Genetics 2024
1/527
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
528 Terms
Chromosome Disorders
A type of genetic disease in which entire chromosomes (or large segments of them) are missing, duplicated, or are otherwise altered
Single Gene Disorders (Mendelian)
a type of genetic disease in which a single gene is altered
Multifactorial Disorders
a type of genetic disease in which single genes are altered, but the disease is also influenced by environmental factors (ex, DM)
Mitochondrial Disorders
a small number of genetic dieases which are caused by alterations in the small cytoplasmic mitochondrial chromosome.
Pattern of DNA coiling
DNA + Histone > Nucleosome > Solenoids > Chromatin Loops > Chromatid x 2 > Chromosome
Transciption Factors
Required for the transcription of DNA to mRNA
Regulated by enhancer and silencer sequences, which can be located thousands of bases away from the transcribed gene
Contain DNA binding motifs
Helix-turn-Helix
Helix-loop-helix
Zinc finger
Leucine zipper
Beta sheets
Gene
The basic unit of inheritance
passed from parents to offspring
most code for specific proteins or segments of proteins
italicized in questions
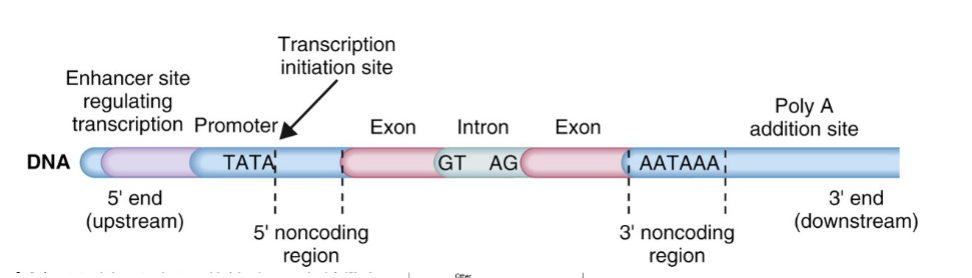
Gene structure
Note that TATA box (promoter) and AATAAA are counted as introns
Chromosome
Threadlike structures made of protein and a single molecule of DNA that serve to carry the genomic information from cell to cell
22 pairs that are numbered
1 pair of sex
For a total of 46
in each pair - one is from mom and one is from dad
Splicing
The process of removing introns from pre-mRNA and joining exons together to form a mature mRNA molecule.
exons contain the mRNA that specifies proteins
Single Copy DNA
45% of the genome
unique and dispersed throughout the genome
Dispersed Repetitive DNA
45% of the genome
repetitive DNA elements that occur together in clusters
Satellite DNA
10% of the genome
Dispersed repeats that are like one another but do not cluster together
Cytogenetics
a branch of biology focused on the study of chromosomes and their inheritance
Germline
referrs to the sex cells that pass on their genomes to offspring
DNA varients in these cells ARE passed onto offspring
Somatic Cells
diploid cells that contain two sets of chromosomes
DNA variants in these cells can affect the individual, but they CANNOT be passed on to their offspring
Single Nucleotide Variant
Change in a single gene
Copy Number Variant
change in a chromosome
Allele
one of two or more versions of a DNA sequence at a given genomic location
one is given from each parent
A capital letter indicates wild type
A lowercase letter indicates a variant
Homozygous
two alleles are the same
Heterozygous
two alleles are different
Hemizygous
only one allele available (eg, varient is in X chromosome in males)
Locus
a physical site, or loctation, within a chromosome
Genotype
a scoring of a type of vairient present at a given location (BB, Bb, bb). These can contribute to an individual’s obserable traits.
Phenotype
Refers to an individual’s obserable traits, such as height, eye color, and blood type.
Determined by both genomic makeup and environmental factors
Autosomal Dominant
pattern of mendelian genetics
gene is on one of the numbered chomosomes
a single copy of this variable gene is enough to cause this disorder
A child of the affected individual has a 50% chance of being affected
rare for an individual to be homozygous for this inheritance type (it would be lethal)
De Novo
New Mutation (parents did not pass it)
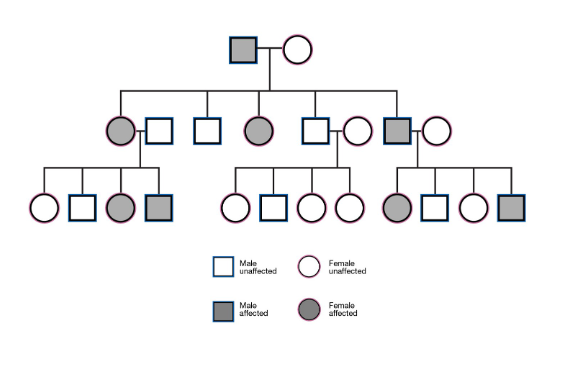
Autosomal Dominant Pedigree
Equal distribution between genders
vertial pedigree (one parent must have the condition)
multiple generations affected
Each affected person (normally) has one affected parent
if not, due to something like reduced penetrance
Autosomal Recessive
pattern of mendelian genetics
gene is located on one of the numbered chomosomes
two copies of the variable gene are needed to cause the disorder
A child a of the affected individual has a 25% chance of being affected via inheritance of two variant alleles
The parents must be carriers of the vatiant allele - will NOT occur de novo
Compound heterozygous
When an individual with an autosomal recessive condition inherited alleles from their mother and father that have different mutations. (however, both are still mutated)
Autosomal Recessive Pedigree
Horizontal pedigree pattern, with one or more siblings affected (however, often only one)
Skips generations
Males and Females equally affected
can be the product of consanguineous relations
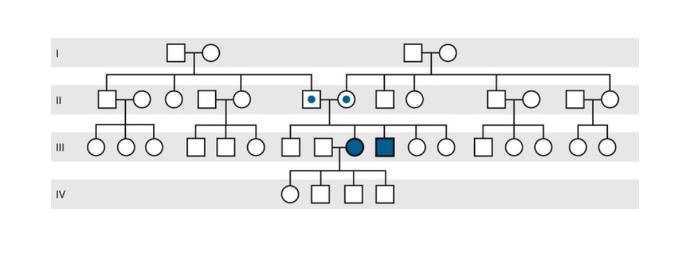
Consanguinity
having a highly shared genetic background due to being in the same family (incest is really only used if there is a close relationship, like with a parent, child, sibling, or grandchild)
increases the chances of autosomal recessive conditions
Penetrance
The percent of individuals who have a particiular genome who also present with the associated phenotype.
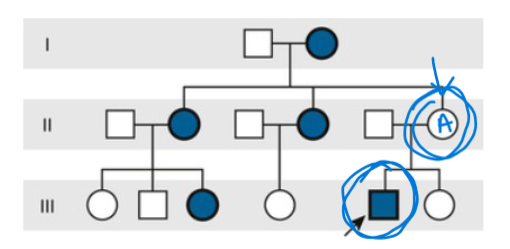
Reduced penetrance
Occurs when individuals with a disease-causing gene variant do not exhibit the associated traits or symptoms.
in this image, “A” has the genotype for the condition, but does not display the expected phenotype
Variable Expressivity
When the phenotypes among individuals with the same genotype show variable features.
predigrees will typically have various shades to represent this phenomena
ex, Marfan syndrome, Neurofibromatosis Type I
Pleitropy
a single-gene disease with many symptoms that affect many body parts/symptoms
seen in genes that controll several functions
Allelic Heterogeneity
Several pathogenic variants at a given loci result in the same phenotype
ex, 1000 different mutations in the CFTR gene cause Cystic Fibrosis
Locus Heterogeneity
When variants of genes at different loci (locations) have similar and even indinstinguishable disorders
Clinical Heterogeneity
When different variants in the same gene may produce different phenotypes (eg, different disorders)
ex, Charcot-Marie Tooth and Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria are caused by different variations on the same gene, LMNA
Marfan Syndrome mode of inheritance, gene, and molecular tests
Inheritance: AD
Gene: FBN1
Tests: FBN1 sequencing
Marfan Syndrome Clinical Features
CV:
dilation or dissection of the ascending aorta
Skeletal
pectus carinatum or excavatum
reduced upper/lower segment or arm span
scoliosis
pes planus
Eye
extopia lentis (the dislocation or displacement of the natural crystalline lens)
Marfan Syndrome Disease mechanism and key genetic concepts
Disease Mechanism:
Dominant negative effect of mutant forms of fibrillin
Key Genetic Concepts:
Dominant Negative Mutations (variants)
Variable expressivity
Allelic Heterogeneity (eg, several different mutations to the gene can cause this diease)
Achondroplasia mode of inheritance, gene, and molecular tests
Inheritance: AD, 80% De Novo
Gene: FGFR3
Molecular Tests: 98% FGFR3 G1138A; ~1% FGFR3 G1138C
Achondroplasia Clinical Features
Short stature
rhizomelic shortening (shortening of limbs)
trident hand (digits are all of equal length)
frontal bossing (prominent forehead)
midface hypoplasia
macrocephaly
Achondroplasia disease mechanism and key genetic concepts
Diease mechanism:
constitutive activation of FGFR (Fibroblast growth factor receptors)
GOF mutation - activation of negative growth controls
Key Genetic Concepts:
Gain of Function mutations
Advanced paternal age influences development of condition
De Novo mutation
Neurofibromatosis mode of inheritance, gene, and molecular tests
Inheritance: AD
Gene: NF1
Molecular Tests: over 500 mutations reported
Neurofibromatosis clinical features
Cafe au lait spots (flattened areas of dark skin)
2 or more neurofibromas
axillary or inguinal freckling
optic glioma
2 or more lisch nodules
1st degree realtive with the same condition
Neurofibramatosis Disease Mechanism and Key Genetic Concepts
Disease Mechanism
Impairs RAS GTPase mediated cellular proliferation and tumor supression
LOF mutation
Key Genetic Concepts
Variable expressivity
Extreme pleiotropy
tumor supressor gene
Loss of function mutations
Allelic heterogeneity
De novo variants
Holoproscencephaly mode of inheritance, gene, and molecular tests
Inheritance: AD
Gene: SHH (Sonic Hedgehog)
Molecular Tests: Sequencing
Holoprocencephaly Clinical Features
Ventral forebrain maldevelopment
Cleft lip palate
Facial dysmorphism
Developmental delay
microcephaly
seizures
short stature
Holoprocencephaly Disease Mechanism and Key Genetic Concepts
Disease mechanism
gene is involved in establishing fate of cells in development
LOF mechanism
Key Genetic Concepts
Developmental Regulatory gene
Allelic Heterogeneity
Position effect variants
Reduced penetrance
variable expressivity
Polycystic Kidney Disease mode of inheritance, gene, and genetic tests
Inheritance:
AD for PKD1 and PKD2
AR for PKD3
Genes:
PKD1
PKD2
PKHD1
Tests: US, MRI
Polycystic Kidney Diease Clinical Features
Enlargement of both kidneys
renal cysts
hematuria
polyuria
flank pain
renal stones
urinary infection
cysts in thr liver, pancreas, and intestine
Polycystic Kidney Disease disease mechanism and key genetic concepts
Mechanism:
unclear
Key Genetic Concepts
Variable expressivity
locus heterogeneity
two-hit hypothesis
Charcot Marie Tooth Disease mode of inheritance, genes, and molecular tests
Inheritance: AD
Genes: MANY
Molecular tests: gene sequencing
Charcot Marie Tooth Disease clinical features
Slow, progressive weakness and atrophy of distal mucles in the feet/hands beginning in the 1-3rd decade of life
hearing loss
pes cavus foot deformity
hip dysplasia
Charcot Marie Tooth Disease disease mechanism and key genetic concepts
Mechanism:
abnormal peripheral myelination
GOF (for PMP22)
Key Genetic Concepts:
GOF for PPM2
Dominant negative mutations
Locus Heterogeneity
Gene dosage
Cystic Fibrosis mode of inheritance, gene, and molecular tests
Inheritance: AR
Gene: CFTR
Testing: various (dont need to know)
Cystic Fibrosis clinical features
Chronic Airway infection
chronic sinusitis
meconium ileus
malabsorption due to pancreatic insufficiency
male infertility (azoospermia)
progression to end stage lung disease
congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD)
Cystic Fibrosis Disease mechanism and key genetic concepts
Disease Mechanism:
CFTR forms a cell membrance Cl- channel - w/o it massive issues occur
Key genetic Concepts:
Ethnic variation in mutation frequency
variable expressivity
allelic heterogeneity
tissue specific expression of mutations
genetic modifiers
environmental modifiers
Sickle Cell Diease mode of inheritance, gene, and molecular tests
Inheritance: AR
Gene: HBB
Molecular Tests: E7V pathogenic variant, also commonly referred to as E6V
Sickle Cell Disease clinical features
vaso-occlusive events
chonic hemolytic events
anemia
Sickle Cell Disease Disease mechanism and key genetic concepts
Mechanism:
LOF
Key Genetic Concepts
heterozygote advantage
ethnic variation in allele frequencies
Deafness mode of inheritance, gene(s), and molecular tests
Inheritance: AR (sometimes…)
Gene: GJB2 (Cx26), GJB6 (Cx30)
Molecular tests: multiple
Deafness Diagnotic criteria
congenital mild-profound SNHL
sensorineural ___ ____
Deafness disease mechanism and key genetic concepts
Mechanism:
loss of Gap Junctions prevents recycling of toxic ions and metabolites away from hair cells leading to their death
Key Genetic Concepts:
Allelic Heterogeneity with both AD and AR patterns
Locus heterogeneity
Newborn screening
PKU mode of inheritance, gene, and molecular testing
Inheritance: AR
Gene: PAH
Molecular Testing: newborn screening, sequencing
PKU clinical features
Prenatal onset
microcephaly
seizures
short stature
phenylalanine elevation in blood
PKU disease mechanism and key genetic concepts
Disease mechanism:
LOF in the enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of phenylalanine to tyrosine
Key genetic concepts:
enzyme
allelic heterogeneity
pleiotropy
mutations
Tay Sach Disease mode of inheritance, gene, and testing
Inheritance: AR
Gene: HEXA
Testing: Cherry Red Spot on eye exam
Tay Sach Disease clinical features
infantile weakness starts at 6 months
exaggerated startle response
seizures and vision loss by the end of first year
neurodegeneration —>
deafness
inability to swallow
weakening of muscles
eventual paralysis
Tay Sach disease mechanism and key genetic concepts:
Disease Mechanism:
acculmulation of GM2 gangliosides in the brain
Key genetic concepts:
enzyme
founder effect
X linked disorders
Genetic disorders of traits that are on the X chromosome
Why do men have more of a disposition to X-linked disorders
Men only have one X chromosome, so if the one they inherit has the mutated trait, they will display the disease
X inactivation
The natural process where one of a females X chromosomes is condensed into a barr body in their cells because it is not needed.
This process is random - which accounts for why females who only have one X chromosome with a mutant allele may have milder (or no) symptoms.
There are some genes that remain active in both X chromosomes (approx 15% expressed in both)
NO genes on the single X chromosome of males are turned off.
X inactivation Center
A region on the X chromosome that plays a crucial role in the X inactivation process, ensuring that one of the two X chromosomes in females is inactivated.
XIST
A gene located on the X chromosome that is crucial for initiating X inactivation by coating the inactive X chromosome. Expressed only on the inactivated X chromosome
Skewed X-inactivation
This process of barr body production is normally split 50-50 between the X chromosomes inherited from the mother and father in a womans cells
When this process is not even, more of a working gene can be expressed, or more of the mutant gene can be expressed.
X linked dominant
Both males and females affected, but affected females are greater in number
in males this Mode of inheritance is normally lethal
Affected males can only transmit to their daughters, and ALL their daughters will be affected
they WILL NEVER pass to their sons
Ex, Rett Syndrome, Ornithine Transcrabamylase deficiency, Fabry disease
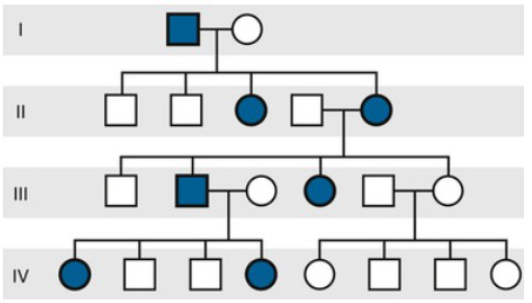
X linked Recessive Pedigree
“Knights move” pedigree pattern
Affects mainly Males, with females most often being carriers that pass to their sons.
NEVER transmitted father to son
Affected males may have affected maternal uncles
Frequently De Novo
Ex, Duchene Muscular Dystrophy, Hemophilia A, G6Pase Dehydrogenase deficiency, Red/Green color blindness
Y linked
ONLY in males, NEVER in females
Fathers will pass to ALL their sons
Mitochondrial Disorders
Inheritance of this type will only be passed through a child’s mother
Mutations of this inheritance type often result in
Loss of energy production
excessive production of ROS
Abnormal integration of apoptotic signaling
Abnormal retrograde signaling
Mitochondrial Inheritance
Vertical pedigree patten
children of affected men are never affected
all children of an affected woman MAY be affected - but diseases of this inheritance are overall variable
Heteroplasmy, which induces variable expressivity, and threshold effect can be reasons why individuals are not being affected in the pedigree
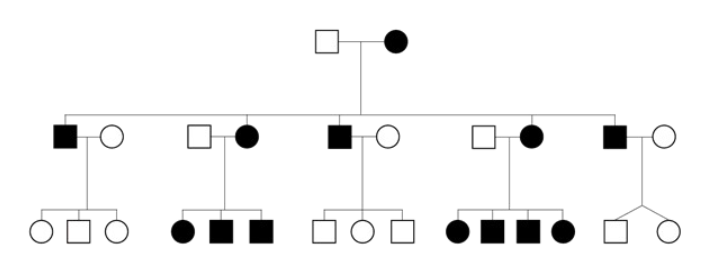
Homoplasmy
Mitochondrial DNA within a cell contains ALL the same DNA - either all wild type or mutant
most often mRNA/rRNA is altered
Heteroplasmy
Mitochondrial DNA is mixed - a cell has both wild type and mutant DNA
most often tRNA is altered
_________ + AGE = variable expression in mitochondrial disorders
Threshold Effect
The point where the number of mutant variants of mitochondrial DNA is enough to show a phenotype
Organs specifically targeted with mitochondrial disorders
Brain
Colon
Inner ear
Blood
Pancreas
Kidney
Liver
Eye
Heart
Skeletal Muscle
Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)
Inheritance: Mitochondrial aka Maternal
Largely homoplasmic
Gene: 1178A>G in the ND4 subunit of Complex I ETC
Phenotypes:
BIlater central vision loss
optic nerve atrophy
some recovery of vision depending on mutation
Leigh Syndrome
Inheritance: Mitochondrial aka Maternal
Heteroplasmic - variable expression
Gene: Point mutations in ATPase subunit 6 gene
Phenotypes:
early onset progressive neurodegeneration w/ hypotonia
developmental delay
optic atrophy
respiratory abnormalities
POLG
Inhertiance: AR
name is the same as the gene that encodes mitchondrial DNA polymerase gamma
Causes: mtDNA depletion syndrome-4A(MTDPS4A), which manifests as Alpers Syndrome
Phenotype → Triad seen in young children:
psychomotor retatdation
intactable epilepsy
liver failure
MELAS
Inheritance: Mitochondrial aka Maternal
Heteroplasmic
Gene: Point mutations in tRNAleu(UUR) most commonly 3243A>G
Phenotypes:
Myopathy
Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy
Lactic Acidosis
Stroke
Deafness (NOT MENDELIAN)
Inheritance: Mitochondrial aka Maternal
Homoplasmic
Gene: 12S rRNA gene with either
1555A>G
7445A>G
Phenotypes:
progressive sensorineural deafness
Kearns-Sayre Syndrome
Inheritance: Mitochondrial aka Maternal
Heteroplamic
Gene: the ~5kb large deletion (dont need to know really)
Phenotypes:
Triad of:
onset before age 20
pigmentary retinopathy
PEO → Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia
progressive myopathy
cardiomyopathy
heart block
ataxia
DM
MERRF
Inheritance: Mitochondrial aka Maternal
Heteroplasmic
Gene: Point mutations in tRNAlys most commonly 8344A>G
Phenotypes:
Myoclonic Epilepsy with Ragged Red muscle Fibers
myopathy
ataxia
sensorineural deafness
dementia
Rett Syndrome Mode of Inheritance, genes, and tests
Inheritance: XLD
Gene: MECP2
Tests: MECP2 Sequencing
Rett Syndrome Clinical Features
Developmental regression (esp language and hand use)
microcephaly
wringing hand movements
paroxysmal laughing
Rett Syndrome Disease mechanism and key genetic concepts
Mechanism:
Decreased function or LOF MECP2, which normally binds methylated CpG islands
Key genetic concepts:
LOF mutation
Variable expressivity
Sex-dependent phenotype
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy mode of inheritance, gene, and tests
Inheritance: XLR
Gene: DMD
Tests: PCR
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy clinical features
present before age 5
progressive symmetrical muscle weakness
calf hypertrophy
dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM)
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy disease mechanism and key genetic concepts
Mechanism:
Mutation that leads to lack of Dystropin expression
Dystrophin binds actin and other membrane proteins
Key Genetic Concepts:
High frequency of new mutations
allelic heterogeneity
manifesting carriers
variable expressivity