Human Anatomy BIO 2340 Quiz #6 Ch 25: Respiratory, Ch 26: Digestive
1/94
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Functions of the Repsoratory System
Air passageway
Gas exchange
Gas conditioning
Detection of odors
Sound production
Upper Repsiratory Tract Organs
Nose
Nasal cavity
Pharynx
Lower Respiratory Tract Organs
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchus
Bronchiole
Terminal bronchiole
Tissue of Nasal Cavity & Paranasal Sinuses
Pseudostratifed ciliated columnar epithelium
Tissue of nasopharynx (pharynx)
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Tissue of oropharynx
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Tissue of laryngophaynx
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
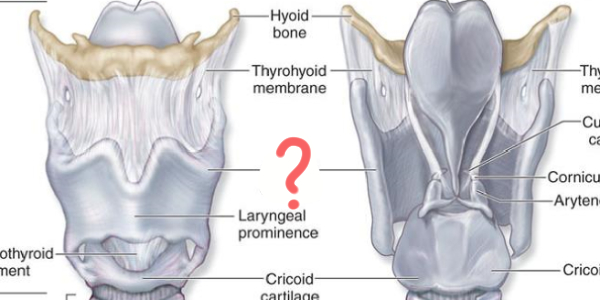
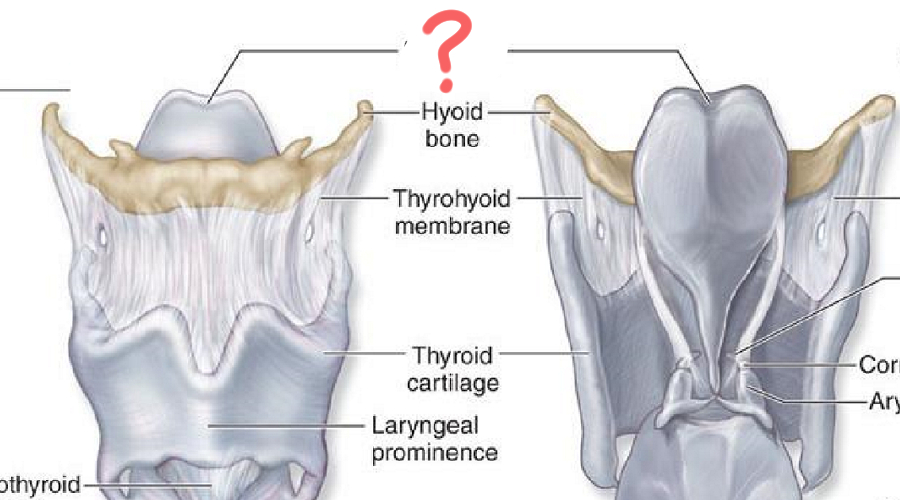
1st Larynx Major Cartilage
Thyroid Cartilage:
Largest cartilage
No posterior wall
Laryngeal prominence (Adam’s Apple")
2nd Larynx Major Cartilage
Cricoid Cartilage:
Inferior to thyroid cartilage
Complete ring shape
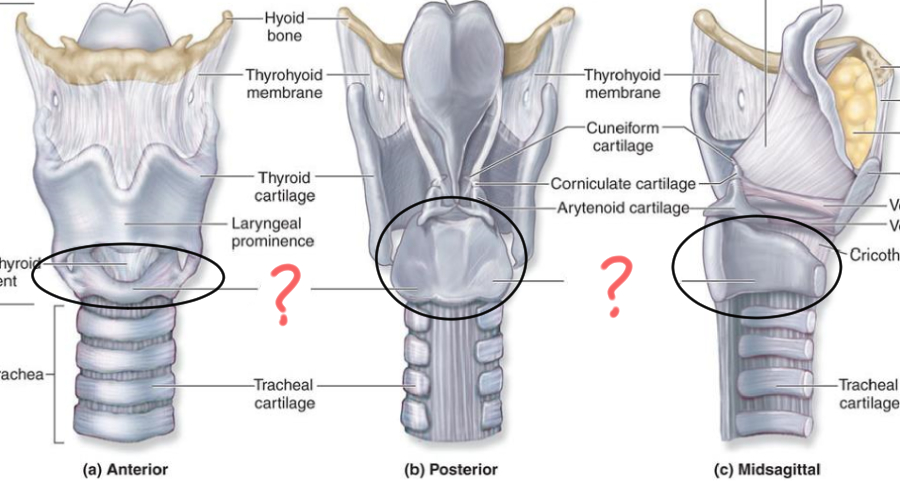
3rd Larynx Major Cartilage
Epiglottic Cartilage:
Flap-like structure that covers the trachea during swallowing (Deglutition)
Minor Cartilage of Larynx
Arytenoid
Corniculate
Cuneiform
Sound Production
Tissue type of trachea (windpipe)
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells
1° Bronchi
1. innervate what?
2. how many in each?
Innervates lungs
Right (1) Left (1)
2° Bronchi
1. innervate what?
2. how many in each?
Innervates lung lobes
Right (3) Left (2)
3° bronchi
1. innervate what
2. how many in each?
Bronchopulmonary Segment
Right (10) Left (8-10)
Tissue type of Bronchioles
Simple ciliated columnar epithelium
Alveoli
site of _______
Gas exchange
Alveolar type I cell
Function
Tissue
Rapid diffusion of gasses
Simple squamous epithelium
Alveolar type II cel
Function
Secrete pulmonary surfactant, coats surface of alveoli to prevent collapse
Alveolar macrophage
1. function
Engulf microorganisms that are in alveolus
Alveoli - Respiratory Membrane
Fused basement membrane of both cells
Type I alveolar cell & pulmonary capillary cell
Conducting Portion Structures
Paranasal Sinuses
Nasal Cavity
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Terminal bronchioles
Respiratory Portion Structures
Respiratory Bronchioles
Alveolar Ducts
Alveoli
Lungs & Pleura
visceral pleura
pleural cavity
parietal pleura
Mediastinal surface of Lung
Hillum (Root)
Bronchi
Pulmonary vessels
Lymphatic vessels
Nerves
Left Lung
2 Lobes
Cardiac impression (heart_
Oblique Fissure
Right Lung
3 lobes
Oblique and horizontal fissure
Superior, middle, and inferior lobes
Blood going to alveoli through pulmonary
Pulmonary arteries
Blood going to alveoli (high or low?) in oxygen
Low in oxygen
Blood leaving the alveoli through pulmonary
Pulmonary vein
Blood leaving the alveoli (high or low?) in oxygen
High in oxygen
Blood going to bronchi through pulmonary
Bronchial arteries
Blood going to bronchi (high or low?) in oxygen
The blood going to the bronchi via the bronchial arteries is high in oxygen because it originates from the aorta
Blood leaving the bronchi through pulmonary
Bronchial veins
Blood leaving the bronchi (high or low?) in oxygen
low in oxygen
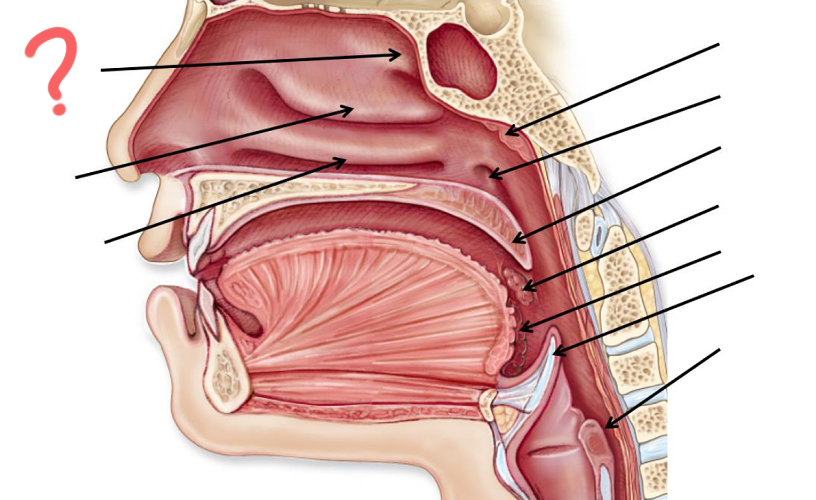
Superior nasal concha
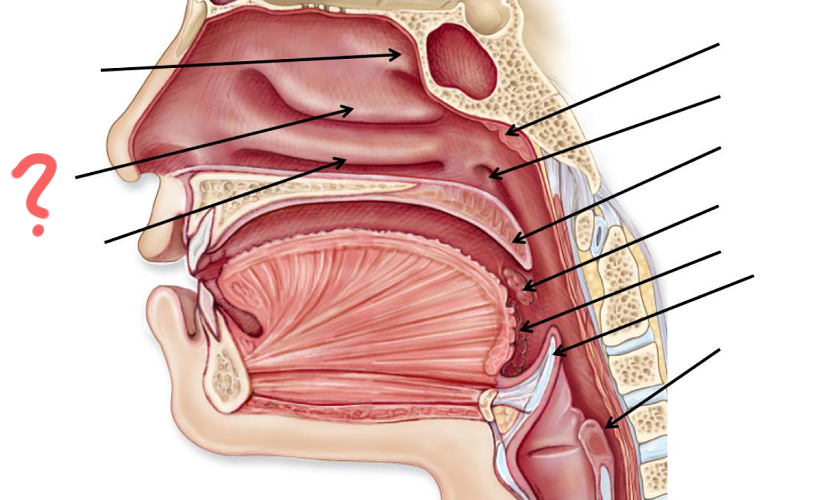
Middle nasal concha
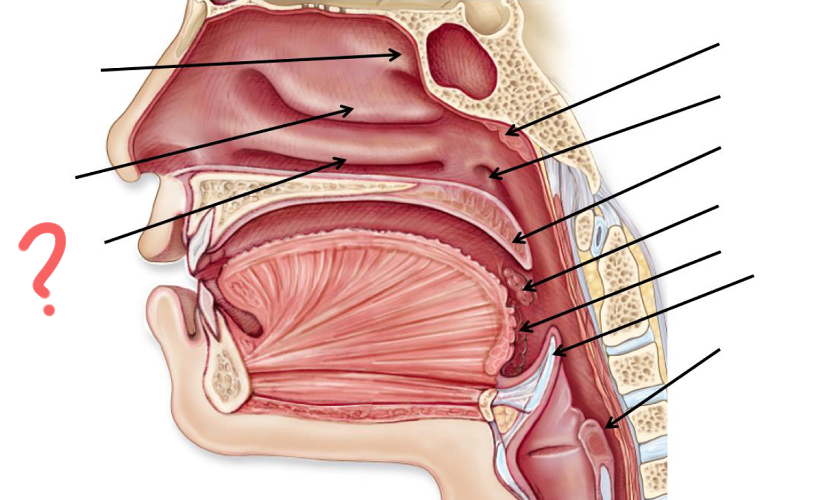
Inferior nasal concha
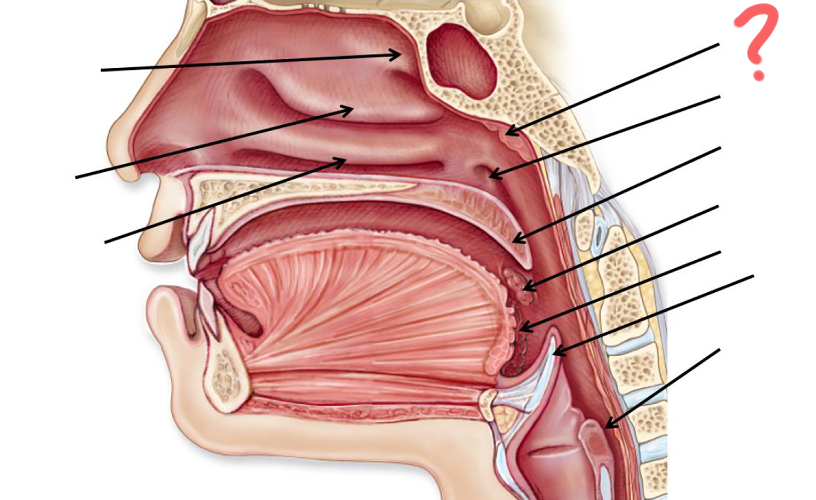
Pharyngeal tonsil
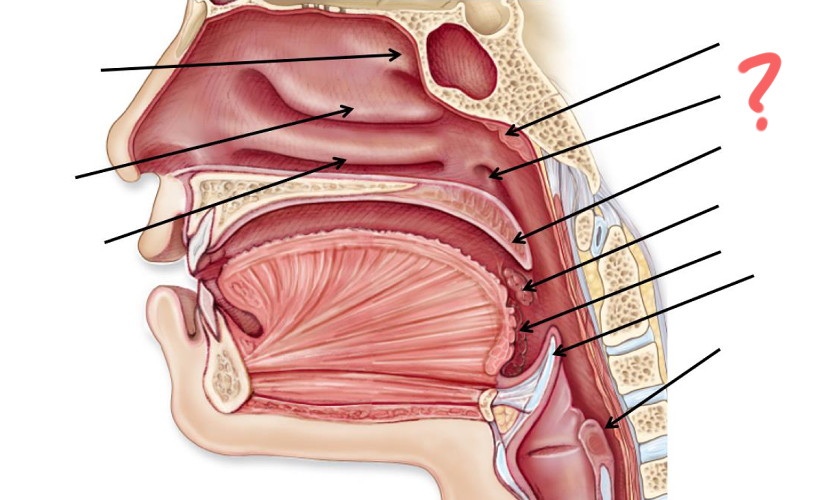
Opening of auditory tube
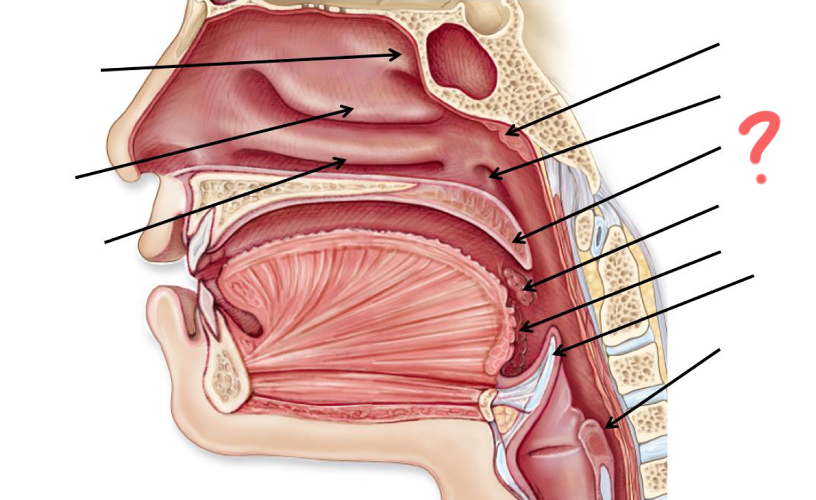
Uvula
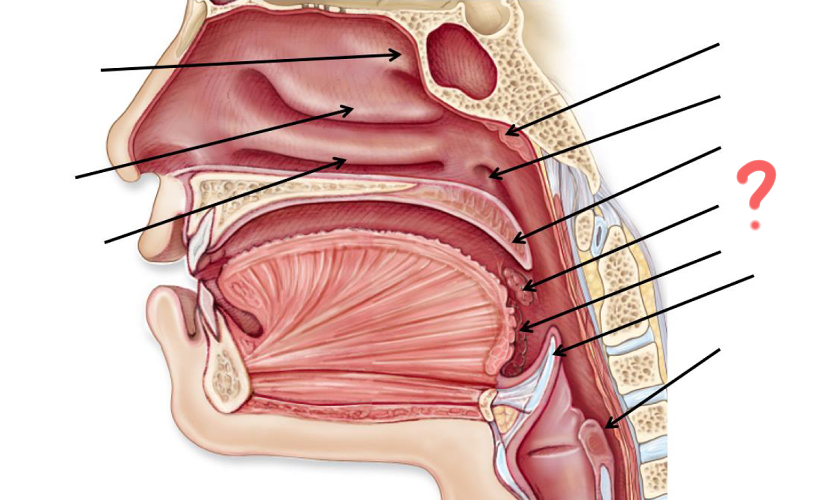
Palatine tonsil
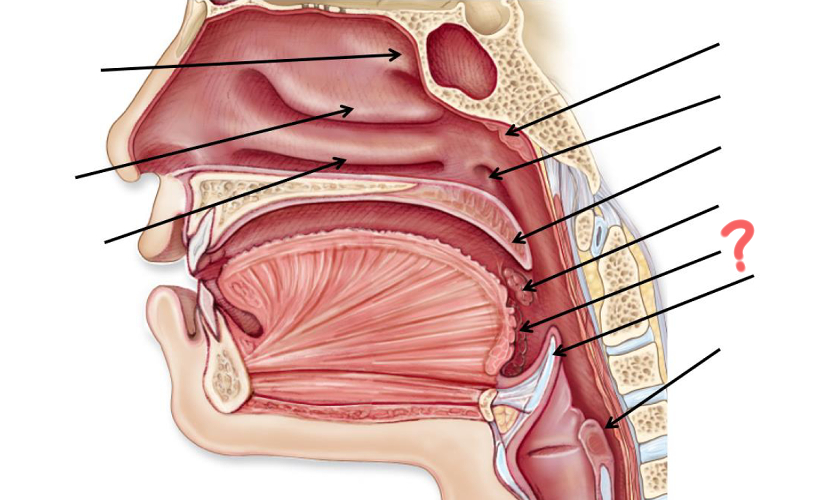
Palatine tonsil
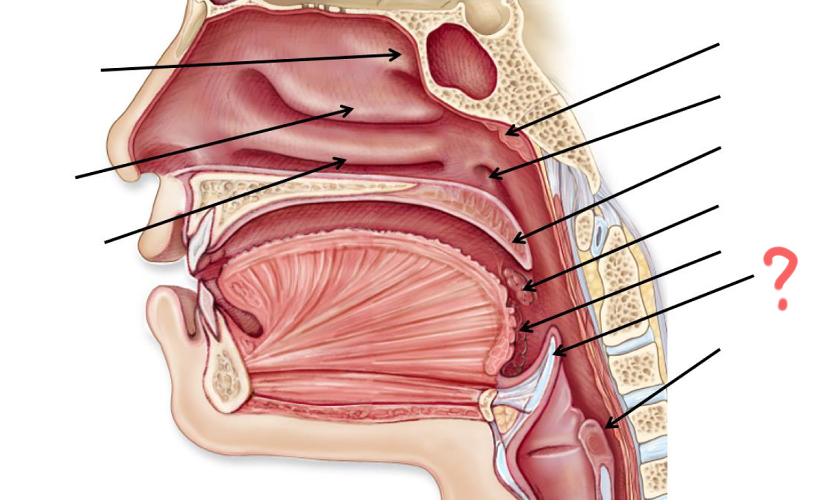
Epiglottis
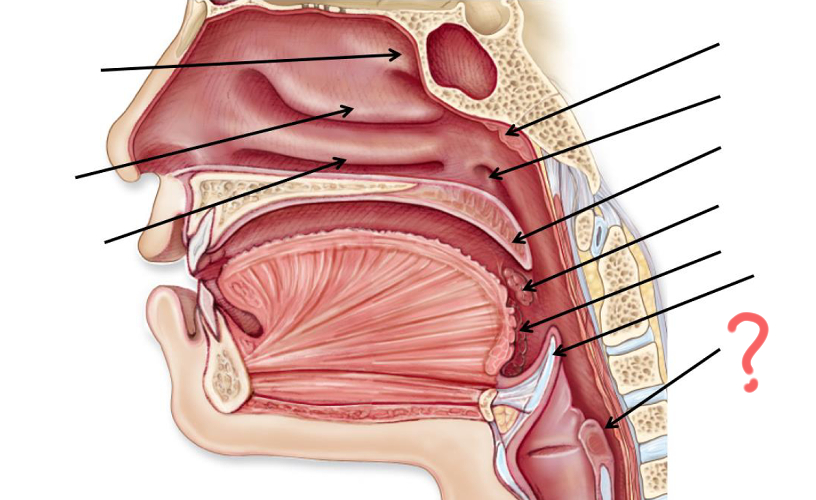
Esophagus
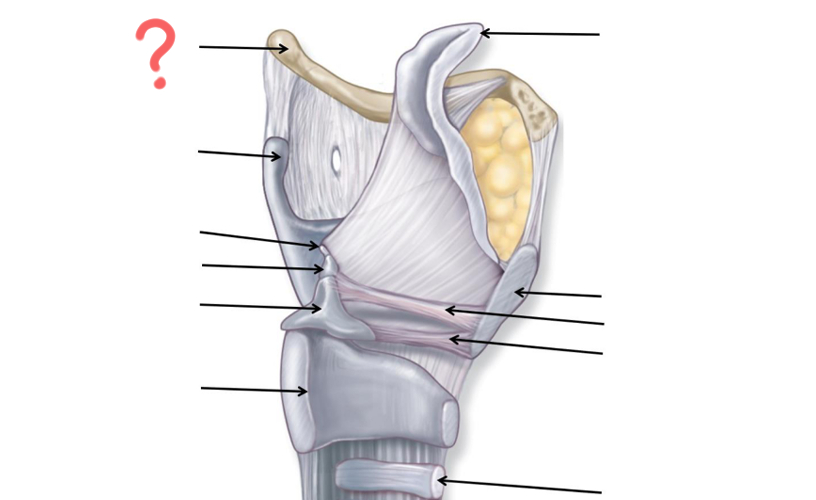
Hyoid Bone
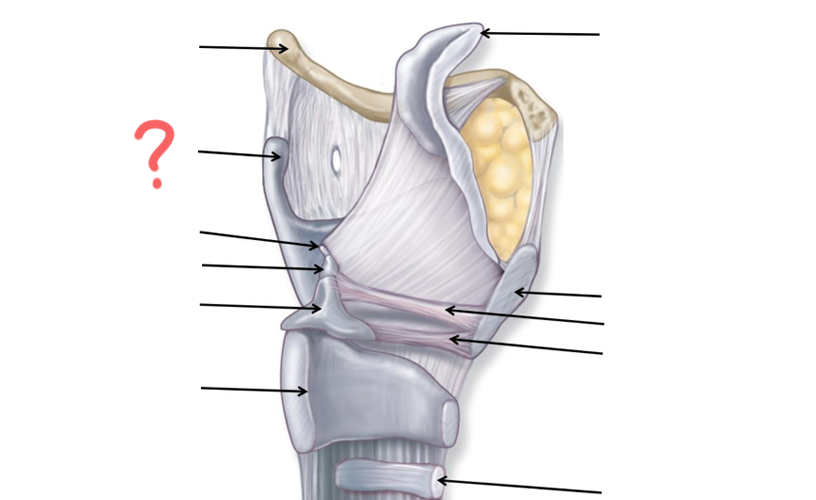
Thyroid Cartilage
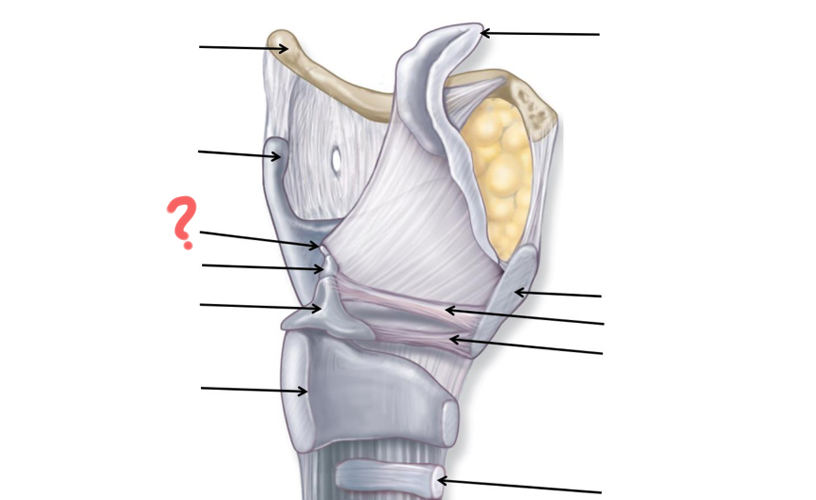
Cuneiform
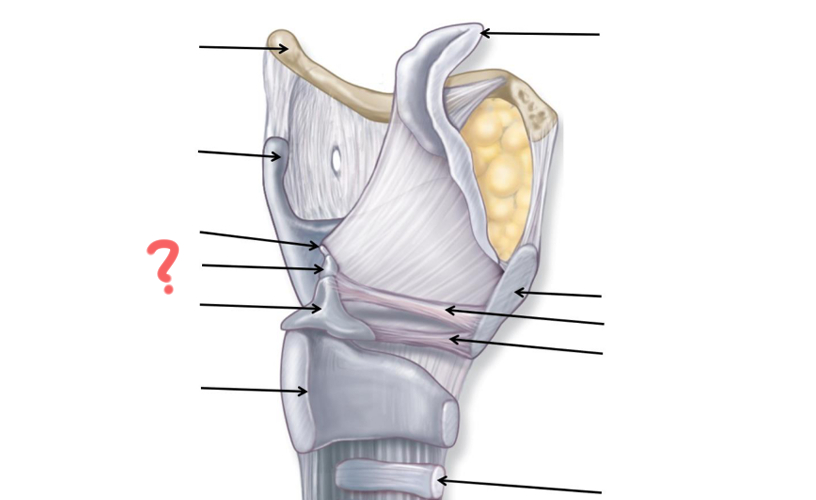
Corniculate
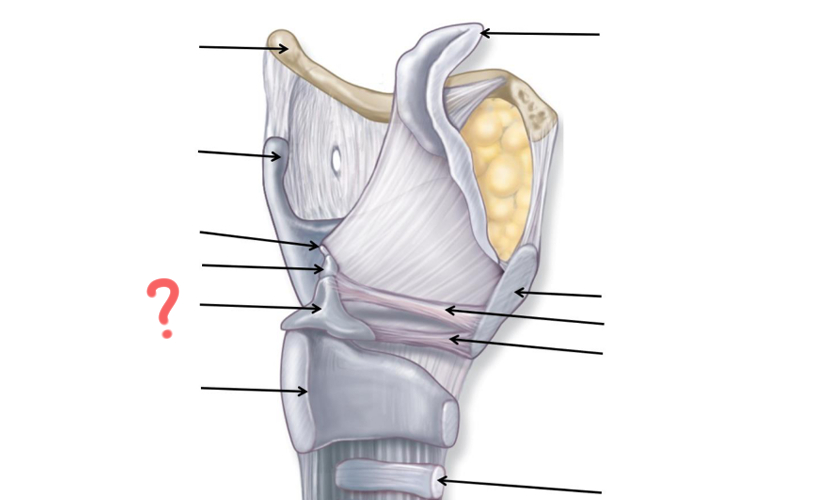
Arytenoid
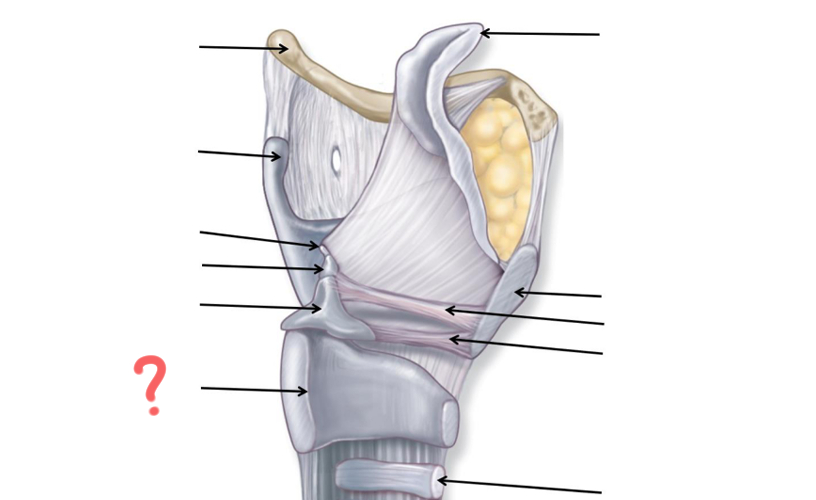
Cricoid
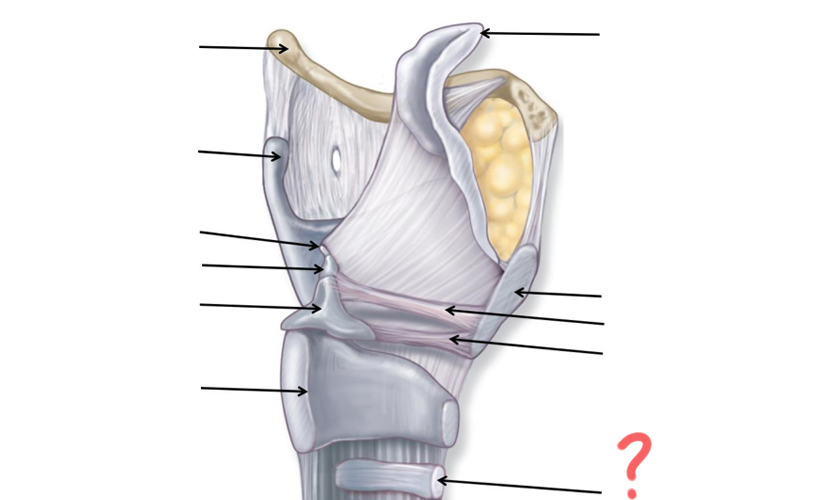
Tracheal Cartilage
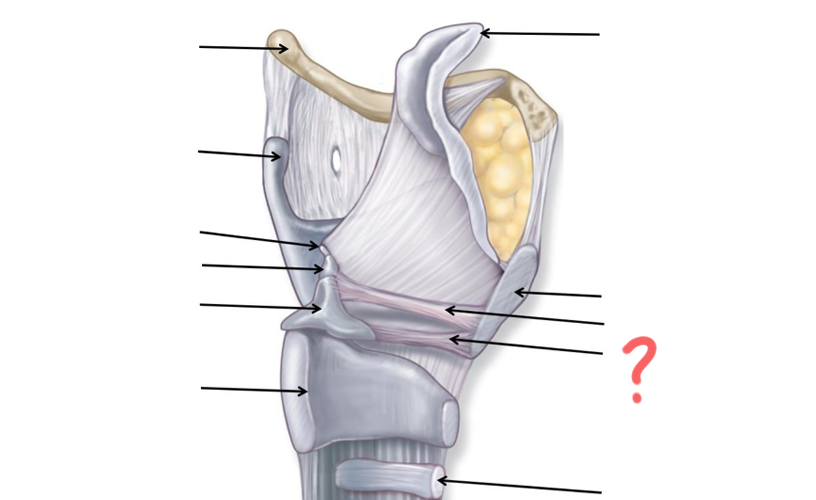
Vocal ligament
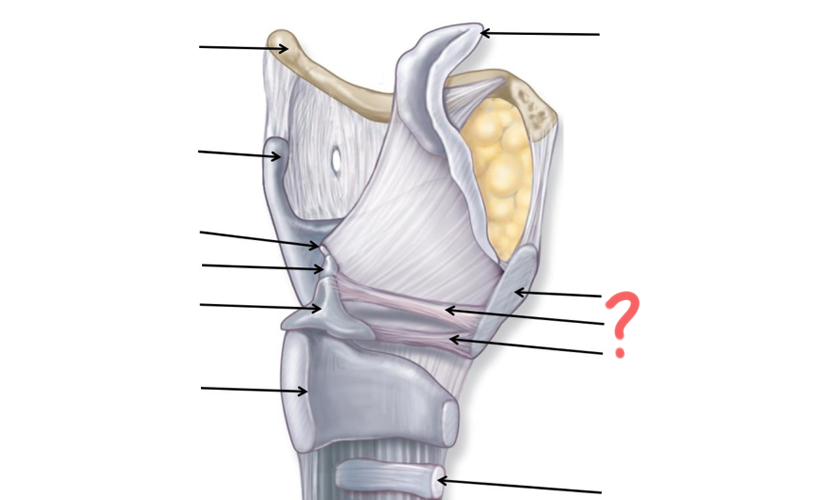
Vestibular ligament
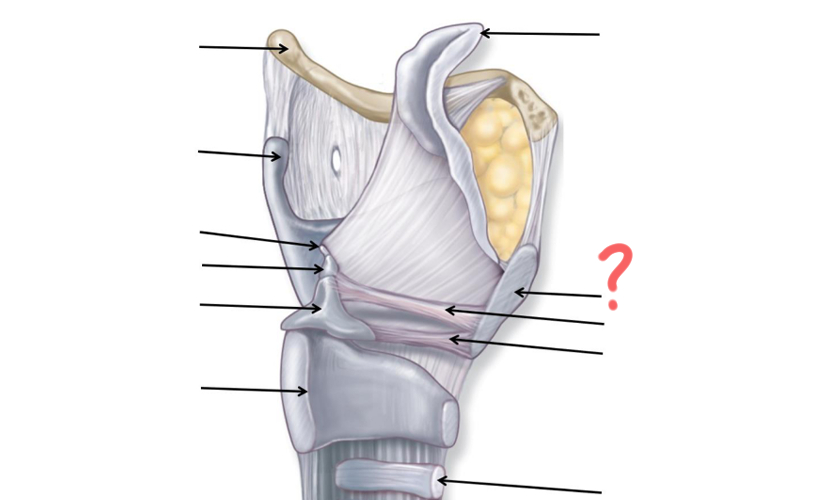
Thyroid cartilage again
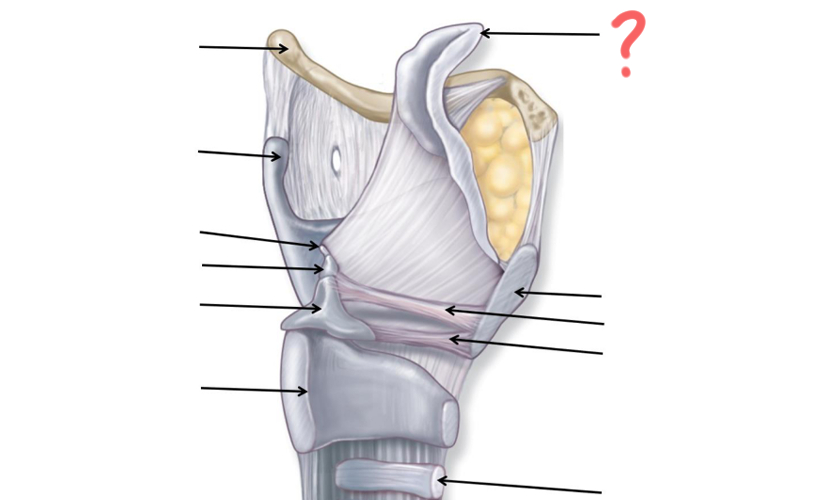
Epiglottis
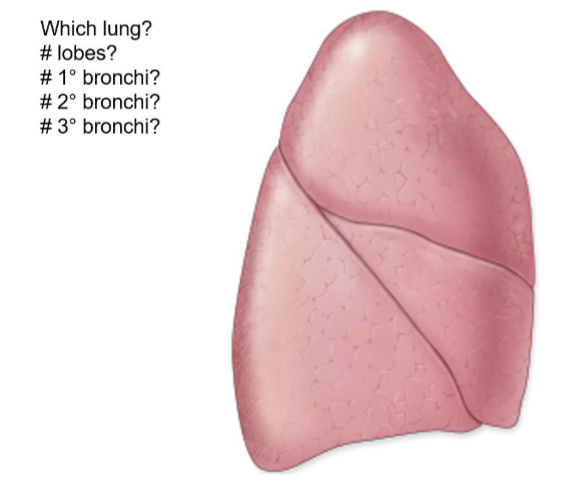
Right Lung
3 lobes
1
3
10
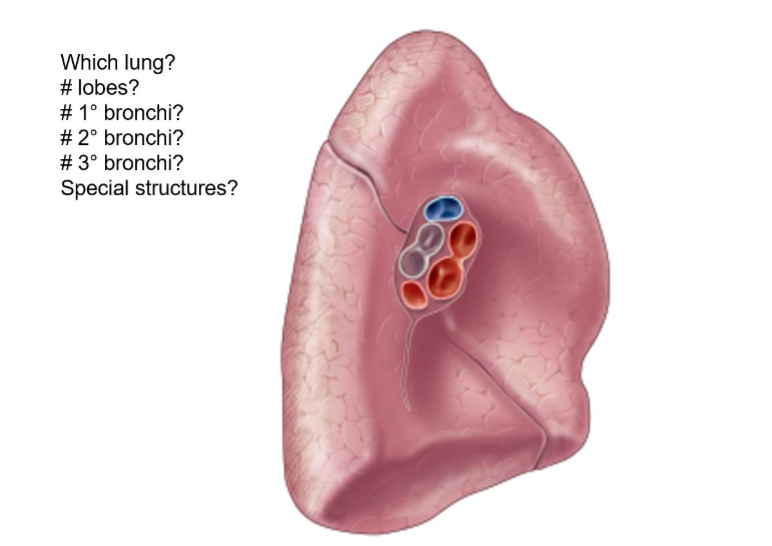
Left Lung
2 lobes
1
2
10-8
Cardiac notch/fissure
GI Tract (deepest)
epithelium type?
Mucosa
Simple columnar epithelium w/microvili (except esophagus)
Capillaries: Areolar CT (Lamina propia)
Muscularis mucosa :Thin layer of smooth muscle
GI Tract (2nd Deepest, 3rd superficial)
Submucosa
Larger blood & lymph vessels
submucosal nerve plexus
GI Tract (2nd layer)
Muscularis
2 layers smooth muscle
Inner circular (circumference)
Outer longitudinal (lengthwise)
Myenteric nerve plexus
GI (Superficial)
Serosa/Adventitia
Areolar CT, collagen
Oral Cavity
a. function
b. tissue type?
Ingestion
Digestion (Mechanical and chemical)
Tongue, teeth, saliva
Stratified squamous epithelium (non-keratinized)
Salivary glands
function
names of glands
Moisten food into bolus, digestion of starch
Parotid – largest
Submandibular – secretes the most saliva (65%)
Sublingual- small, multiple ducts
Pharynx
tissue type
uvula function during deglutition
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Uvula seals off nasopharynx during swallowing
Esophagus
a. function
b. tissue type
c. *exception to histology layers
propulsion (involuntary)
Stratified squamous epithelium non-keratinized
Mized in skeletal muscle for strength to swallow
Stomach
a. function
b. *exception to histology layers
Bolus chemically and mechanically digested
3 instead of 2 muscularis layers
added oblique (diagonal) layer
Bolus becomes chyme (more liquid)
Small Intestine
Absorbs 90% f nutrients and water
simple columnar epithelium with microvilli
Segmented & peristalsis
Small intestine - duodenum
5% of length
Major duodenal papilla: bile and pancreatic juice mixer
Jejunum
most digestion & absorption occurs here
35% of length
Ileum
connects to cecum
60% of length
Small intestine - Surface area
circular folds: speed bumps
villi
microvilli: brush border
Large intestine
Function
*exception to histology layers
Absorption of water from reaming chyme to turn into feces
defecation
Teniae coli - reduced outer longitudinal layer of muscularis (segmentation)
Liver
a. functions
b. ducts
produce and secretes bile
emulsify fat
detoxifies
Left/right haptic duct converges to common hepatic duct
Gallbladder
a. functions
b. ducts
Inferior surface of liver
stores, concentrates, and release bile that liver produces
Cystic duct
Pancreas
a. functions
b. ducts
Endocrine: insulin and glucagon
Exocrine: pancreatic juice
Mucin, digestive enzymes & bicarbonate (neutralizes acidic chyme from stomach)
Main pancreatic duct merges with common bile duct towards major duodenal papilla
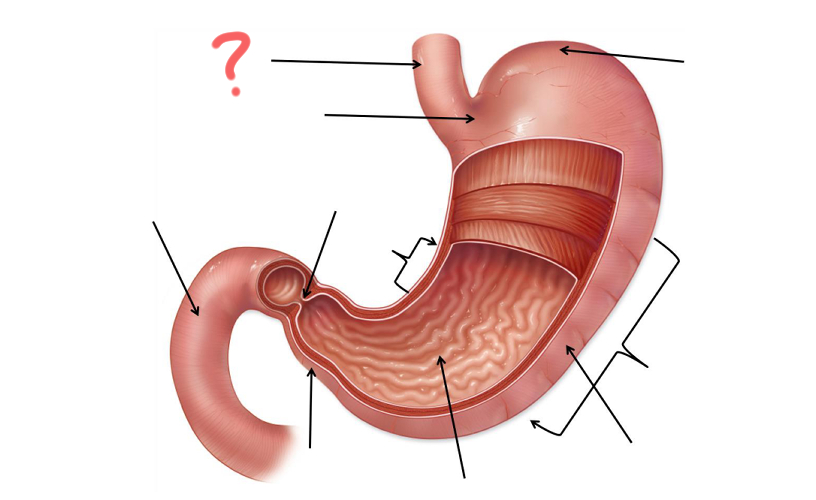
Esophagus
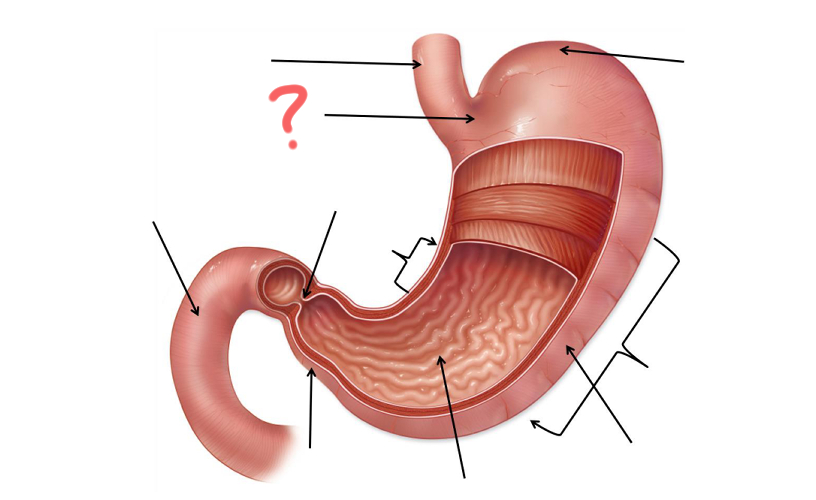
Cardia
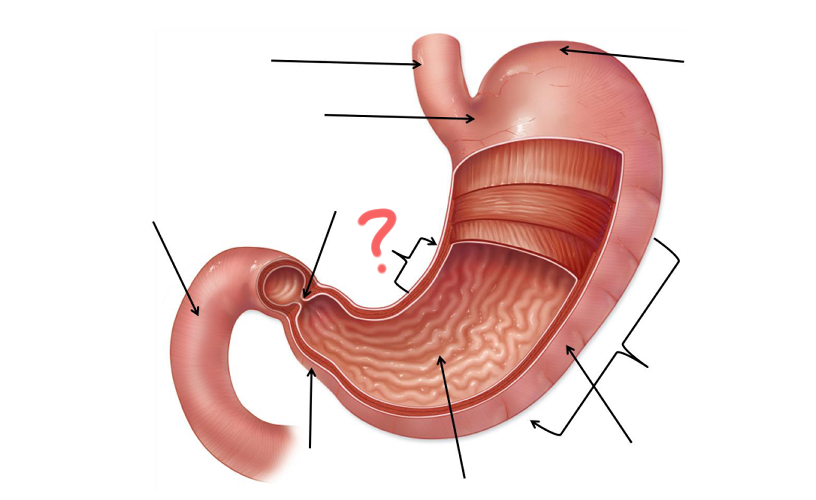
Less Curvature
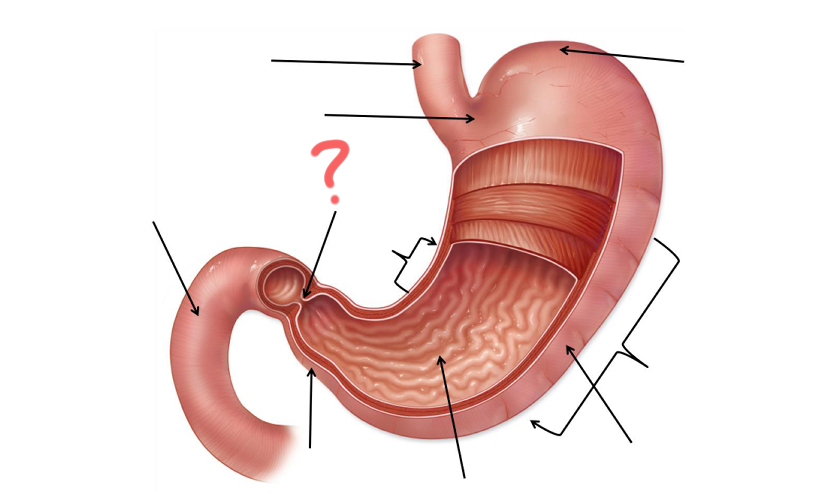
Pyloric Sphincter
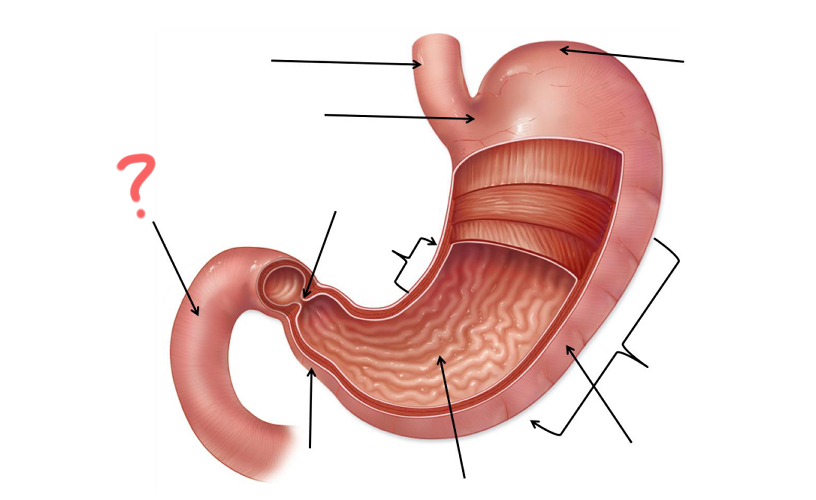
Duodenum
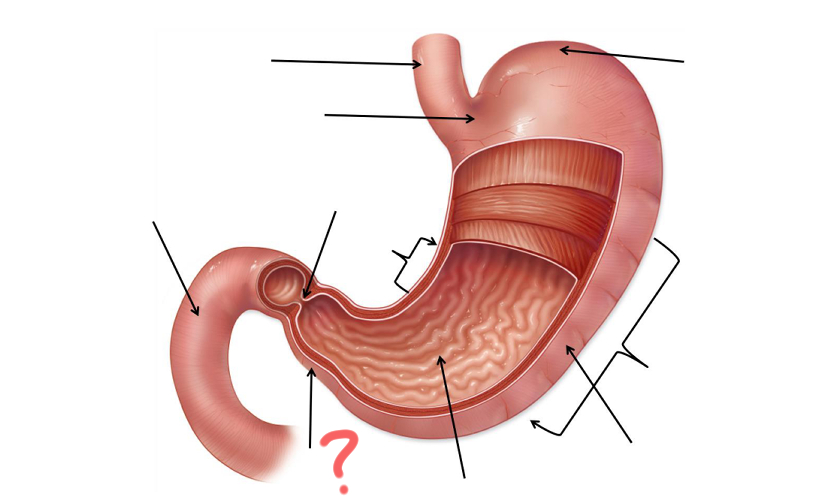
Pylorus
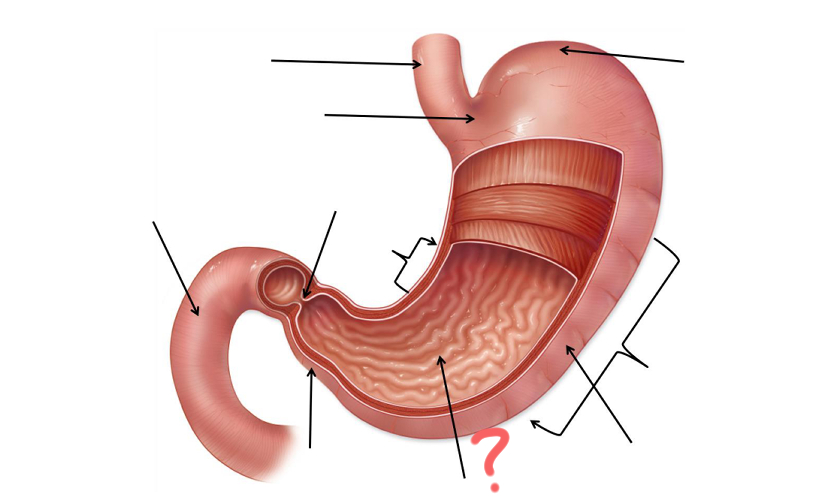
Gastric Folds
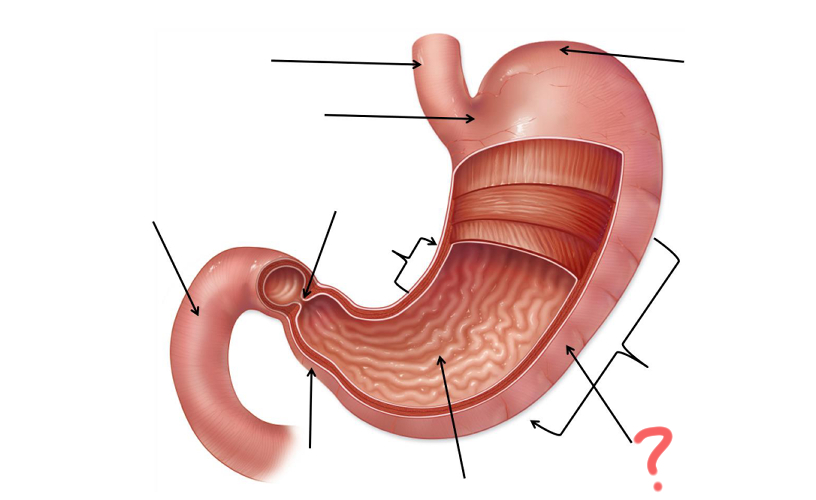
Body
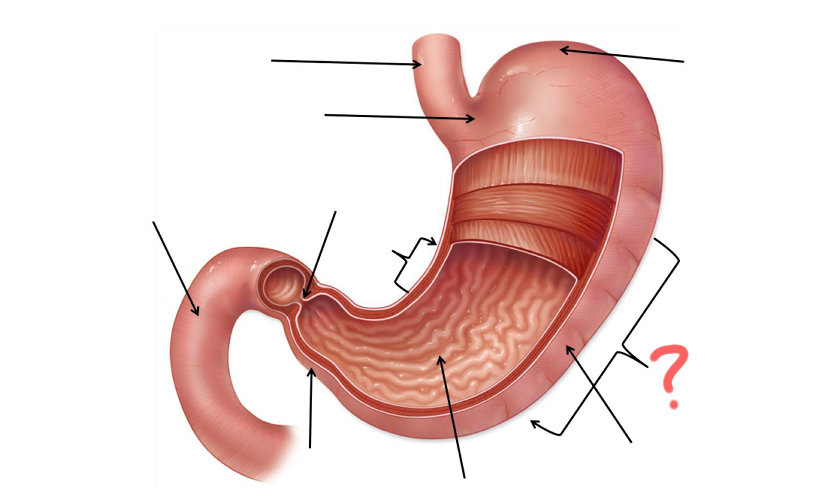
Greater curvature
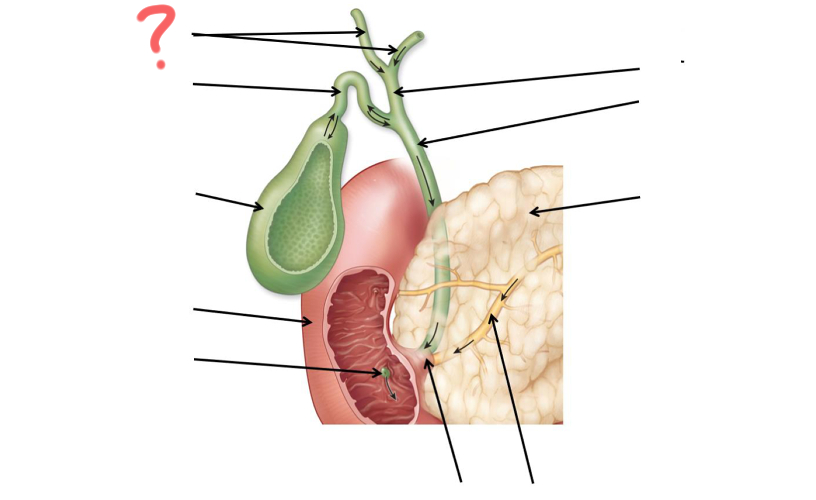
Left and right hepatic duct
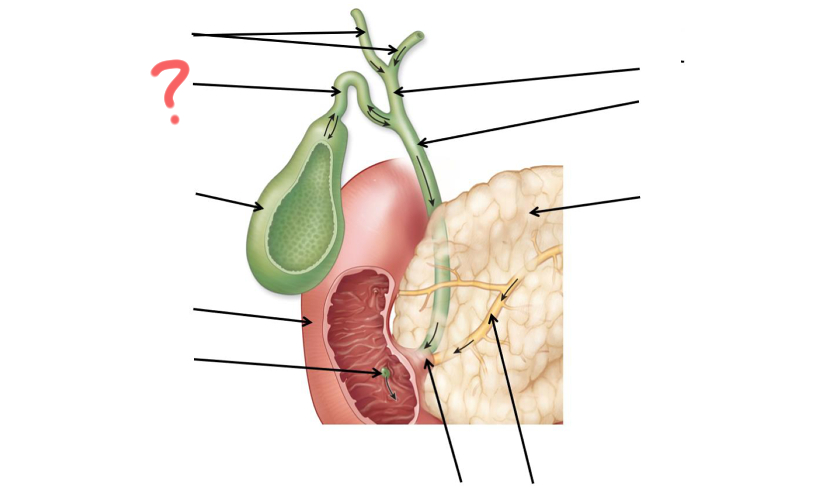
Cystic duct
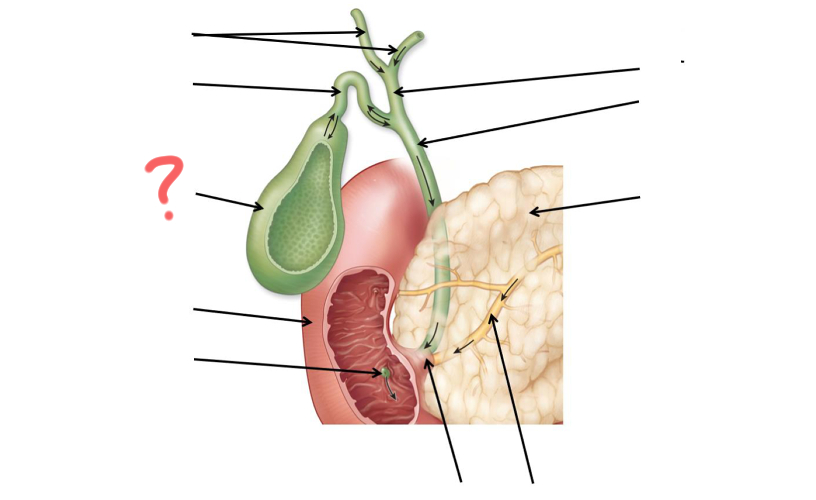
Gallbladder
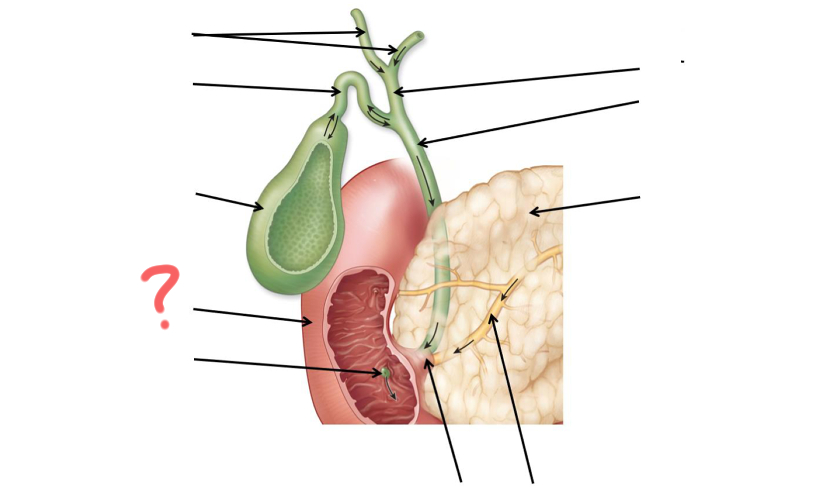
Duodenum
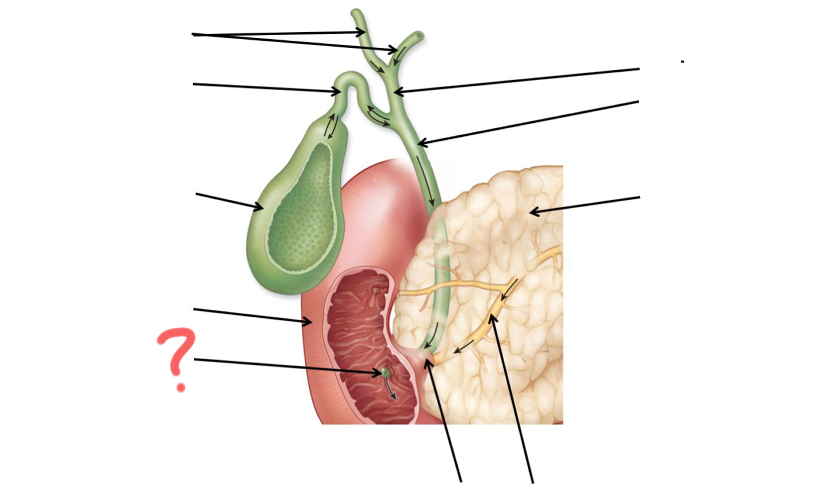
Major duodenal papilla
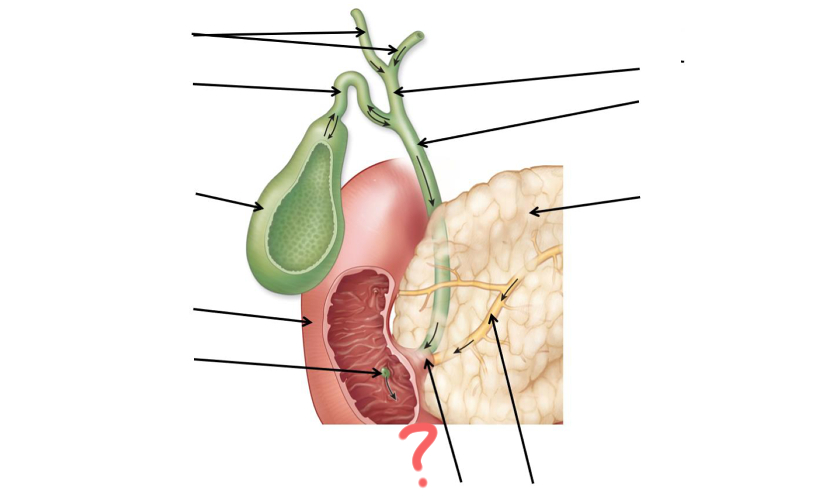
Main pancreatic duct merges with common bile duct
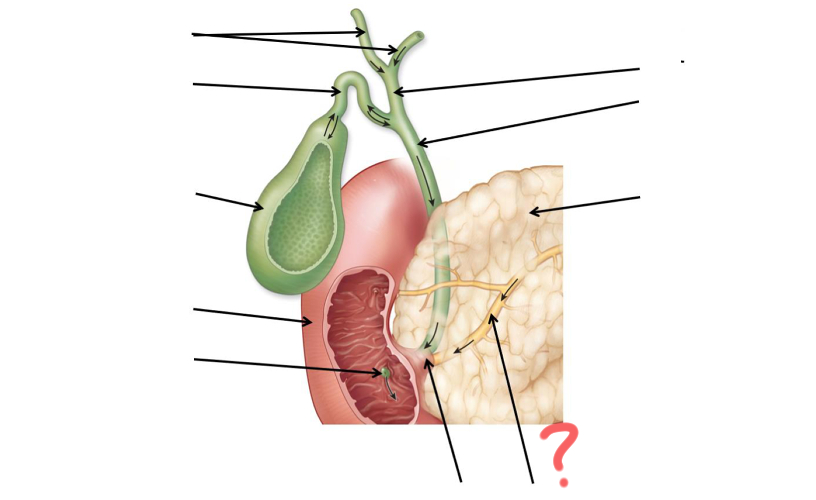
Main pancreatic duct

Pancreas
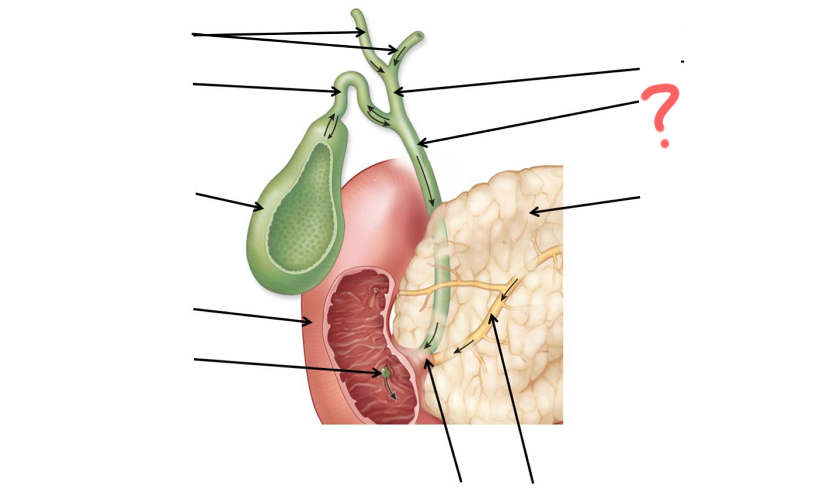
Common bile duct
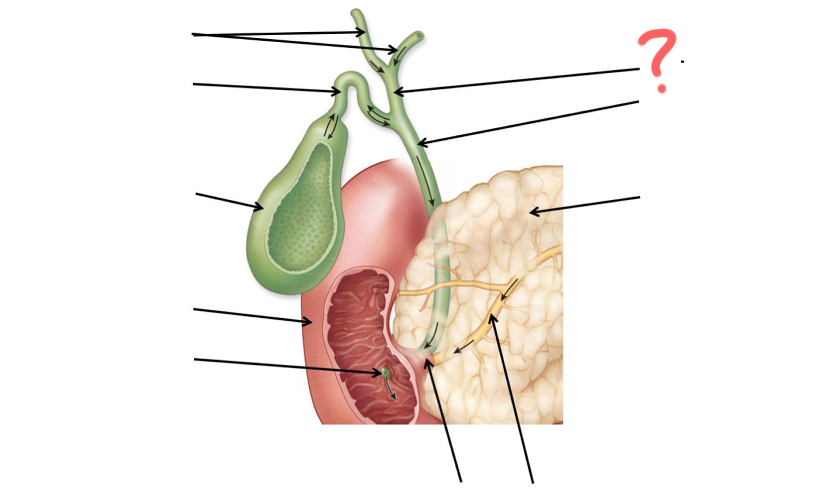
Hepatic duct