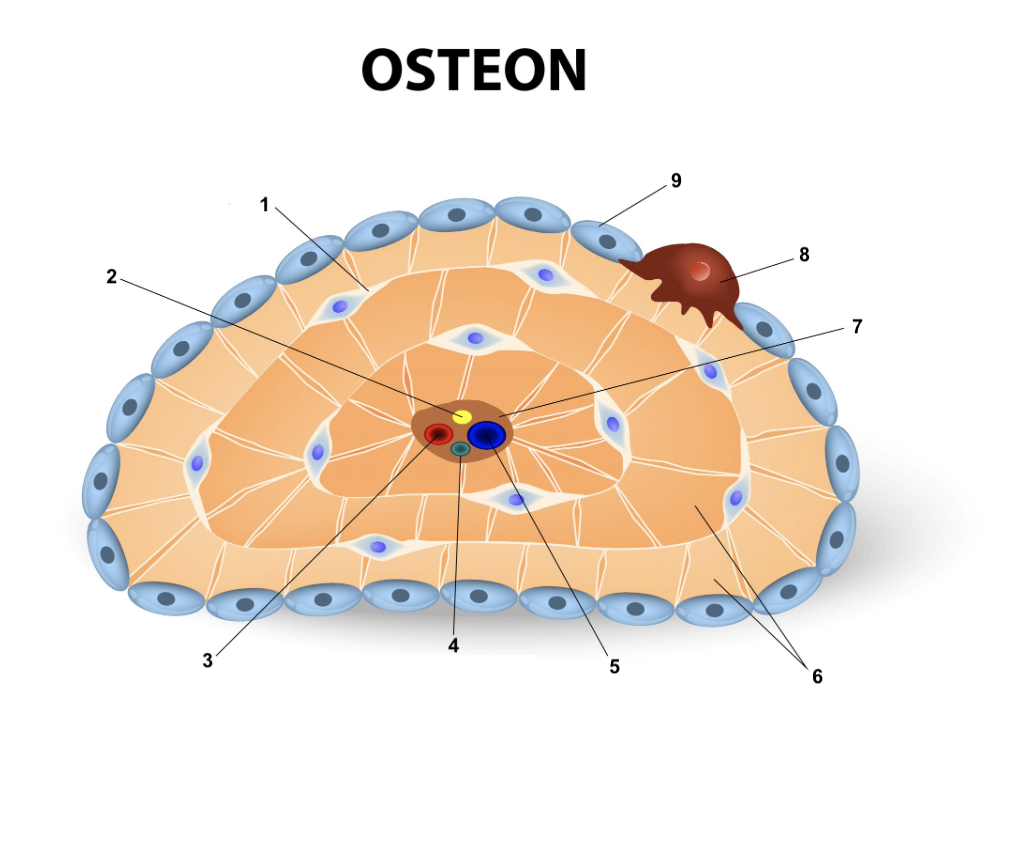
62
New cards
Osteogenic cell
63
New cards
Osteoblast
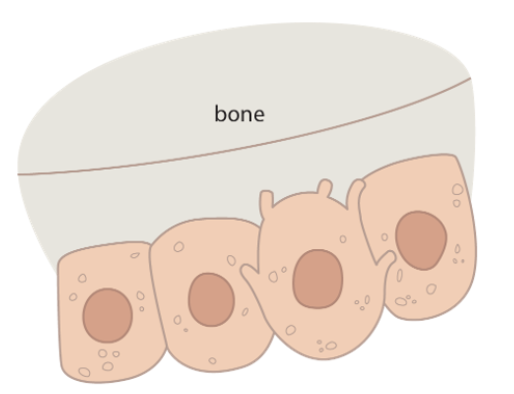
64
New cards
Osteocyte
\
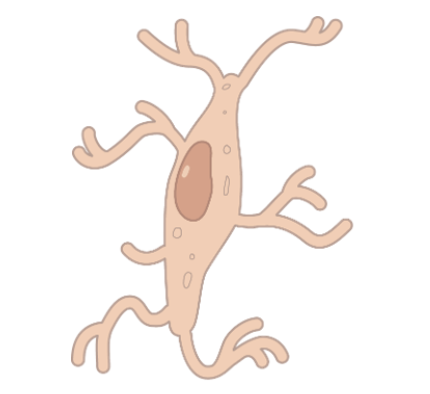
65
New cards
Osteoclast
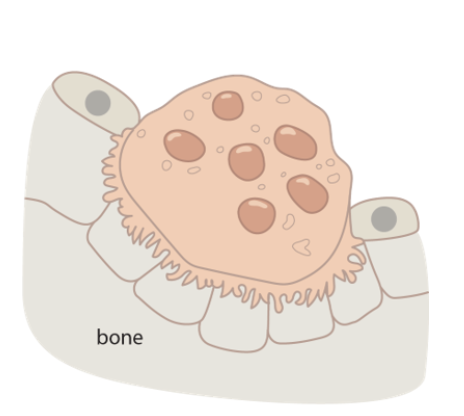
66
New cards
Proximal epiphysis
1
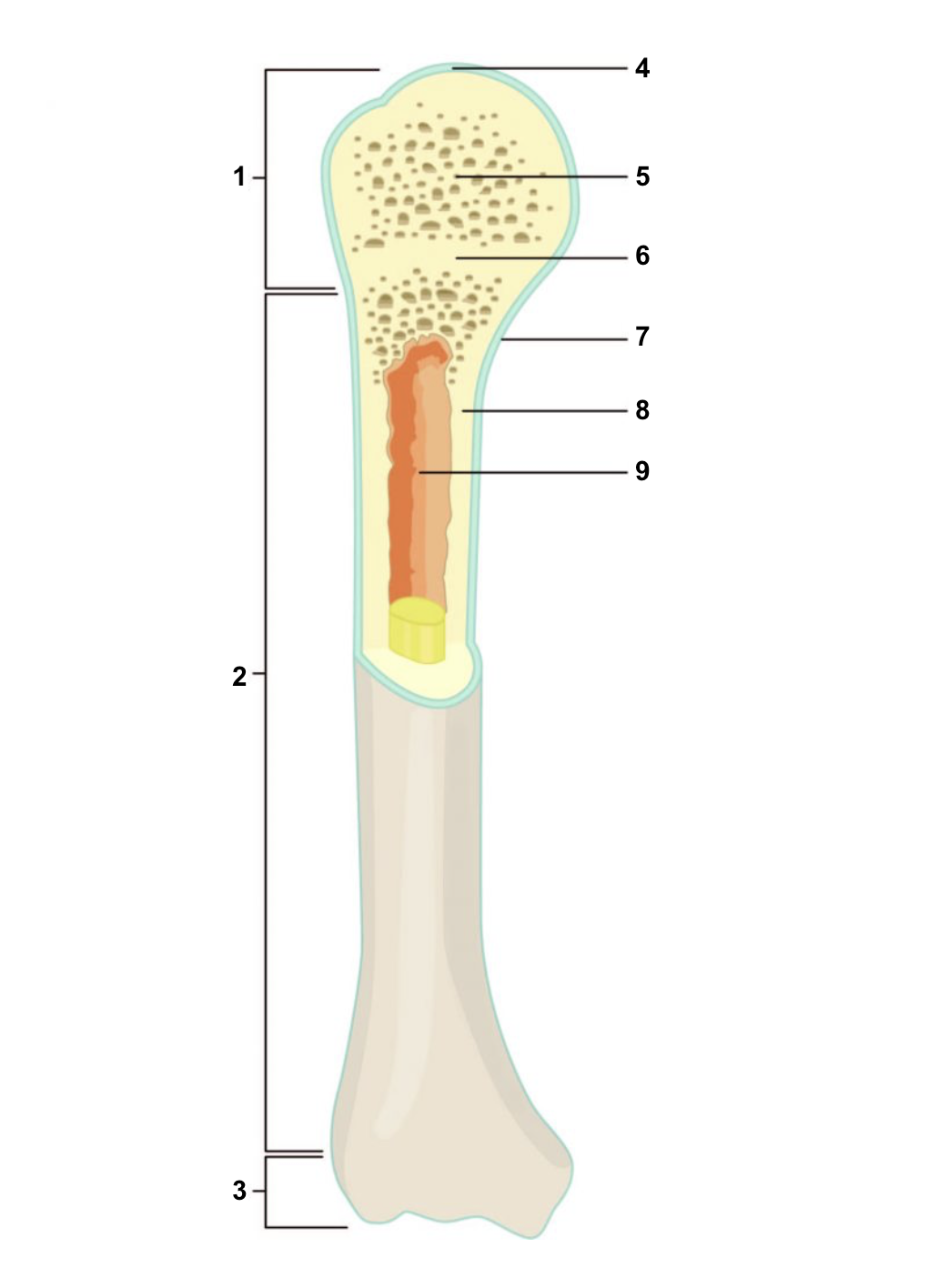
67
New cards
Diaphysis
2
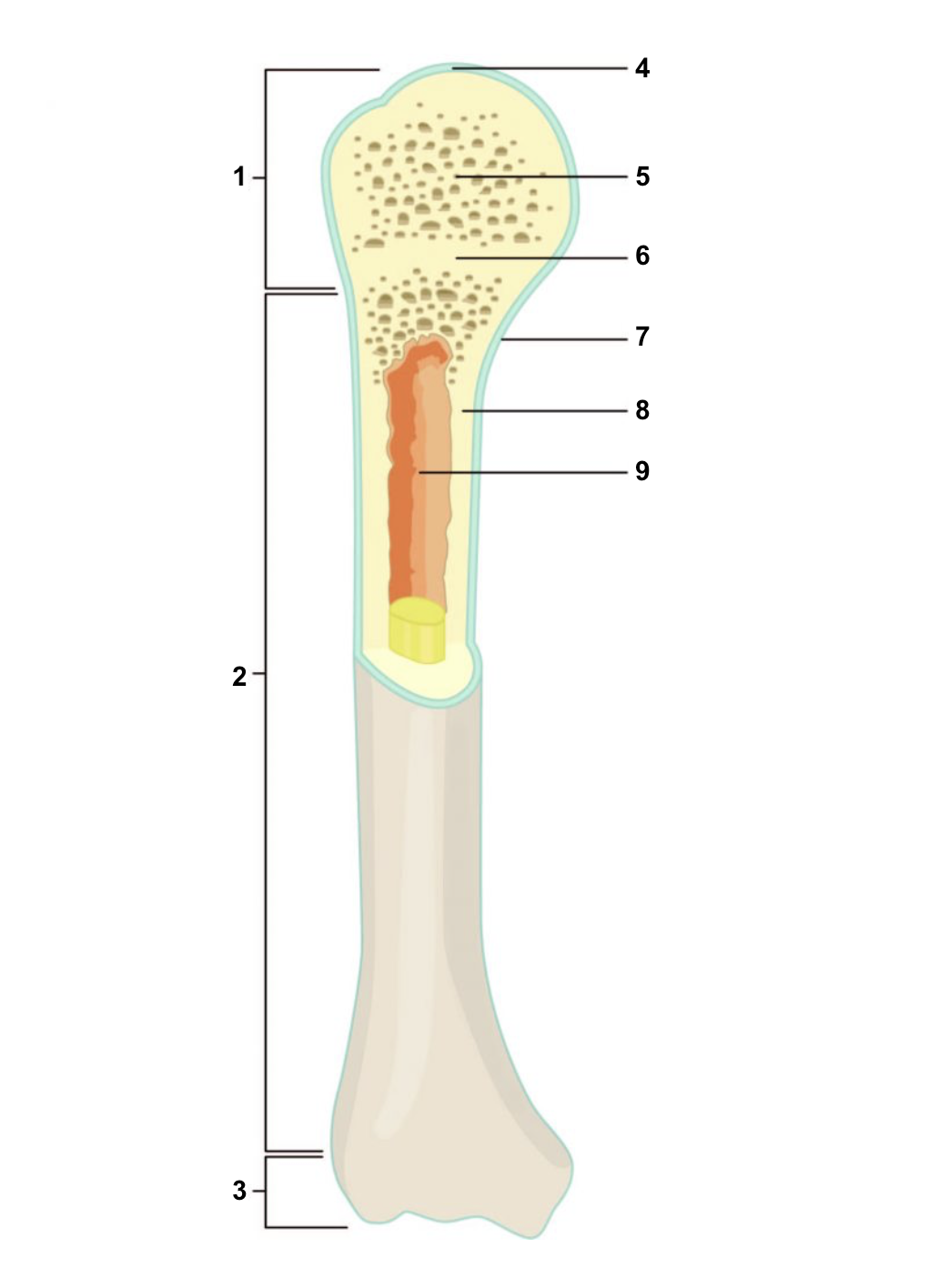
68
New cards
Distal epiphysis
3
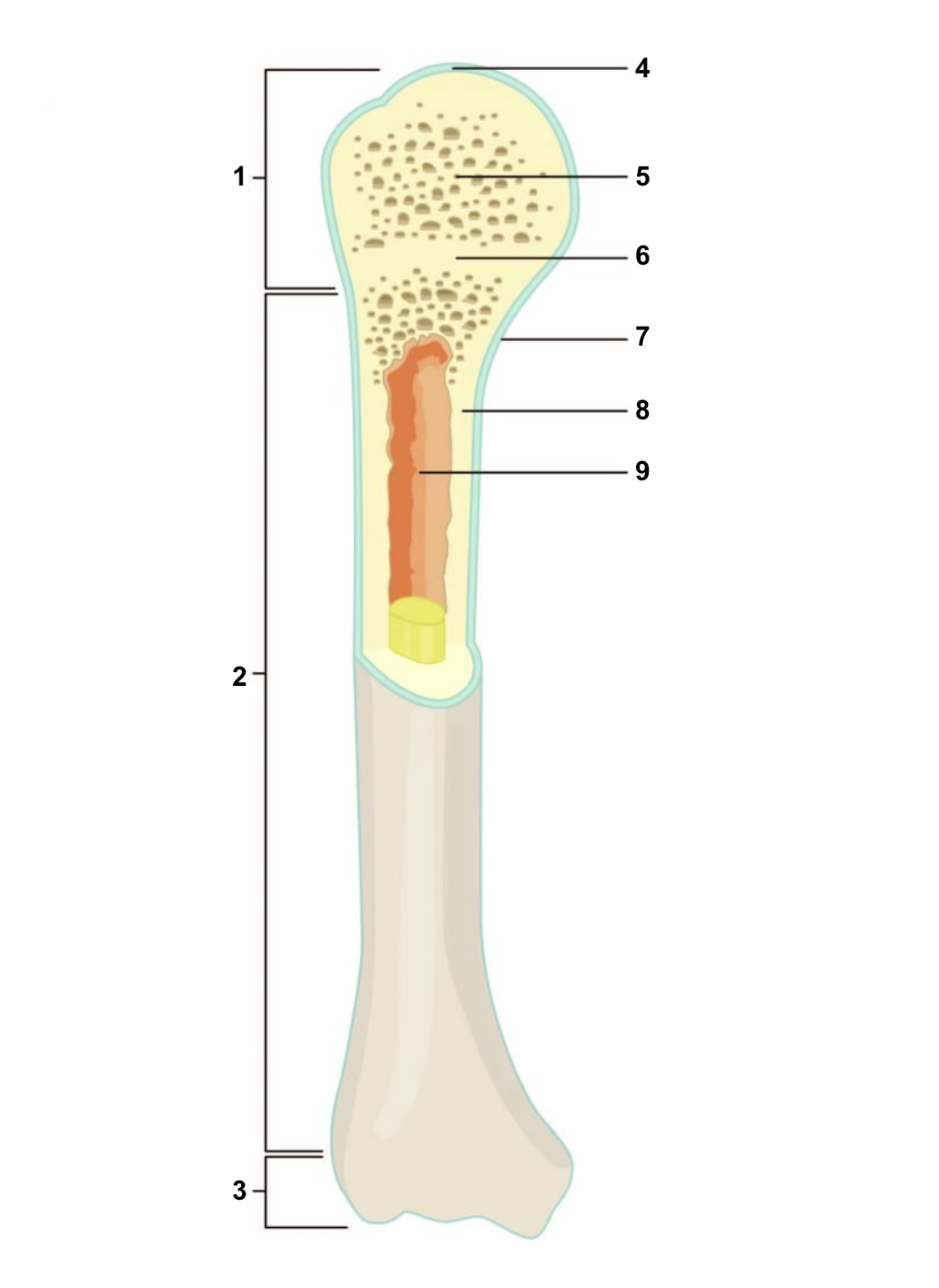
69
New cards
Articular cartilage
4
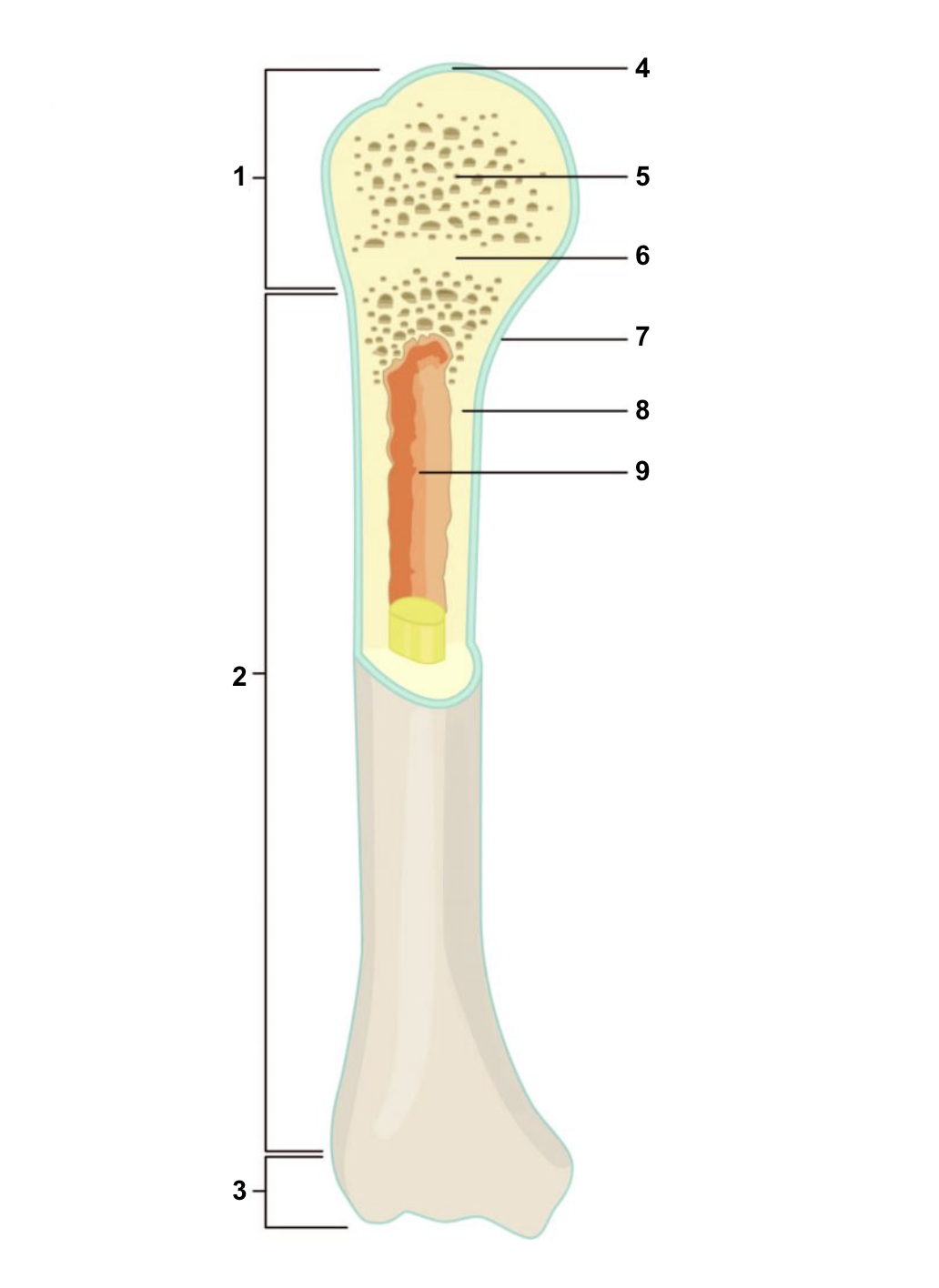
70
New cards
Spongy bone
5
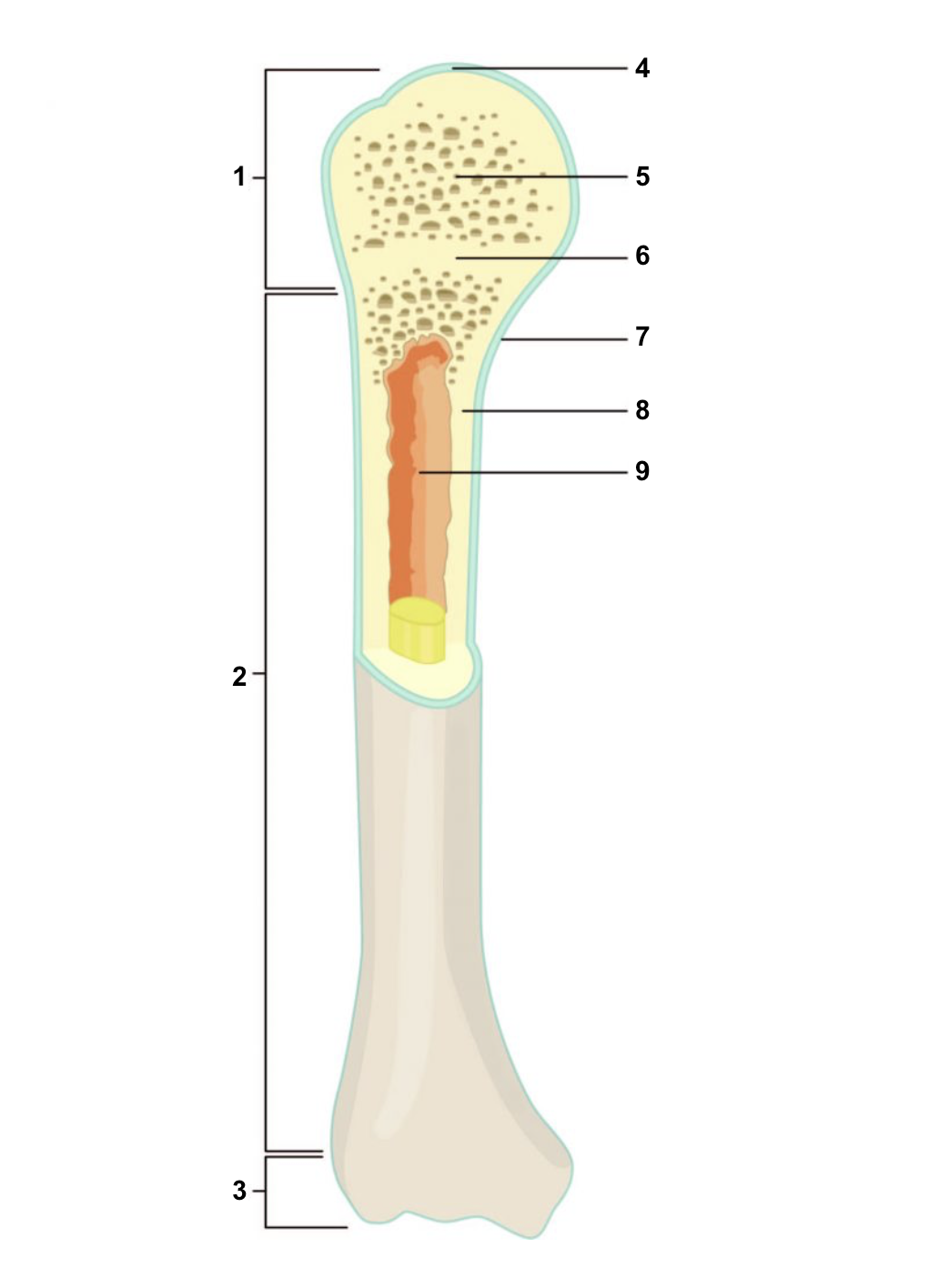
71
New cards
Epiphyseal line
6
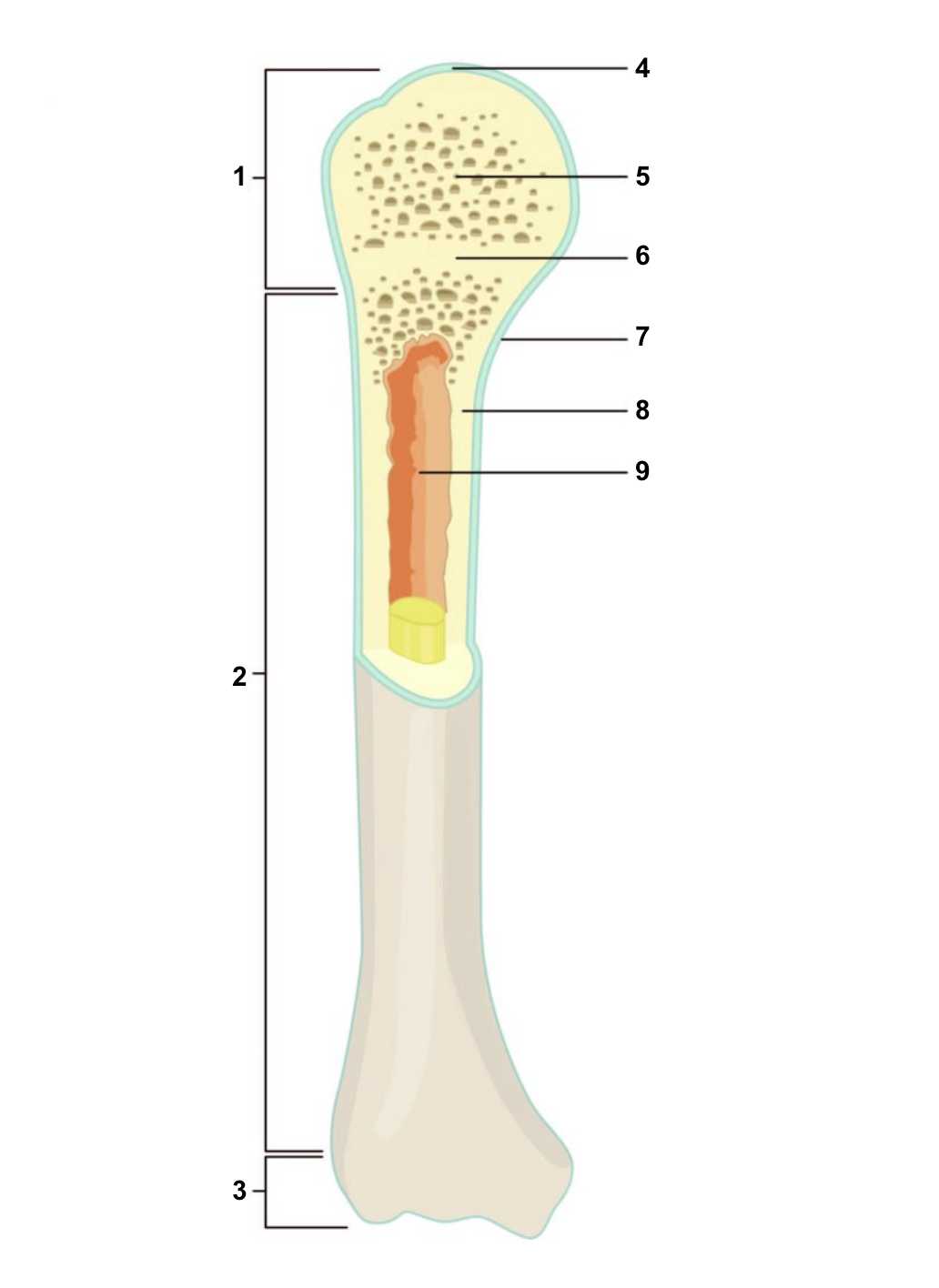
72
New cards
Periosteum
7
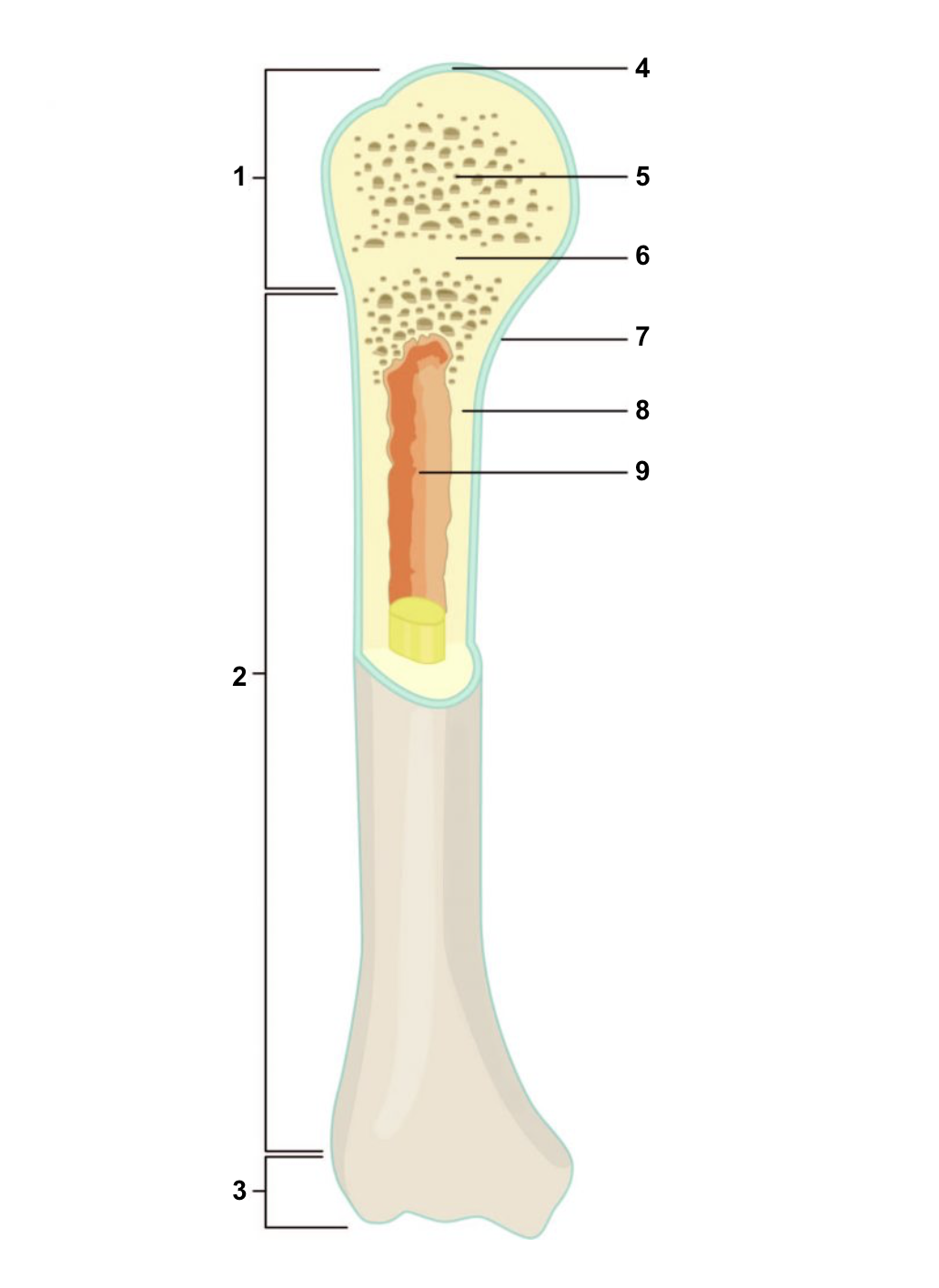
73
New cards
Compact bone
8
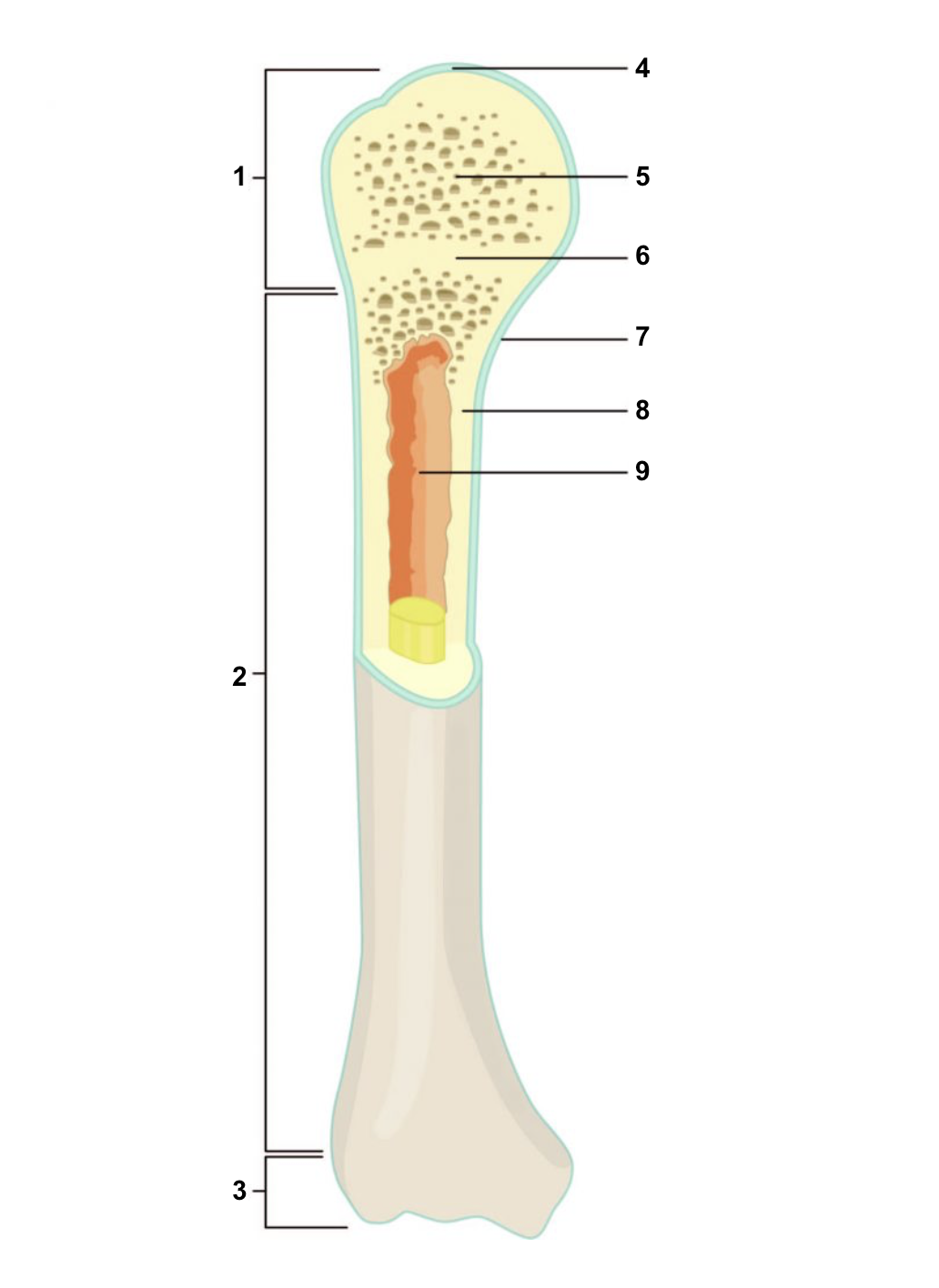
74
New cards
Medullary cavity (lined by endosteum)
9
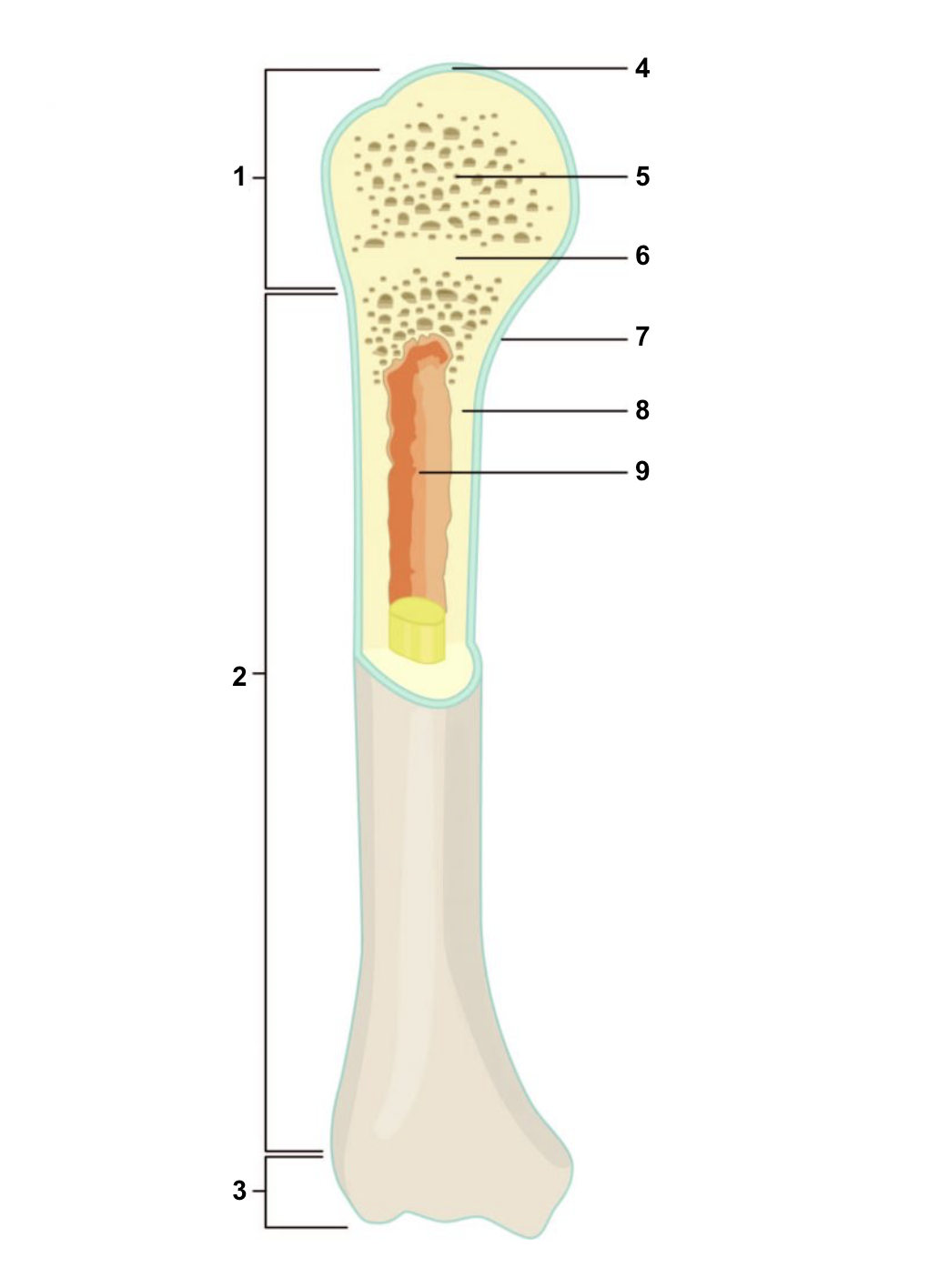
75
New cards
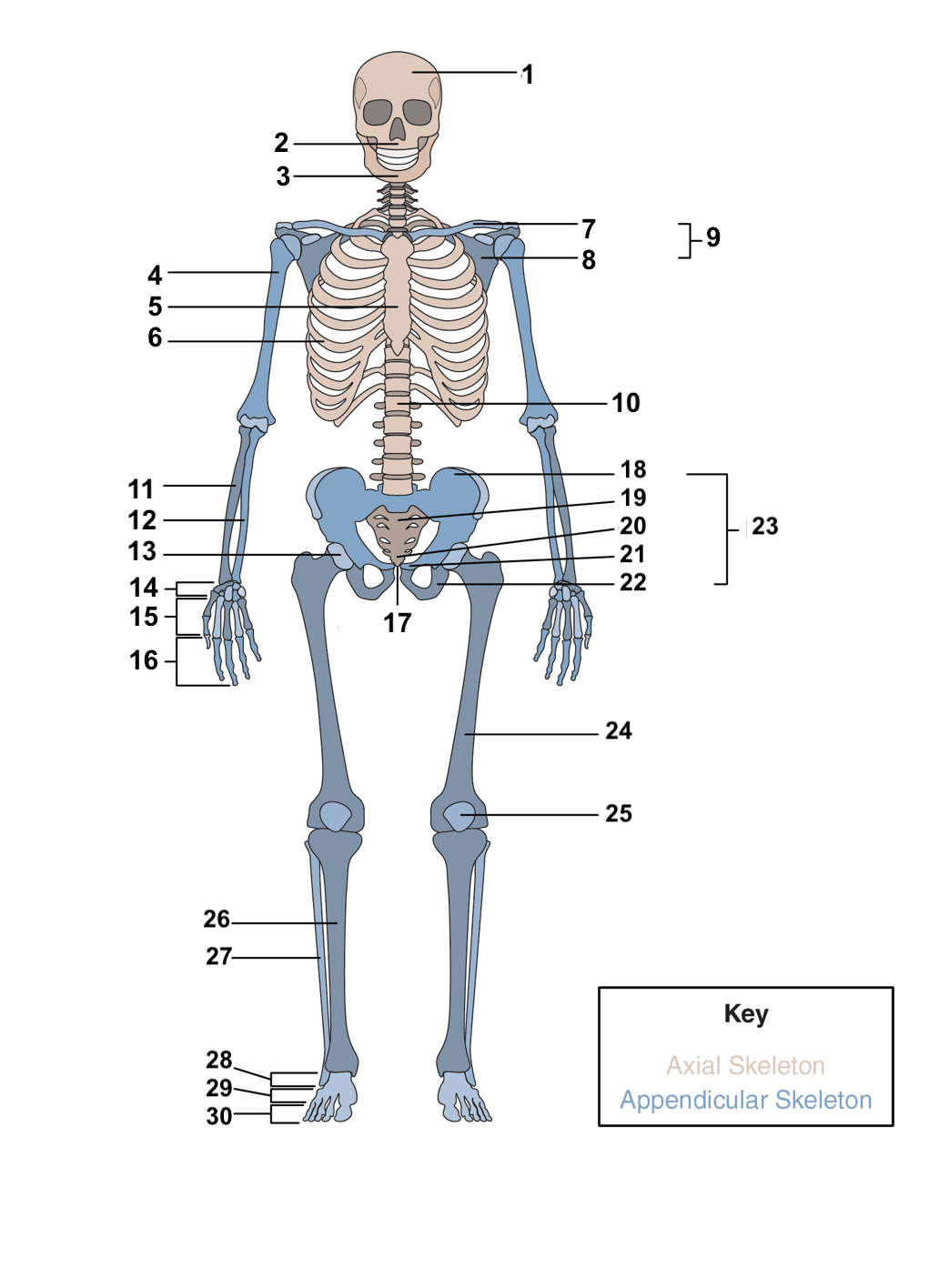
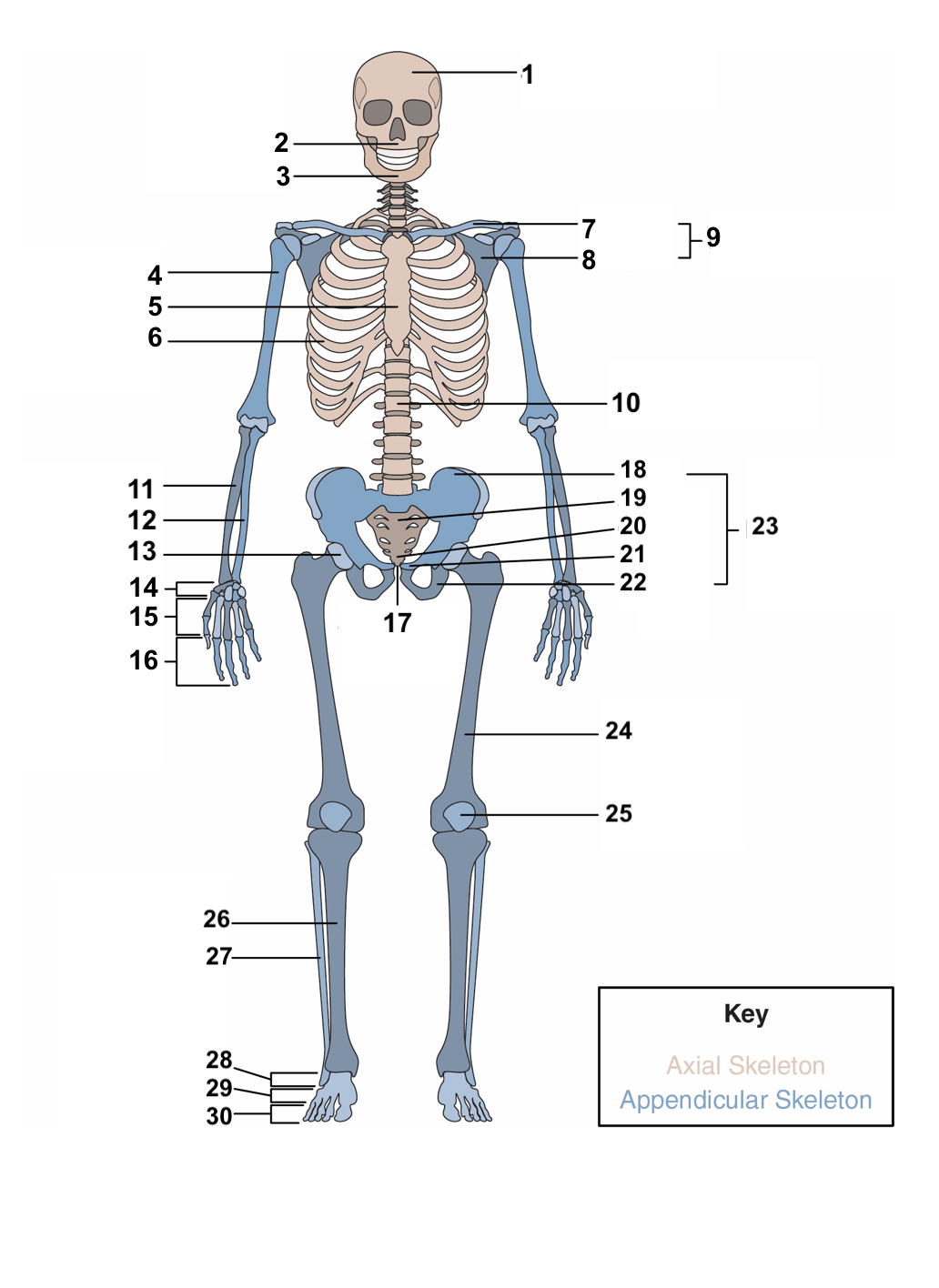
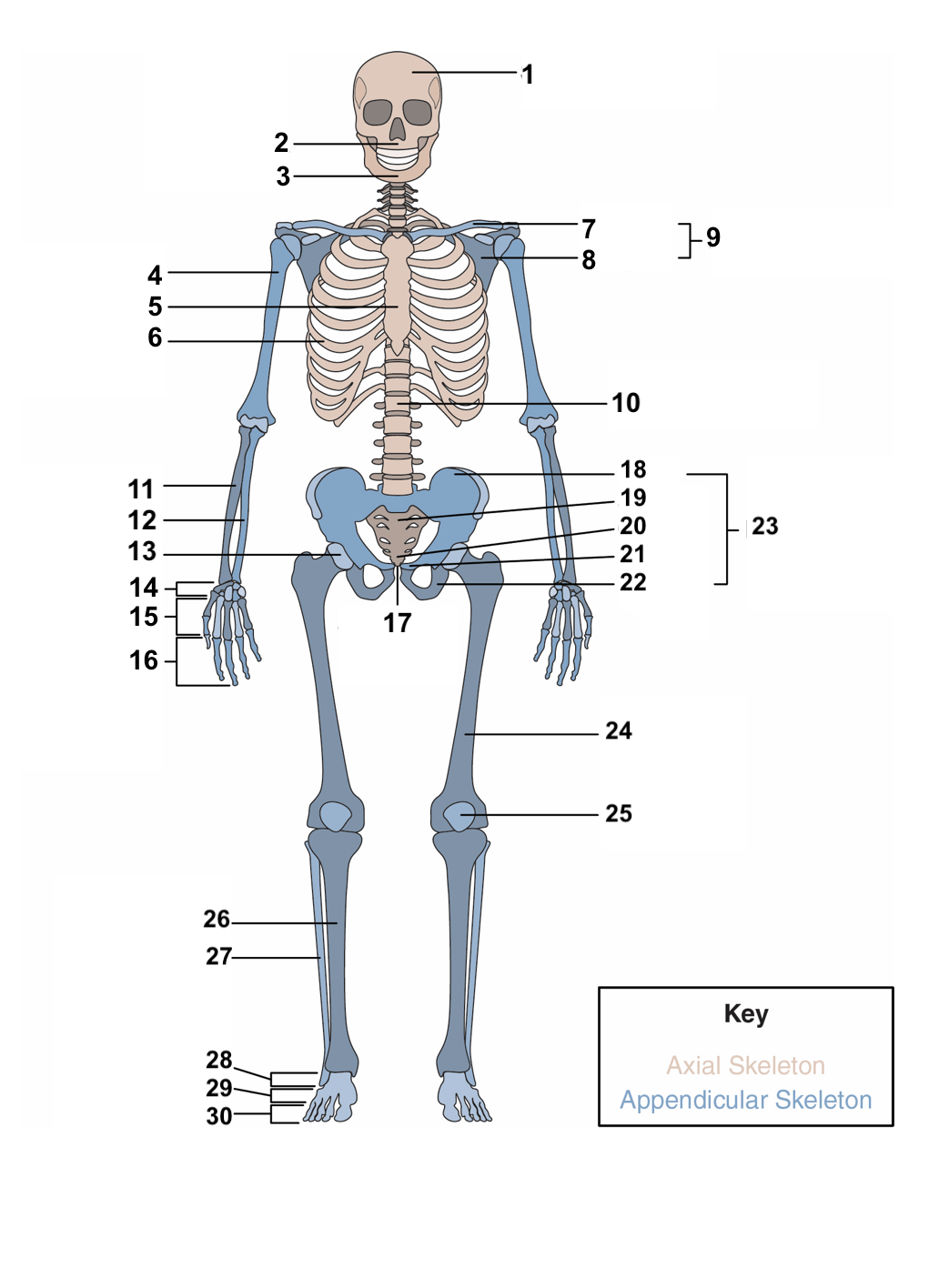
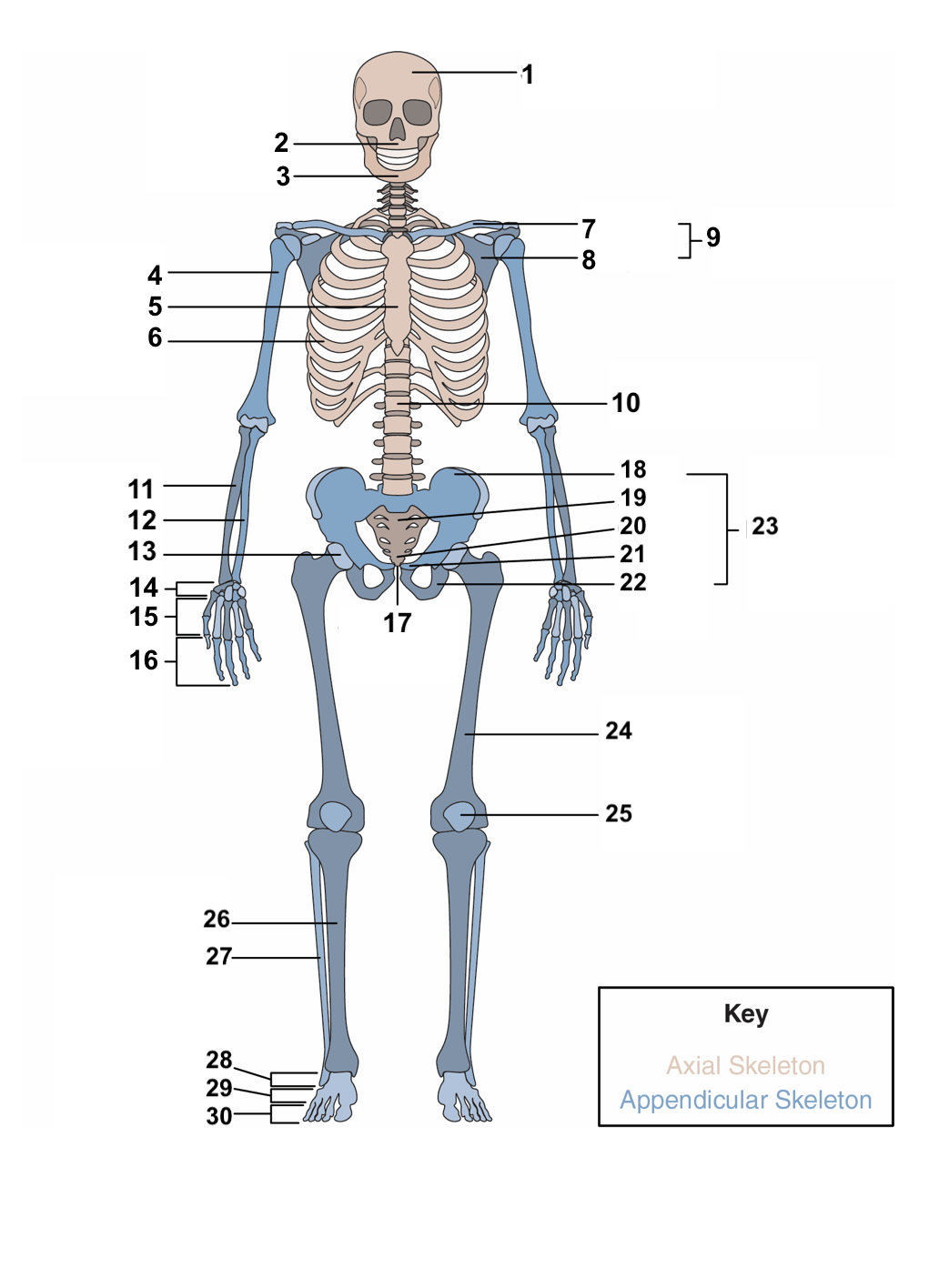
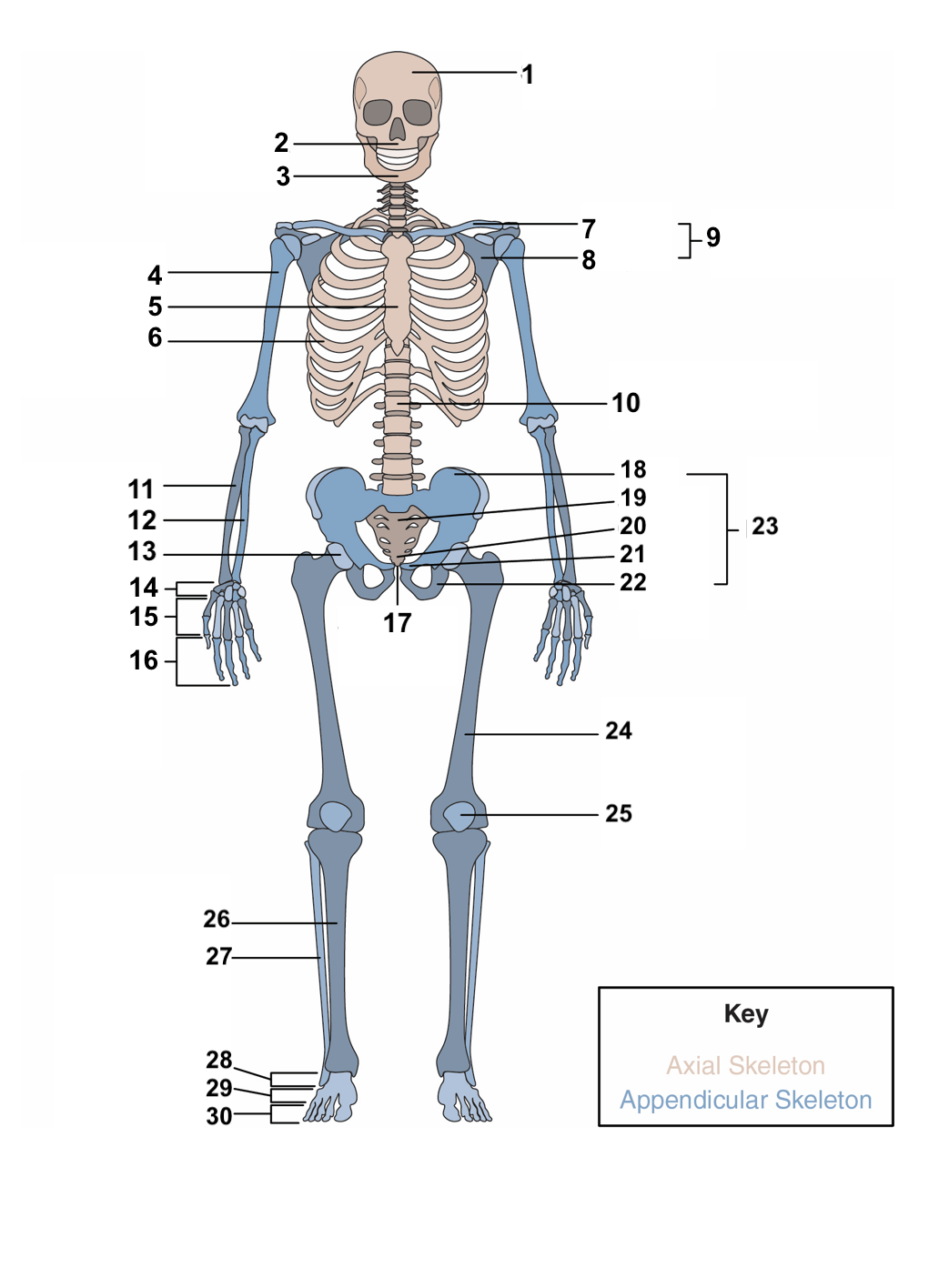
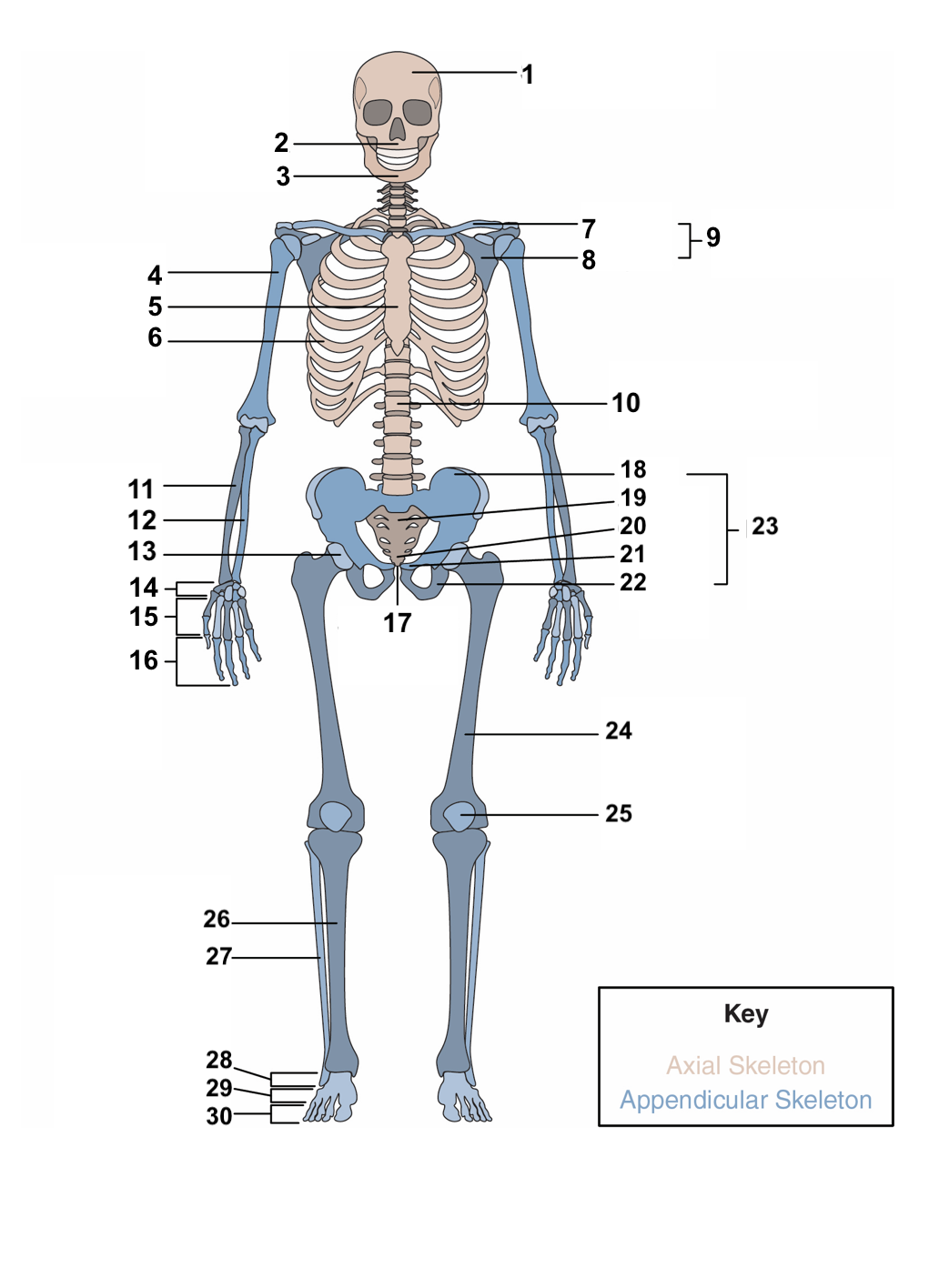
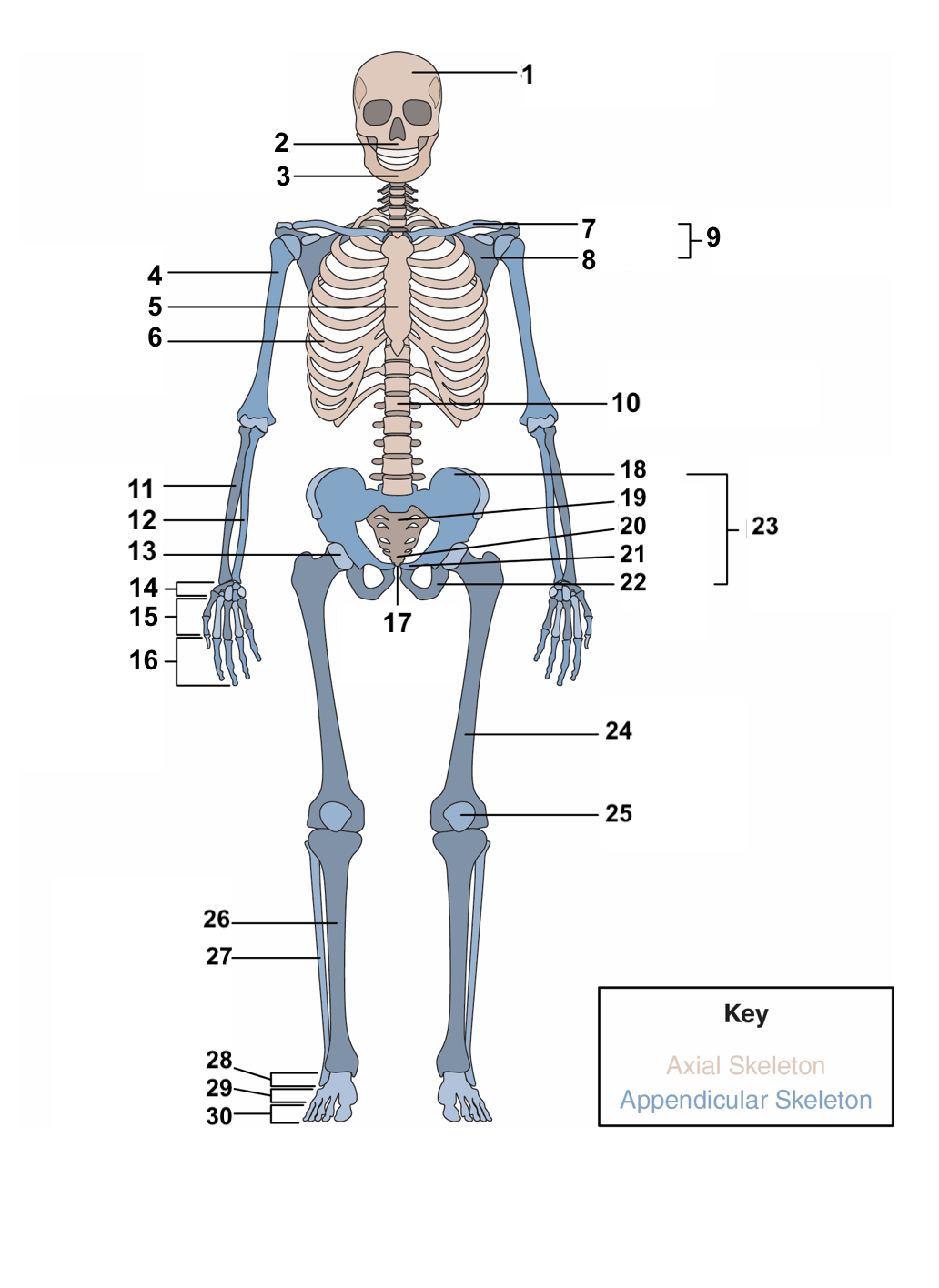
skull
1
76
New cards
maxilla
2
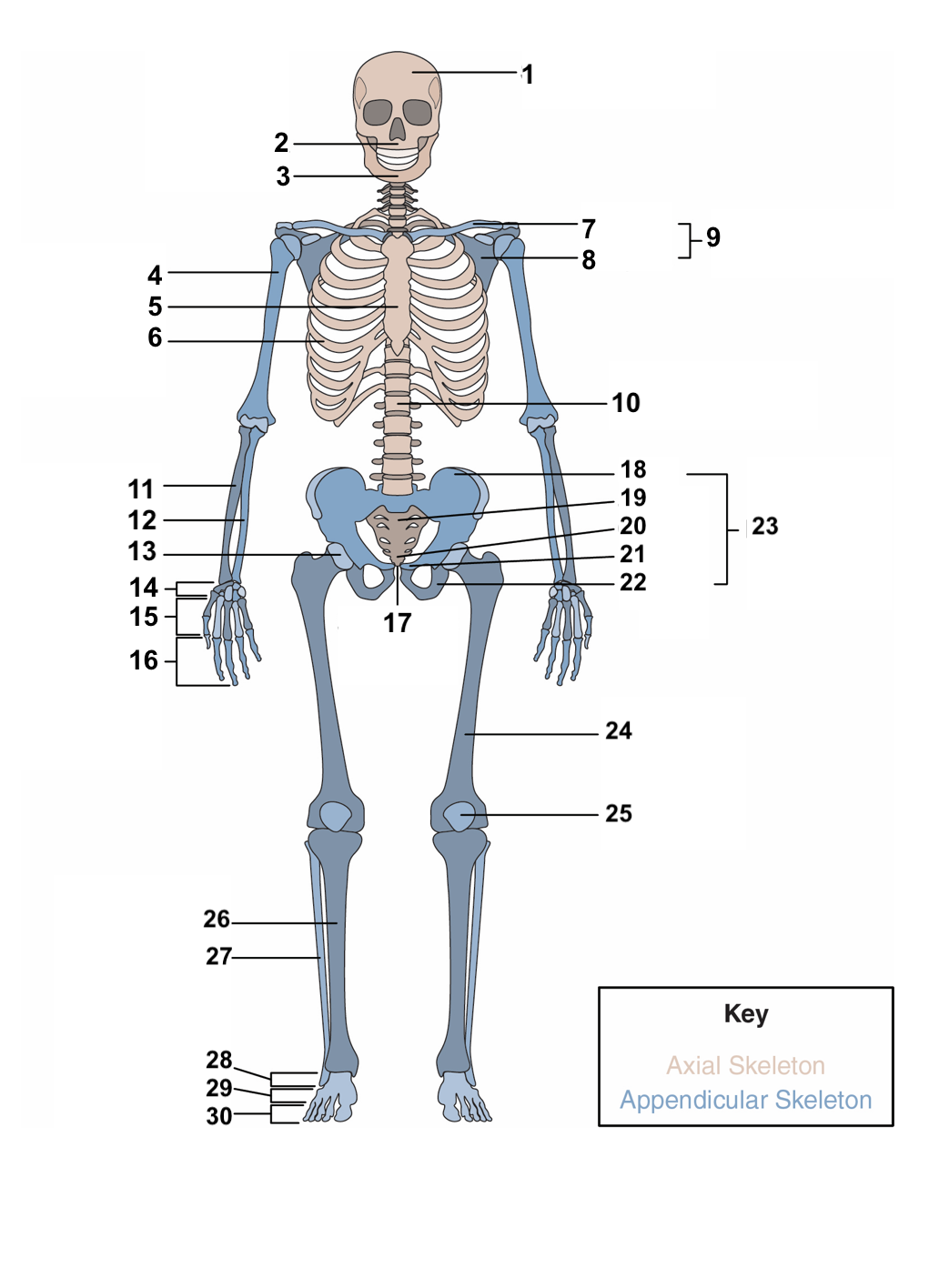
77
New cards
mandible
3
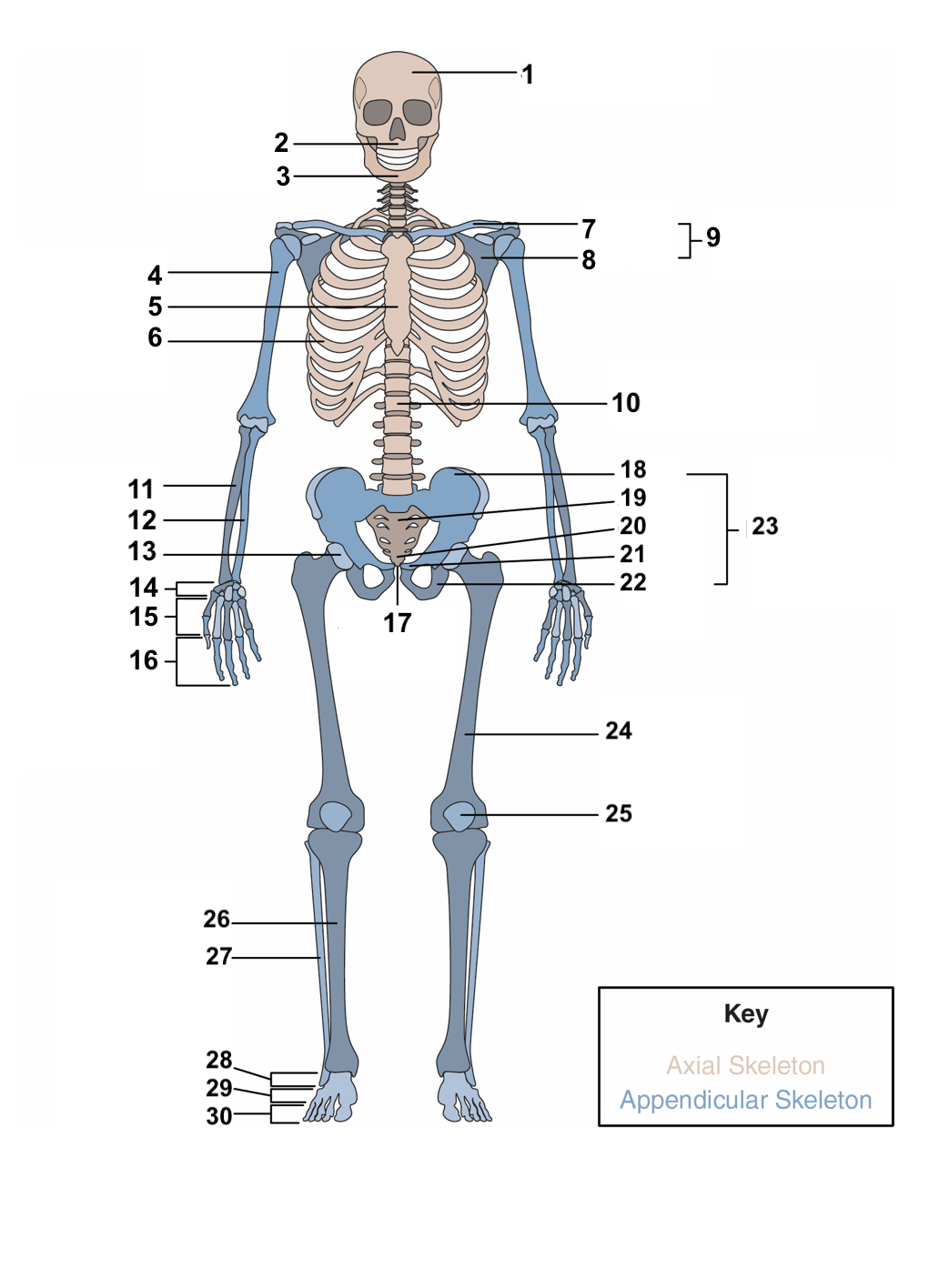
78
New cards
humerus
4
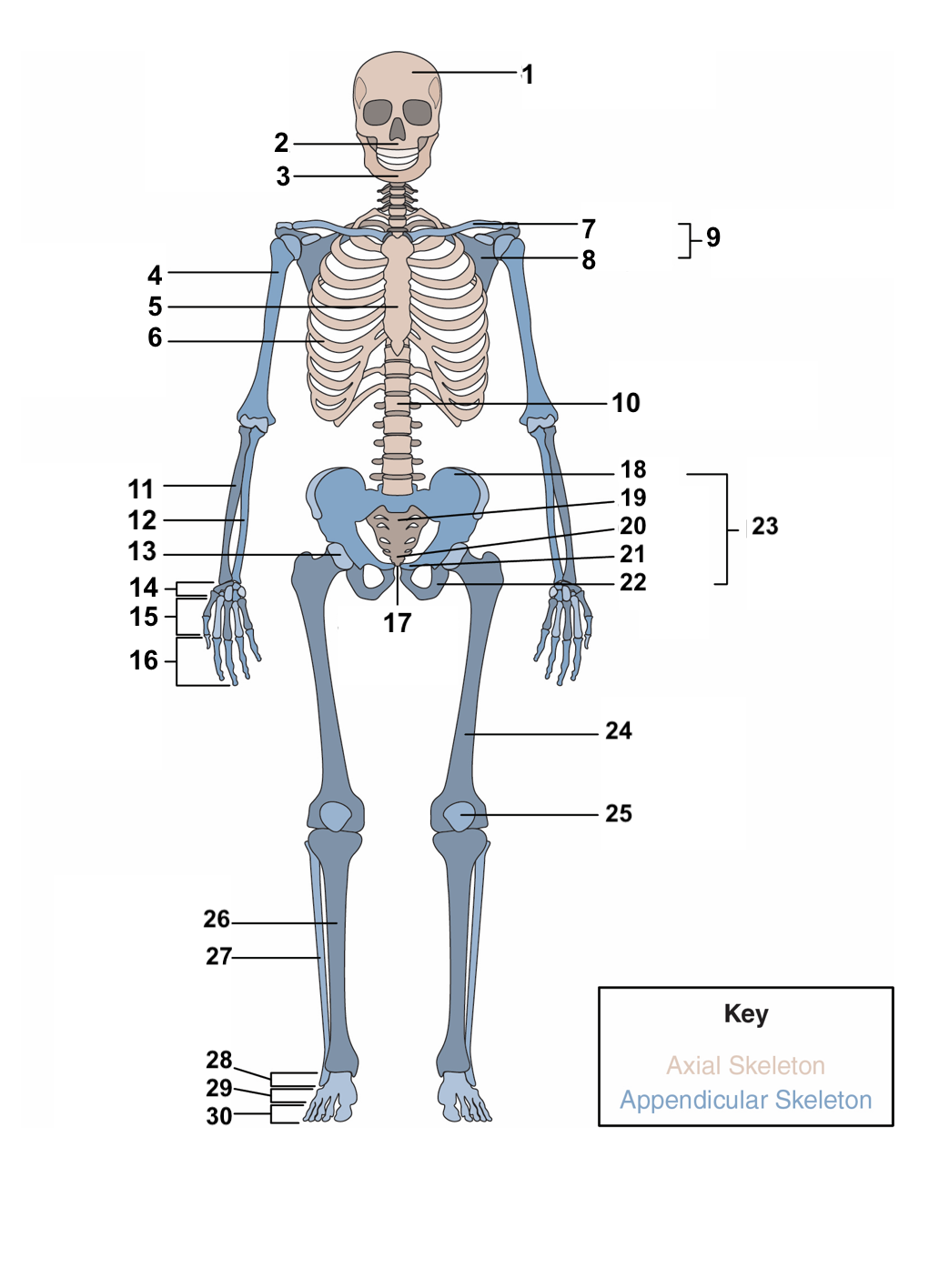
79
New cards
sternum
5
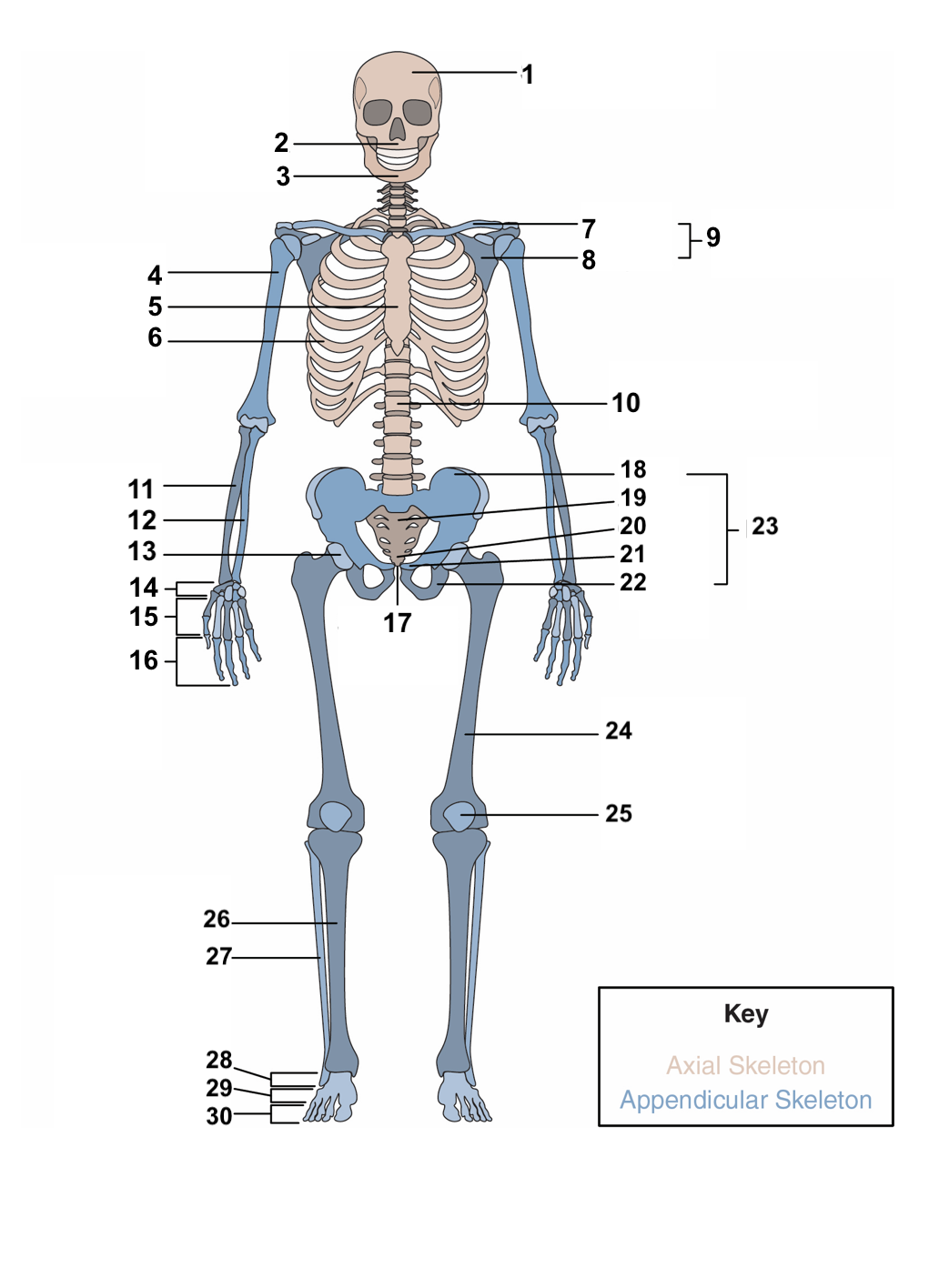
80
New cards
ribs
6
81
New cards
clavicle
7
82
New cards
scapula
8
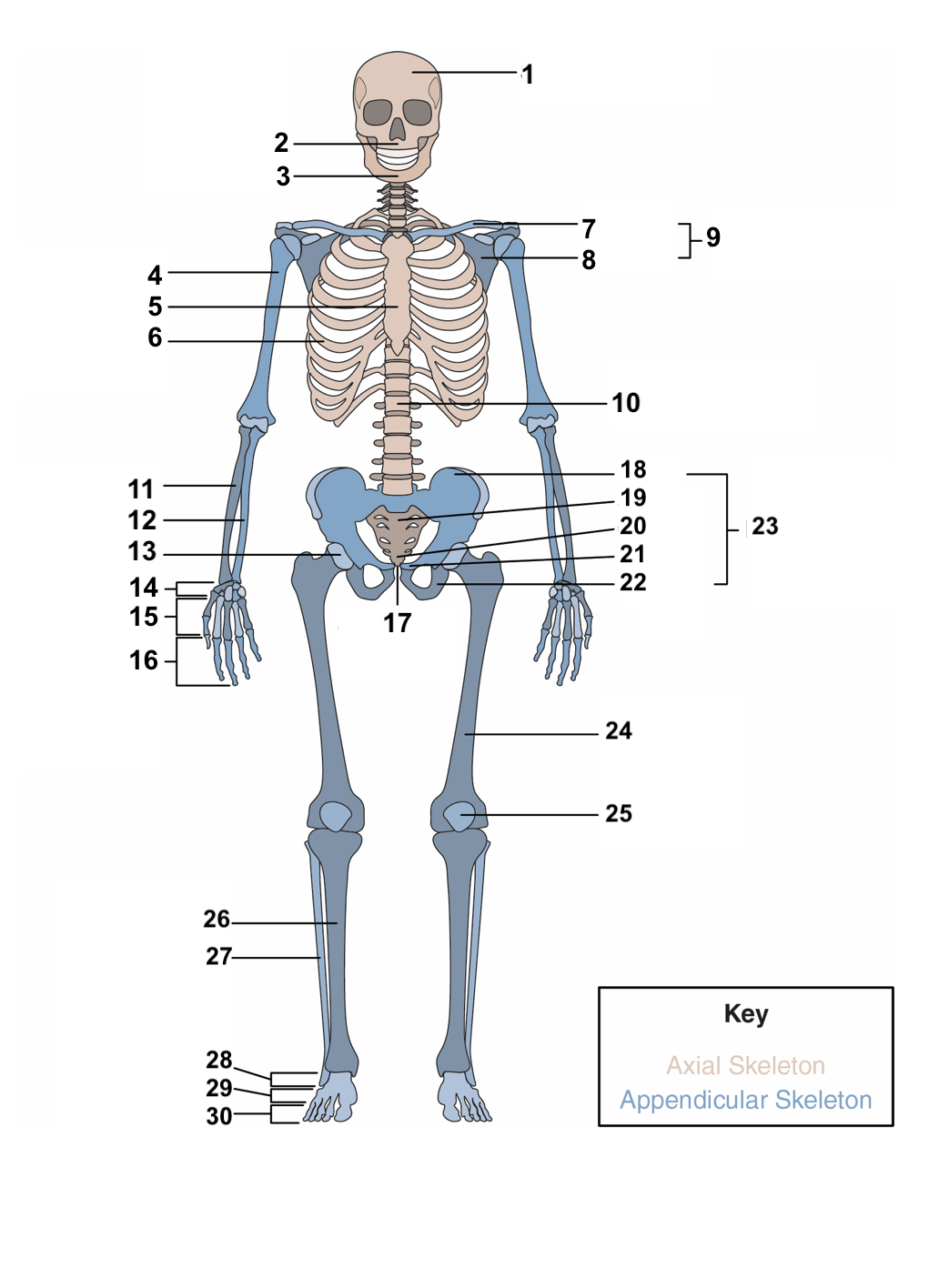
83
New cards
pectoral girdle
9
84
New cards
vertebral column
10
85
New cards
radius
11
86
New cards
ulna
12
87
New cards
acetabulum
13
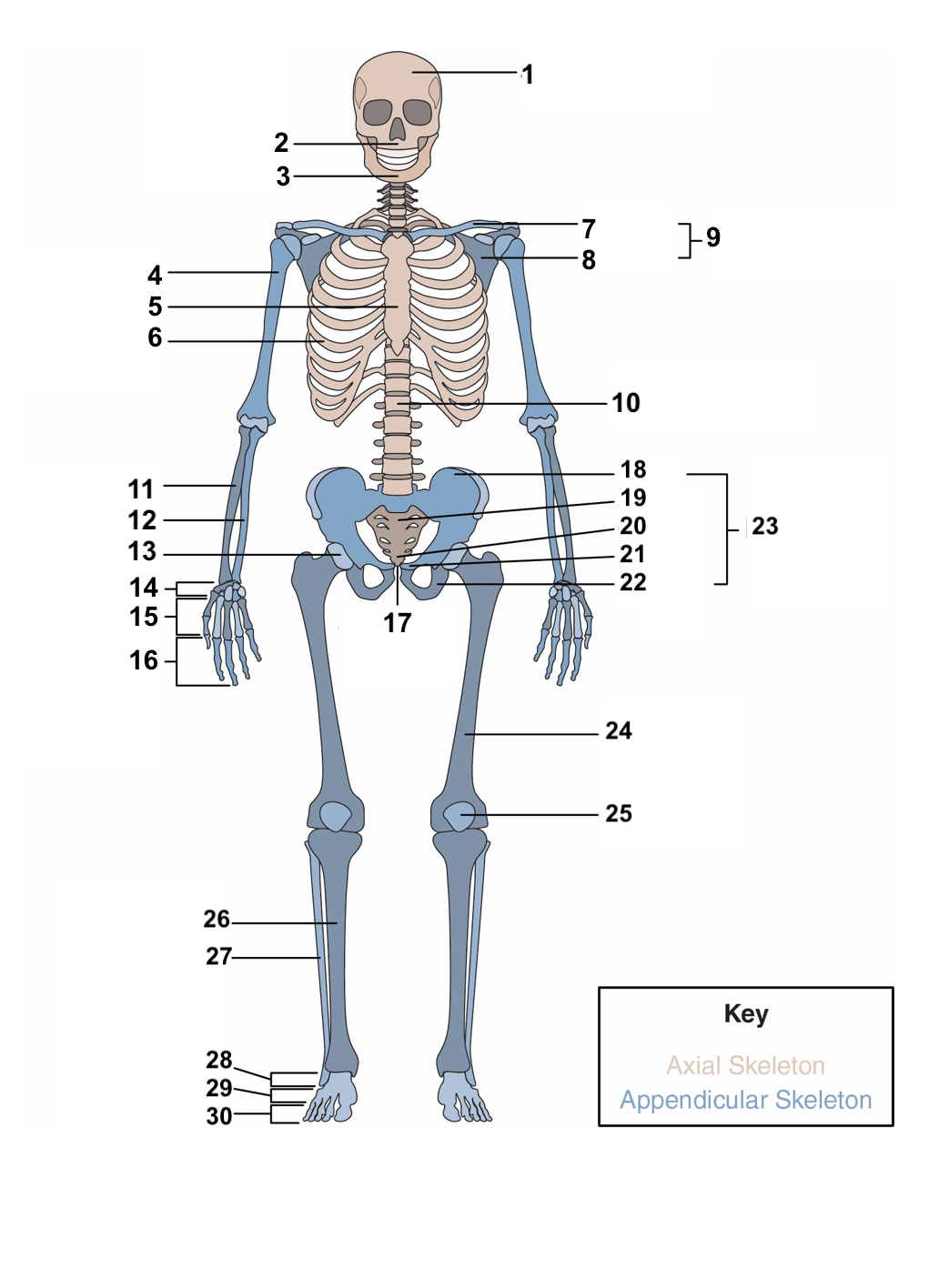
88
New cards
carpals
14
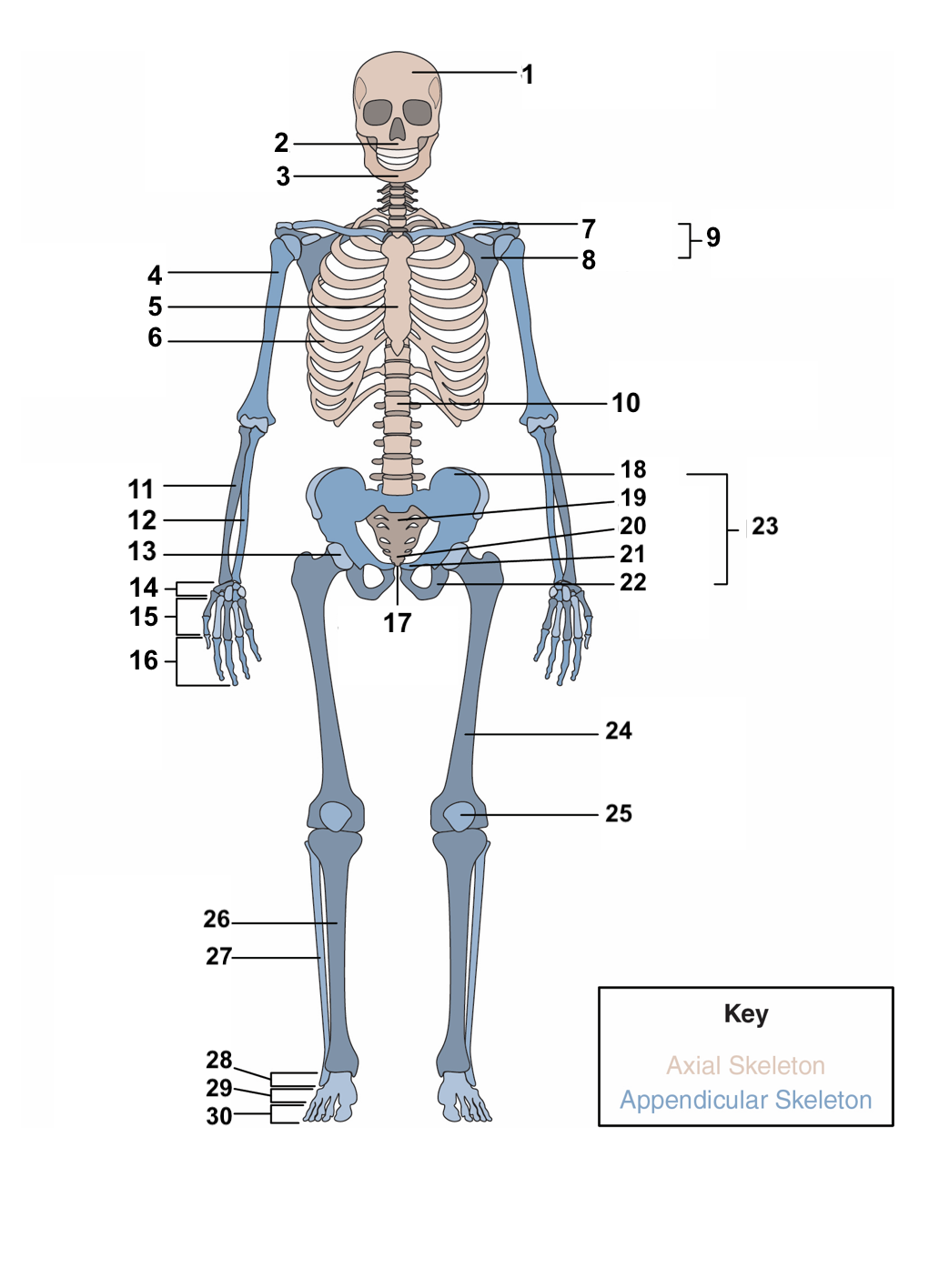
89
New cards
metacarpals
15
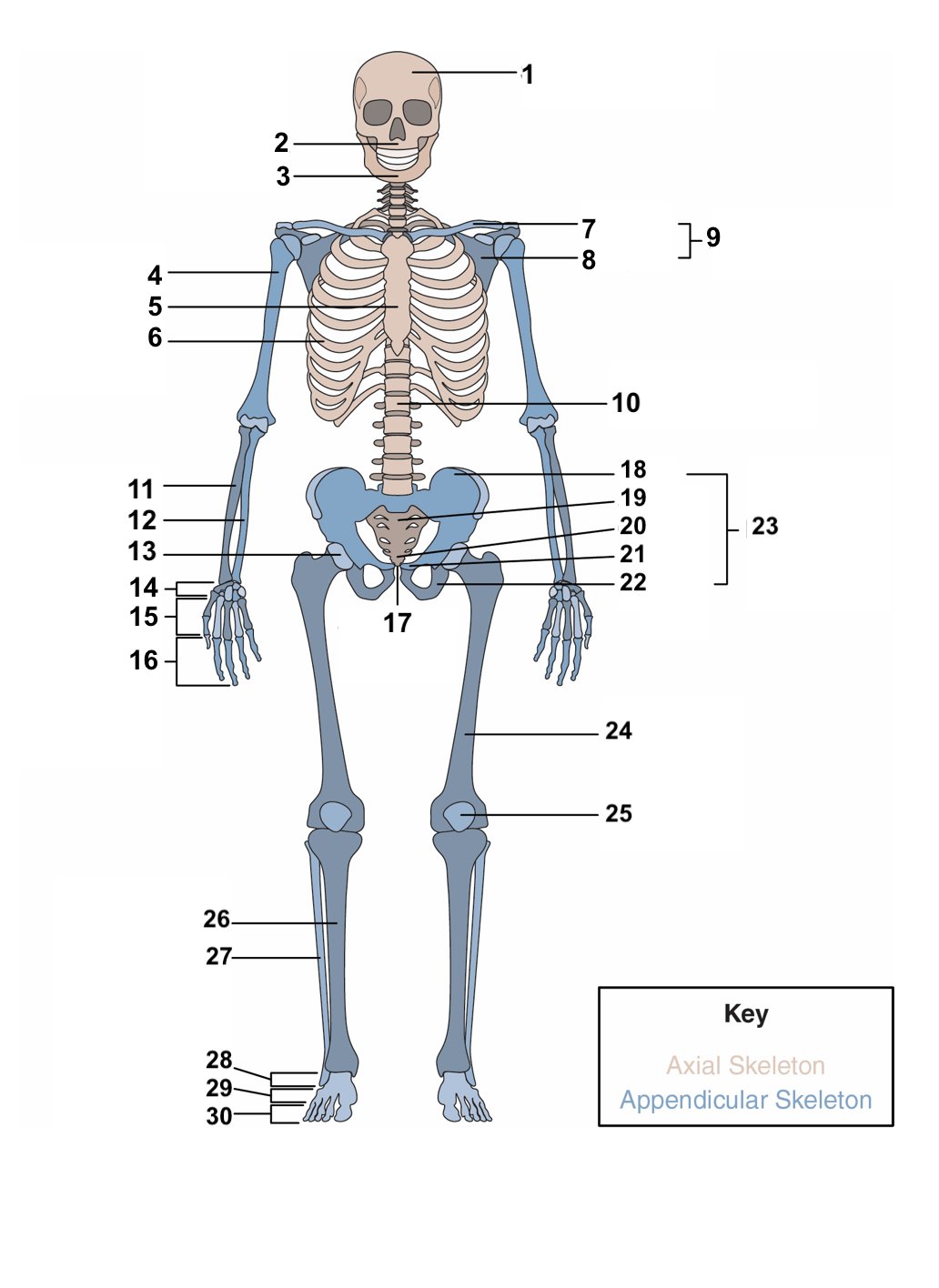
90
New cards
phalanges
16
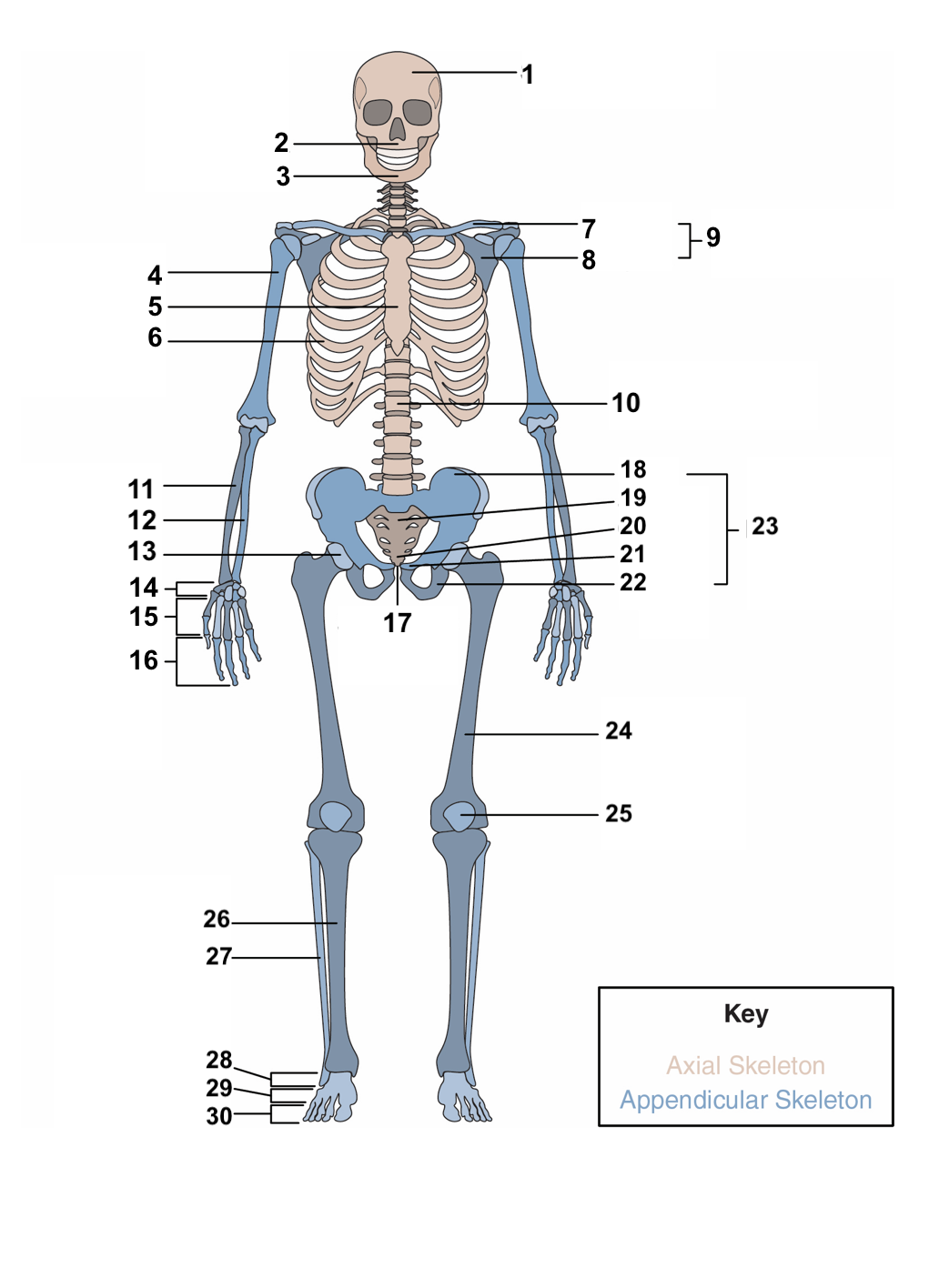
91
New cards
symphysis pubis
17
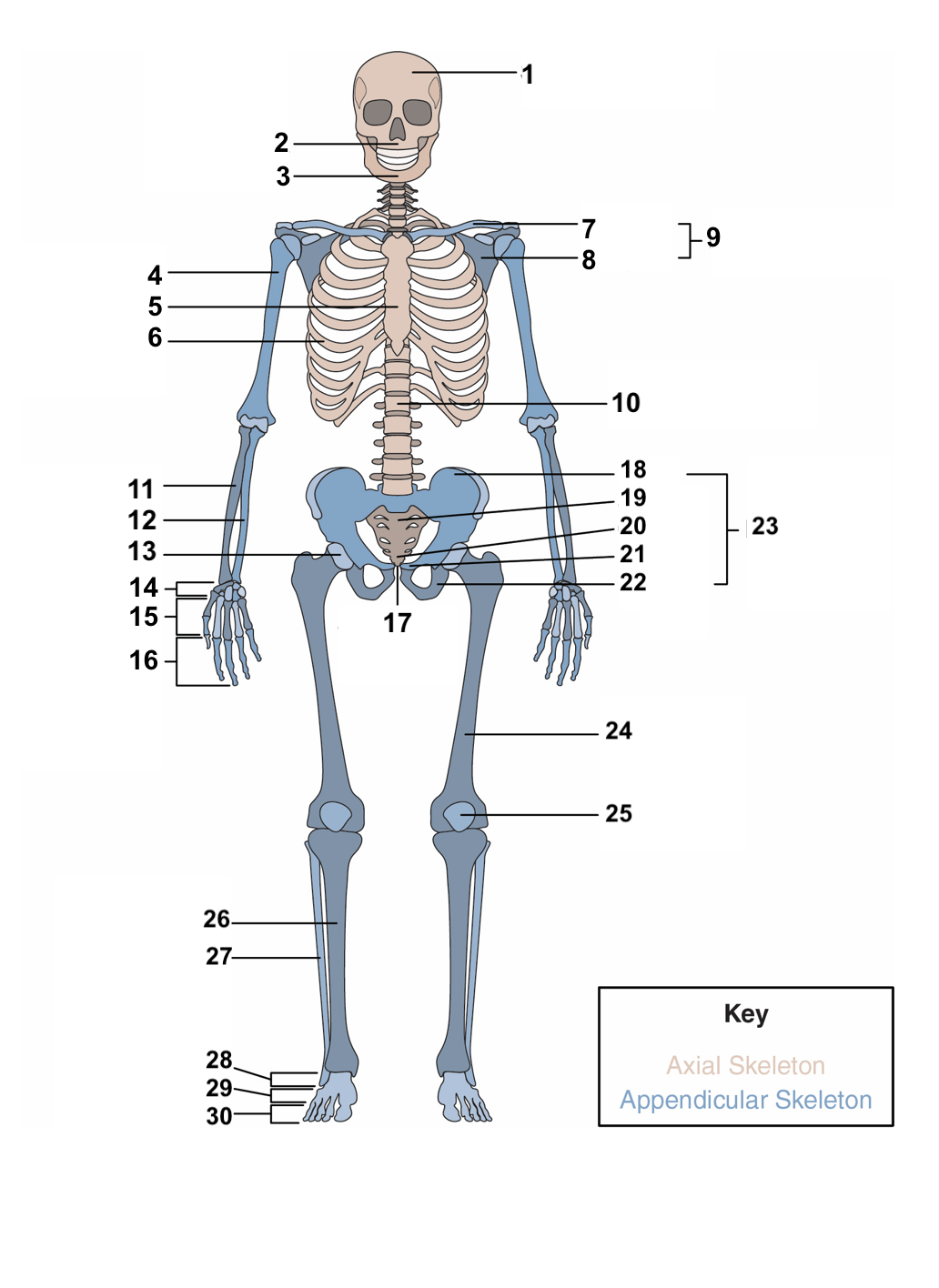
92
New cards
ilium
18
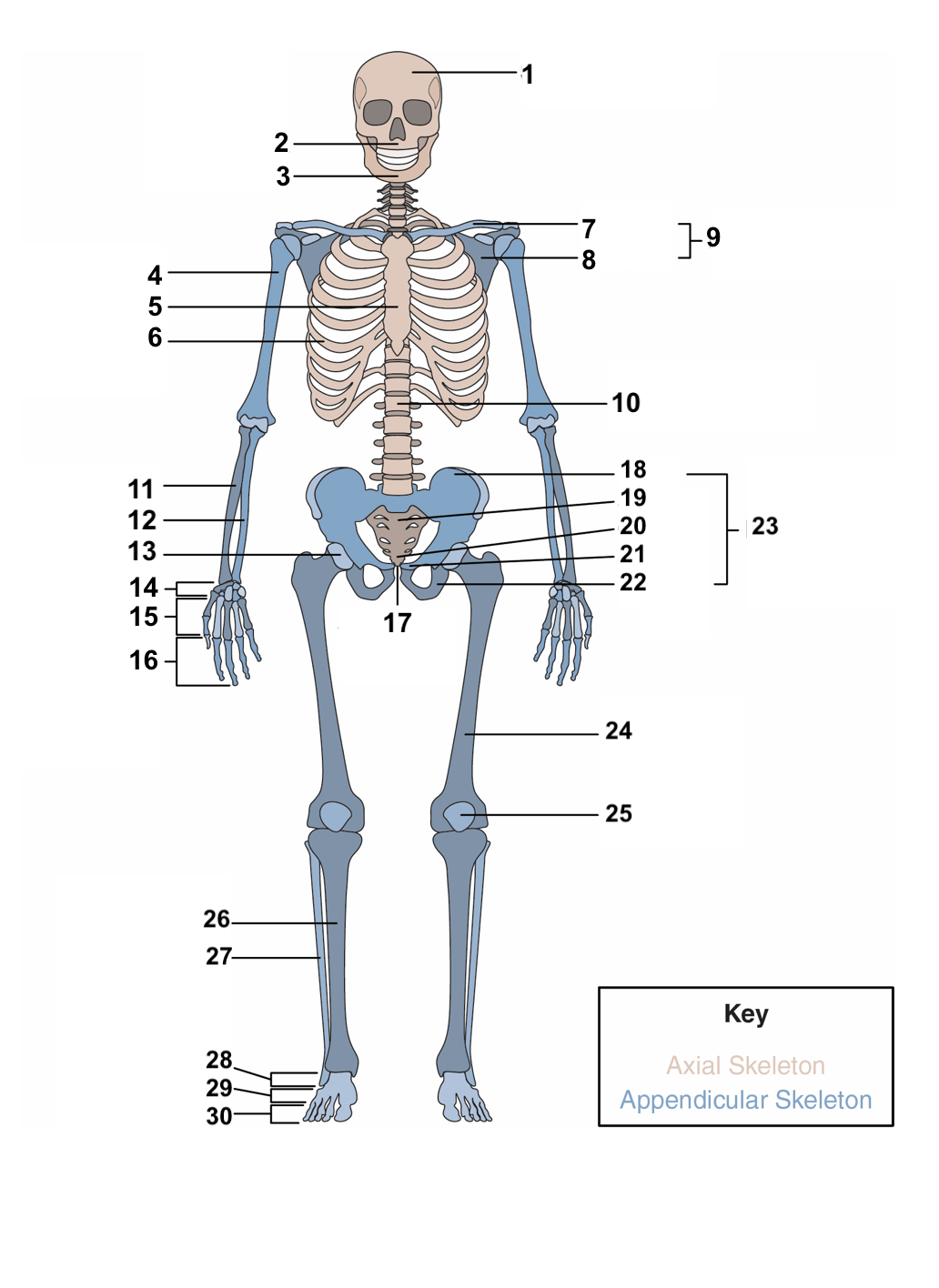
93
New cards
sacrum
19
94
New cards
coccyx
20
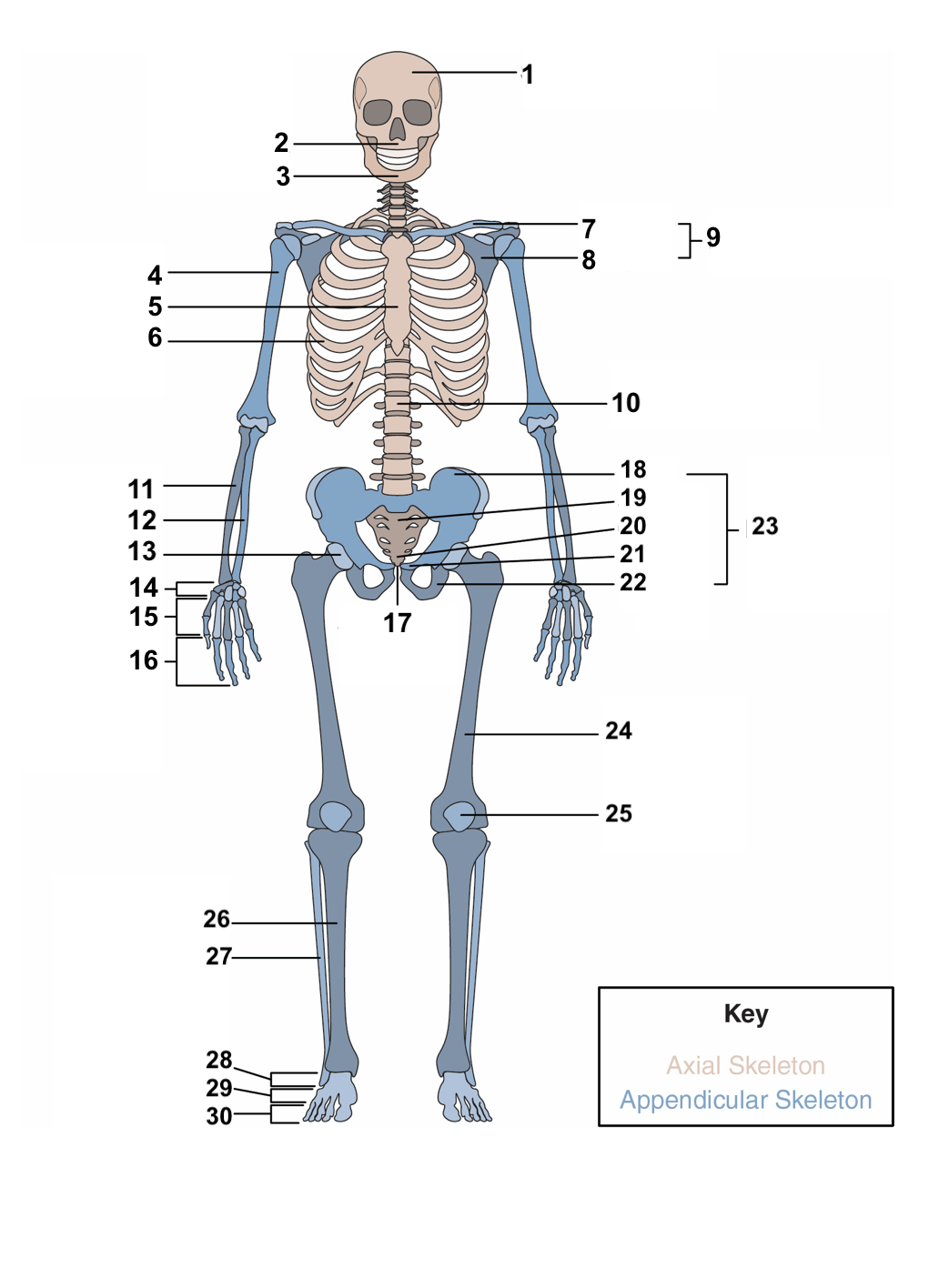
95
New cards
pubis
21
96
New cards
ischium
22
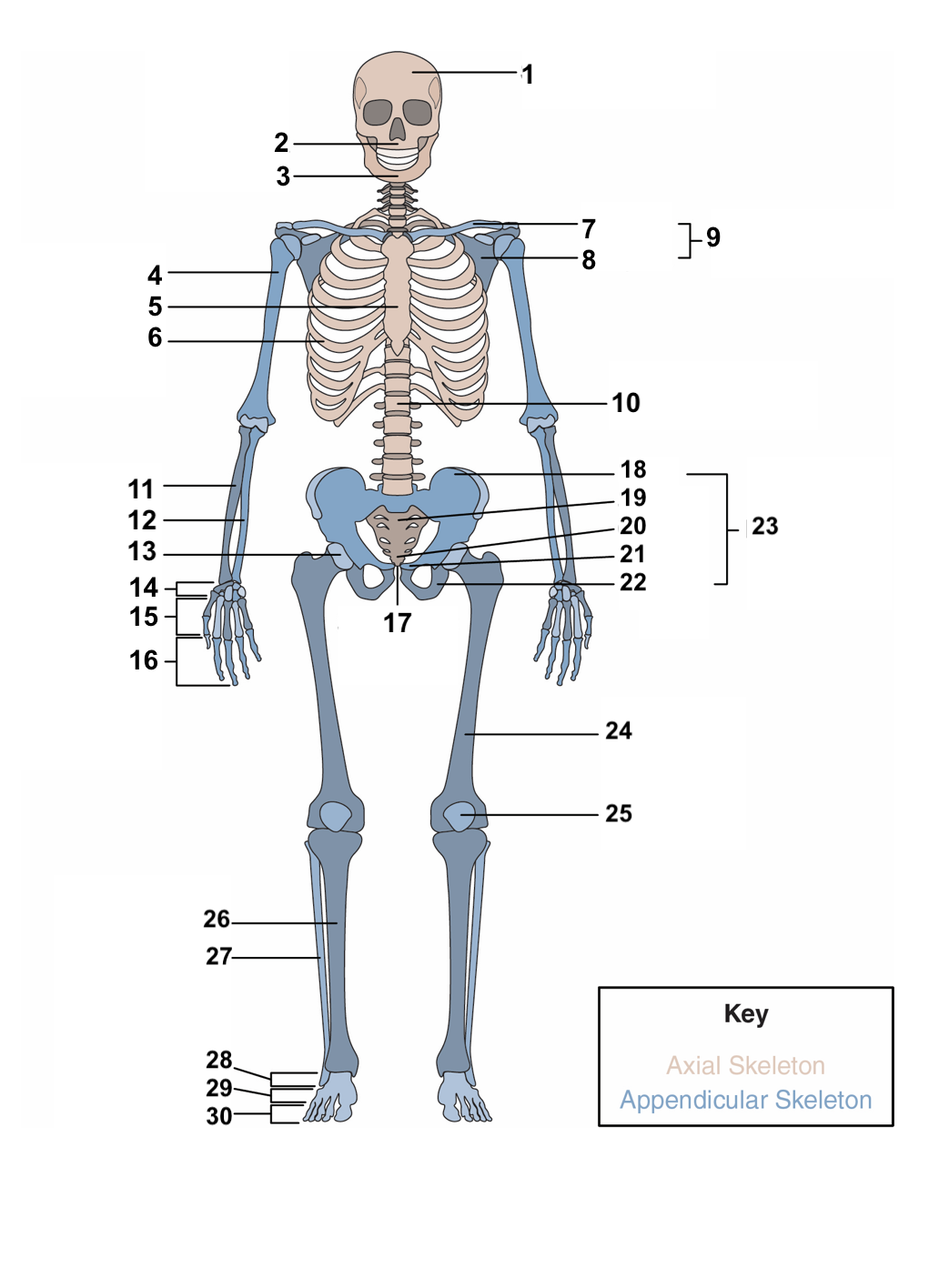
97
New cards
pelvic girdle
23
98
New cards
femur
24
99
New cards
patella
25
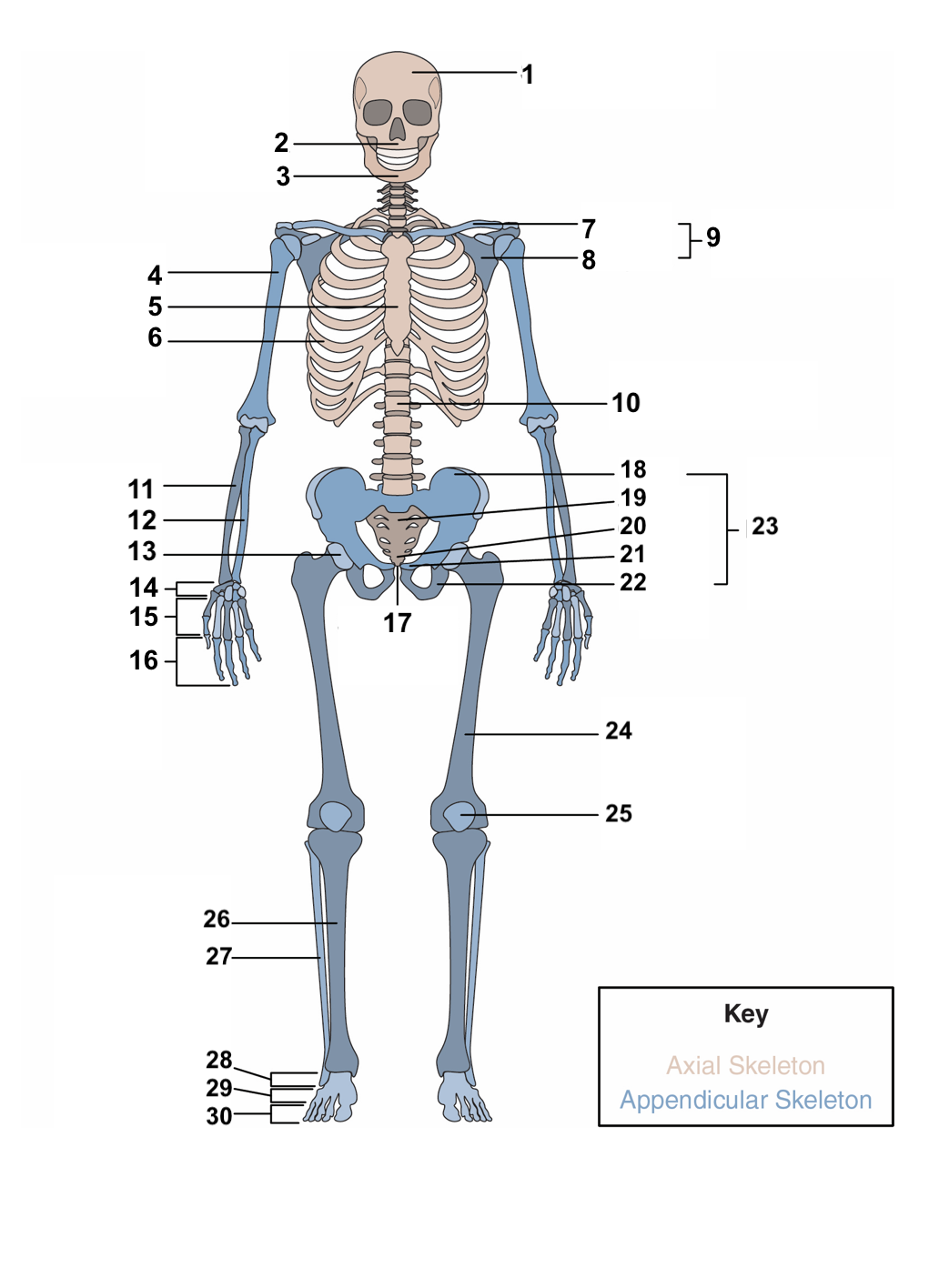
100
New cards
Tibia
26