Stopping distances: Forces: Physics: GCSE (9:1)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Stopping distance
The sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance
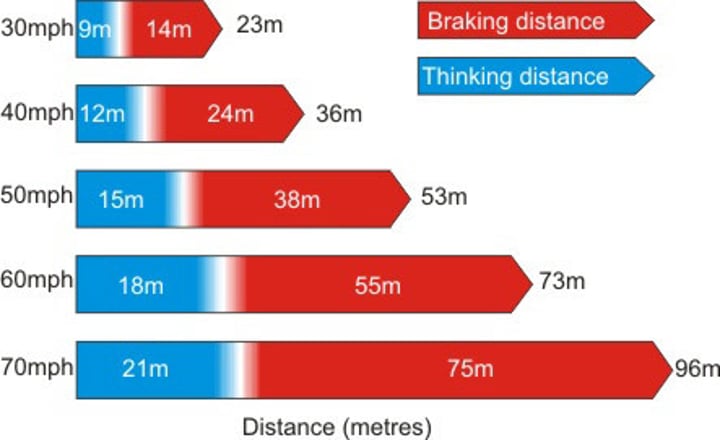
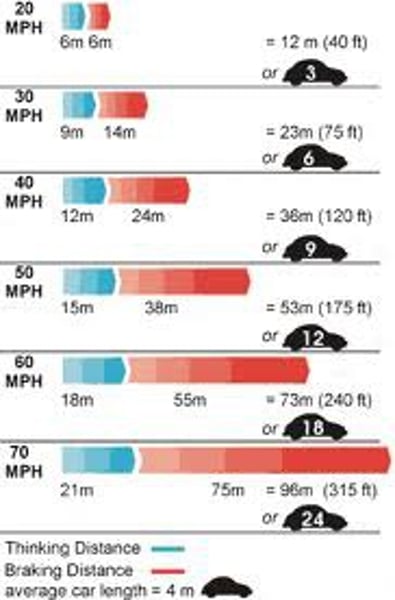
Thinking distance
The distance a vehicle travels during the driver’s reaction time
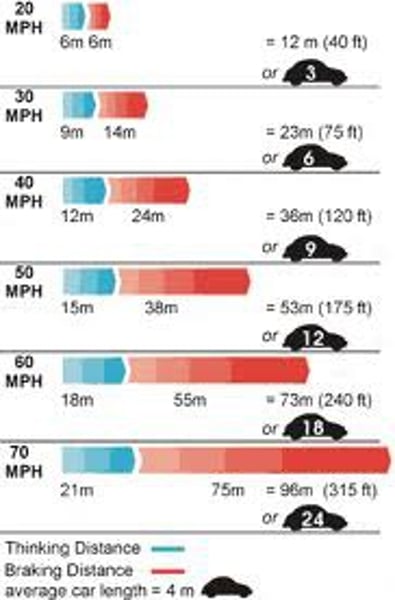
Braking distance
The distance a vehicle travels under the braking force
Reaction time
The time it takes for a person to respond to a specific stimulus
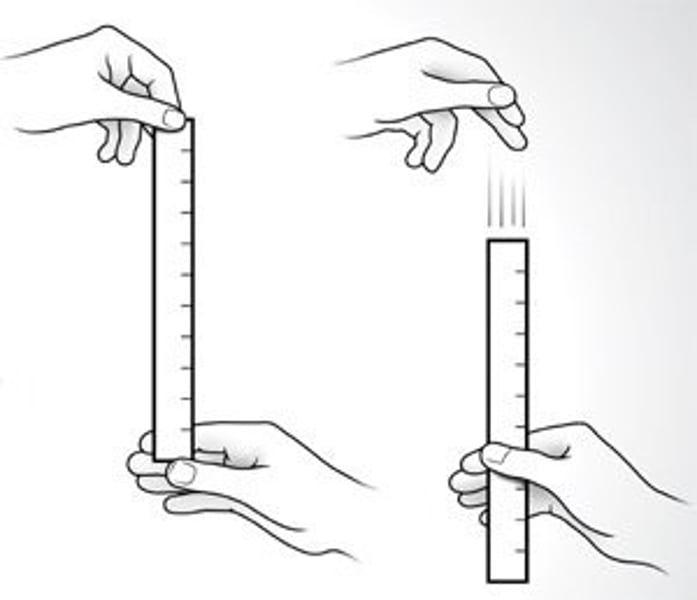
Typical reaction time
Typical values range from 0.2 s to 0.9 s
Factors affecting reaction time
Tiredness, drugs, alcohol, distractions

Effect of increased reaction time on thinking distance
Longer reaction times increase the thinking distance required
Effect of increased reaction time on braking distance
Longer reaction times have no effect on the thinking distance required
Factors affecting braking distance
Adverse road and weather conditions (wet or icy) and poor vehicle conditions (worn brakes or tyres)

How braking reduces speed
Work done is by the friction force between the brakes and the wheel to reduce the kinetic energy (and therefore speed) of the vehicle

Effect of work being done when braking
The temperature of the brakes increases
Relationship between speed and braking force
The greater the speed of a vehicle the greater the braking force needed to stop the vehicle in a certain distance
Relationship between braking force and deceleration
The greater the braking force the greater the deceleration of the vehicle
Effect of large decelerations
May lead to brakes overheating and/or loss of control of the vehicle
Relationship between thinking distance and speed
Thinking distance is proportional to speed because reaction time is taken as a constant
Relationship between braking distance and speed
Braking distance is proportional to speed squared because it depends on the kinetic energy of the vehicle