paediatric optometry - lecture 5 , visual development
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What can hinder visual development in a child?
- deprivation
- amblyopia
- congenital cataract
- strabismus etc.
Von Hofsten et al. (2014) and vision
Suggested that
newborns were able to
discriminate facial
expressions from 30
cm.
• More difficult when
distance was greater
than 120 cm
How can we tell if infants can see?
- forced preferential looking( can be quantitative as recording sine gratings seen )
- electrophysiology
- ocular following movements
What is preferential looking?
AKA forced preferential looking (FPL)
- visual fixation responds to certain stimuli more readily than others
- FPL can be used as a quantitative measure (different sine gratings)
What is electrophysiology?
- electronic brain responses triggered by visual stimuli
What are the different measurements that you can get from electrophysiology?
- electroretinograms (ERG's): retinal components
- Electrooculograms (EOG's): retinal pigment epithelium
- Visual evoked potentials (VEP's): cortical measurement
how does visual electrodiagnostic work
-sensory accessory at the front of the eye ( cornea) or back of head
- EOG front of eye
- VEP back of the head
- goes to amplifier
- then to analyser
- present stimulus
- can see where in the retina and vc is working
downside of elecrophysiology
more invasive method
What is electrophysiology used for?
- to assess visual function in infants as young as 1 week old
What are the limitations of using an optokinetic drum?
- depends on the mood and attention of the child
- stimulates a larger area of the retina so not as sensitive as a snellen letter
How is ocular following movements measured?
- using an optokinetic drum
- both infants and adults make reflexive eye movements following the presentation of a moving target
-optokinetic nystagmus
- change the grating
- involuntary response
Limitations of ocular movement
- depends on mood and attention
- stimulates larger area of retina so less sensitive than stellen
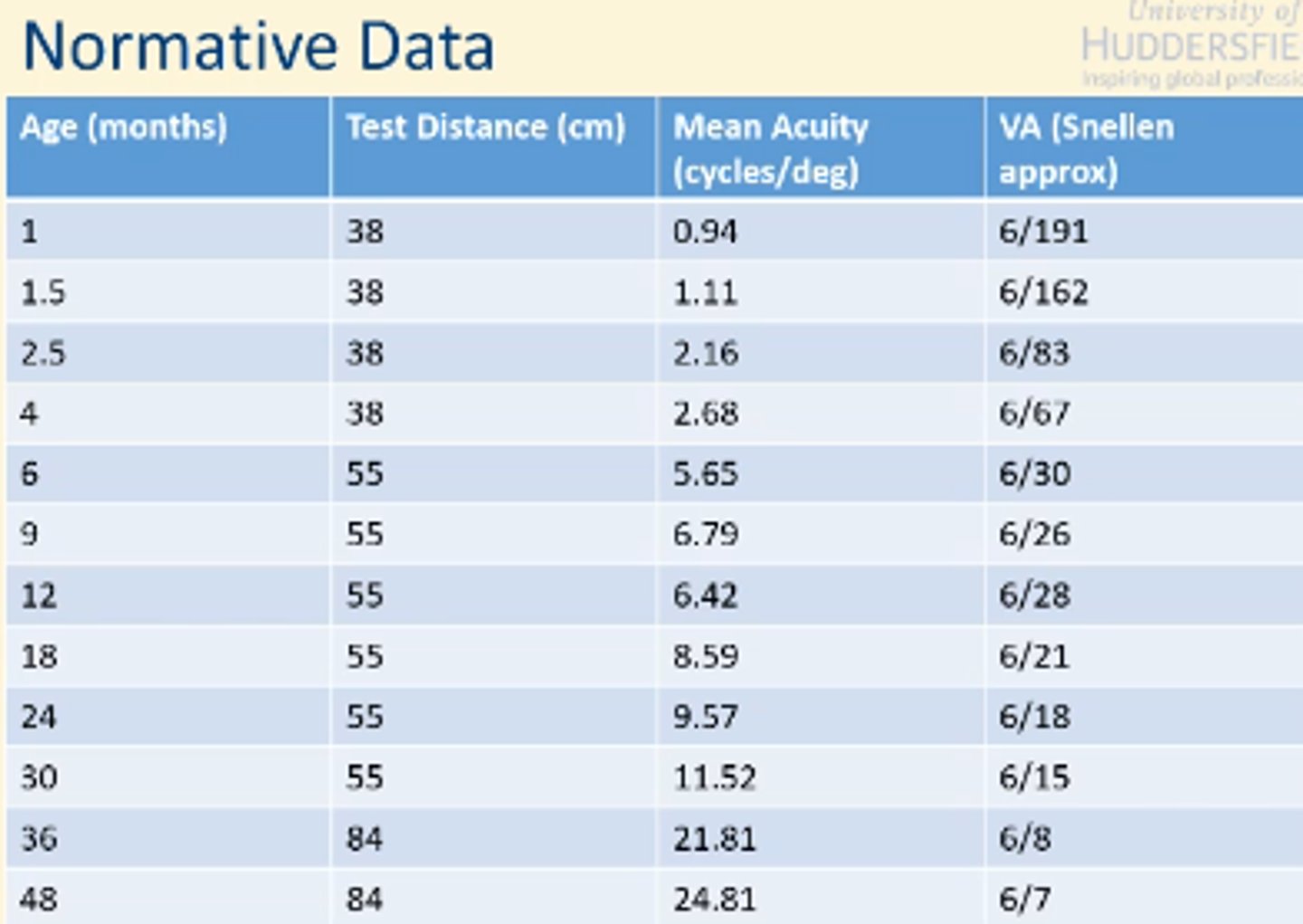
mayer et al and VA
used FPL to measure VA in 460 children ages 1 month-4years
- can be used to determine norm
Norm data VA children
What method shows higher acuities?
- VEPs tends to show higher acuities compared to FPL
VEP vs FPL
subjective vs objective
VEP
What is emmetropisation?
The rapid reduction in RE over first few years of life towards emmetropia.
-axial length
- refracting power of the cornea
- refractive power of the lens
- depth of the AC
How long does infant hyperopia last?
- subsides within the first 3 years of life with the most significant decrease occurring in the first year
What is the axial length of a childs eye?
- On average, the childs eye grows from 18mm at birth to 23mm by the age of 3.
What is the average adult eye axial length?
24mm
What did atchison et al suggest regarding axial length and refraction?
- an increase of 0.35mm increases myopic Rx by 1D
- This is NOt seen in normal development
What are some ocular components which can compensate for axial length?
- lens
- cornea
- AC depth
How does cornea effect Rx?
data is equvolm
How does anterior chamber depth change as you grow?
- it increases by 0.9 to 1mm from birth to 1.5 years
- 0.3mm to 0.4mm from 1 to 7 years
- 0.1mm from 8 to 13 years
- AC depth growth normally stops by the age of 15 years.
How does anterior chamber depth effect Rx?
0.1mm = 0.2D
- not a big effect
what does research suggest about a lens when growing?
- as the eye gets bigger and expands, it stretches the lens, making it thinner and reduces its dioptric power
- this tends to stop at the age 9 to 10
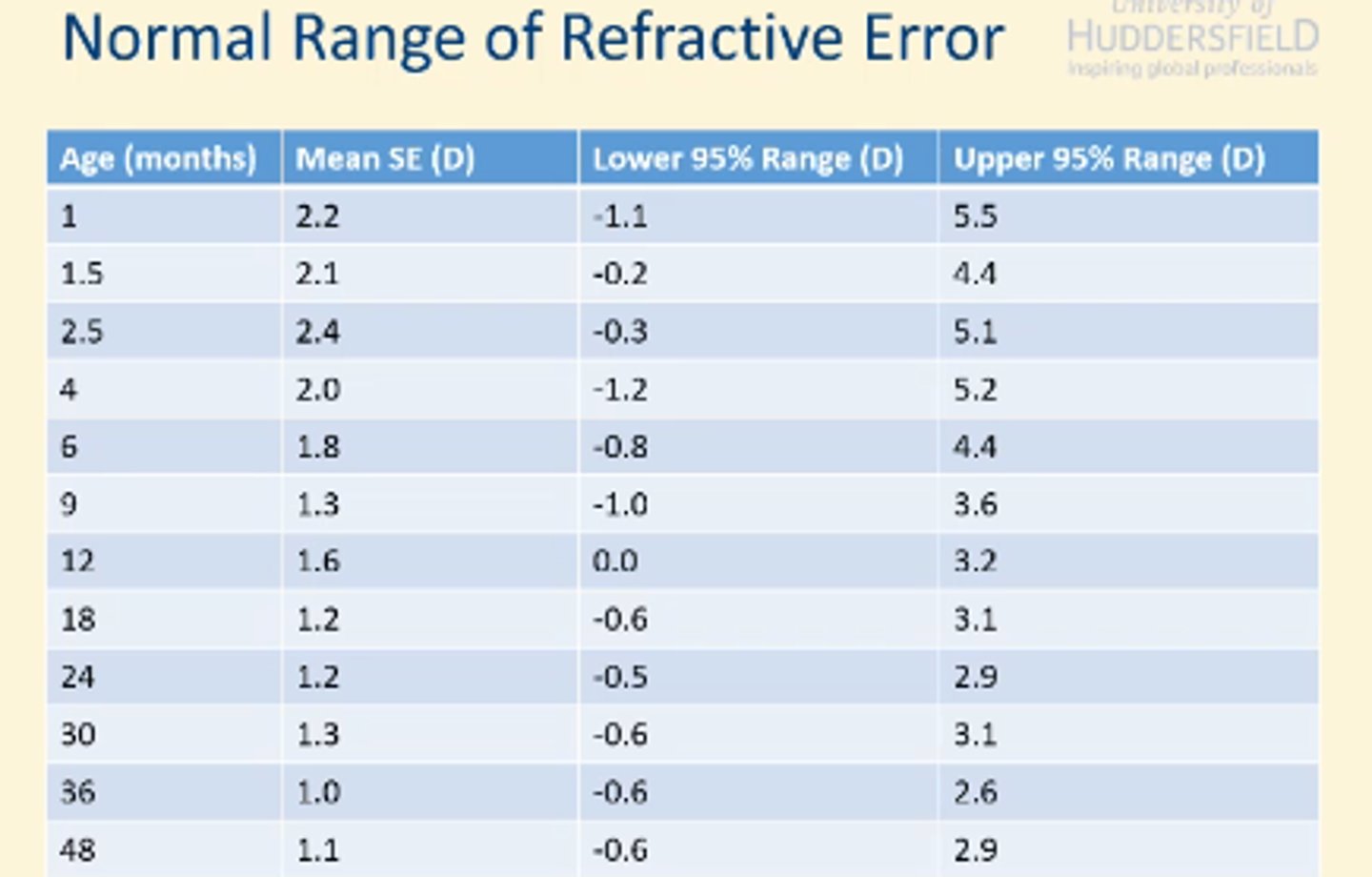
children rx normal data (1 month -4 years)
younger age, larger variarion of RE
With ranges below age norm values , RE remains more stable
With ranges of RE higher than normal values there is a steep decrease of RE as we age
it is okay of child is at lower 95 and upper 95 ( emmetropisation is likely to occur)
What is contrast sensitivity?
the ability to differentiate an object and its background
At what parts is contrast sensitivity particularly reduced in children?
- at mid and high spatial frequencies
Contrast Sensitivity• Westell et al. (1992)
Used FPL to assesscontrast sensitivity in 30 infants and children ranging in age from 3months to 5 yrs
westerly peak cs
Peak Contrast Sensitivities
3 months
5 at 1 cpd
6-8 months
10 at 3 cpd
->30 months
Close to 100 at 5-6 cpd