Kaplan MCAT Physics Chapter 2: Work and Energy, MCAT Physics and Math Chapter 2: Work and Energy
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Energy definition and units
The property of a system that enables it to do something or make something happen, including the capacity to do work.
SI units= joules (J)
Joule
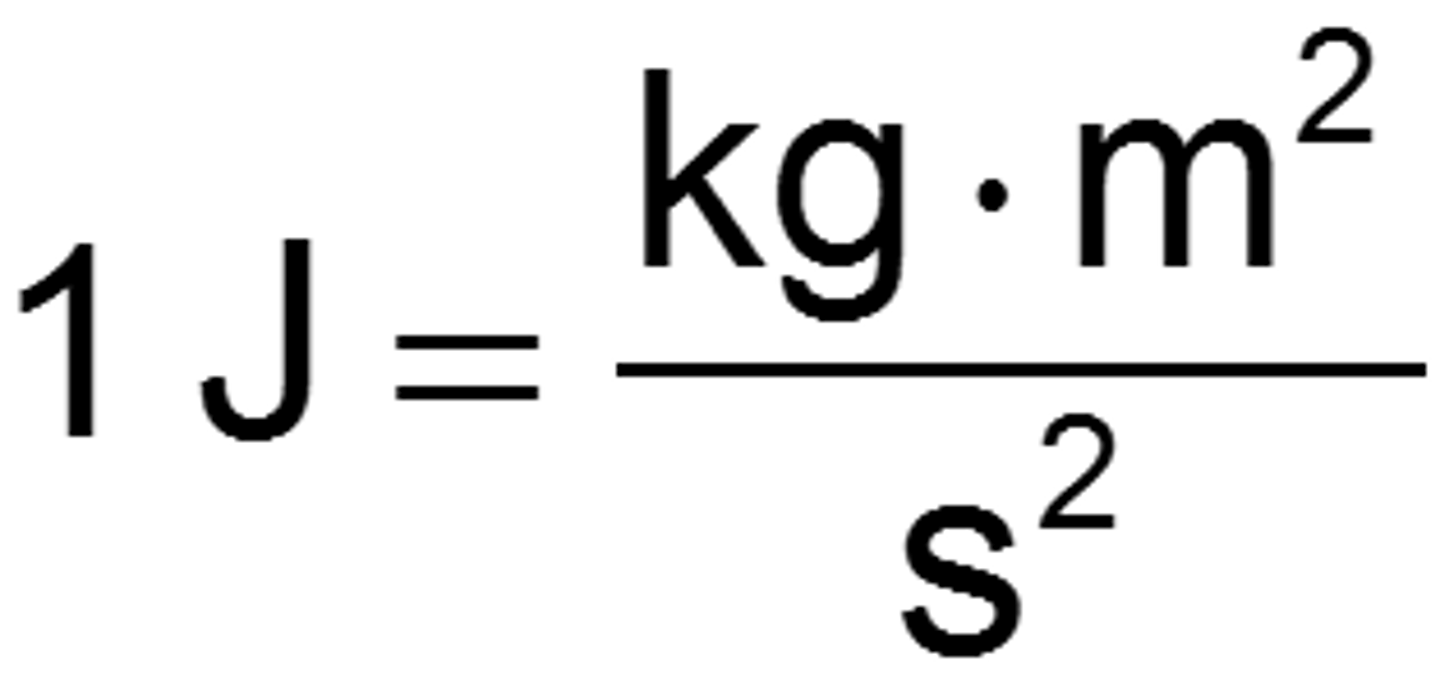
Kinetic energy
The energy associated with the movement of objects. It depends on the mass and speed (not velocity).
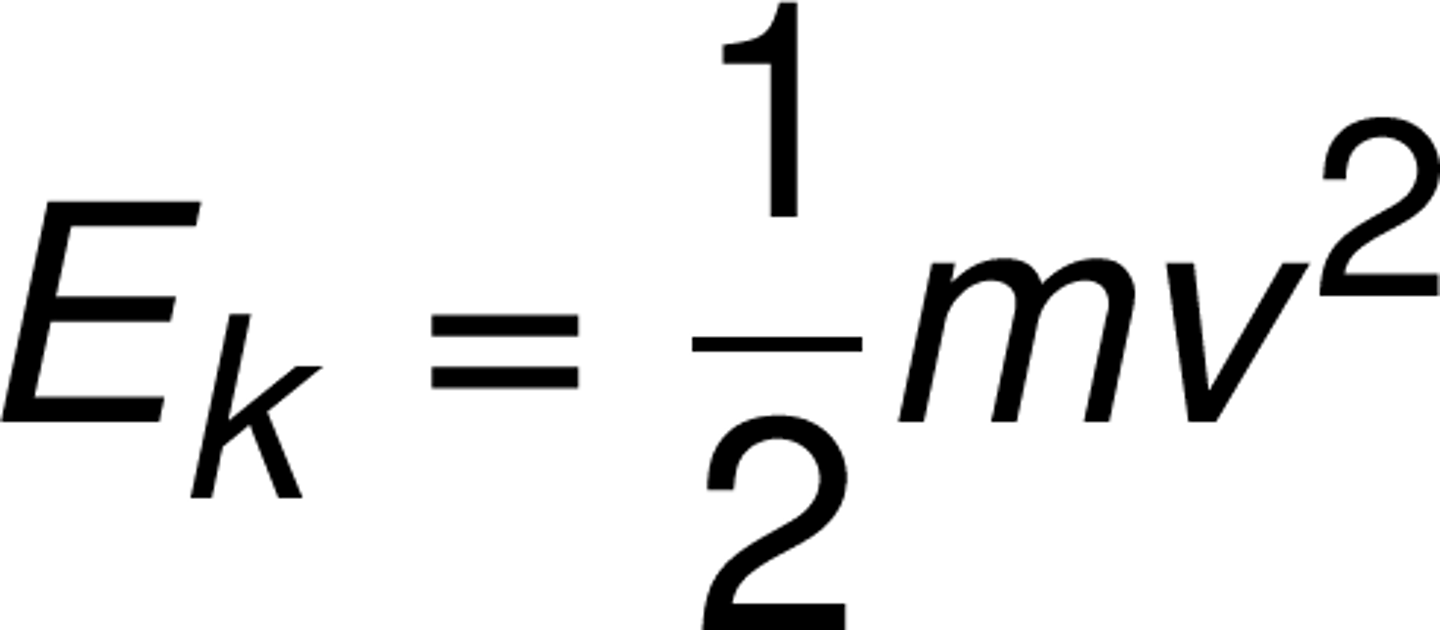
Potential energy (types)
The energy stored within a system. Types:
1) Gravitational
2) Electrical
3) Chemical
4) Elastic
Gravitational potential energy
Related to the mass of the object and its height above 0, called the datum.
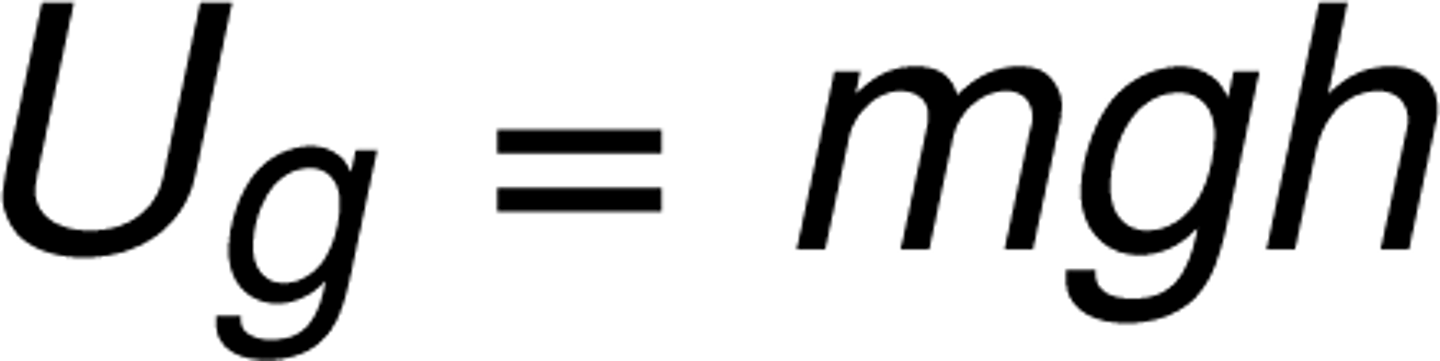
Elastic potential energy
Released to spring constant, k (a measure of the stiffness of the spring) and the degree of stretch or compression of a spring squared.
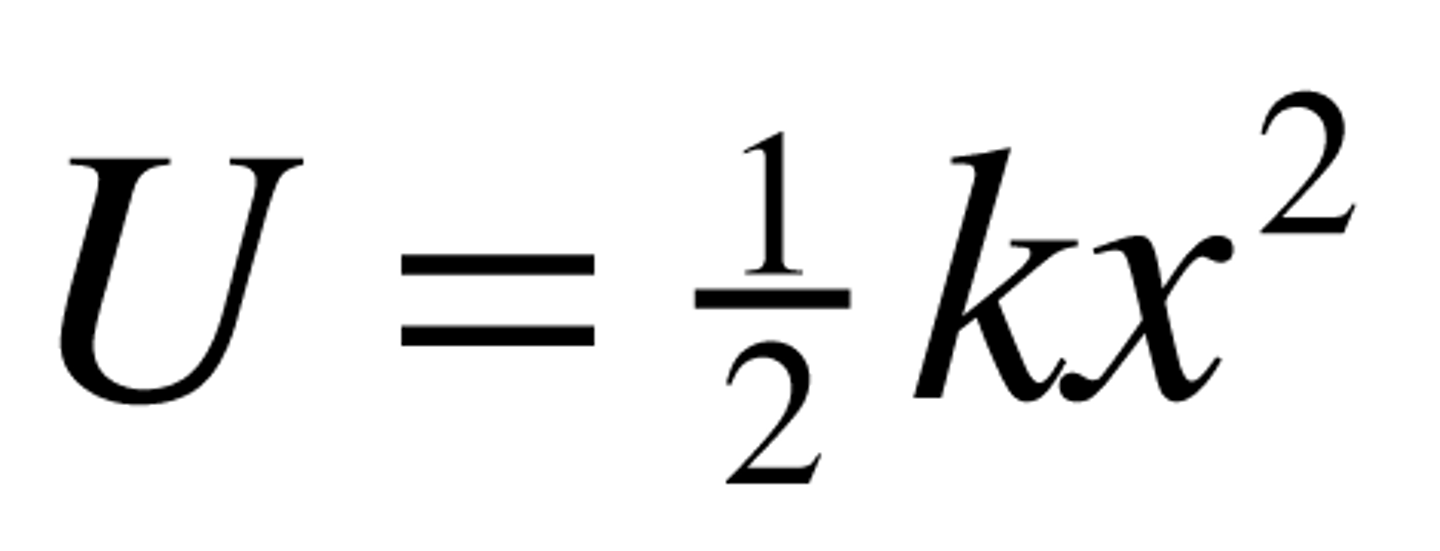
Electrical potenial energy
Energy presents in objects in which positively and negativley charged particals are seperated
Chemical potential energy
The energy stored in the bonds of compounds
Total mechanical energy
The sum of kinetic and potential energies in a system.
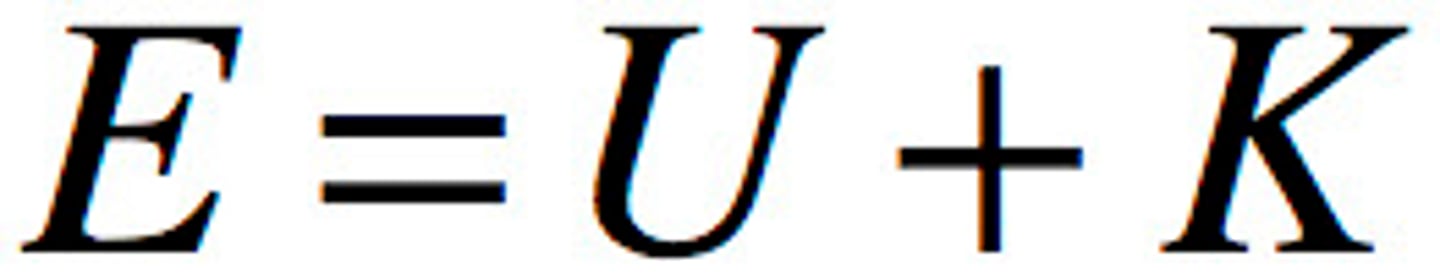
first law of thermodynamics
conservation of mechanical energy, energy is never created nor destroyed it is transferred from one form to another
Conservative forces
Path independent and do not dissipate the mechanical energy of the system.
1) If only conservative forces are acting on an object, the total mechanical energy is conserved.
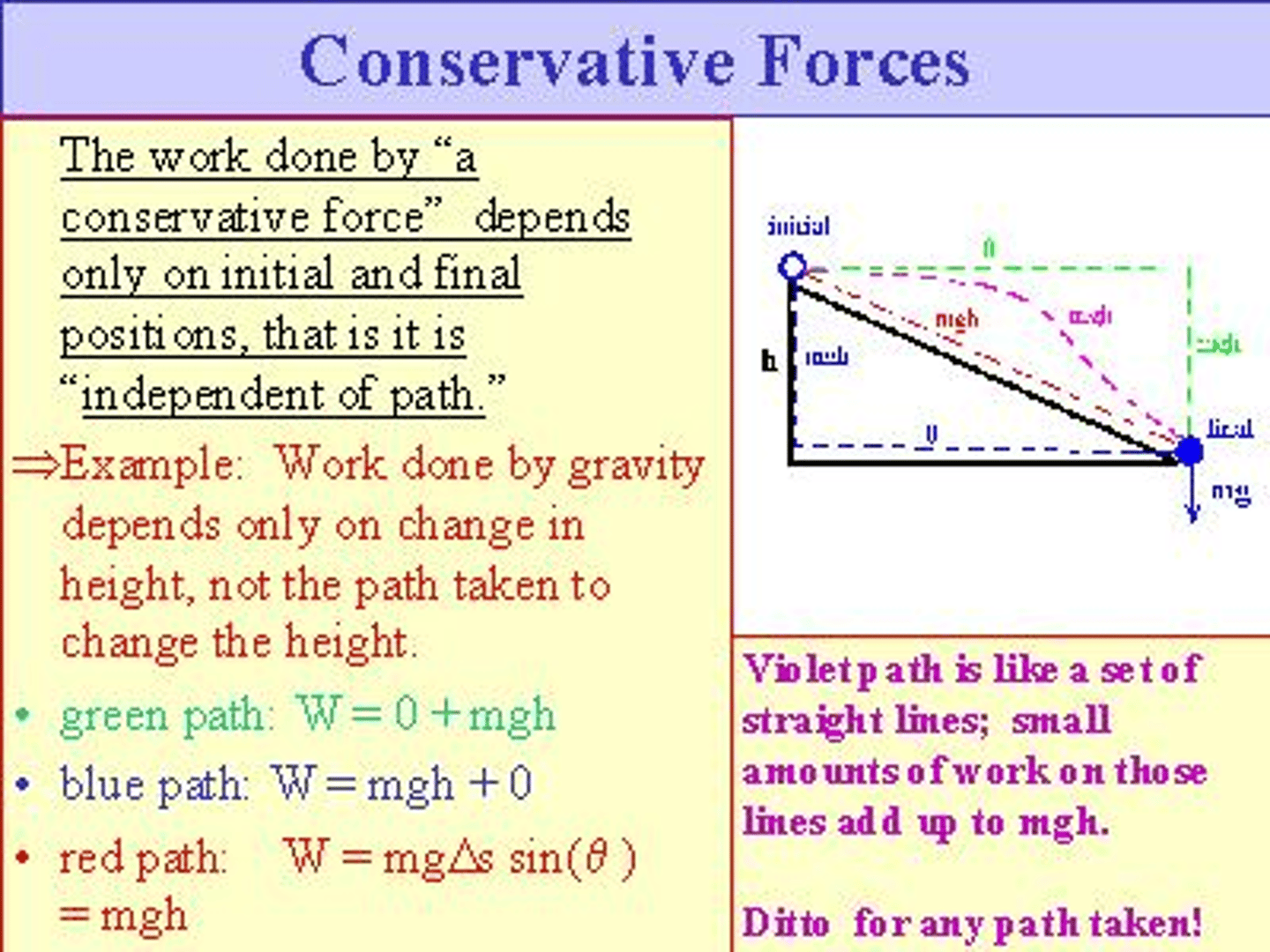
Conservative forces examples
Gravity and electrostatic forces. Elastic forces, such as those created by springs, are nearly conservative.
Nonconservative forces
Path dependent and cause dissipation of mechanical energy from a system.
1) While total energy is conserved, some mechanical energy is lost as thermal or chemical energy
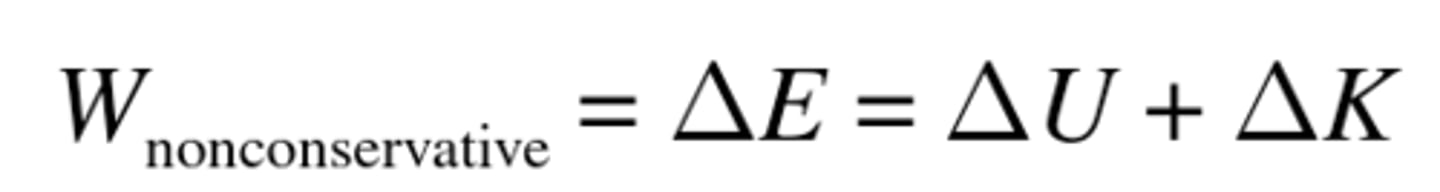
Nonconservative forces example
Include friction, air resistance, and viscous drag.
Work
The process by which energy is transferred from one system to another.
work is dot product, function of the cosine of the angle between the vectors
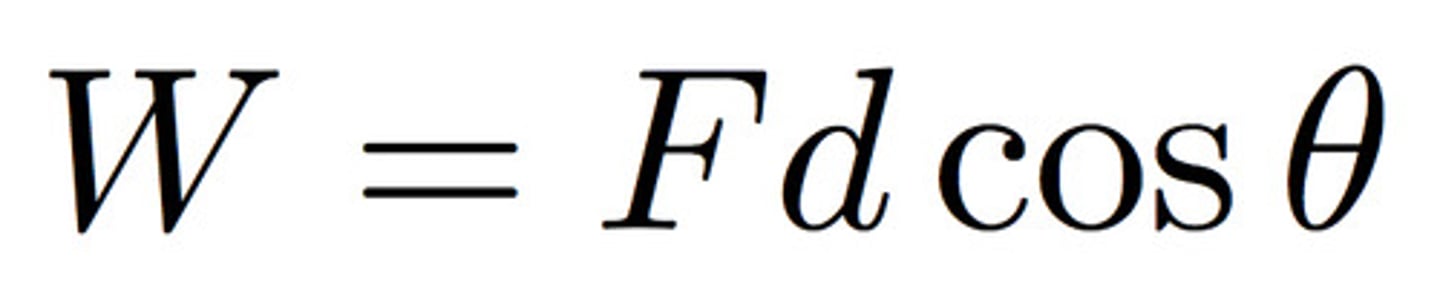
PV graph
work done on or by a system undergoing a thermodynamic process can be determined by finding the area enclosed by the corresponding pv curve
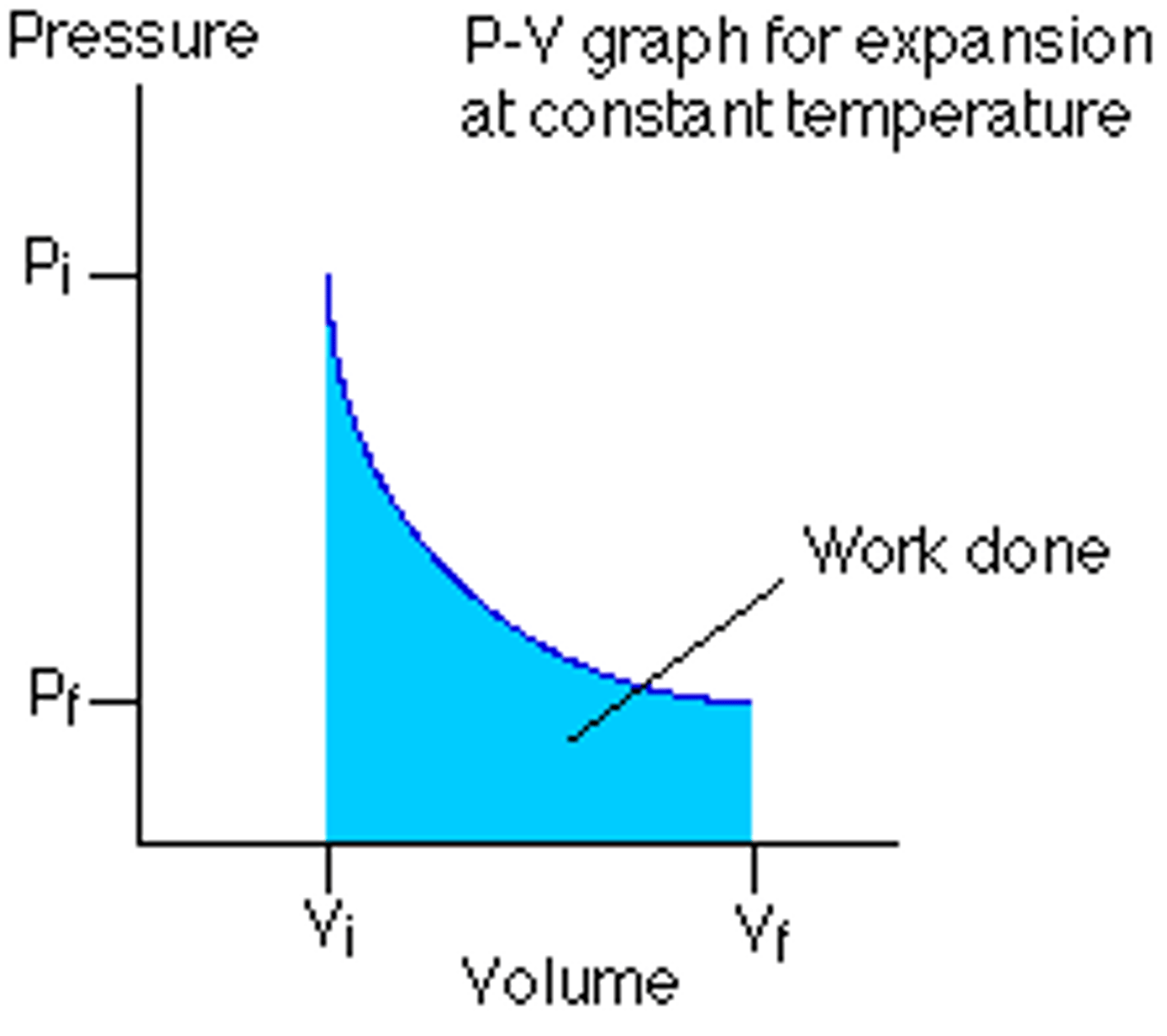
work done by a system
positive
work done on a system
negative
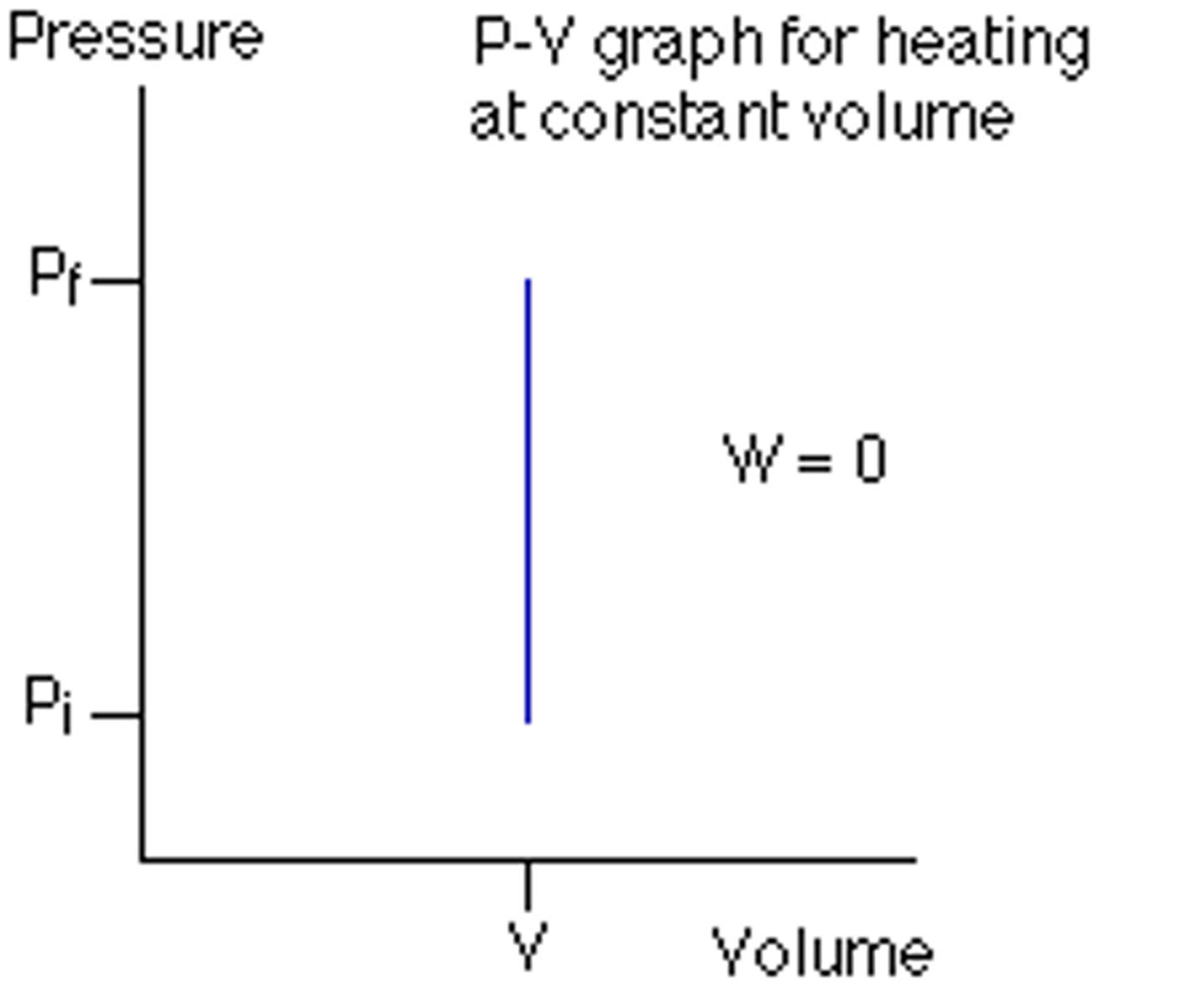
Isovolumetric
or isochoric
If volume stays constant as pressure changes then no work is done because there is no area to calculate on the P-V Curve
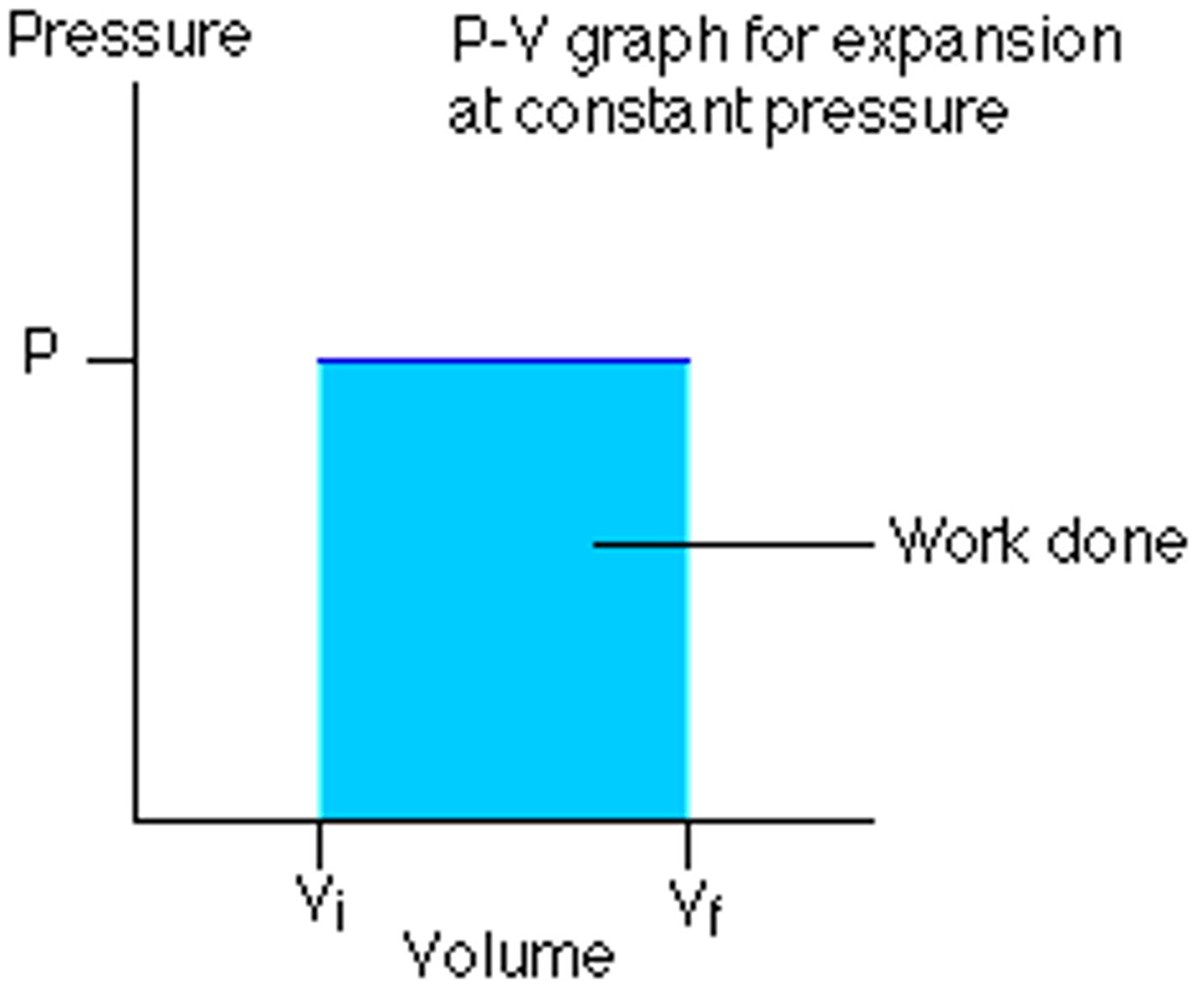
isobaric
pressure remains constant, work can be calculated
Power? unit? equation?
The rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. The SI unit for power is watt (W)
Power = Work/ time = Energy/time
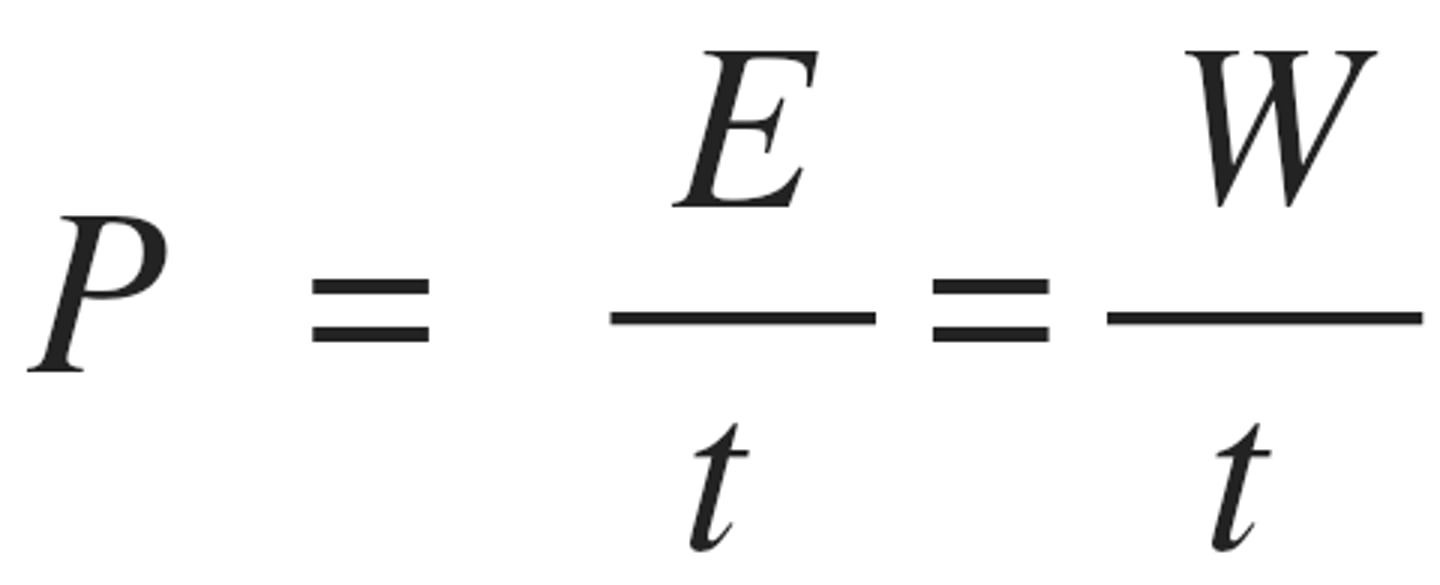
Watt
W = J/s
unit for power
Work-energy theorem
States that when work is done on or by a system. the system's kinetic energy will change by the same amount. In more general applications, the work done on or by a system can be transferred to other forms of energy as well.
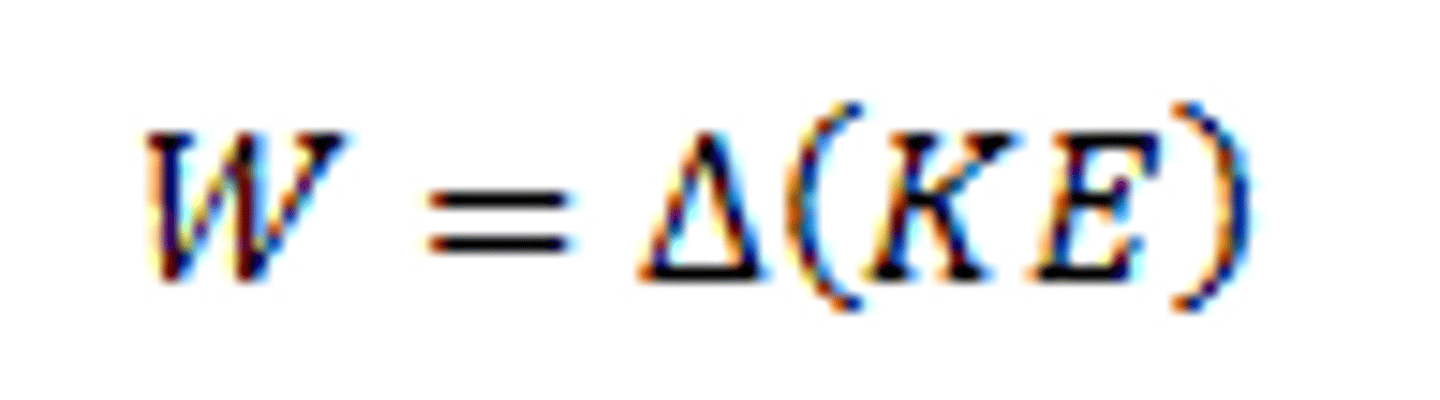
Mechanical advantage
The factor by which a simple machine multiplies the input force to accomplish work.
The six simple machines
1) Inclined plane
2) Wedge
3) Wheel and axle
4) Lever
5) pulley
6) screw
What is the benefit of mechanical advantage?
It allows you more easily accomplish a given amount of work because the input force necessary to accomplish the work is reduced.
The distance through which the input force is applied increases by the same factor.
Load
The output of force of a simple machine, which acts over a given load distance to determine the work output of the simple machine.
Effort
The input force of a simple machine, which acts over an effort distance to determine the work input of the simple machine
to lift an object to a certain height in the air, one must pull through a length of rope equal to
twice that displacement (but half the force needed)
Efficiency
The ratio of the machines work output to the work input when nonconservative forces are taken into account.
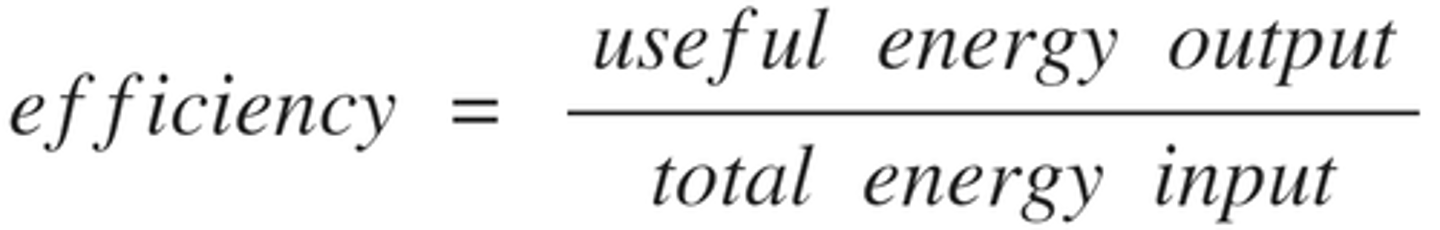
6 pulleys, effort is now ______ total load
1/6 total load (6 times amount of rope, efficiency will decrease due to weight of pulleys and friction)
Uniform circular motion
no work is done because the displacement vector and the force vector are always perpendicular
potential energy is constant
At terminal velocity
the force of gravity and air resistance are equal, leading to translational equilibrium
What are the 2 criteria for Ek?
you must have mass and you must be moving
Kinetic Energy Equation
Ek = 1/2 mv^2
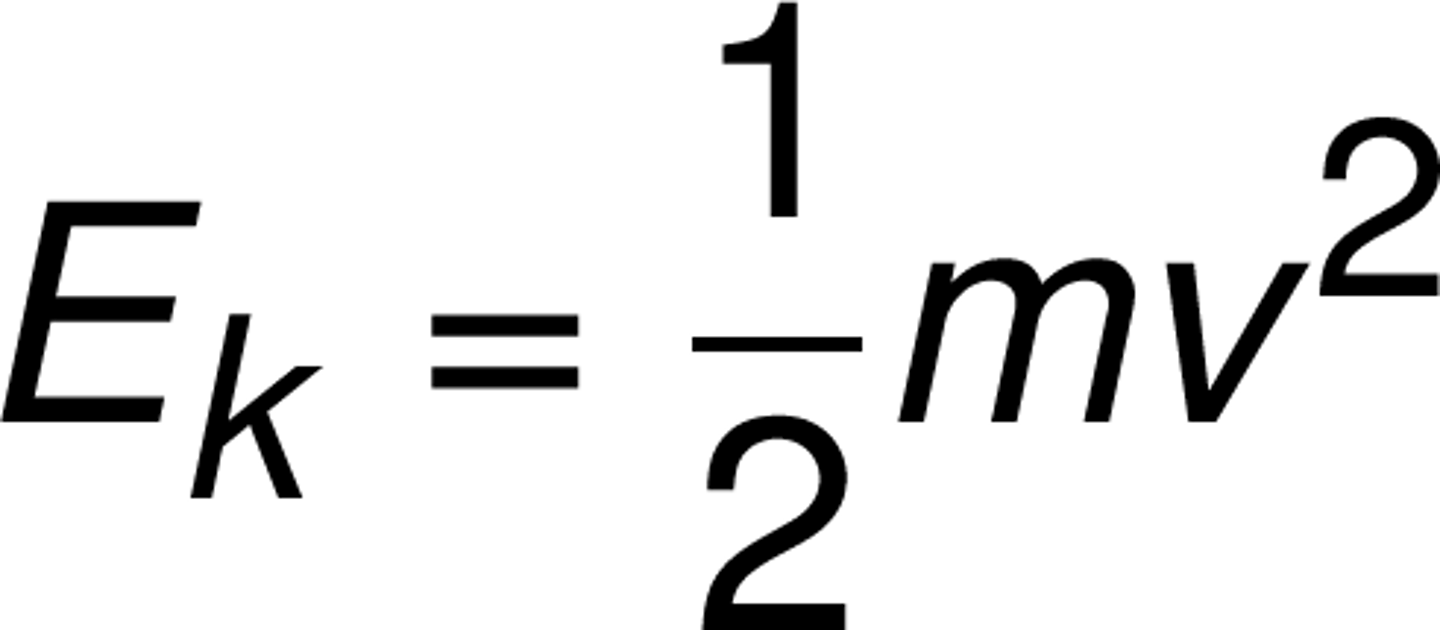
1 J is represented by SI units of...
kgm^2/s^2
Kinetic energy's relation to speed/velocity
related to SPEED, not VELOCITY (direction does not matter); and its related to speed squared (make sure to know the relative increases type logic; if speed doubles, Ek quadruples)
Dynamic Pressure
the kinetic energy of a flowing liquid; this is a term in Bernoulli's Equation
Potential Energy
energy with the POTENTIAL to do work; energy associated with 1) an object's position in space or 2) the qualities of a system (chemical bonds, electrostatic attraction, gravity, elastic)
Gravitational Potential Energy
energy relative to object's position to the datum (0 Eg; ground level)
What is 'datum'?
the 'ground level' in gravitational potential energy; 0J
How is the datum/0J point of Eg chosen?
convenience; sort of just base it off where an object will fall (pencil onto desk, or person onto ground)
Gravitational Potential Energy Equation
Eg = mgh
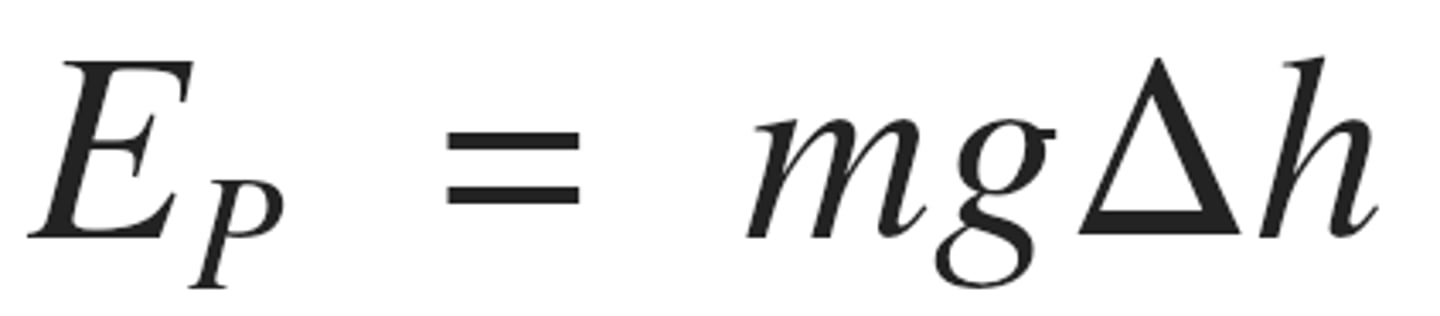
What values can h take in Ep = mgh?
both positive and negative; note h is relative to the datum, so if you're below it, your height is negative!
Elastic Potential Energy
energy when some elastic (e.g., spring) is stretched form its characteristic equilibrium length
Elastic Potential Energy Equation
Ee = 1/2 kx^2 (k is the spring constant, a measure of stiffness; x is the magnitude of displacement)
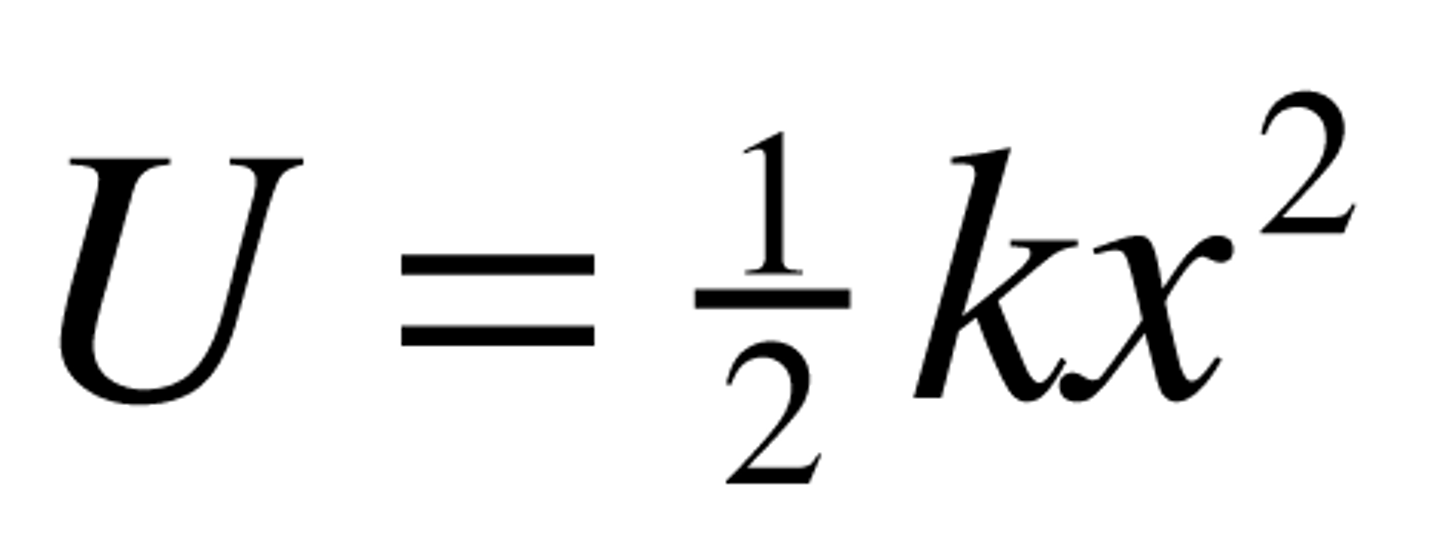
k in the Ee equation
spring constant; measures stiffness of elastic/spring
Total Mechanical Energy
the sum of all potential and kinetic energies of an object: E = Ep + Ek (Ep = Eg + Ee)
First Law of Thermodynamics
Conservation of (mechanical) Energy; energy is never created or destroyed, just changed forms; accounts for all energy, not just Ek and Ep like total mechanical energy does (e.g., if something experiences friction, it loses its energy as heat and does not violate the law)
If an object experiences friction, where is that kinetic energy lost?
as heat
Conservative vs Non-conservative force
definition as to whether or not a force applied keeps the energy IN THE SYSTEM (OBJECT) or not
Non-conservative Forces
Forces that cause an object to not conserve its mechanical energy and LOSE energy (ΔE < 0); e.g., friction slowing it down rids it of all Ek and Ep, viscous drag, air resistance
What is performed on an object by non-conservative forces?
WORK
Non-conservation of energy equation
W(non-conservative) = ΔE = ΔEp + ΔEk; the work done on the object by the non-conservative force is the change in energy it experiences, equal to the energy lost from the system (converted into something else)
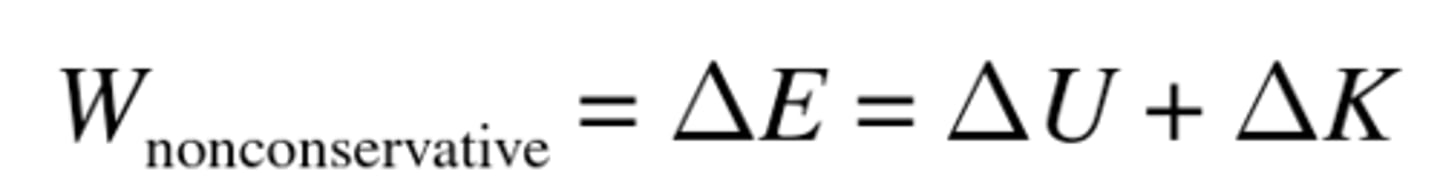
Non-conservative forces vs path
they are path-dependent; the longer the distance they act, the more energy lost by the object they work on
Conservative Forces
Forces that are path-independent and do not dissipate energy (E = Ek + Ep); associated with potential energy; includes gravitational and electrostatic forces
2 most common MCAT conservative forces
gravitational and electrostatic; do not lose energy from a system, but convert it to potential
How do you determine if a force is conservative?
1) if it takes a round trip path (back to same starting position) and ΔE is 0, or 2) if ΔE is equal for taking ANY path between 2 points... = the force is conservative; it takes energy from 1 form and gives it back as another, E total remains the same, no loss to non-conservative force!
Conservation of Mechanical Energy Equation
ΔE = ΔEp + ΔEk = 0
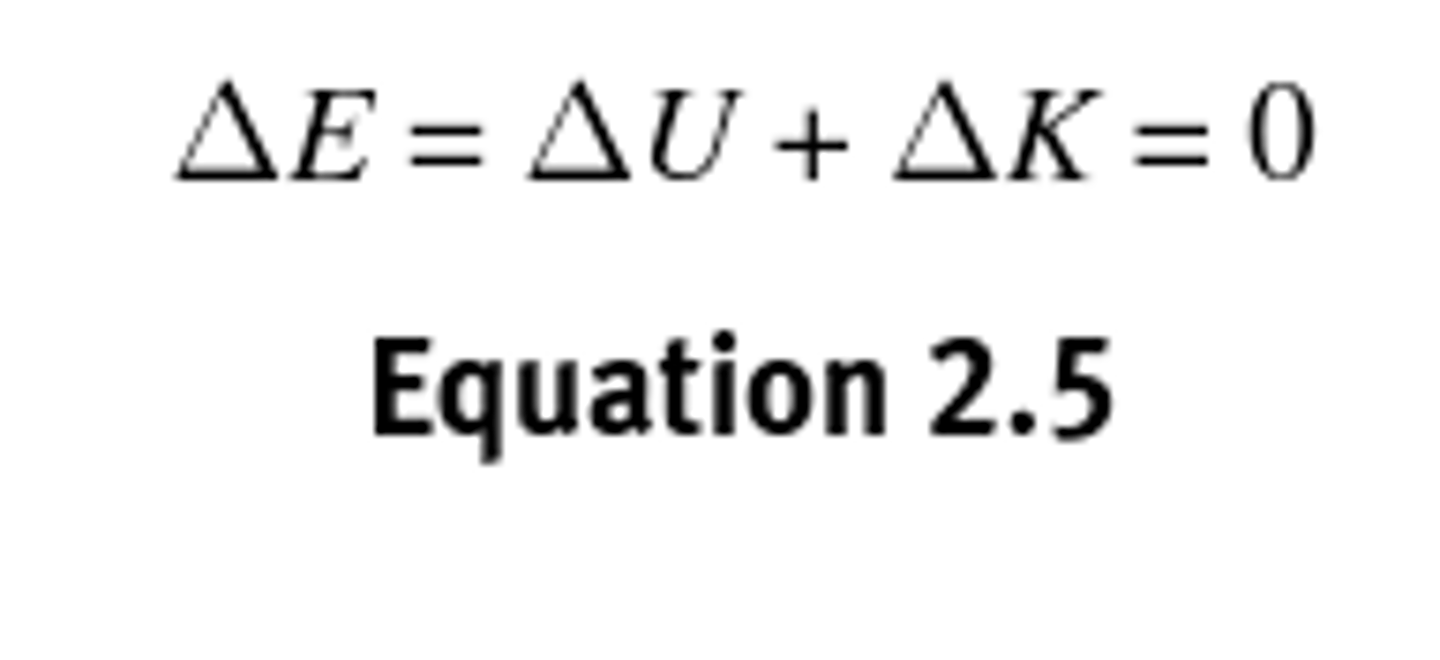
Work
the transfer of energy from one system to another (one of two ways to do so; other = heat), e.g., you roll a ball up a hill, your chemical energy is converted to that object's Eg
2 ways to transfer energy
work and heat ONLY!!!!!!!!!!!
ATP Energy Transfer
energy harnessed from ATP as heat; this is the same as WORK on a microscopic level simply because atoms move and exert force
Is work 100% efficient?
no, some is lost as heat (think about yourself heating up when exercising)
Work Equation
W = F ∙ d = Fdcos𝜃 (dot product!) (theta = angle between the displacement and force applied)
In work, what component of force actually does work?
the component PARALLEL (antiparallel) TO THE DISPLACEMENT VECTOR
Pressure and Work
the 'density of energy' that can occur from work
Piston
the part of a gas cylinder that presses a gas to apply pressure
What happens when gas pushes up on a piston?
it does work to move it up, volume increases
What happens when a piston pushes down on a gas?
it does work on the gas, compressing it
What signifies that work has been done on a volume of gas?
a change in volume has occurred from applied force
P-V Graphs
graphs with pressure on y and volume on x; graphically represents expansion and compression of gas; the work done on/by the system IS THE AREA BETWEEN P1, P2, V1, V2
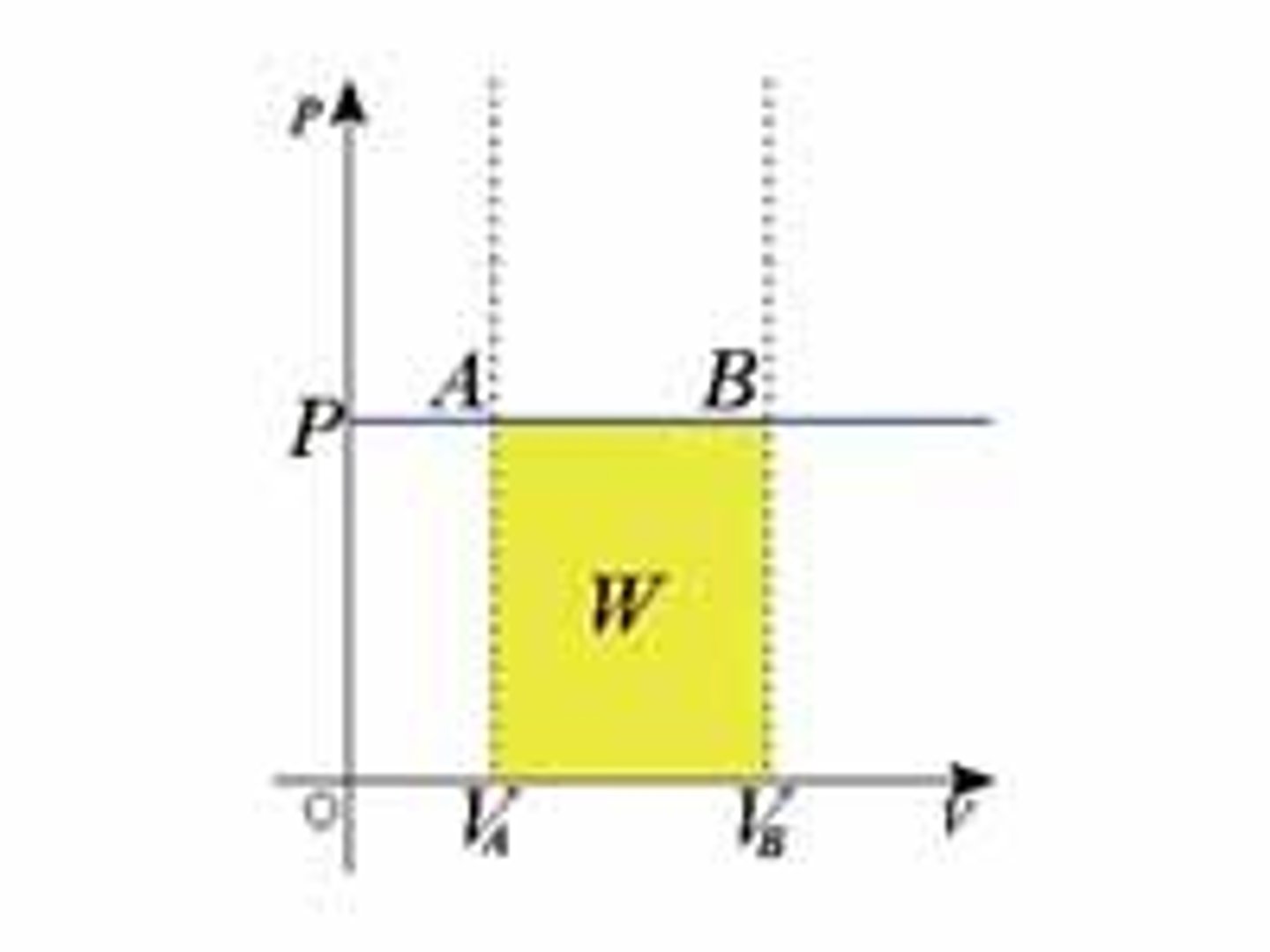
What sign is work DONE BY THE SYSTEM? What does this mean?
positive (+); means the system (gas) has expanded
What sign is work DONE ON THE SYSTEM? What does this mean?
negative (-); means the system (gas) was compressed
If ΔV = 0 for a gas system, how much work has been done?
0 J! no work; there is no area to calculate under a P-V curve; isovolumetric/isochoric process
Isovolumetric/Isochoric Process
when ΔV = 0 in a gas system although pressure changes, indicating that 0 Work was done
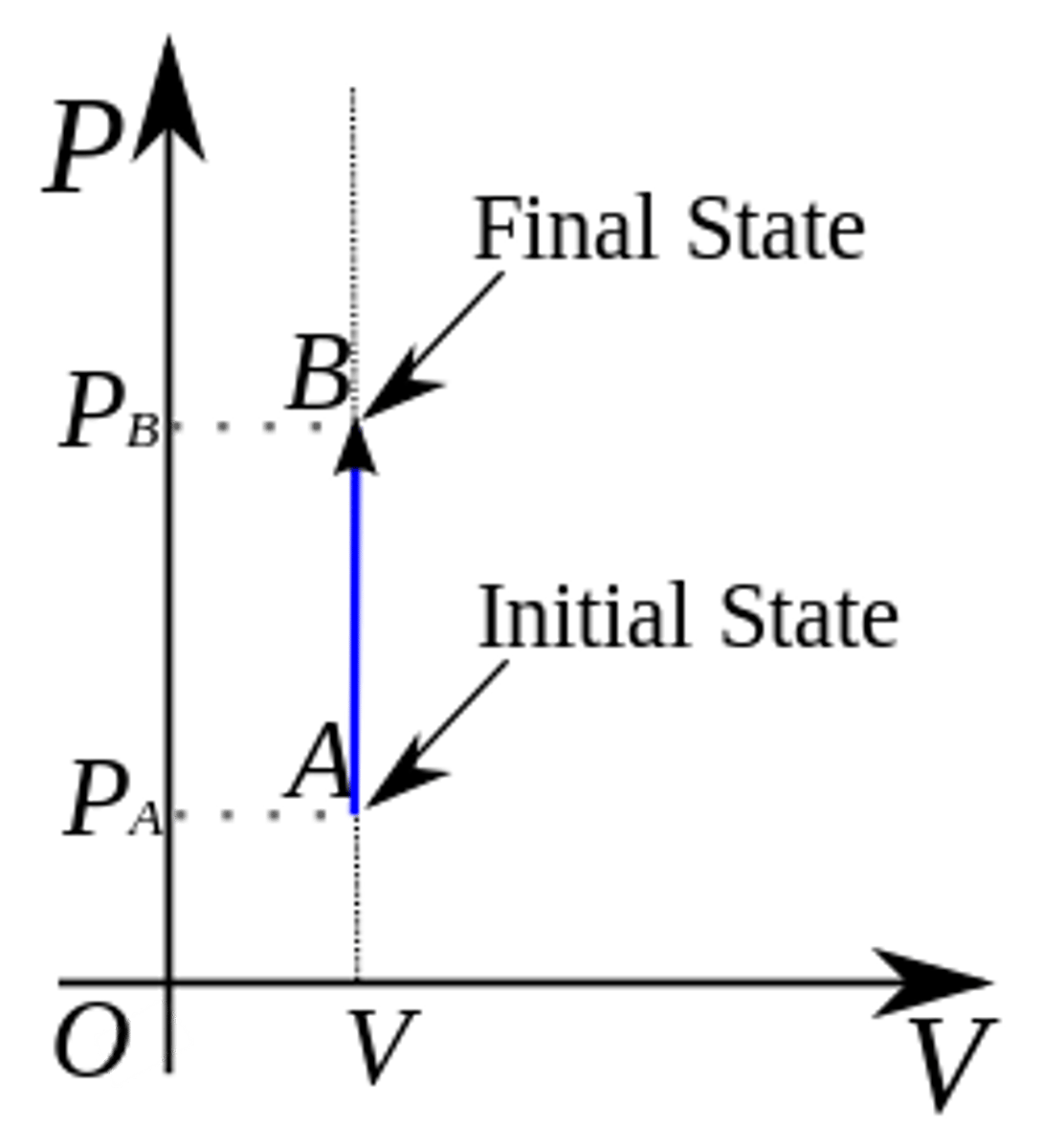
If ΔP = 0 for a gas system, how much work has been done?
W = PΔV joules of work; on a P-V graph, this makes a rectangle; Isobaric Process
Isobaric Process
ΔP = 0 but volume changes, meaning work HAS been done; W = PΔV
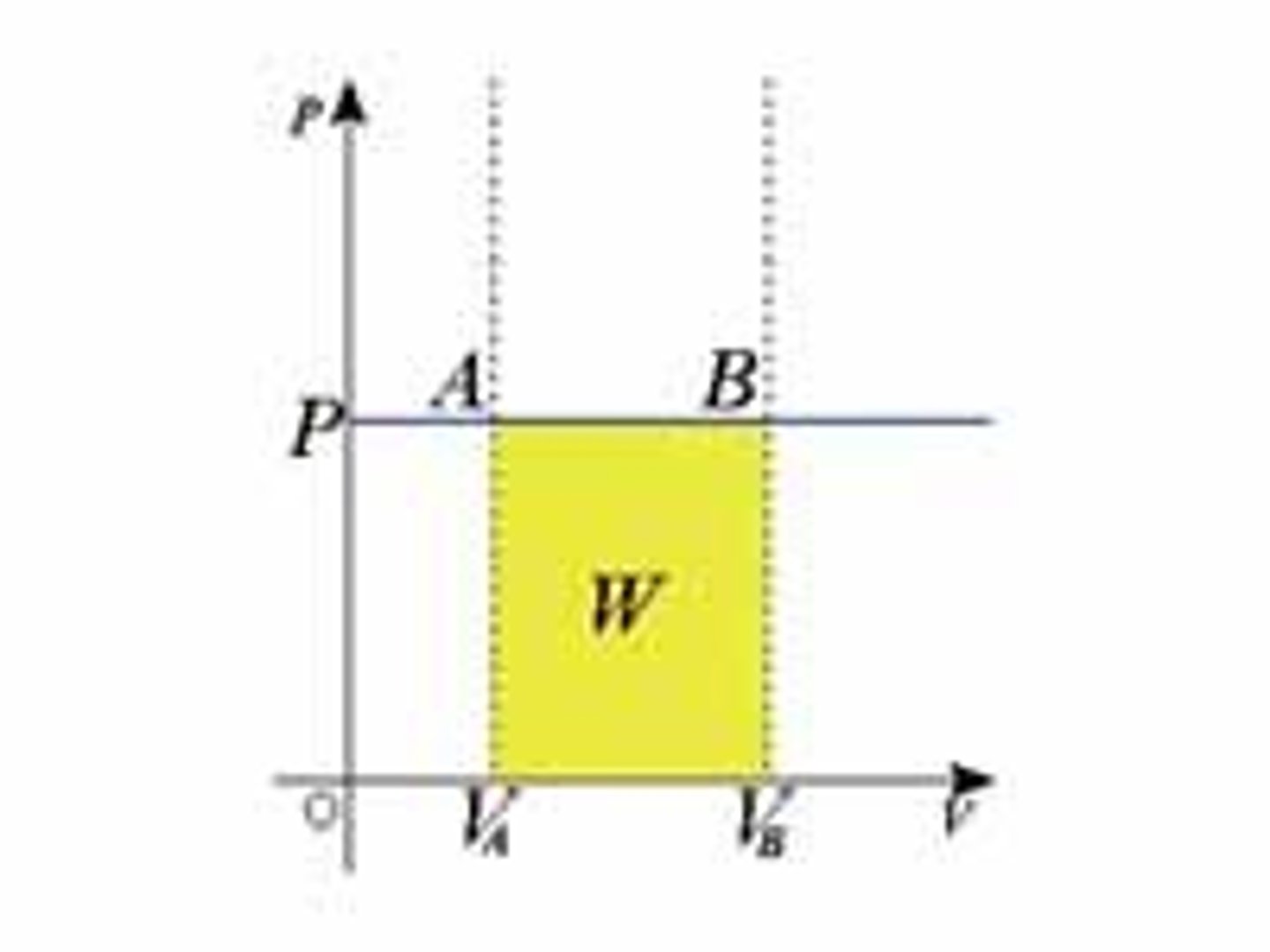
What happens if a P-V graph has 3 points that go back to the same point?
the P and V have changed throughout and gone back to the original; work has still been done and is the area enclosed by the consecutive points
Does the MCAT require physics-based calculus?
Nope.
Power
the rate of energy transfer from one system to another (e.g., electrical current to heat in your toaster!)
Power Equation
P = W/t = ΔE/t
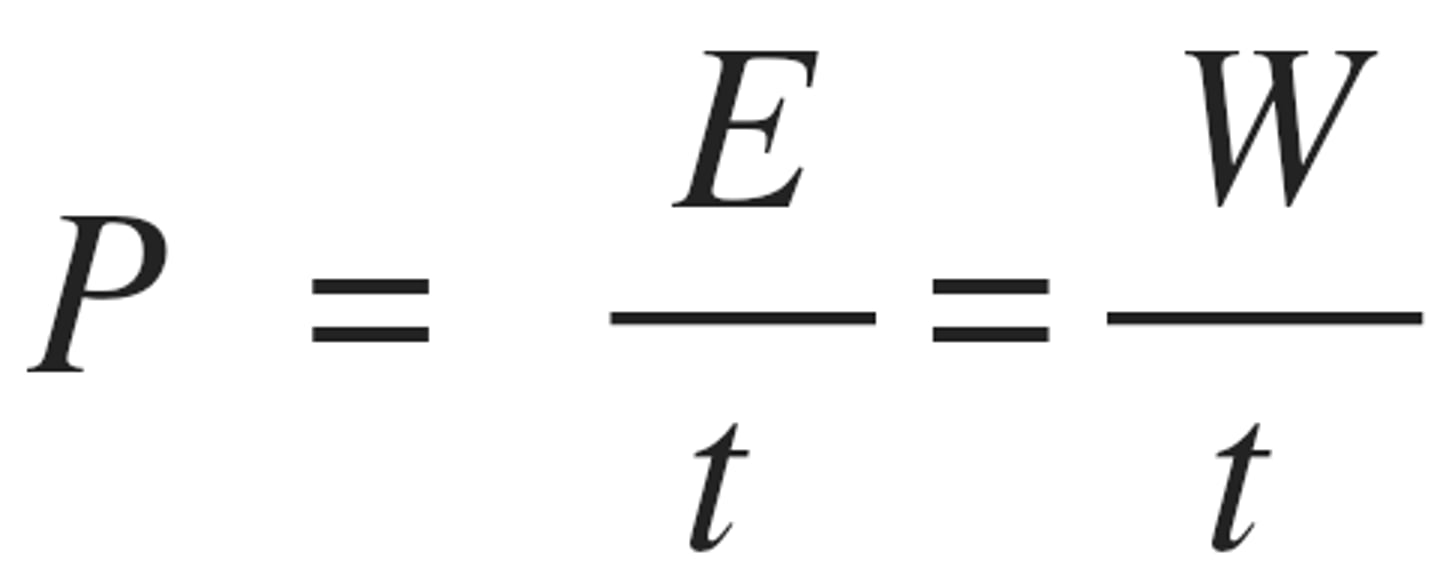
Power Equation in VOLTAGE/ELECTRICS
P = IV (current; voltage)
Unit of power
J/s, aka kgm^2/s^3
Work-Energy Theorem
expression of relationship between work and energy; ALL the forces acting on an object TOGETHER will work on it to change its kinetic energy: Wnet = ΔEk = Ek2 - Ek1; this is the same as the first law of thermodynamics: ΔEp = Q - W (MAKE SURE THE SIGNS ARE RIGHT IN YOUR WORK!!!)
Ep-Heat-Work Relation (first law of thermodynamics)
ΔEp = Q - W
Simple Machines
things that provide mechanical advantage (provide same work with less force); 6 of them
6 Simple Machines
1) inclined plane, 2) wedge (2 merged inclined planes), 3) wheel and axle, 4) lever, 5) pulley, 6) screw (rotating inclined plane)
Wedge
a simple machine that is 2 merged inclined planes

Screw
a simple machine that is a rotating inclined plane

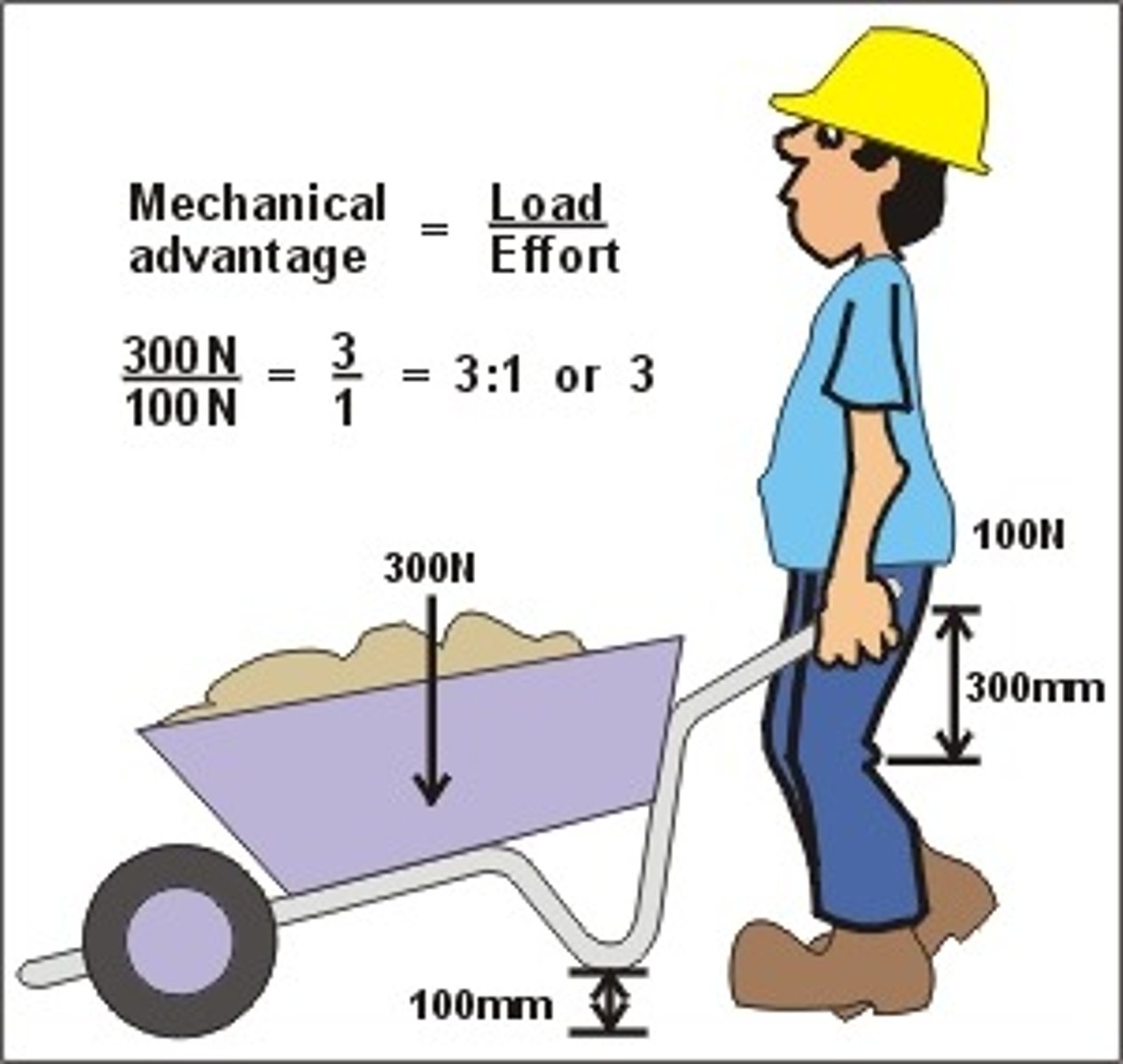
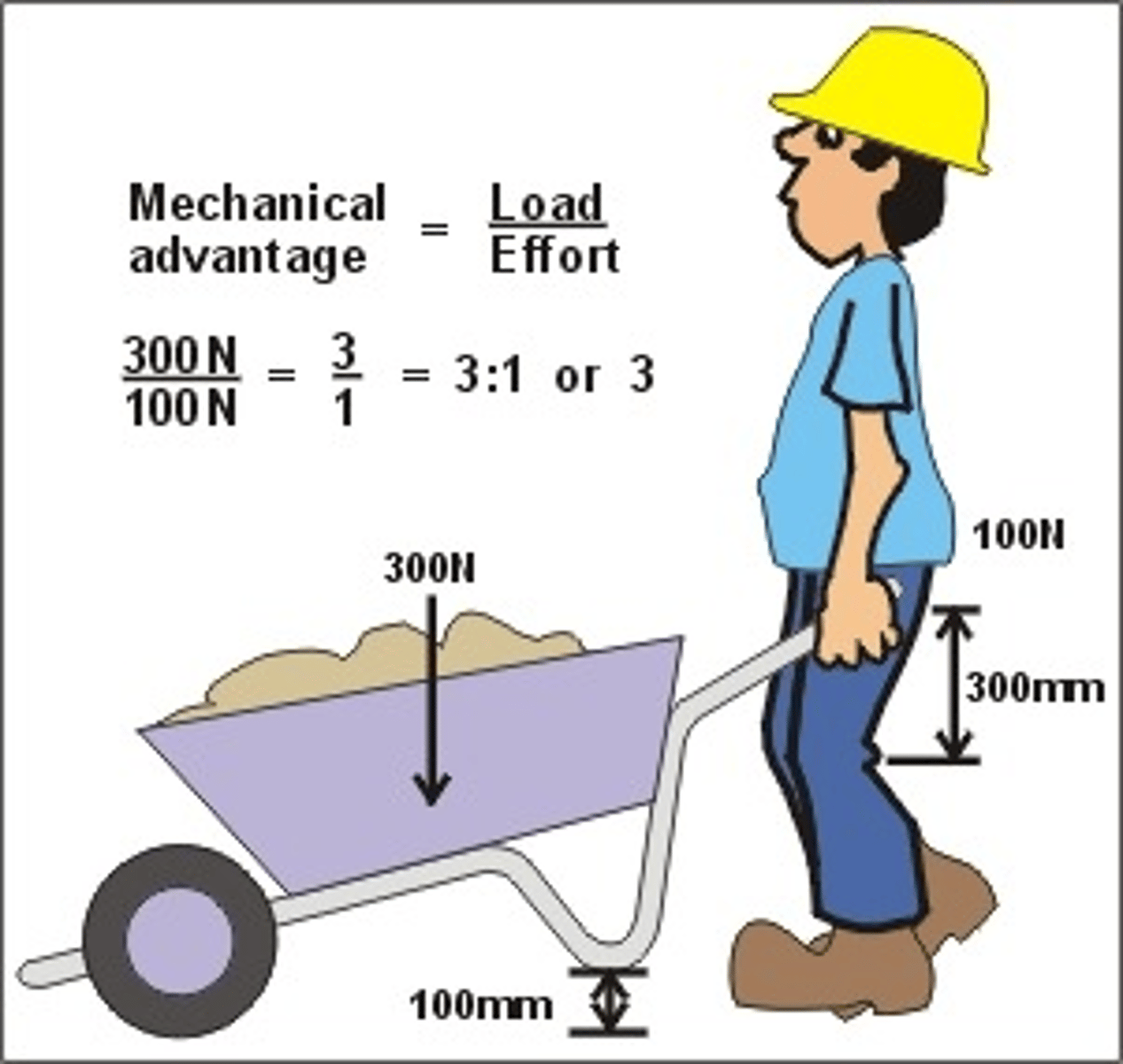
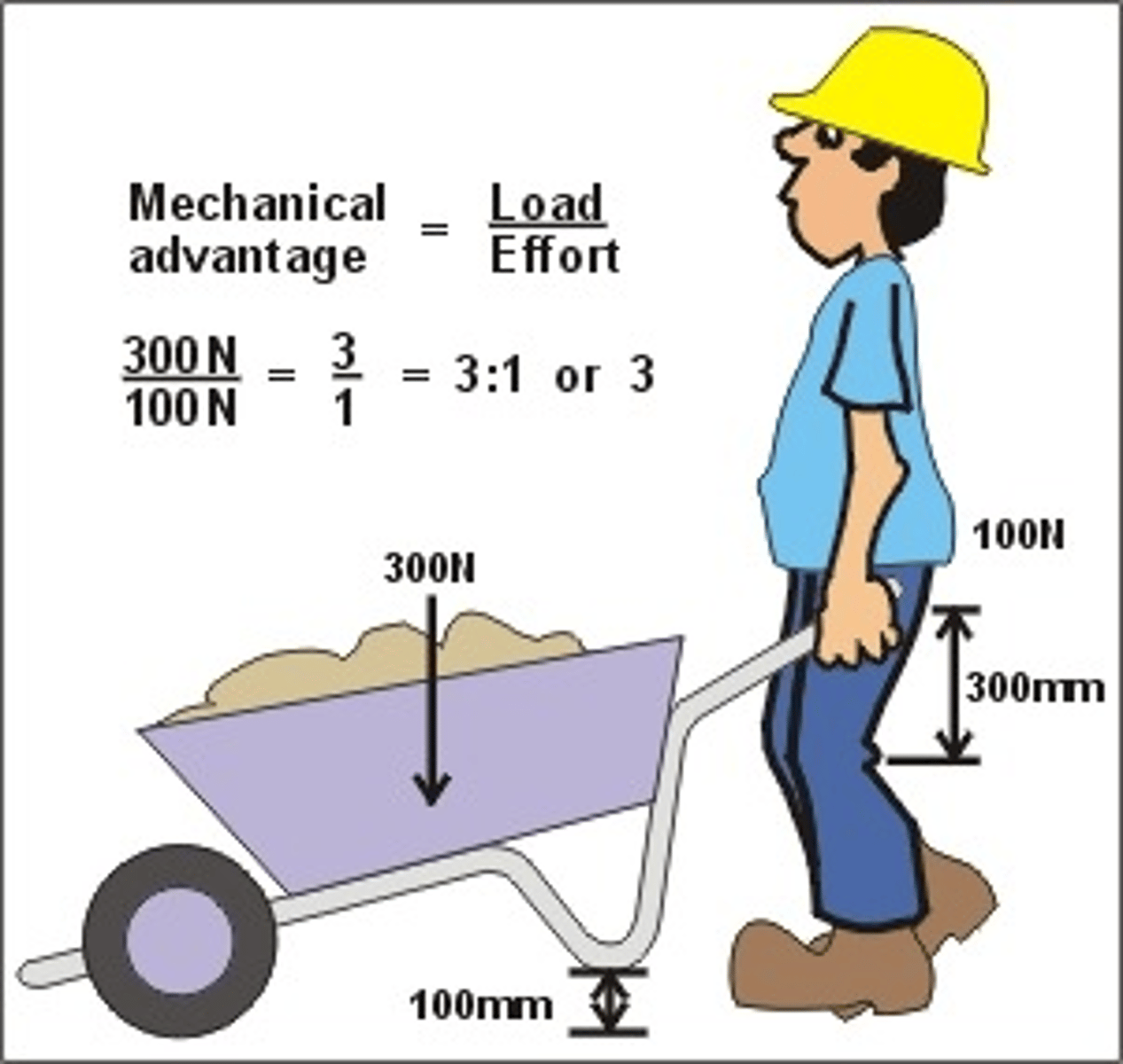
Mechanical Advantage
the measure of the increase of force accomplished by a machine (F(out)/F(in)); reduces force required to achieve same work
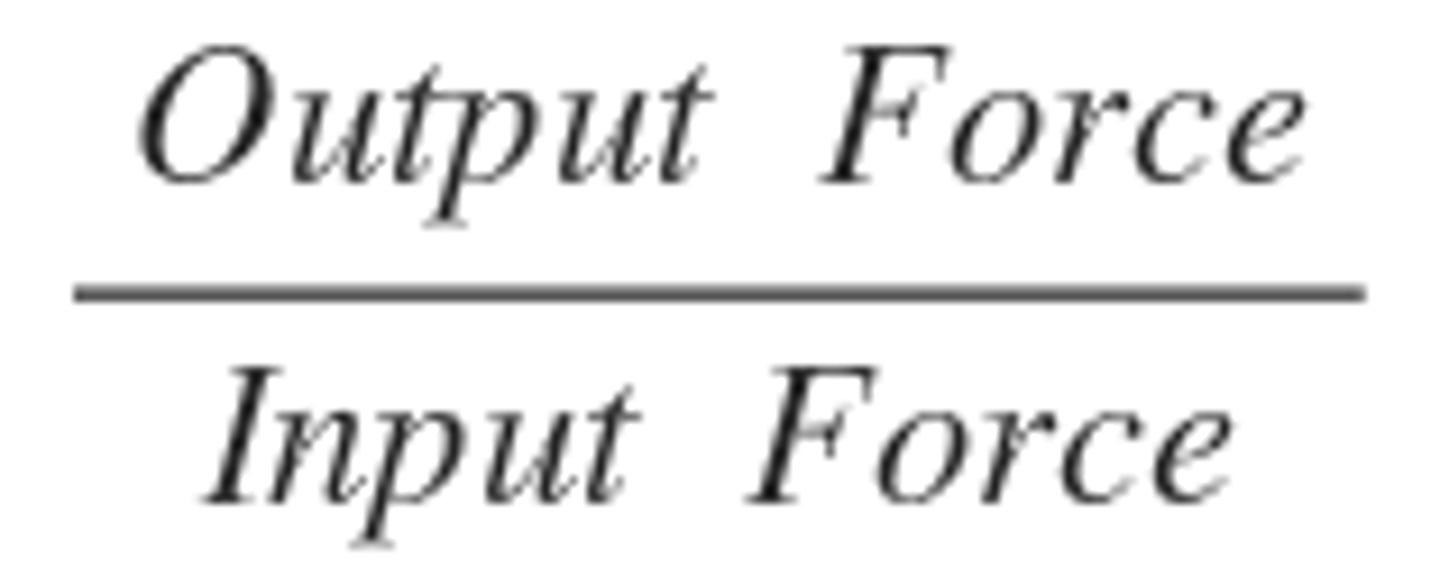
Why do slopes lower force required?
they distribute work over a larger distance
Mechanical Advantage Equation
ME = F(out)/F(in); ratio of force created to the force you put in; no dimensions or units (a ratio)
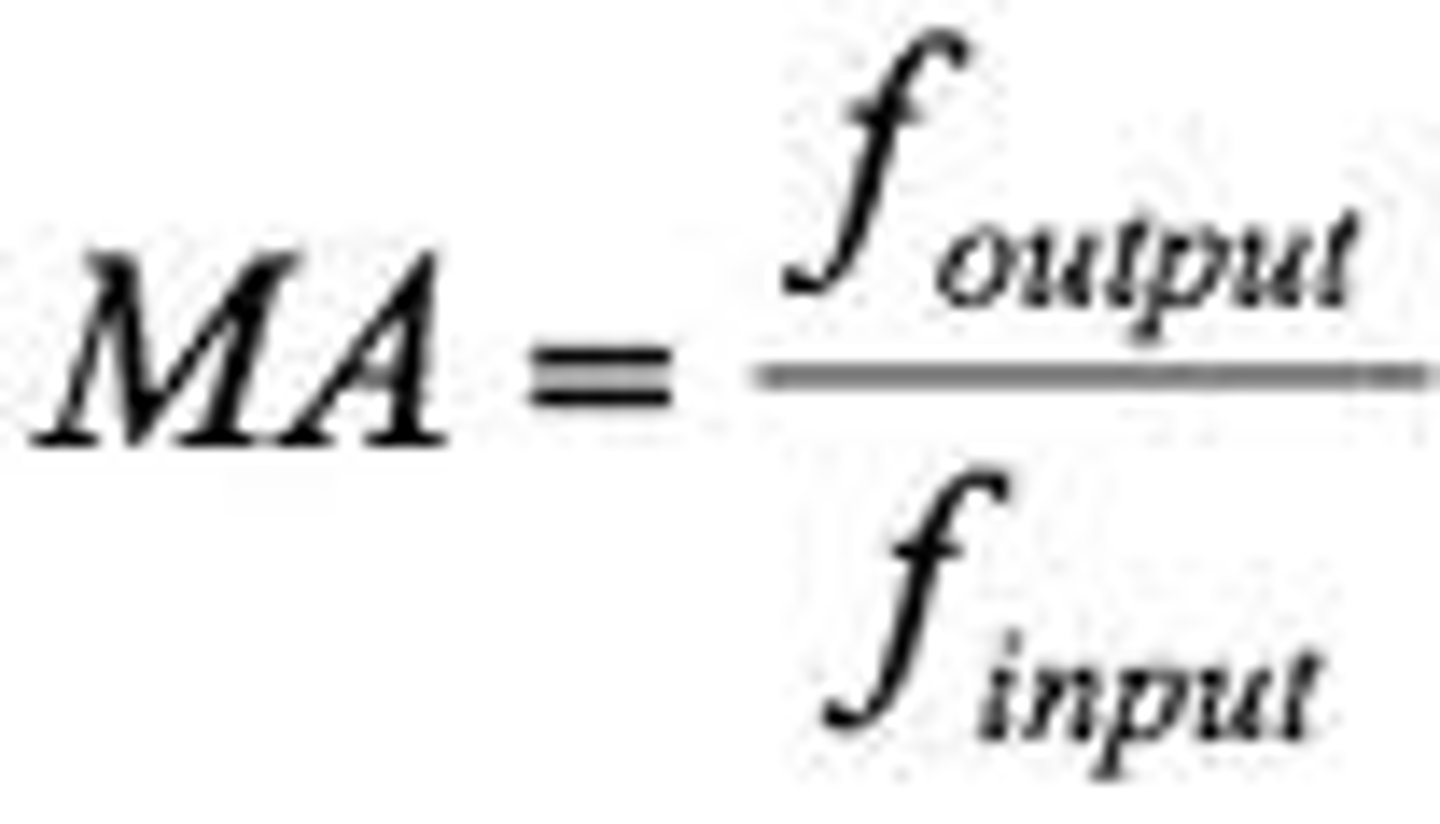
To achieve mechanical advantage, what is increased?
the DISTANCE (NOT displacement) that the force is applied (think about W = F∙d; to increase W when F is lowered, DISPLACEMENT must be increased; pathway independent)
What is the force required to push a block up a ramp?
Fgsin𝜃; the parallel component of gravity that becomes Fnet/Fa
If you calculate doing work in 2 different ways (that should incur mechanical advantage), what will be different between calculations? What will be the same?
WORK will be the same in both, but the FORCE and DISPLACEMENT will be different
Pulleys
simple machines that provide mechanical advantage (same work for lower force over a greater distance)
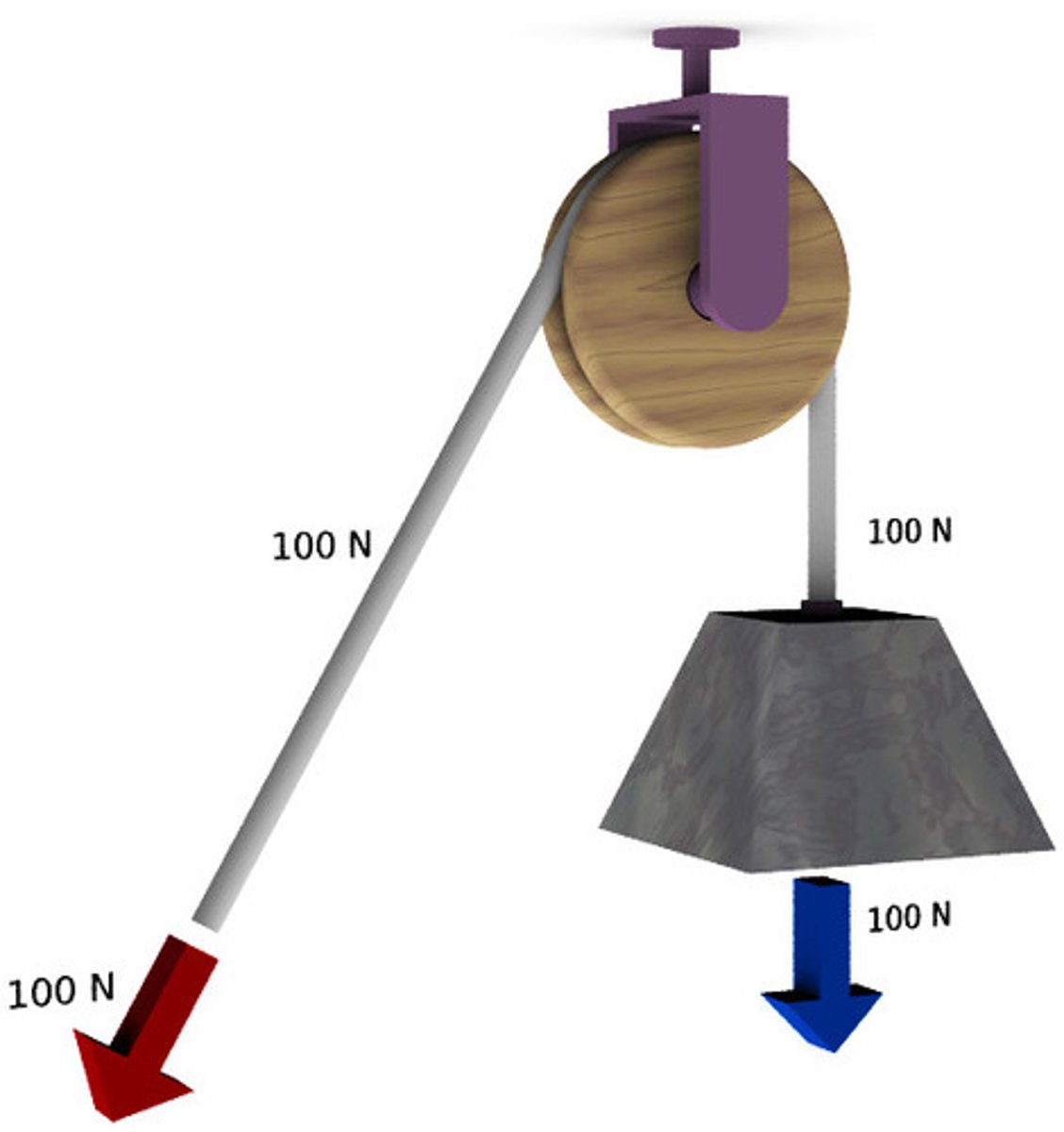
What is the work to lift an object USUALLY? What is the force to lift it using a machine?
Fg = mg usually; LESS than Fg is using a machine (pulley, ramp, etc.)
If the distance to lift something = the displacement to lift something, what force is required? What needs to change for less force?
Fg (lifting it against gravity); not that increasing the DISTANCE greater than the displacement will make it LESS THAN FG!!!
If a block is suspended by 2 ropes, what are the forces acting?
T1 T2 and Fg; note T1 + T2 = Fg is it is not accelerating (translational equilibrium)!
If 2 ropes hang an object AT REST, what is the value of the 2 tensions?
EQUAL; if they weren't, the object would rotate until they were; they each support 1/2 of the load