Biological Psychology
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
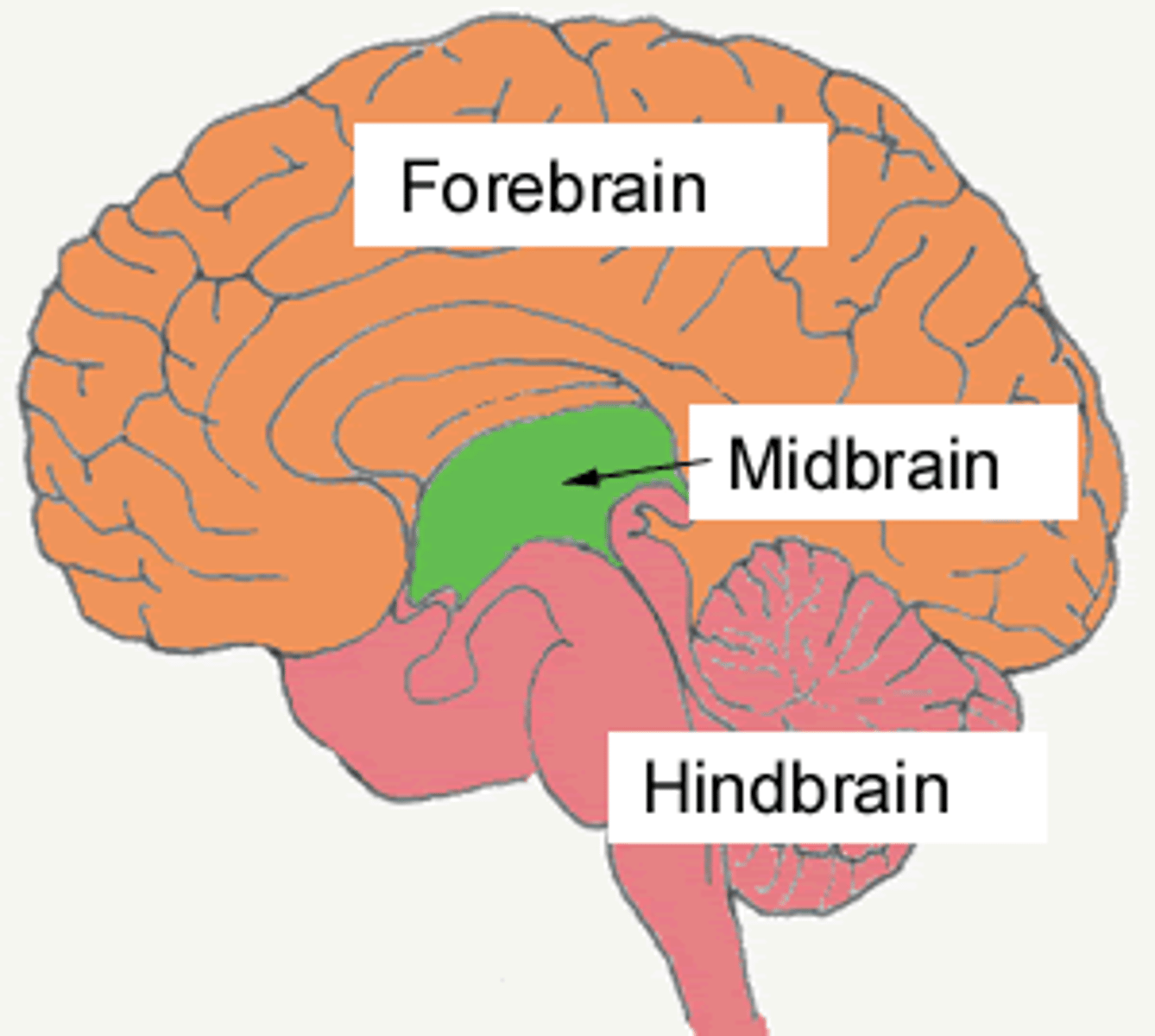
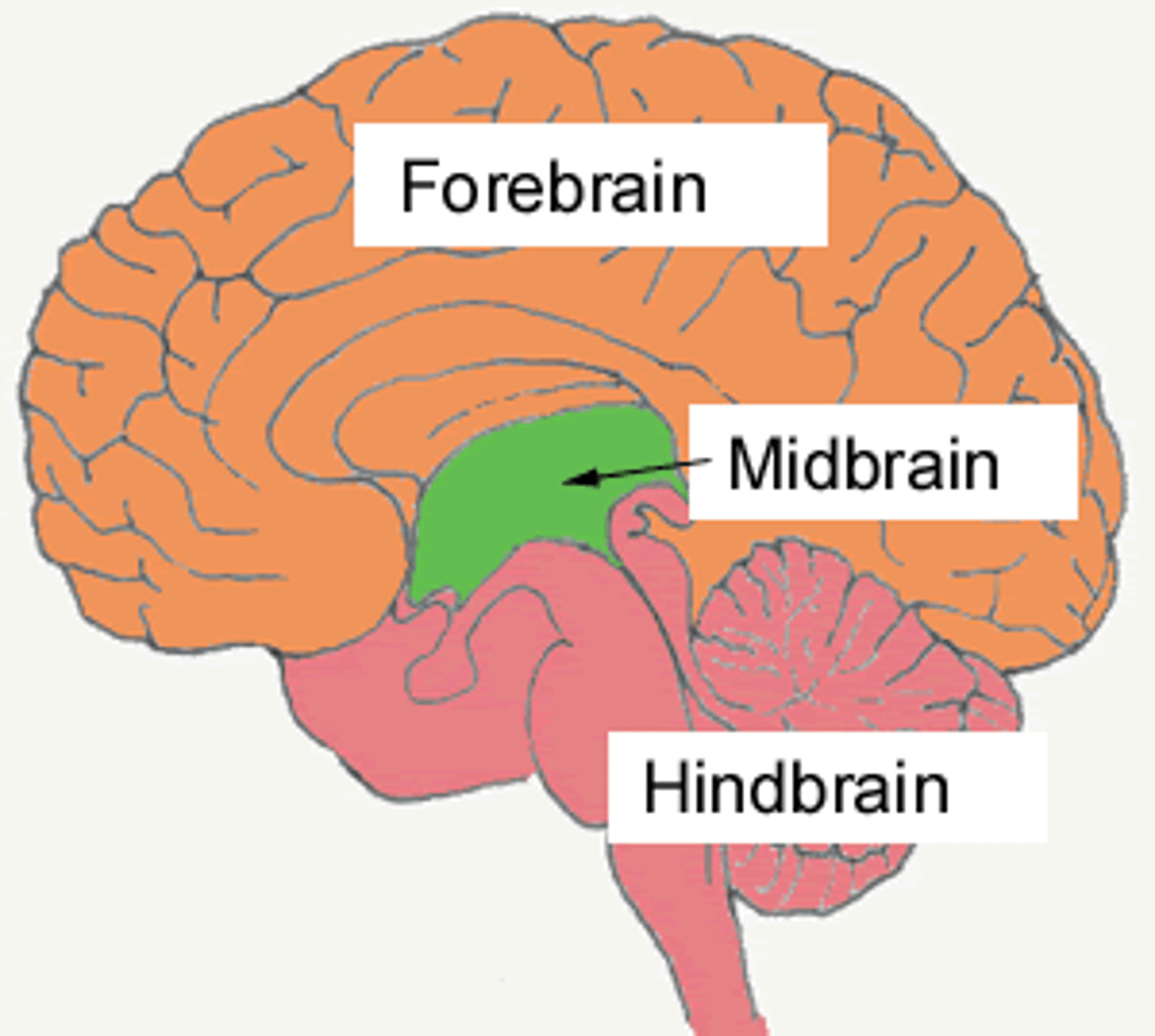
Forebrain
-Responsible for voluntary actions, thinking, and processing
-Limbic System: Emotion/motivation/memory
-Includes hypothalamus, thalamus, amygdala and hippocampus.
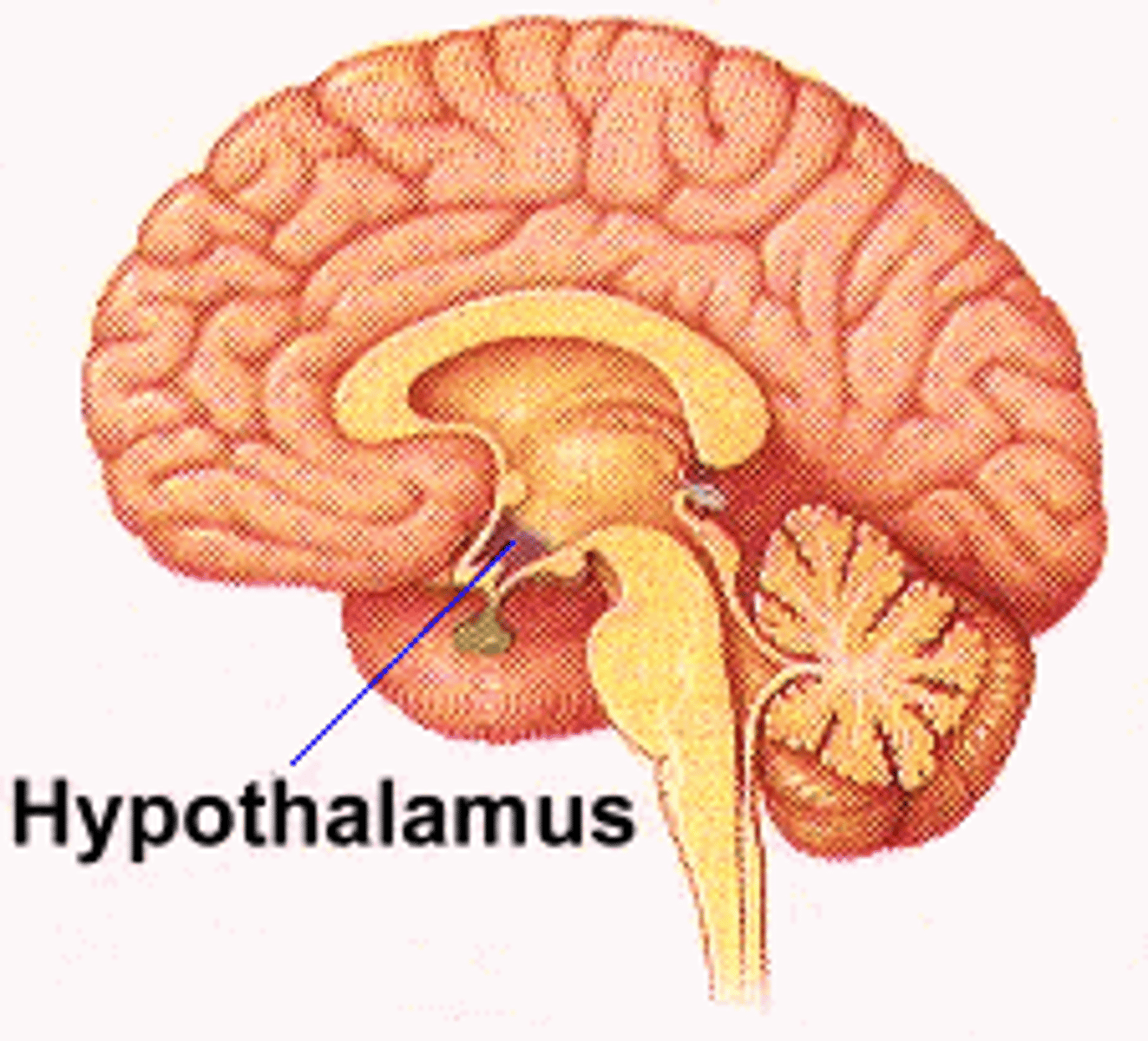
Hypothalamus
Regulates 4 F's
Fighting: aggressive behaviors and body's response to threats (fight or flight)
Fleeing: urge to escape danger, part of stress response system
Feeding: hunger, appetite, food intake, energy levels
Fornication: sexual urges, hormone release
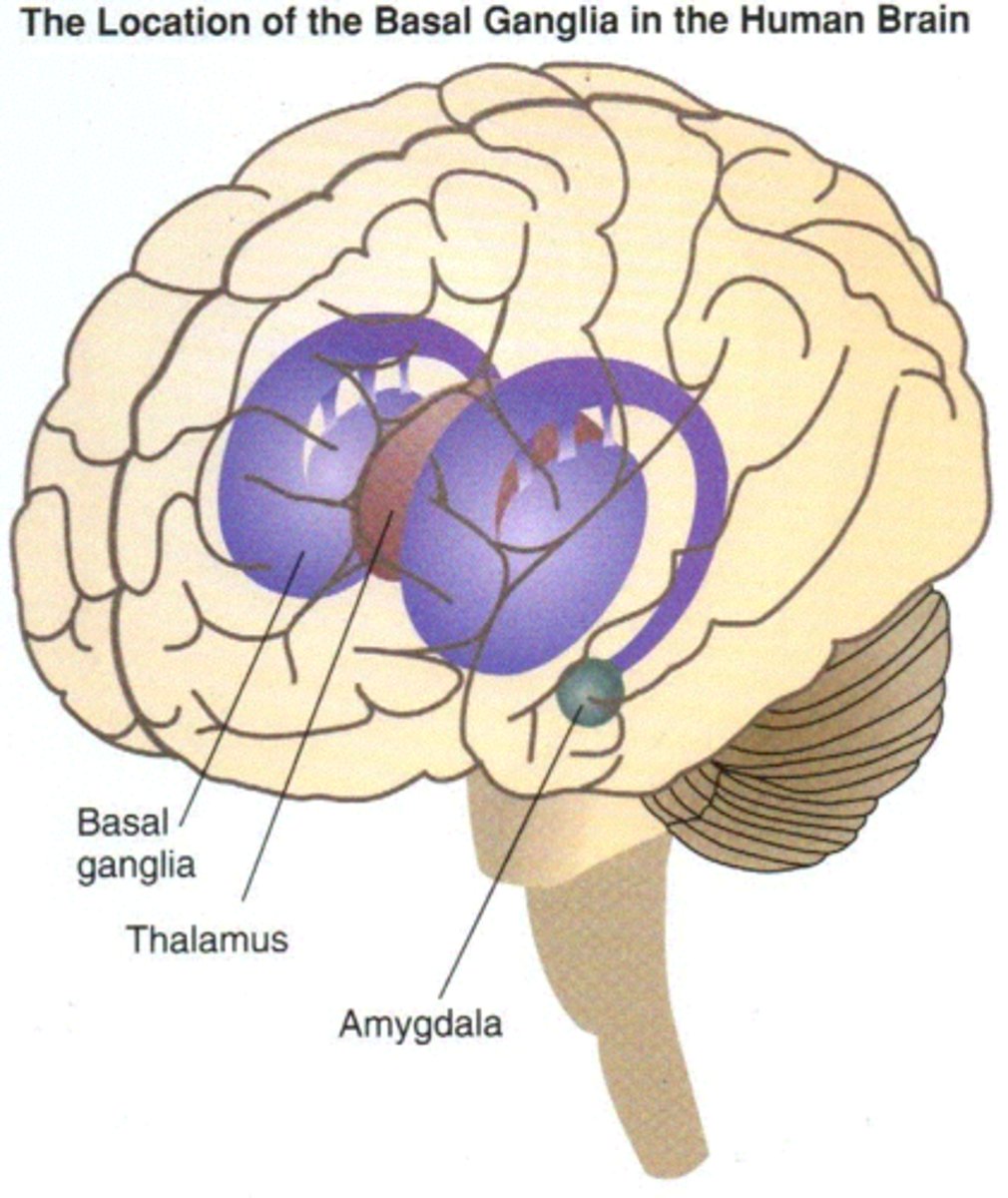
Thalamus
Filters and transmits information from senses to the cerebral cortex.
Amygdala
Emotional processing and essential for emotional learning.
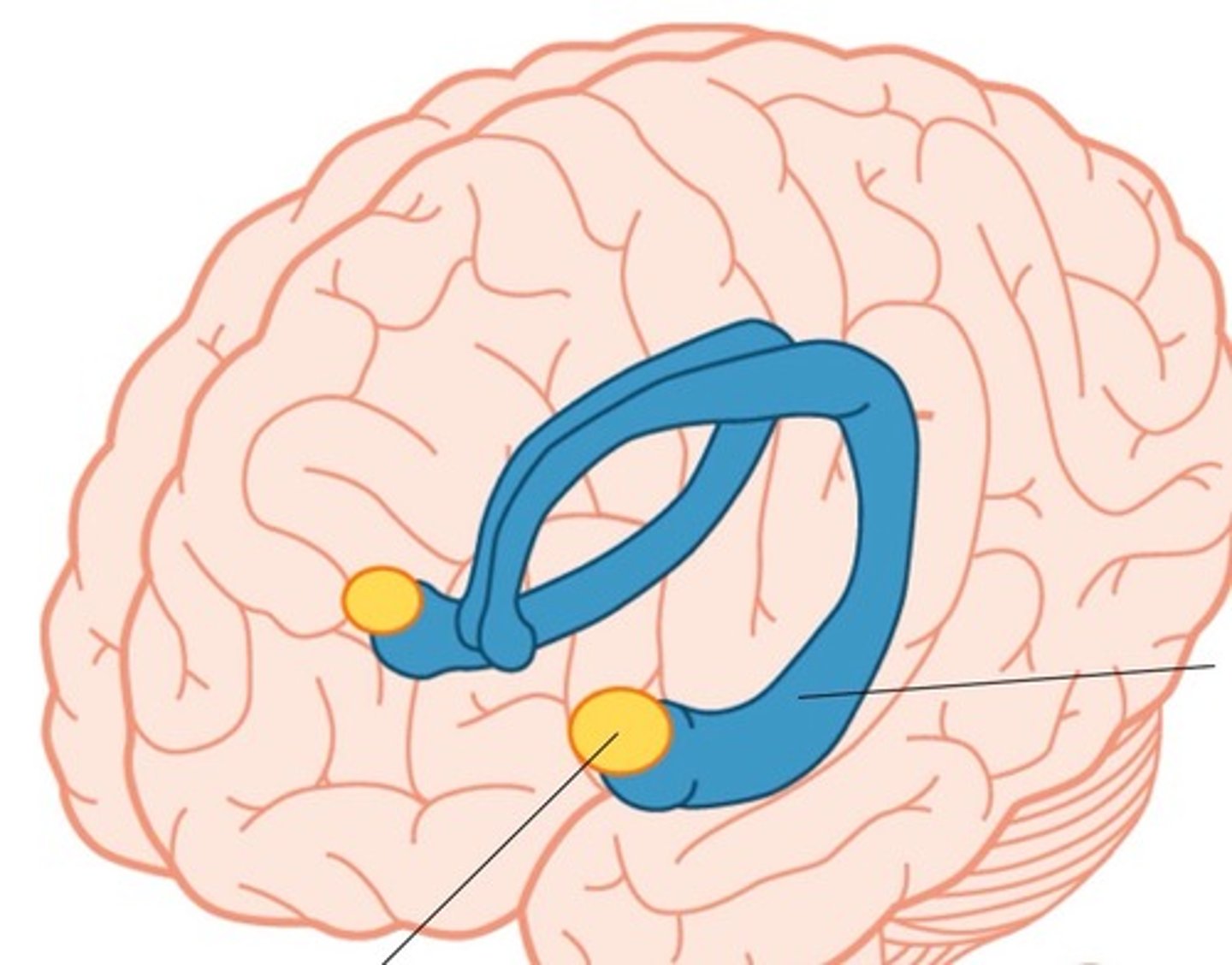
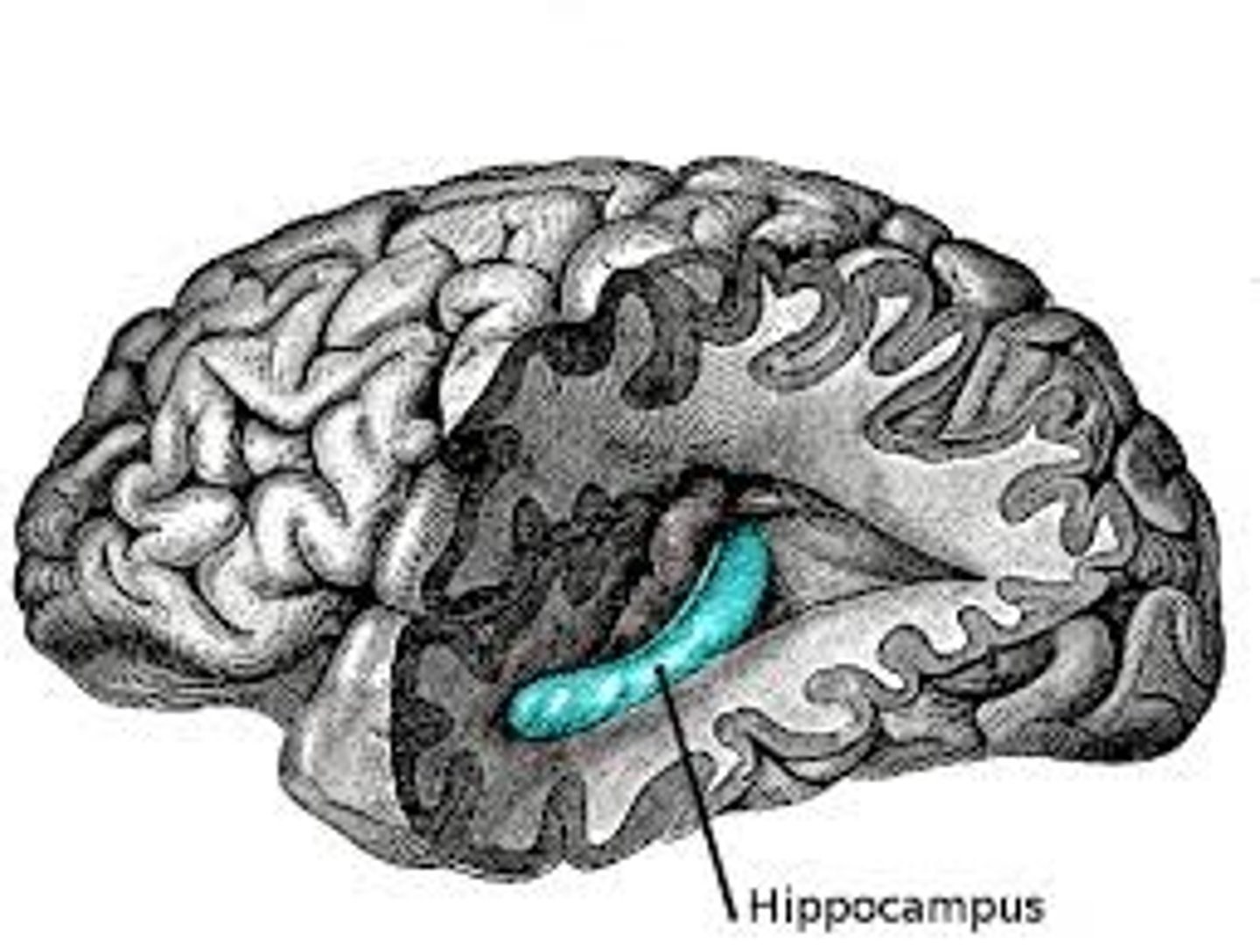
Hippocampus
Critical for creating and integrating new memories (seahorse shape)
Basal Ganglia
Directs intentional movement and plays a role in reward processing.
Cerebral Cortex
-Gray matter responsible for higher functions like thought, language, memory, perception, conciousness.
-Large surface area is folded so it can be placed into the limited volume of the skull.
Midbrain
-Small central part of the brainstem.
-Includes tegmentum and tectum
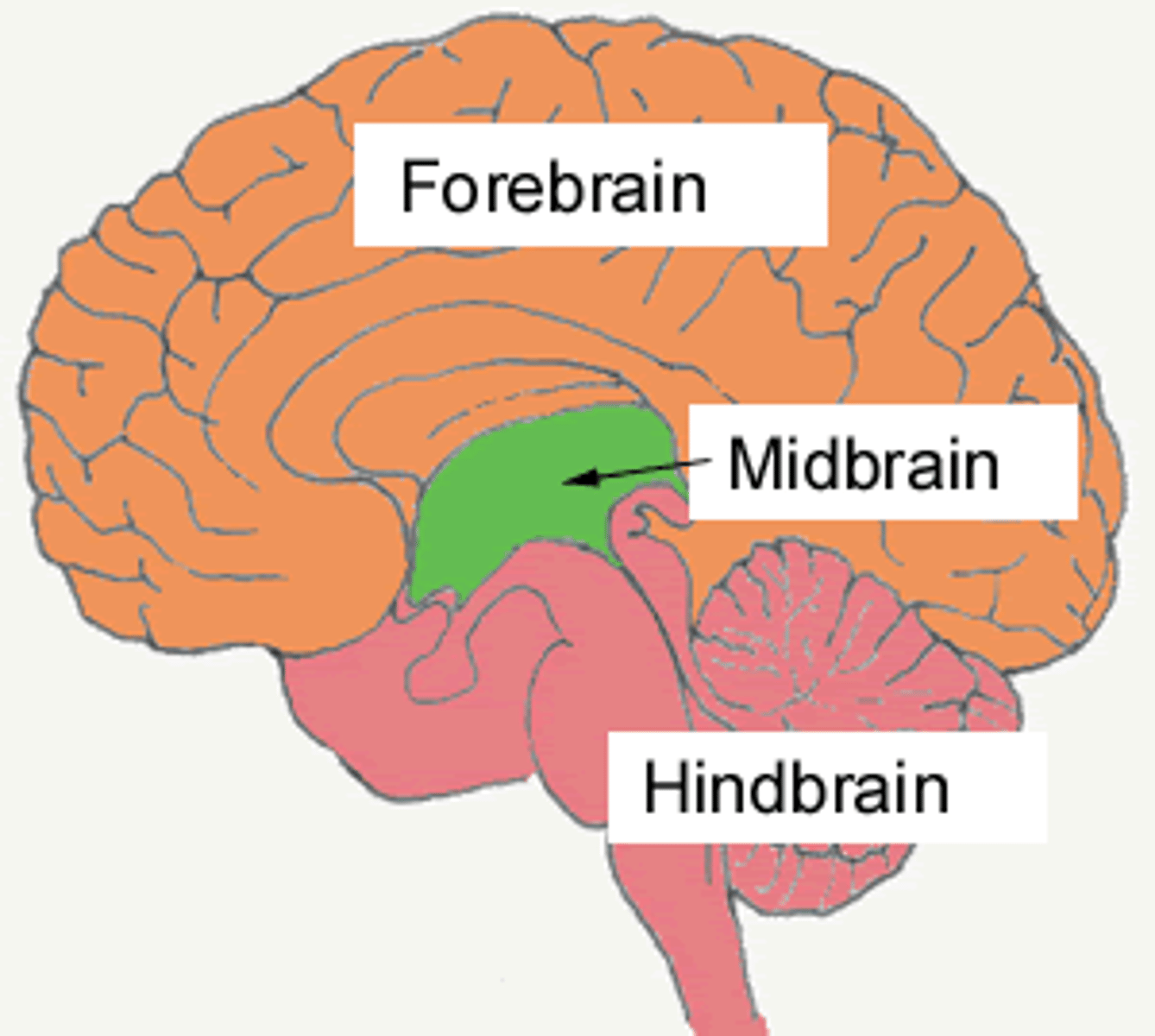
Hindbrain
-Manages autonomic functions, motor coordination, balance
-Includes cerebellum, medulla, reticular formation, pons
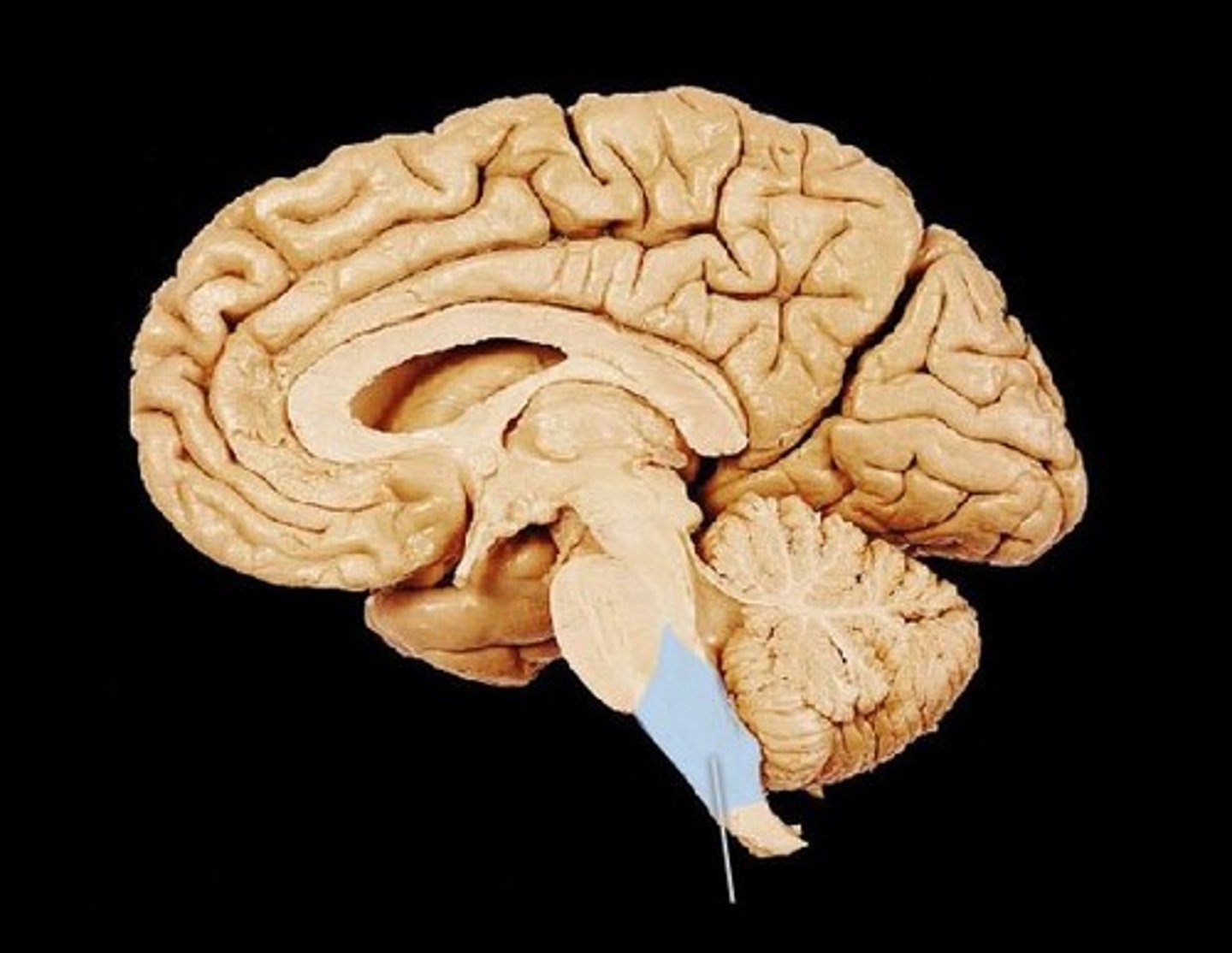
Cerebellum
Motor coordination, control, balance.
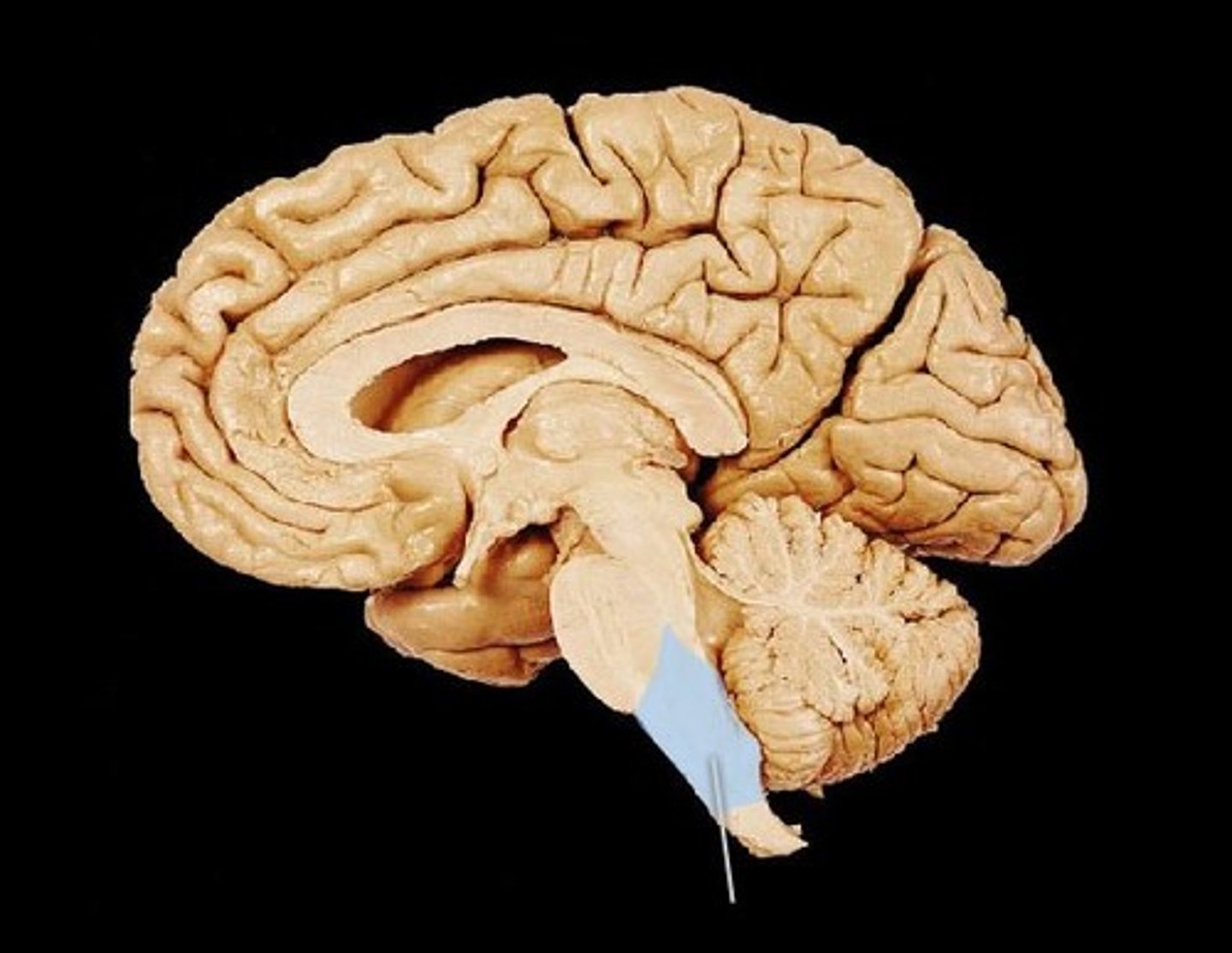
Medulla
Coordinates heart rate, circulation, respiration.
Reticular Formation
Regulates sleep, wakefulness, and arousal.
Pons
Relays information from cerebellum to the rest of the brain.
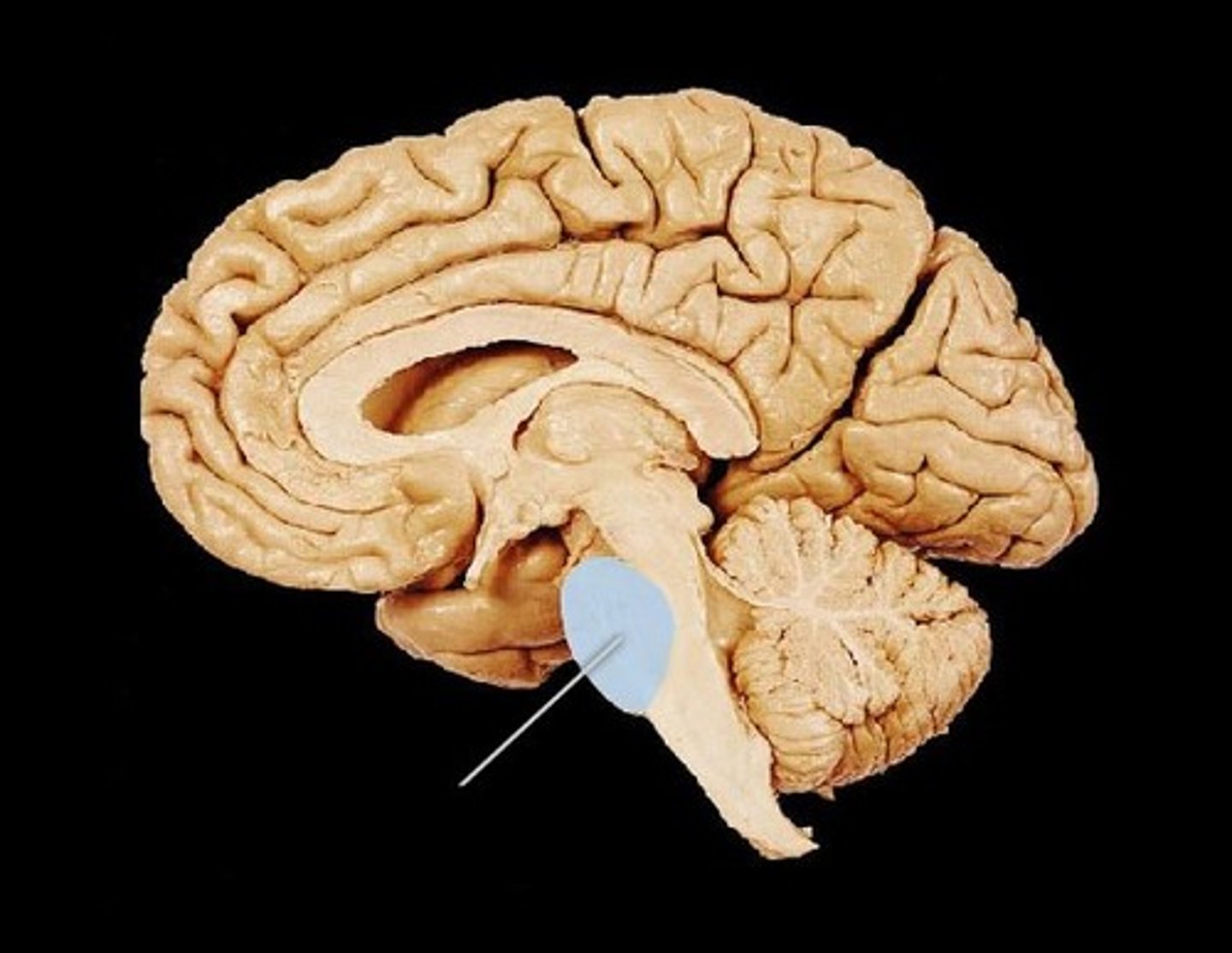
Retrograde Amnesia
The inability to recall memories, events, or information acquired before a brain injury, disease, or psychological trauma.
Anterograde Amnesia
The neurological condition where a person cannot form new memories after a specific event, while memories before the event remain intact.
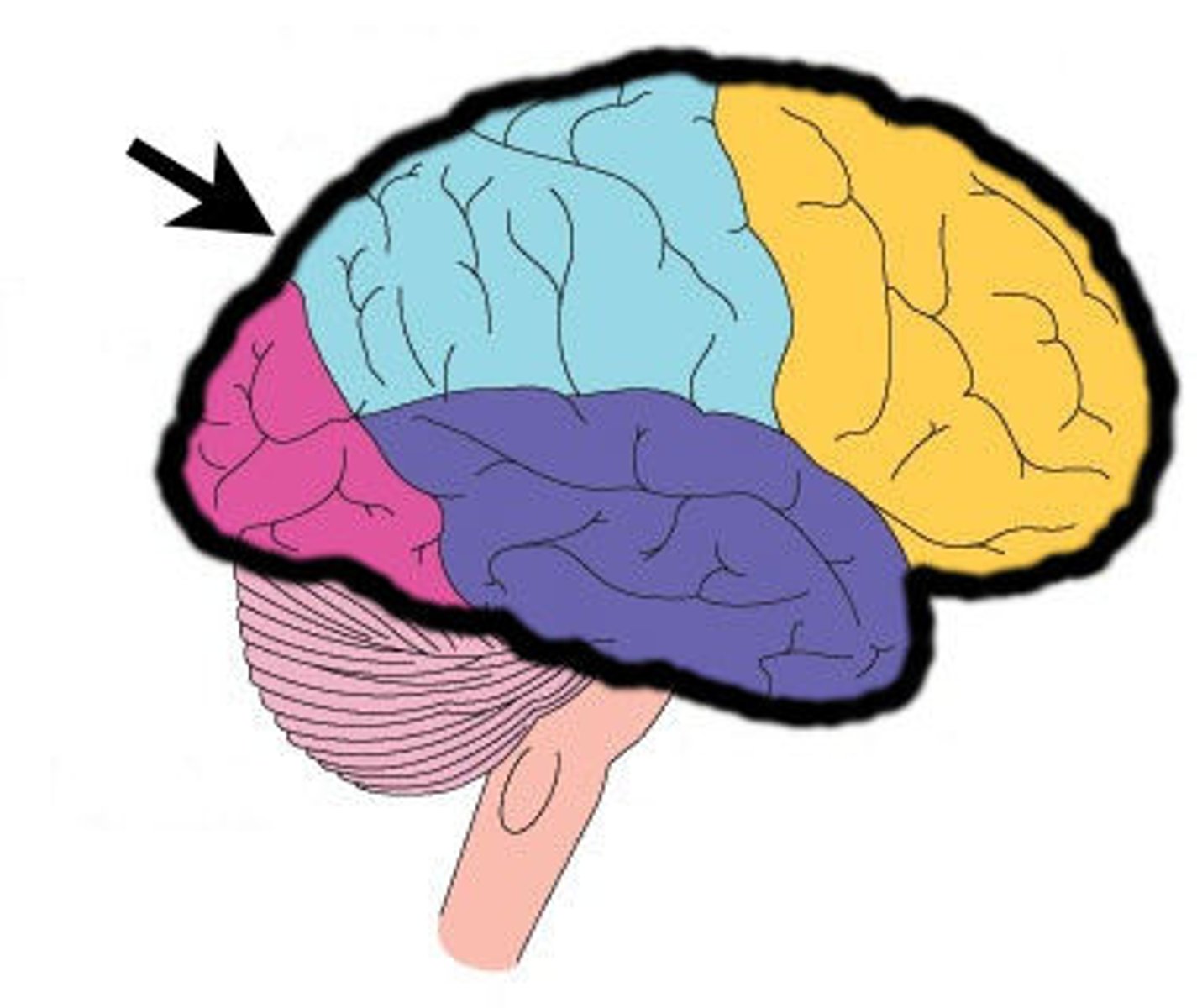
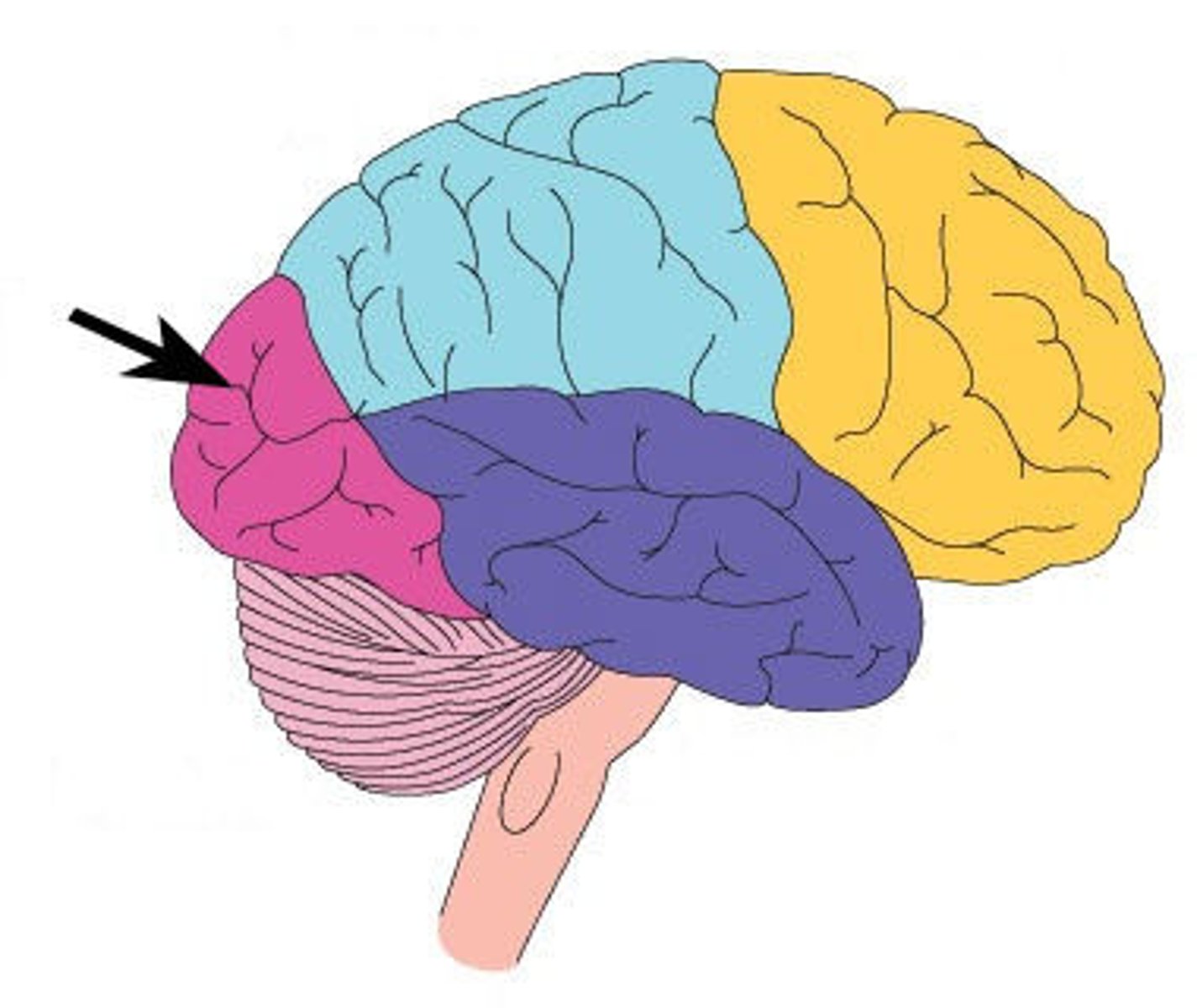
Frontal Lobe
-High-level executive functions.
-Planning, organizing, problem-solving, decision-making, emotional control.
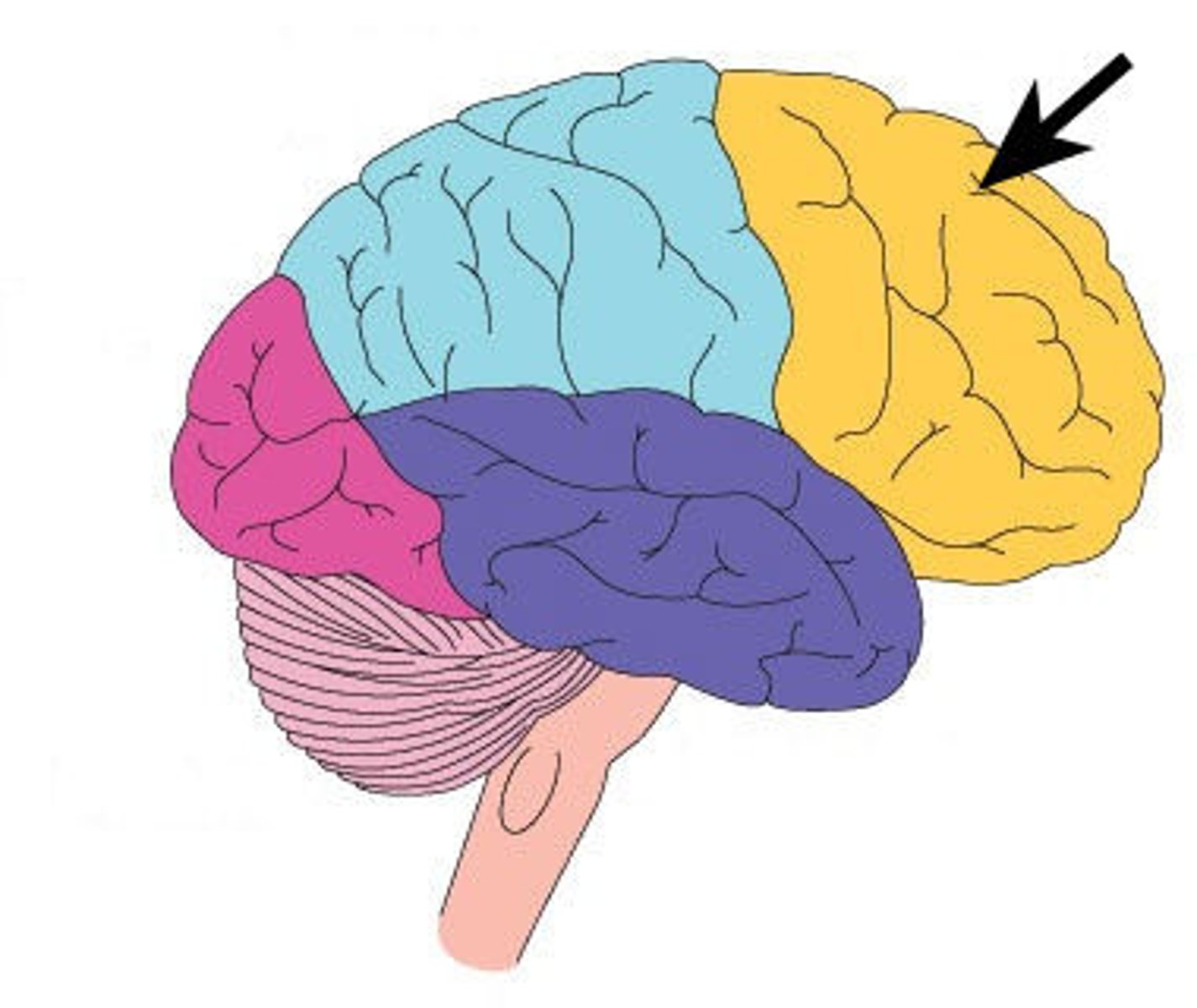
Parietal Lobe
-Processes sensory information like touch, pain, temperature, and pressure.
-Integrates sensory input (vision, hearing, touch).
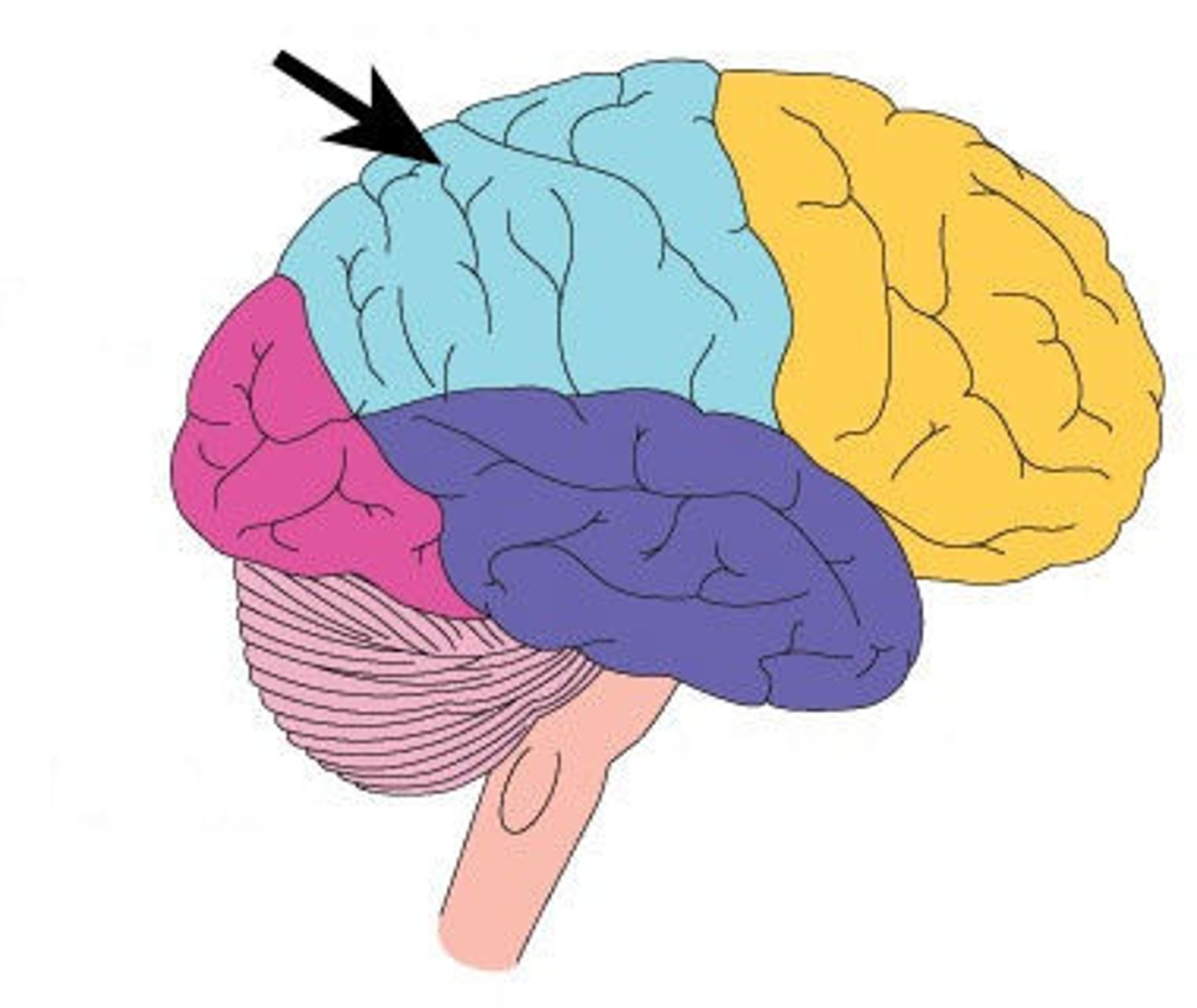
Temporal Lobe
Processes auditory information, language comprehension, and formation of long-term memories.
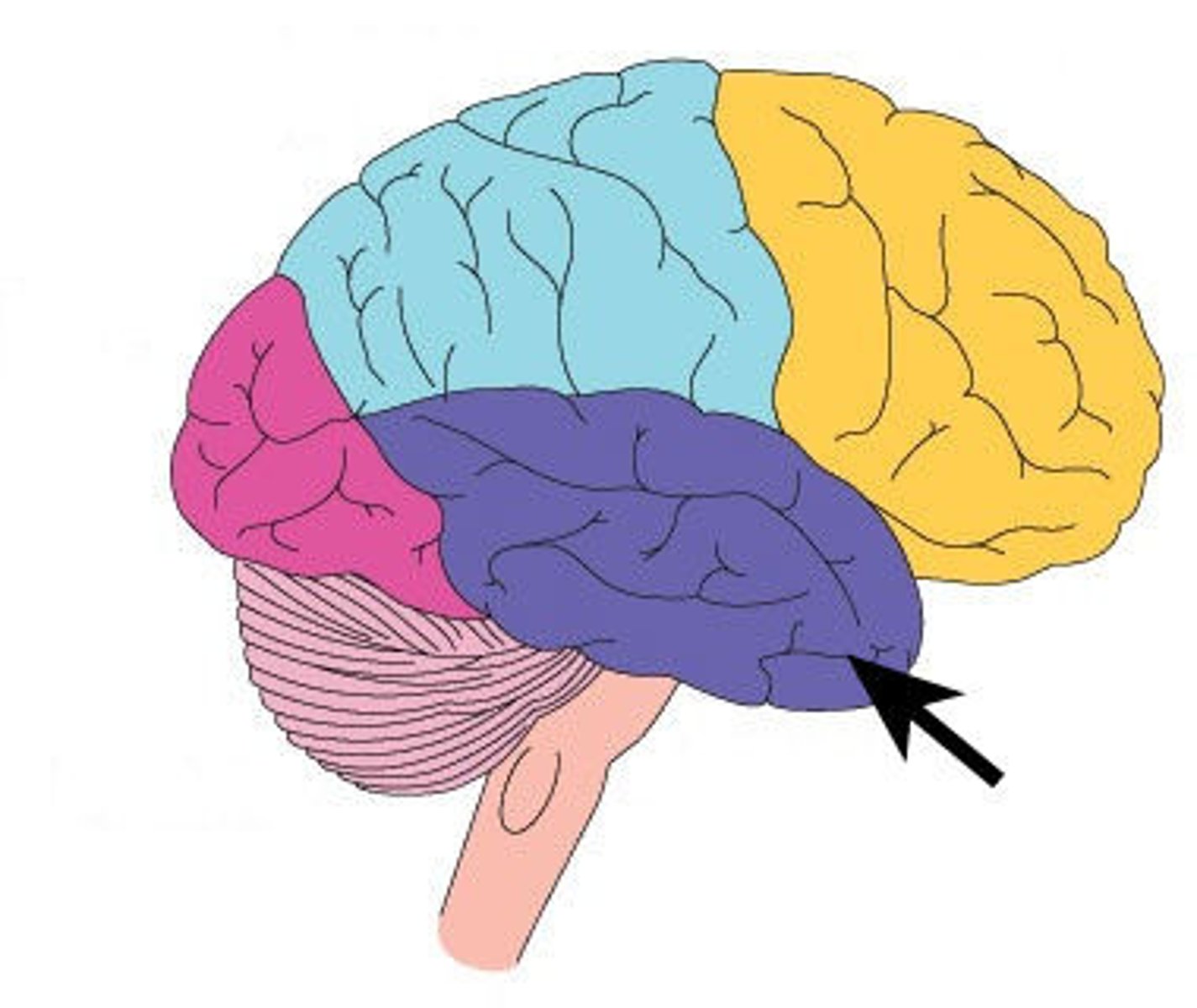
Occipital Lobe
Primary visual processing center responsible for interpreting visual stimuli.
Somatosensory Cortex
-Processes sensory input.
-If a body area is more sensitive, a larger part of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to it.
Broca's Area
Language production (frontal lobe)
Wernicke's Area
Speech comprehension (temporal lobe)
Aphasia
-The loss of ability to use of understand speech/language.
-Broca's: halting speech, repeating words/phrases, disordered grammar/syntax, comprehension intact
-Wernicke's: fluent speech, little repetition, adequate grammar/syntax, comprehension not intact
Contralateral Organization
The left hemisphere controls the right side of the body and vice versa.
Split Brain
-The corpus callosum is cut in surgery.
-Left hemisphere dominant for language and right hemisphere dominant for spatial tasks.
-Picture on left visual field (right hemisphere) cannot be named as it is non-verbal, but can be selected by left hand.
-Picture on right visual field (left hemisphere) can be named.
Neuron
Cell that specializes in receiving and transmitting information.
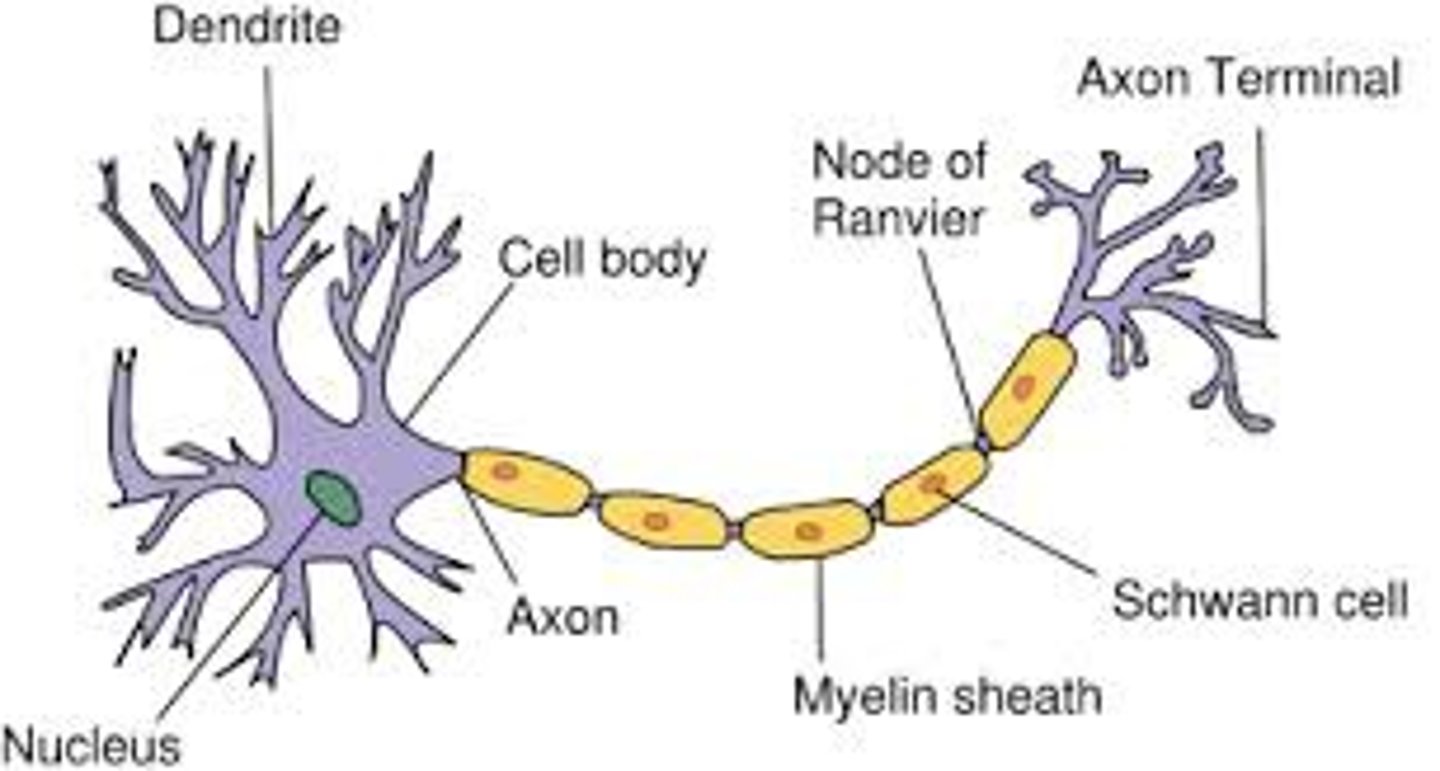
Parts of a Neuron
-Cell Body: coordinations information-processing tasks and includes nucleus
-Dendrites: receive information from other neurons and relays it to the cell body
-Axon: carries information to other neurons, muscles, or glands
-Synapse: region between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another
-Myelin Sheath: fatty sheath that insulates axons resulting in increased speed/efficiency of neural communication
Resting Potential
-Outside is (+) charged by (Na+, Cl-)
-Inside is (-) charged by (K+, A-)
-Resting potential = -70mV
Action Potential
An electrical signal that is conducted along the length of a neuron's axon to a synapse (all-or-nothing).
Depolarization
When stimulated, sodium channels open and Na+ ions rush in the cell.
Repolarization
After sodium gates close, K+ ions move out and restore the resting potential.
Synaptic Cleft
When the action potential reaches the synaptic terminals, it causes the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals released that allow neurons to communicate with each other.
Acetylcholine (Ach)
Involved in a number of functions including voluntary motor control.
Dopamine
-Regulates motor behavior, motivation, pleasure, and emotional arousal.
-Degeneration of these neurons is linked to Parkinson's
Serotonin
Involved in regulating sleep, wakefulness, eating behavior
Excitatory Neuron
Increase the likelihood of an action potential by causing the membrane potential to be less negative.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitter
Decrease the likelihood of an action potential by causing the membrane potential to be more negative.
Summation of Postsynaptic Potentials
If the neuron is pushed past the firing threshold (-55mV) then the neuron will initiate an action potential.
Agonist Drug
Increase the action of a neurotransmitter
Antagonist Drug
-Diminishes the function of a neurotransmitter
-Ex: Botox is an Ach antagonist
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Uses magnetic field to produce high-quality images of the brain and it's structure.
fMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
-Used to examine changes in ongoing brain activity by measuring changes in the blood's oxygen levels
-Great for determining location (spatial resolution) but not timing (temporal resolution)
EEG (Electroencephalography)
-Records electrical activity from large populations of simultaneously active neurons.
-Direct measure of neural activity.
-Great for temporal resolution but poor spatial resolution.