AS AQA Biology Topic 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:03 PM on 11/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
Magnification
the number of times bigger the image/drawing is compared to the object/real size
2
New cards
Resolution
the minimum distance needed to differentiate between 2 adjacent objects
3
New cards
Electron microscope
Beams of electrons are used to visualize structures in a vacuum. Electrons have a smaller wavelength than light so electron microscopes have a higher resolution than light microscopes.

4
New cards
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
A type of electron microscope which bounces beams of electrons off the surface of an object to develop a 3D image of the specimen (no need therefore for thin sections).
5
New cards
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
A type of electron microscope which asses a beam of electrons through a very thin section of specimen (which often has been stained with heavy metals to show up the fine internal structures).
6
New cards
Cell fractionation
The process where cells are broken up and the different organelles they contain are separated out.
7
New cards
Homogenation
The first stage of cell fractionation when cells are broken up by a homogeniser (blender) and organelles are released from the cell.
8
New cards
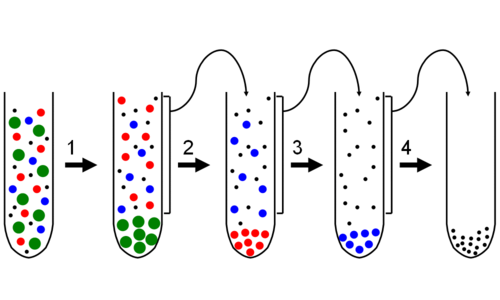
Ultracentrifugation
The second stage of cell fractionation when the fragments in filtered homogenate are separated in a machine called a centrifuge.
9
New cards
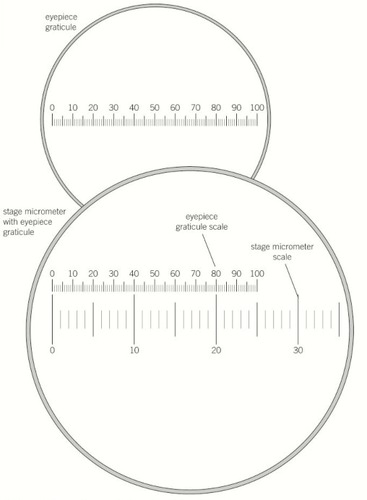
Graticule
A series of lines on a microscope which can be used to calculate the size of objects.
10
New cards
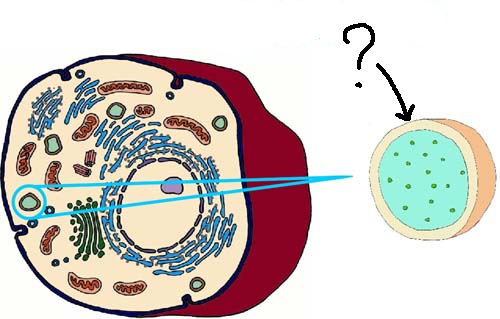
Organelle
A part of a cell.
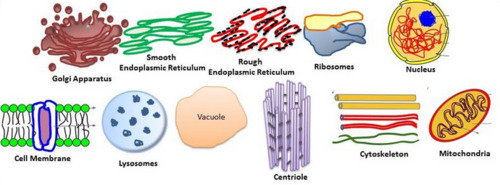
11
New cards
Nucleus
Organelle which contains the hereditary material (DNA) which codes for she synthesis of proteins in cytoplasm.
12
New cards
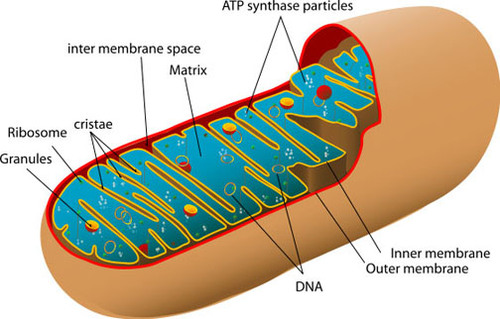
Mitochondria
Organelle where energy is released in aerobic respiration
13
New cards
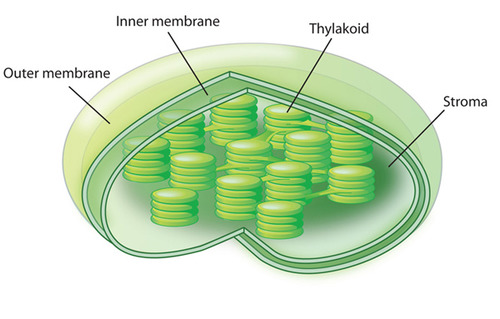
Chloroplast
Organelle that is the site of photosynthesis
14
New cards
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Organelle which provides a large surface area for the synthesis of proteins and glycoproteins and where proteins are transported that are synthesised on ribosomes.
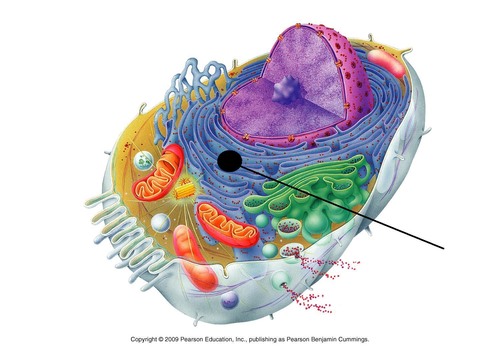
15
New cards
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Organelle where lipids and carbohydrates are synthesized, stored and transported.
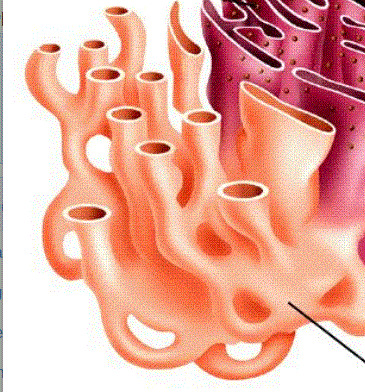
16
New cards
Golgi
Organelle that contains a stack of membranes that make up flattened sacs (cisternae) where glycoproteins are synthesized, lipids are transported, modified and stores, proteins are packaged and lysosomes are formed.
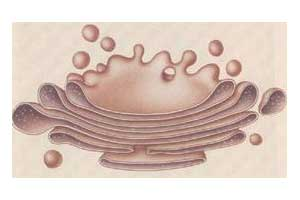
17
New cards
Lysosome
Organelle formed when the vesicles produced by the Golgi apparatus contain enzymes. They are where unwanted materials & worn-out organelles are digested.
18
New cards
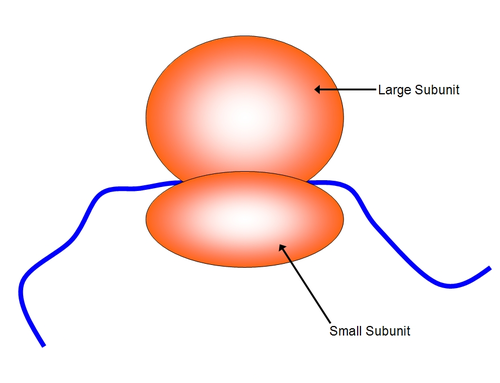
Ribosome
Organelle made of rRNA and protein where protein synthesis occurs.
19
New cards
Cell wall
Organelle which provides mechanical strength to prevent the cell bursting under the pressure created by the osmotic entry of water, to give mechanical strength. Made of cellulose in plants and chitin in fungi.
20
New cards
Vacuole
Organelle which contains a solution of mineral salts, sugars, amino acids, wastes and sometimes pigments such as anthocyanins. They support herbaceous plants by making cells turgid, may provide a temporary food store and if they contain pigments they may colour petals to attract pollinating insects.
21
New cards
Tissue
A collection of similar cells that perform a specific function.
22
New cards
Organ
A combination of different tissues that are coordinated to perform a variety of functions.
23
New cards
Organ system
Many organs work together in an organ system to perform a particular function
24
New cards
Prokaryote
A cell of an organism belonging to the kingdom Prokaryote that is characterized by lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. E.g. bacteria
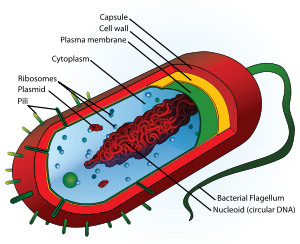
25
New cards
Bacteria
A prokaryote.
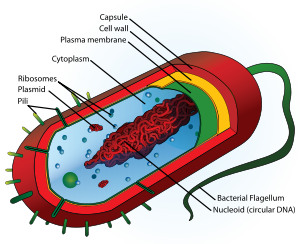
26
New cards
Plasmid
Small circular loops of DNA which contain genes that bacteria can have.
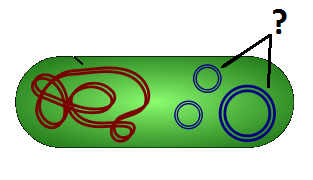
27
New cards
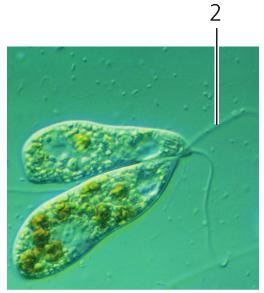
Flagellum
Part of a bacterial cell which helps the bacteria to move.
28
New cards
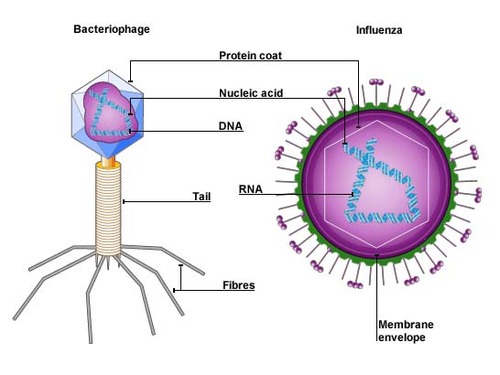
Virus
Acellular, non-living particles that are smaller than bacteria. They contain DNA or RNA but can only multiply inside living host cells.
29
New cards
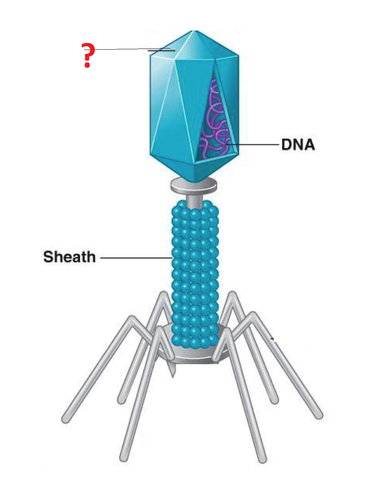
Capsid
A protein coat which encloses the nucleic acid in a virus.
30
New cards
Attachment protein
The capsid can have these which are essential to allow the virus to identify and attach to a host cell.
31
New cards
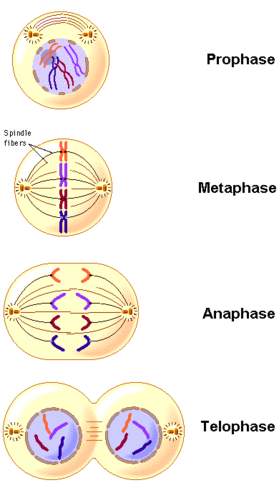
Mitosis
The type of nuclear division in which the daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
32
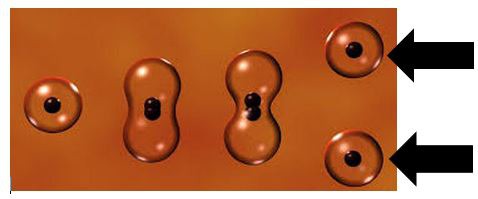
New cards
Daughter cell
The cells that are produced by cell division.
33
New cards
Chromatid
One of the two strands of a chromosome that are joined together by a single centromere prior to cell division.

34
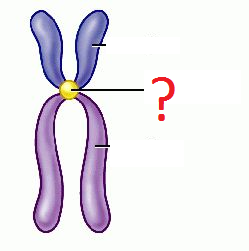
New cards
Centromere
The place where the two copies of DNA after replication are joined together.
35
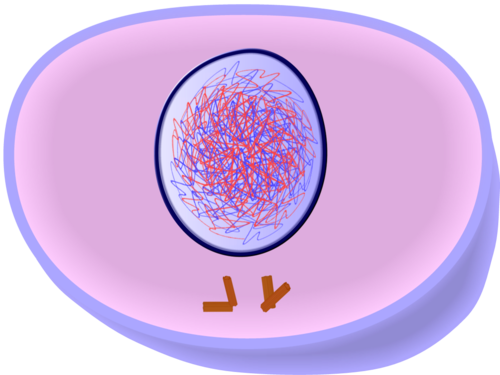
New cards
Interphase
The period of the cell cycle when the cell is not dividing.
36
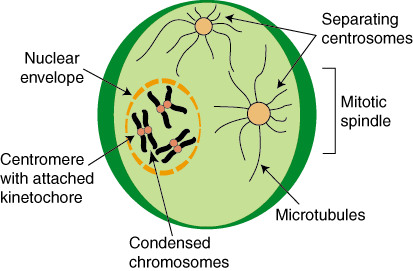
New cards
Prophase
The first stage of mitosis when the chromosomes become visible and when spindle fibres develop. The nucleolus disappears and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
37
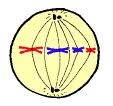
New cards
Metaphase
The second stage of mitosis when the chromosomes arrange themselves across the equator of the cell.
38
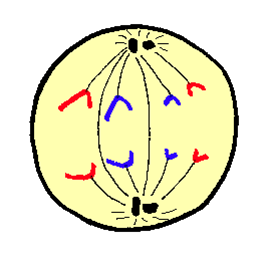
New cards
Anaphase
The third stage of mitosis when the centromeres divide into two and the spindle fibres pull the individual chromatids making up the chromosome apart to their respective, opposite poles of the cell.
39
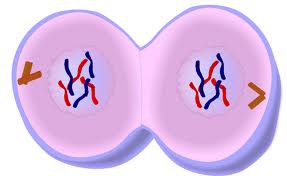
New cards
Telophase
The fourth stage of mitosis when chromosomes reach their respective poles and become longer and thinner, finally disappearing altogether, leaving only widely spread chromatin. The spindle fibres disintegrate and the nuclear envelope and nucleolus re-form.
40
New cards
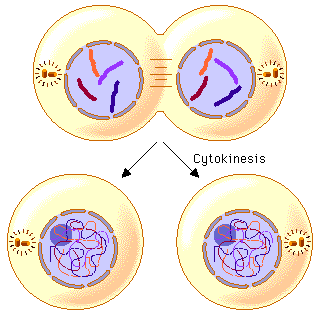
Cytokinesis
When the cytoplasm divides.
41
New cards
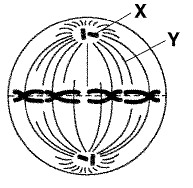
Spindle fibres
These form the spindle apparatus which are responsible for pulling the chromatids to separate ends of the cell.
42
New cards
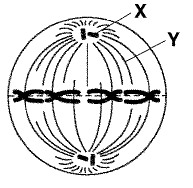
Centrioles
Where the spindle fibres develop from in animal cells.
43
New cards
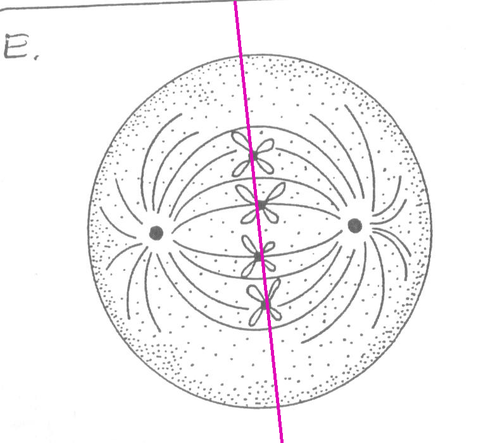
Equator
Where the chromosomes arrange themselves during metaphase.
44
New cards
Binary fission
The process by which cell division occurs in prokaryotic cells.
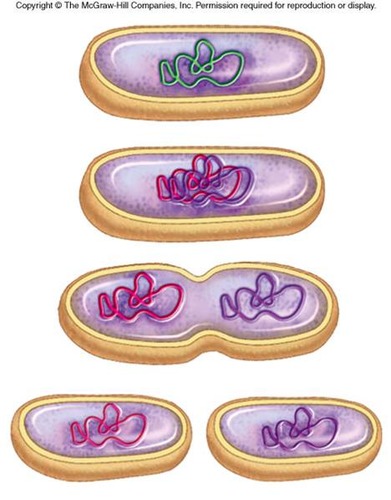
45
New cards
Cancer
A group of diseases caused by a growth disorder of cells as a result of damage to the genes that regulate mitosis and the cell cycle which results in uncontrolled growth and division of cells.
46
New cards
Tumour
A group of abnormal cells which develops and constantly expands in size.
47
New cards
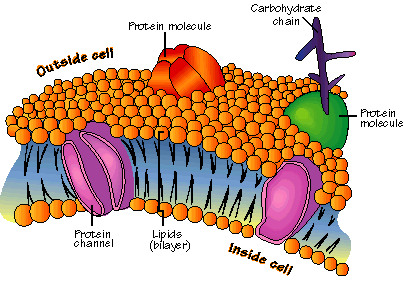
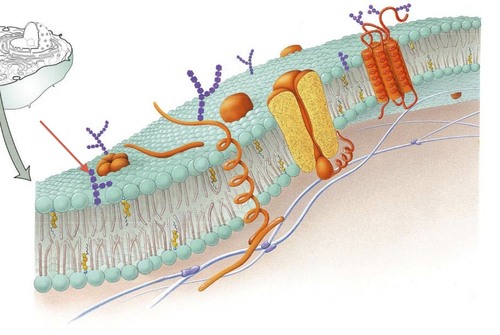
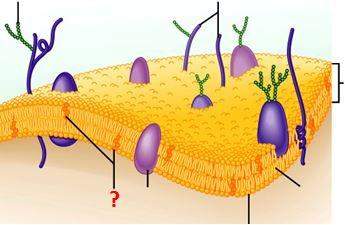
Plasma membrane
Membranes consisting of a phospholipid bilayer found around and within all cells. The cell-surface membrane is the plasma membrane that surrounds cells.
48
New cards
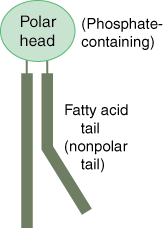
Phospholipid
Triglyceride in which one of the three fatty acid molecules is replaced by a phosphate molecule. Phospholipids are important in the structure an functioning of plasma membranes.
49
New cards
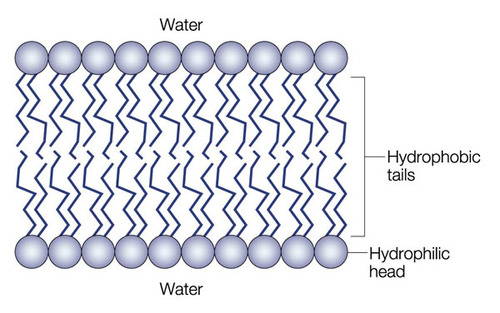
Bilayer
A membrane consisting of two layers of phospholipids.
50
New cards
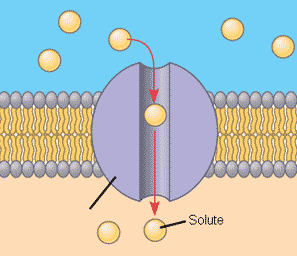
Protein channel
A protein completely spanning the phospholipid bilayer which form water-filled tubes to allow water-soluble ions to diffuse across the membrane.
51
New cards
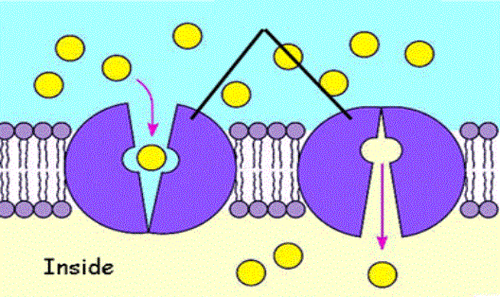
Carrier protein
A protein completely spanning the phospholipid bilayer which bind to ions or molecules then change shape in order to move these molecules across the membrane.
52
New cards
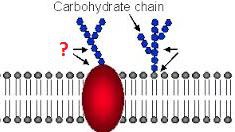
Glycoprotein
Carbohydrate chains attached to a protein (often extrinsic) which are part of the cell surface membrane. They act as recognition sites, help cells to attach to one another and allows cells to recognise one another.
53
New cards
Glycolipid
A carbohydrate covalently bonded with a lipid. They act as recognition sites, help maintain stability of the membrane and help cells attach to one another.
54
New cards
Cholesterol
Lipid that is an important component of cell-surface membranes because it adds strength. Excess in the blood can lead to atheroma.
55
New cards
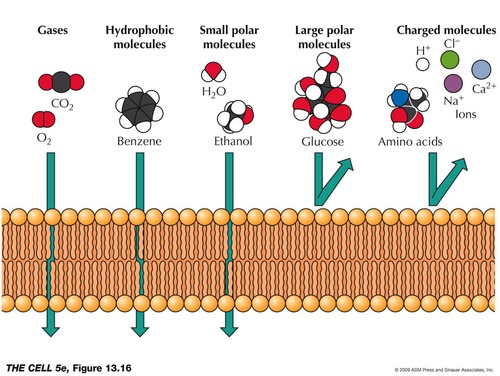
Permeability
How permeable a substance is depends on the size, polarity and charge of the molecule. If it is small, non-polar and fat soluble it is very permeable and can pass through the cell membrane.
56
New cards
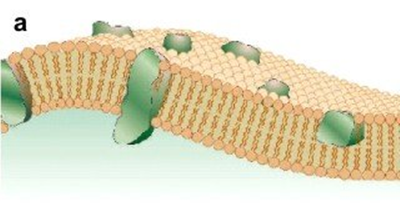
Fluid mosaic model
The arrangement of the various molecules of the cell-surface membrane. Fluid because the individual phospholipid molecules can move relative to one another and mosaic because the proteins vary in shape, size and pattern.
57
New cards
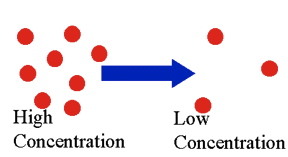
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of molecules (or ions) from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. It is passive.
58
New cards
Facilitated diffusion
Diffusion involving the presence of protein carrier molecules to allow the passive movement of substances (normally large, polar or charged molecules) across plasma membrane.

59
New cards
Osmosis
The passage of water from a region where there is a higher water potential to a region where there is a lower water potential through a partially permeable membrane.
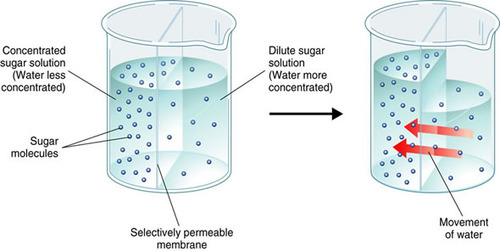
60
New cards
Water potential
The pressure created by water molecules. It is the measure of the extent to which a solution gives out water. The greater the number of water molecules present, the higher (less negative) the water potential. Pure water has a water potential of zero.
61
New cards
Isotonic
A solution which has the same water potential as the cell within it.
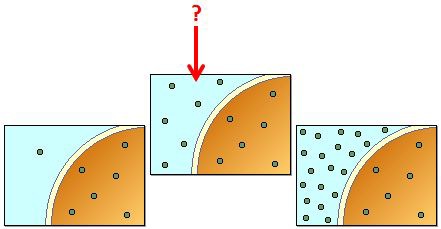
62
New cards
Active transport
Movement of a substance from a region where it is in a low concentration to a region where it is in a high concentration. The process requires the expenditure of metabolic energy in the form of ATP.
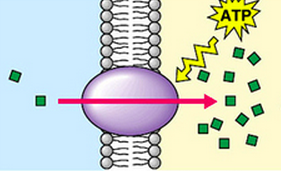
63
New cards
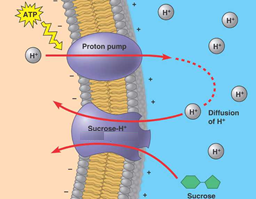
Co-transport
The transport of one substance coupled with the transport of another substance across a plasma membrane in the same direction through the same protein carrier.
64
New cards
Pathogen
A microorganism that causes disease
65
New cards
Self
The body's own cells and molecules.
66
New cards
Foreign (non-self)
Not your own body's cells and molecules.
67
New cards
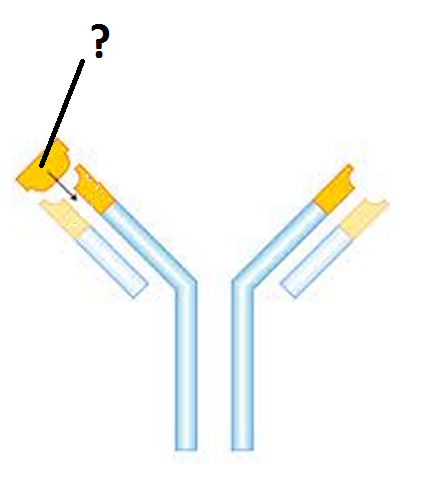
Antigen
A molecule that triggers an immune response by lymphocytes.
68
New cards
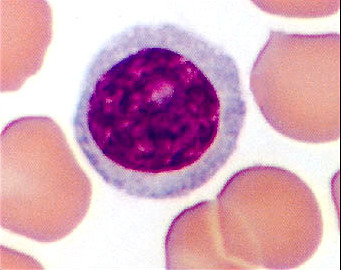
Lymphocyte
Type of white blood cell responsible for the immune response. They become activated in the presence of antigens. There are two types: B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes.
69
New cards
Phagocyte
Type of white blood cell which carries out a non-specific immune response and ingests and breaks down pathogens by phagocytosis.
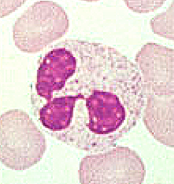
70
New cards
Phagocytosis
Mechanism by which phagocytes engulf particles to form a vesicle or a vacuole.
71
New cards
Lysosome
Contain enzymes called lysozymes which they release into the phagosome which hydrolyse the bacterium.
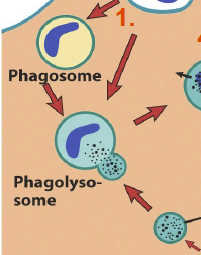
72
New cards
Phagosome
A vesicle formed as the bacterium is engulfed by the phagocyte. The lysosome release their lysozymes into the phagosome.
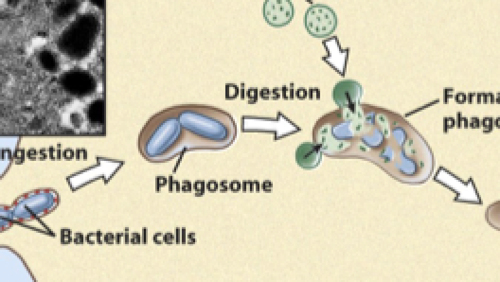
73
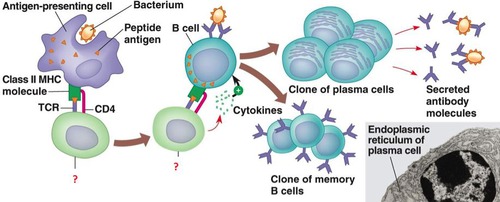
New cards
Antigen-presentation
When an antigen-presenting cell e.g. phagocyte displays foreign antigens on their own cell-surface membrane.
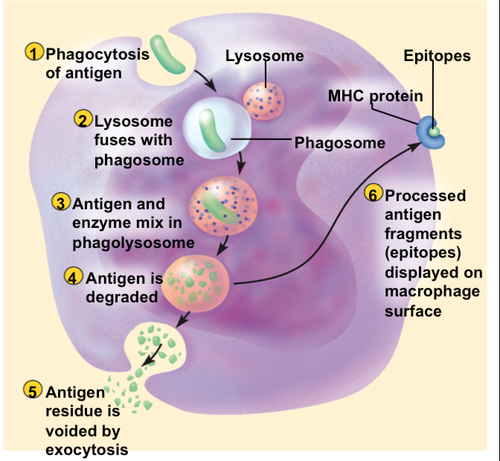
74
New cards
Cell-mediated immunity
The type of response when T lymphocytes respond to antigens that are presented on a body cell.
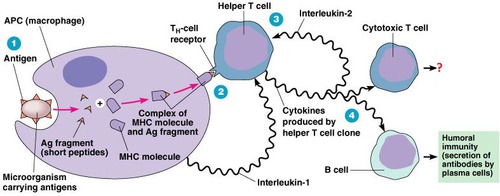
75
New cards
T cells
Cells which mature in the thymus and are associated with cell-mediated immunity.
76
New cards
Clonal selection
As the receptor on a helper T cell attaches to the antigen this activates the T cell to divide rapidly by mitosis and form a clone of genetically identical cells. These cloned T cells stimulate B cells to divide and form a clone of identical B cells all of which produce the antibody that is specific to the foreign antigen.
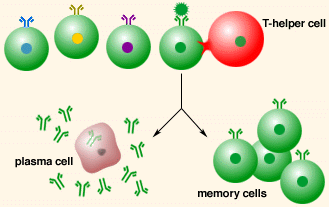
77
New cards
TH cells (helper T cell)
Contain receptors which respond to a single antigen. Many different types of T cell, each one responds to a different antigen.
78
New cards
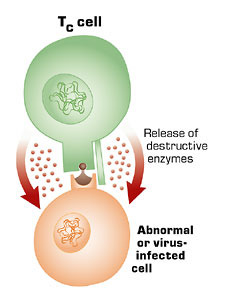
TC cells (cytotoxic T cells)
Kill abnormal cells and body cells that are infected by pathogens by producing a protein called perforin which makes holes in the cell-surface membrane.
79
New cards
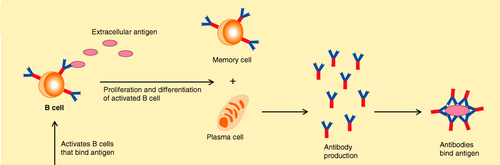
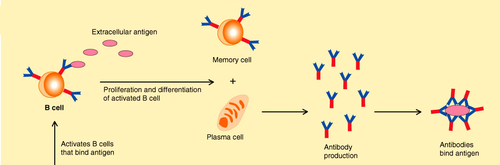
Humoral immunity
The type of response which involves B lymphocytes and antibodies.
80
New cards
B cells
Each type of B cell produces a specific antibody that responds to one specific antigen.
81
New cards
Plasma B cells
When the B cell is activated to divide by mitosis it gives a clone of plasma cells which produce and secrete the specific antibody that exactly fits the antigen on the pathogen's surface.
82
New cards
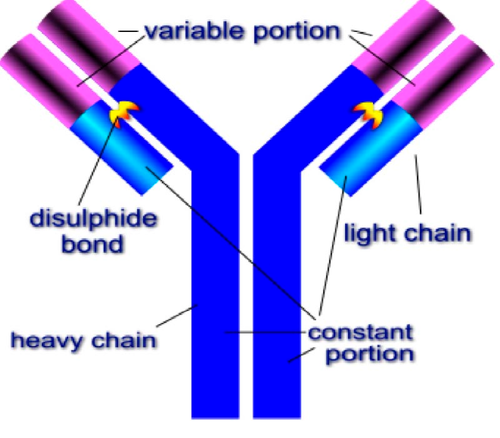
Antibody
A protein with specific binding sites produced by B cells in response to the presence of appropriate antigen.
83
New cards
Memory B cells
Some B cells develop into memory cells which can respond to future infections by the same pathogen by dividing rapidly and developing into plasma cells that produce antibodies as part of the secondary response.
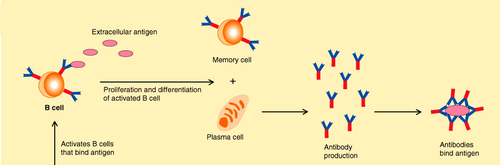
84
New cards
Monoclonal antibodies
Antibodies produced by a single clone of cells.
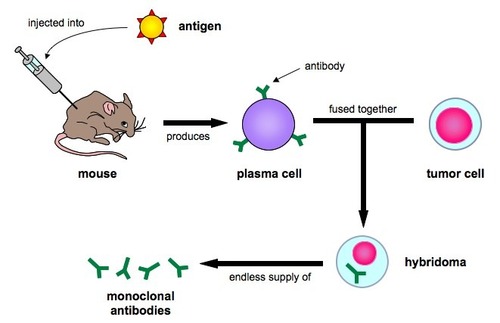
85
New cards
Primary response
Caused by initial response to the antigen which involves the production of antibodies and memory cells.
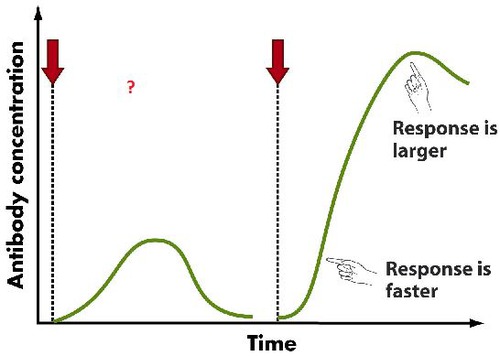
86
New cards
Secondary response
Caused by second exposure to the antigen. Memory cells are responsible for this response - they divide rapidly and develop into plasma cells (which secrete many antibodies quickly) and more memory cells.
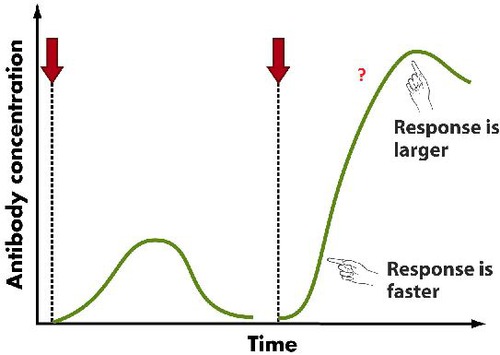
87
New cards
Passive immunity
Resistance to disease that is acquired from the introduction of antibodies from another individual, rather than an individual's own immune system e.g. across the placenta or in the mother's milk. It is usually short lived.
88
New cards
Active immunity
Resistance to disease resulting from the activities of an individual's own immune system whereby an antigen induces plasma cells to produce antibodies.

89
New cards
Natural immunity
A type of active immunity resulting from an individual becoming infected with a disease under normal circumstances.
90
New cards
Artificial immunity
A type of active immunity resulting from vaccination. It involves inducing an immune response in an individual without them suffering symptoms of the disease.
91
New cards
Vaccination
The introduction of a vaccine containing appropriate disease antigens into the body, by injection or mouth, in order to induce artificial immunity.
92
New cards
Herd immunity
Arises when a sufficiently large proportion of the population has been vaccinated which makes it difficult for a pathogen to spread within that population.
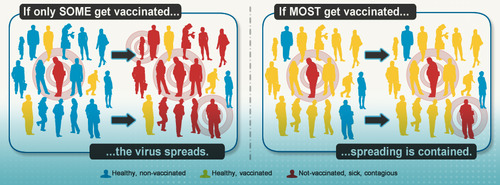
93
New cards
Antigenic variability
Pathogen may mutate frequently so that its antigens change suddenly rather than gradually which means vaccines become ineffective because the new antigens on the pathogen are no longer recognized by the immune system.
94
New cards
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus which causes the disease acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). It has a lipid envelope, attachment proteins, a capsid and two single strands or RNA and enzymes.
95
New cards
Reverse transcriptase
An enzyme in HIV which enables the production of DNA from RNA.
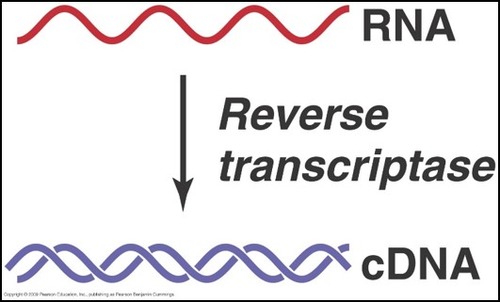
96
New cards
Retrovirus
A group of viruses which have the ability to make DNA from RNA because they have reverse transcriptase.
97
New cards
mRNA
A single stranded polynucleotide found in HIV.
98
New cards
AIDS
The disease caused by HIV.
99
New cards
ELISA
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay which uses antibodies to detect the presence and quantity of a protein in a sample.
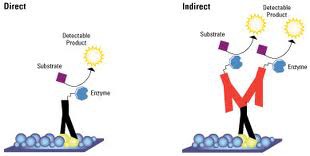
100
New cards
Antibiotic
A substance produced by living organisms that can destroy or inhibit the growth of microorganisms
