Sepsis & Septic Shock
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Sepsis: Prevalence and Vulnerable Populations
Each year in the U.S.:
1.7 million Americans develop sepsis
Roughly 350,000 die from sepsis
1 in 3 patients who die in the hospital has sepsis
The most vulnerable people are:
Older adults
Infants
Pregnant women
Those with chronic conditions
Immunocompromised patients

A form of distributive shock that is caused by a cascade of events:
Initiation of immune system
Inflammatory products activated
Vasodilation and blood vessel permeability (decreased SVR)
Impaired oxygen exchange
Trigged coagulation products
Developments of organ failure, ARDS, DIC
Sepsis is …
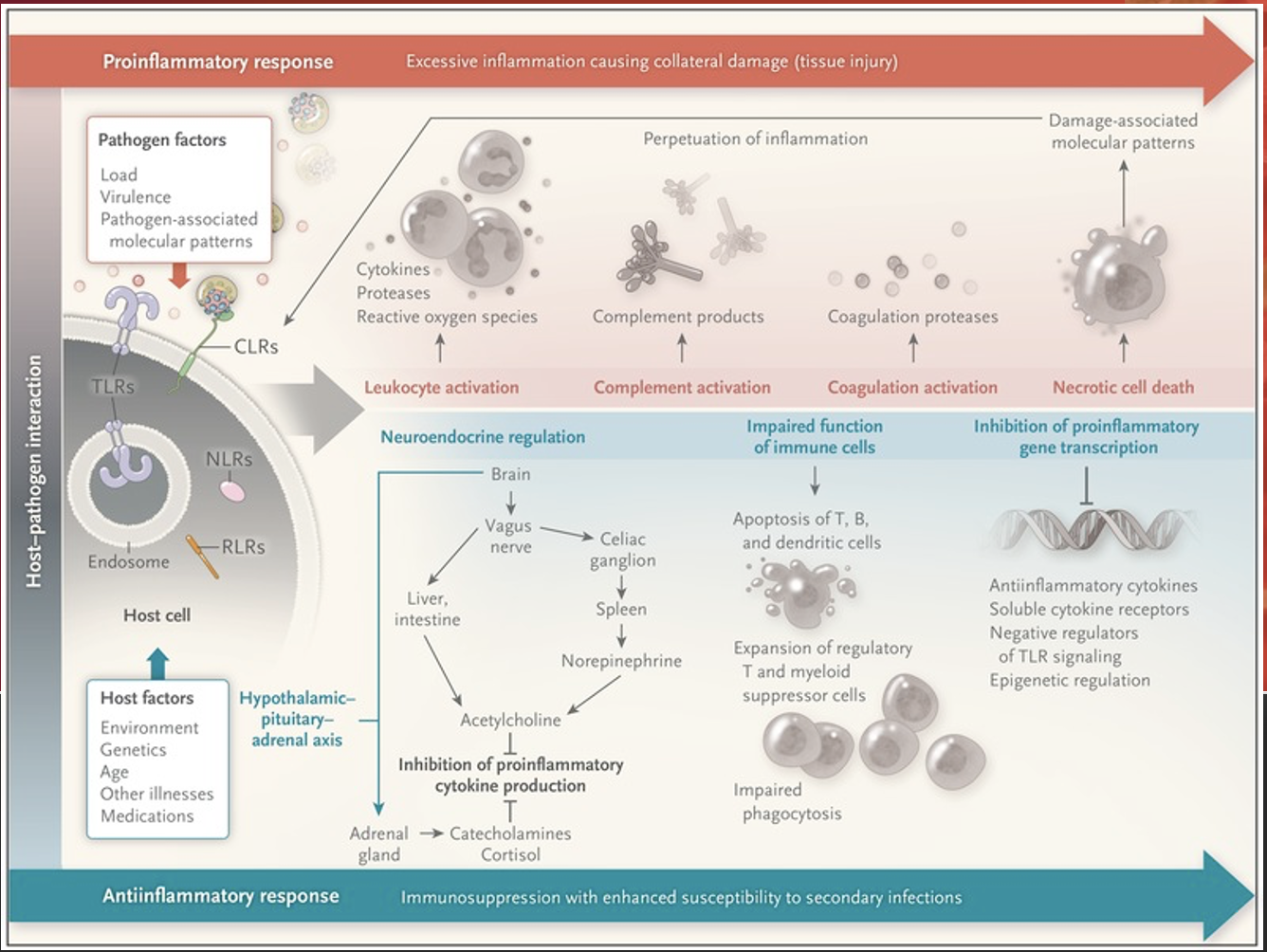
What are the most common HAIs?
Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI)
Central Line Associated Blood Stream Infection (CLABSI)
Ventilator Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
Surgical Site Infection (SSI)
Clostridium Difficile Infection (CDI)
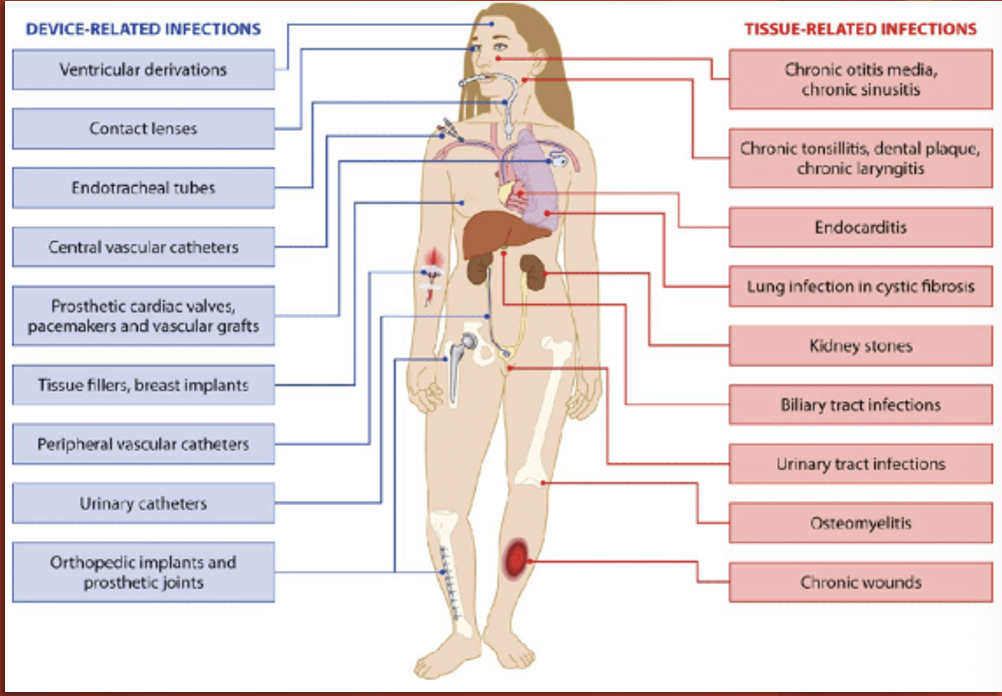
Sepsis: Patient Assessment
Septic patients can present in different ways.
A thorough assessment is key.
Make sure to pay attention to labs!
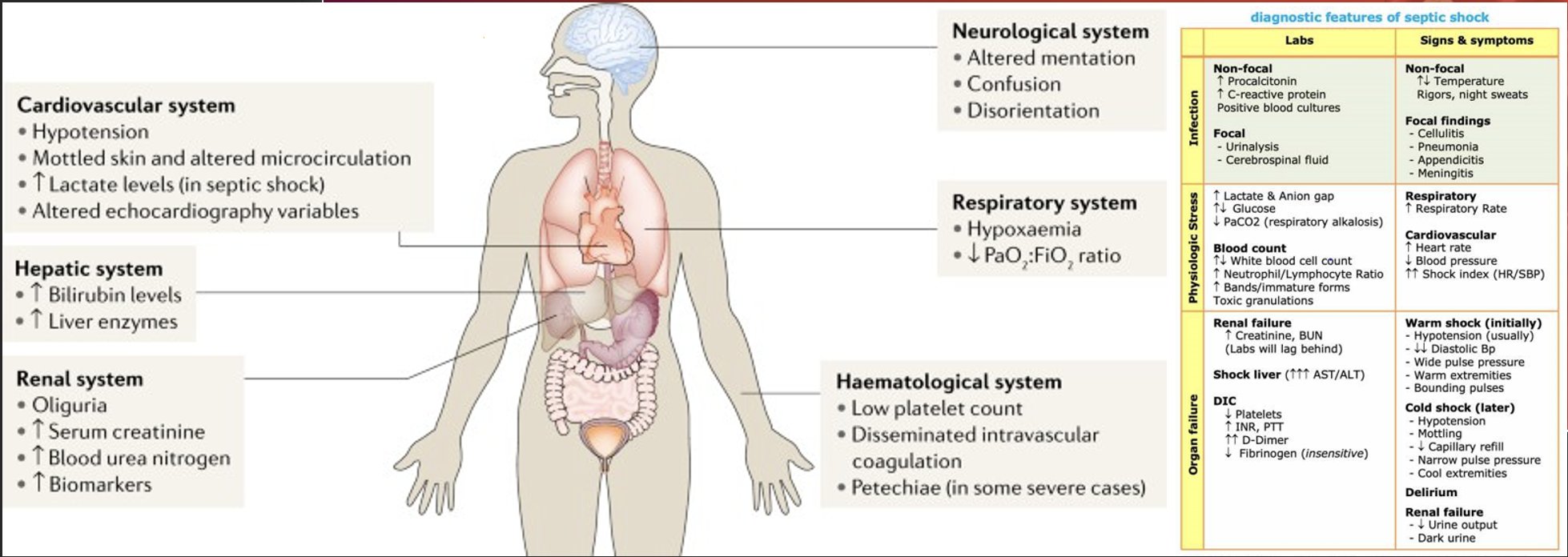
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)
SIRS criteria consists of:
Heart rate > 90 bpm
Respiratory rate > 20 rpm
Temperature > 38.8 C (100.9 F) or < 36.0 C (96.8 F)
WBC > 12,000/mm3 or < 4,000/mm3 or > 10% bands
Altered Mental Status
Glucose > 140 mg/dL in absence of diabetes
**2 or more and you’re positive for SIRS, but not everyone who is positive for SIRS is septic.
SIRS: What are bands?
They are immature WBCs.
Ex: someone’s WBCs went from 5,000 to 9,000—which is WNL, but if their bands are 17%, that means that their body had to ramp up production of WBCs because they have an acute infection.
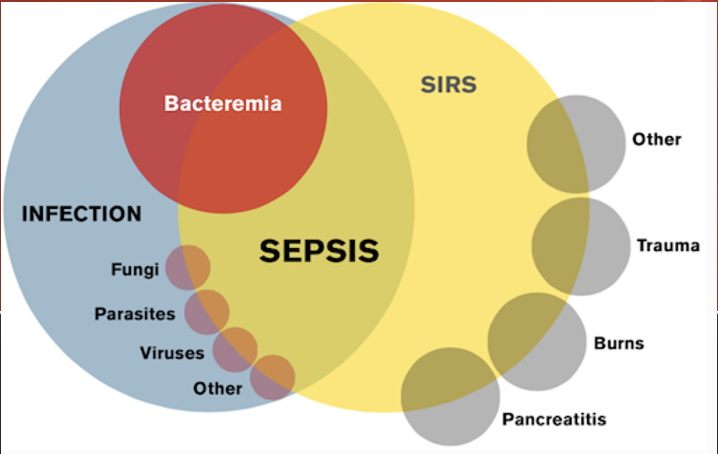
source of infection; 2
A patient needs to already have a ______ __ _________ along with _ or more of the SIRS Criteria to be considered to have sepsis.
Not everyone who is positive for SIRS is septic. What are some examples?
A patient having an asthma exacerbation.
A patient experiencing a panic attack.
A patient suffering from heat exhaustion.
bacteremia
The biggest source of sepsis is __________.
Sepsis: Nursing Responsibilities
Recognize early
Treat promptly:
Follow the Sepsis Bundle**
Fluid Replacement
Pharmacologic
Astute ongoing assessment
The Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC)
Was launched in 2002 as a collaborative initiative of the European Society of Intensive Care Medium (ESICM), the International Sepsis Forum (ISF), and the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM). It is updated every 4 years.
~Sepsis Bundle
Sepsis Nursing Responsibilities Soap Box
Monitor your patient for trends and report significant changes!
Do not just wait for a parameter to cross a predetermined threshold.
Nursing is about anticipation and preemptive action; addressing potential problems before they become actual problems.
If a patient’s SBP was 130, but now is 95, that’s concerning. If their potassium was 3.8, but now it’s 5.0, that’s concerning. If a patient’s WBC was 5.2, but now it’s 10.2, that’s concerning.
Sepsis Progression
Infection
Sepsis (Compensatory)
Severe Sepsis (Progressive)
Septic Shock (Irreversible)
Death or Recovery
Sepsis: Infection Stage
Initial Insult
Infectious Source
Pneumonia
UTI Wounds
Gastrointestinal
Cellulitis
Sepsis: Sepsis Stage
Compensatory Stage
2 SIRS Criteria
Temperature
Heart rate
Respiratory rate
WBC
AMS
Hyperglycemia
Sepsis: Severe Sepsis Stage
Progressive Stage
Organ Dysfunction
Bilirubin
Platelets
Hypotension
AKI
Respiratory failure
INR/PTT
Lactic acidosis
Sepsis: Septic Shock Stage
Irreversible Stage
Presence of either:
Lactic acidosis
Persistent hypotension
*DIC most likely present
Severe Sepsis: Signs of Organ Dysfunction
Respiratory P/F ratio < 250 w/o pneumonia, or < 200 w/ pneumonia
MAP < 65 mmHg, SBP < 90 mmHg, or SBP decrease > 40 from baseline
Creatinine > 2 mg/Dl
UOP < 0.5 mL/kg/hr in 6 hours or < 400 mL in 24 hours.
Bilirubin > 2 mg/dL
Platelets <100,000/mm3
INR > 1.5 or aPTT > 60 secs
Lactate > 2 mmol/L
The Role of Lactate
Lactate is an indicator of global tissue hypoxia.
Increased lactate levels are associated with increased morbidity and mortality.
Lactate levels are used to guide resuscitation efforts.
persistent hypotension; lactic acidosis
Septic shock is classified by __________ ___________ and/or ______ ________ (lactate > 4 mmol/L)
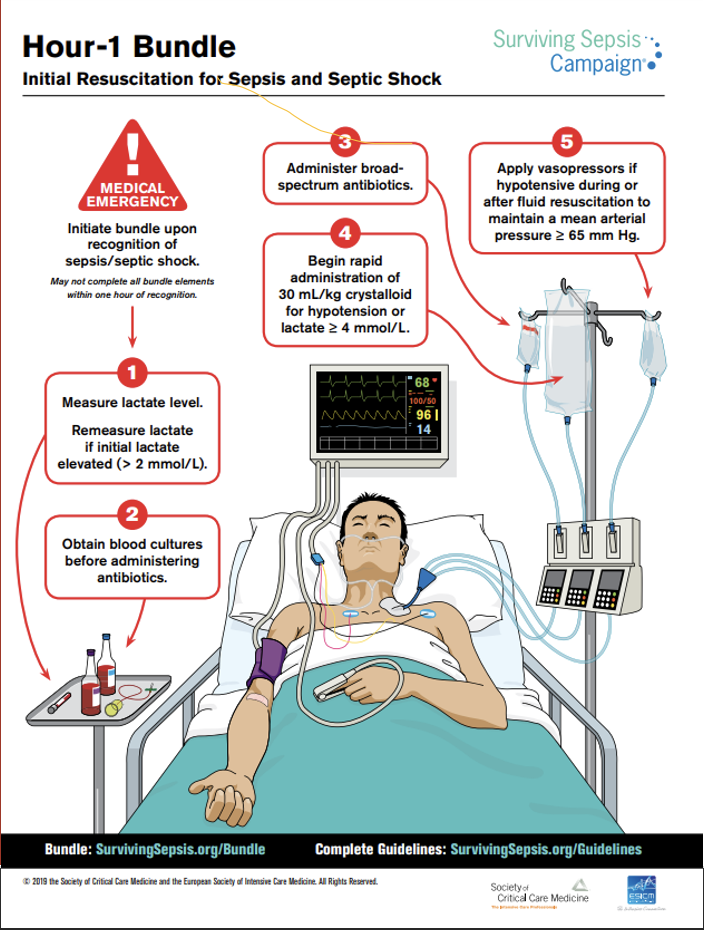
Sepsis 1-Hour Bundle
Our Priorities:
Obtain lactate level
Obtain blood cultures x2 (from two different sites, aerobic + anaerobic—so technically 4)
Administer fluids
Administer broad spectrum antibiotics
Administer vasopressors if needed
Constantly reassess
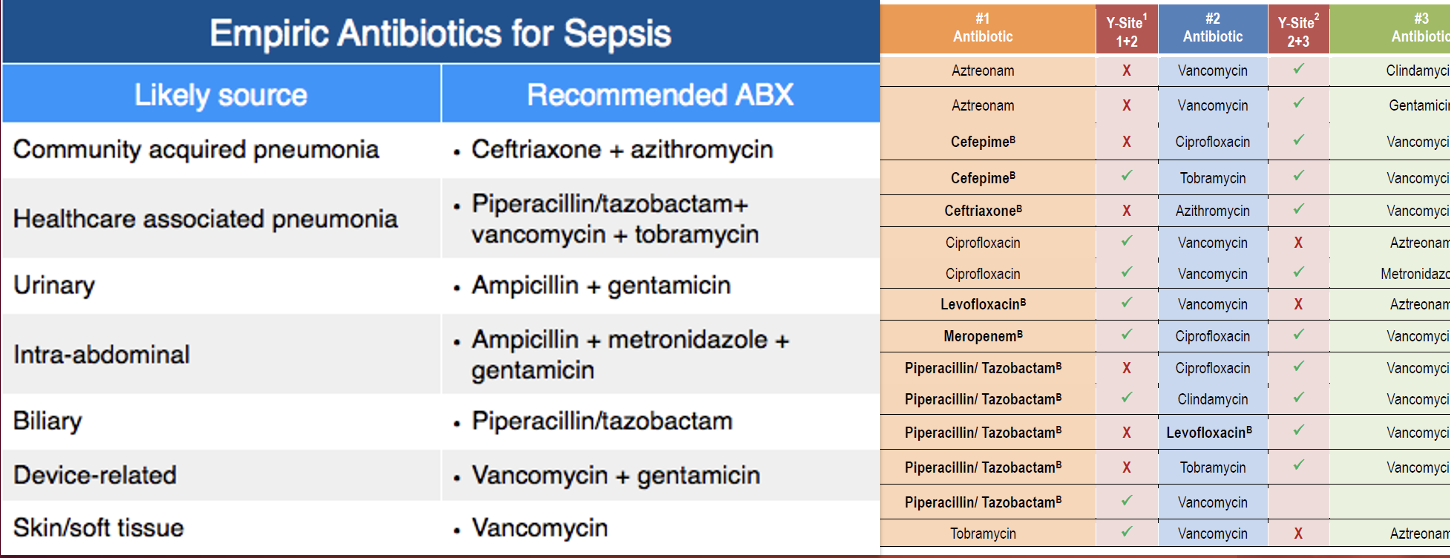
Sepsis: Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
Multiple antibiotics can be used; check for compatibility.
Delay in antibiotic administration is linked to increased mortality.
Administer IM, PO, or IO
If you can’t get IV access on your patient for broad spectrum antibiotics…
Broad Spectrum Antibiotics Compatibility
Incompatible medications can do many things when mixed:
Antagonizing (nullifying) effects
Precipitation (crystallization)
Consistency changes
Gas production, all of which are harmful to our patients!
Always check for compatibility within your documentation software. When in doubt, call the pharmacist!
Sepsis: Fluid Resuscitation
30 cc/kg of isotonic crystalloid solution
Normal Saline
Lactated Ringers
Calculation should be made using Ideal Body Weight (IBW)
FALSE! A history of heart failure does not exempt a patient from receiving a fluid bolus! Careful monitoring is required!
T/F: A history of heart failure exempts a patient from receiving a fluid bolus because it’s too dangerous.
Sepsis: Persistent Hypotension and Vasopressors
IF:
BP is measured every 15 minutes post-fluids, so…
Two consecutive low BP readings indicates persistent hypotension…
THEN:
Vasopressors should be started without delay!
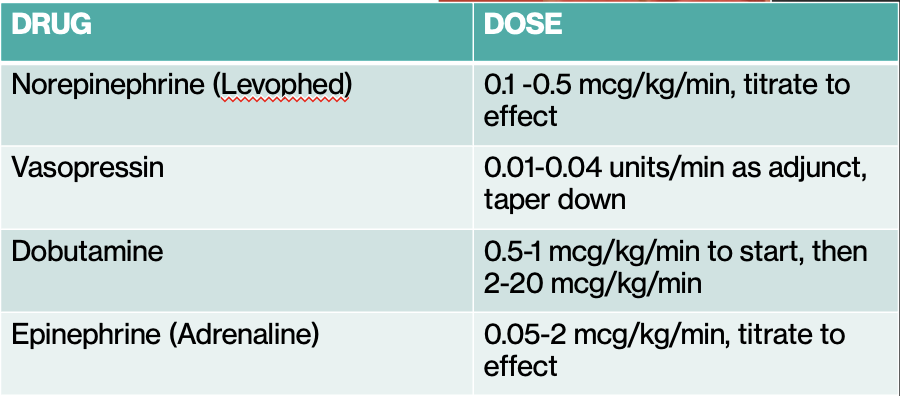
Norepinephrine (Levophed)
What is our first-line vasopressor in septic shock?
Persistent Hypotension and Vasopressors: Norepinephrine Dose + Receptor
Dose: 0.1-0.5 mcg/kg/min, titrate to effect
Receptor: a1 & b1
33.75 mL/hr
You are caring for a patient diagnosed with septic shock and who requires pharmacological blood pressure support. He weighs 198 lbs.
Order: Start norepinephrine IV drip at 0.1 mcg/kg/min and titrate to keep the patient’s MAP >65 mmHg.
Supply: Pharmacy provides you with the medication shown to the right.
What initial setting will you program your IV pump to deliver this medication at in mL/hr.?
Sepsis: Additional Medications
Volume Expanders (such as albumin)
To increase intravascular volume and improve BP (if fluids don’t work)
Corticosteroids (such as hydrocortisone)
Reduce inflammatory response, inhibit creation of nitrous oxide (vasodilator) by endotoxins
PPIs (such as pantoprazole)
To protect the gut from stress ulcers/bleeding
Other medications may include antipyretics for fever, insulin for hyperglycemia, and a LMWH for VTE prophylaxis.