Production and costs
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Production
taking resources and turning them into a finished good or service
productivity
the output produced from a certain amount of input
methods of improving productivity
Improve skills and education of workers
Increase specialisation and division of labour
Use new technology to increase output
Reduce wasted resources
short run
the period of time when at least one factor of production is still fixed
long run
the period of time when all factors of production are variable
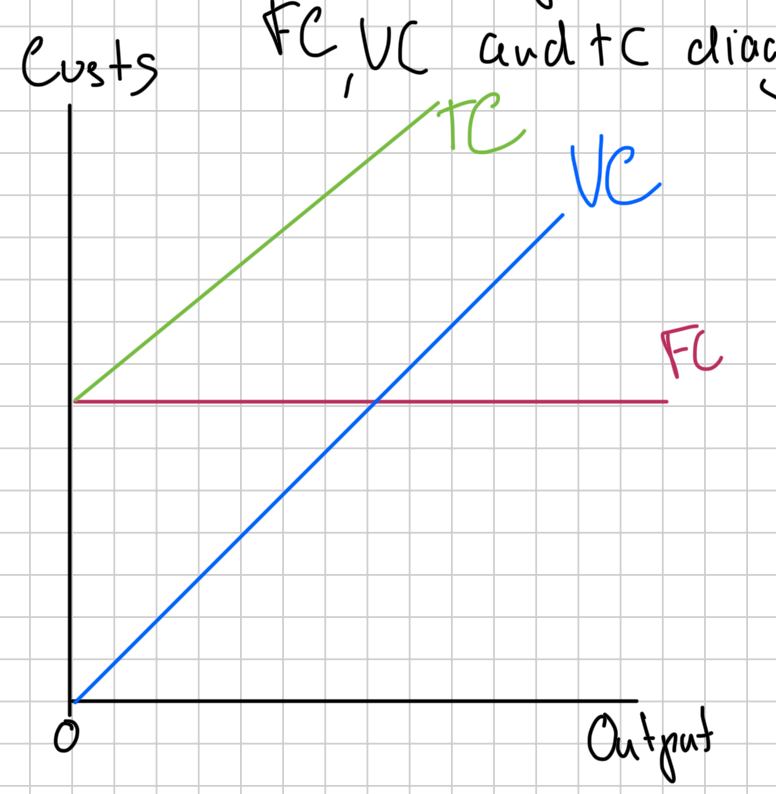
variable costs
costs that change as output changes
fixed costs
costs that do not change as output changes
total costs
the full amount of costs for a firm
marginal costs
the additional cost of producing one more product
Sales revenue
the money earned from selling products
total sales revenue
the total money from all products sold
average sales revenue
money earned per product
marginal revenue
the additional revenue earned from selling one more product
FC, VC and TC diagram
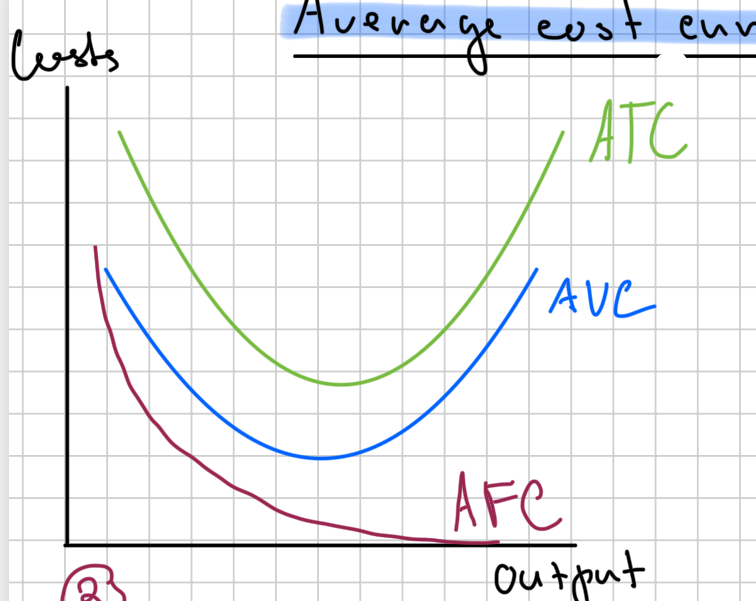
Average cost diagram
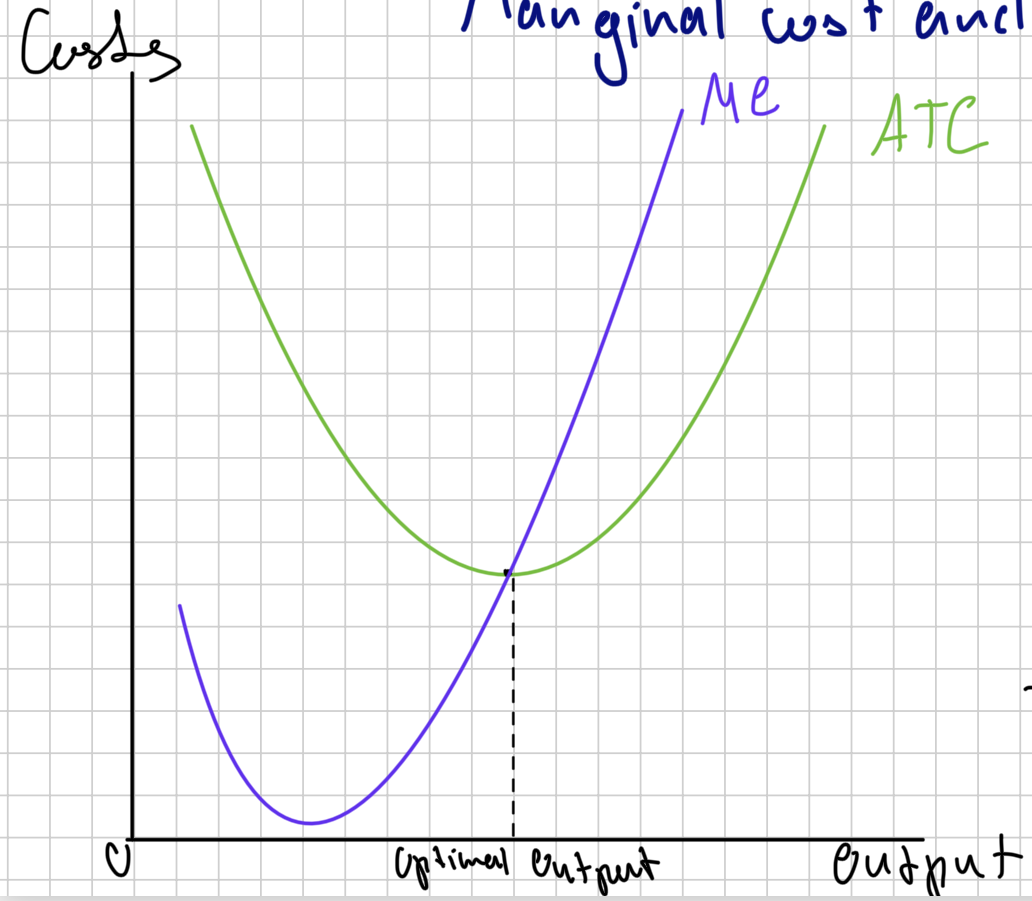
marginal cost and average total cost diagram
profit
the money left once all costs are paid
normal profit
the minimum level of profit an entrepreneur has to earn to keep them running this firm
abnormal profit
any profit earned over and above normal profit
loss
when the total costs of a firm are greater than total revenue
short run shutdown diagram
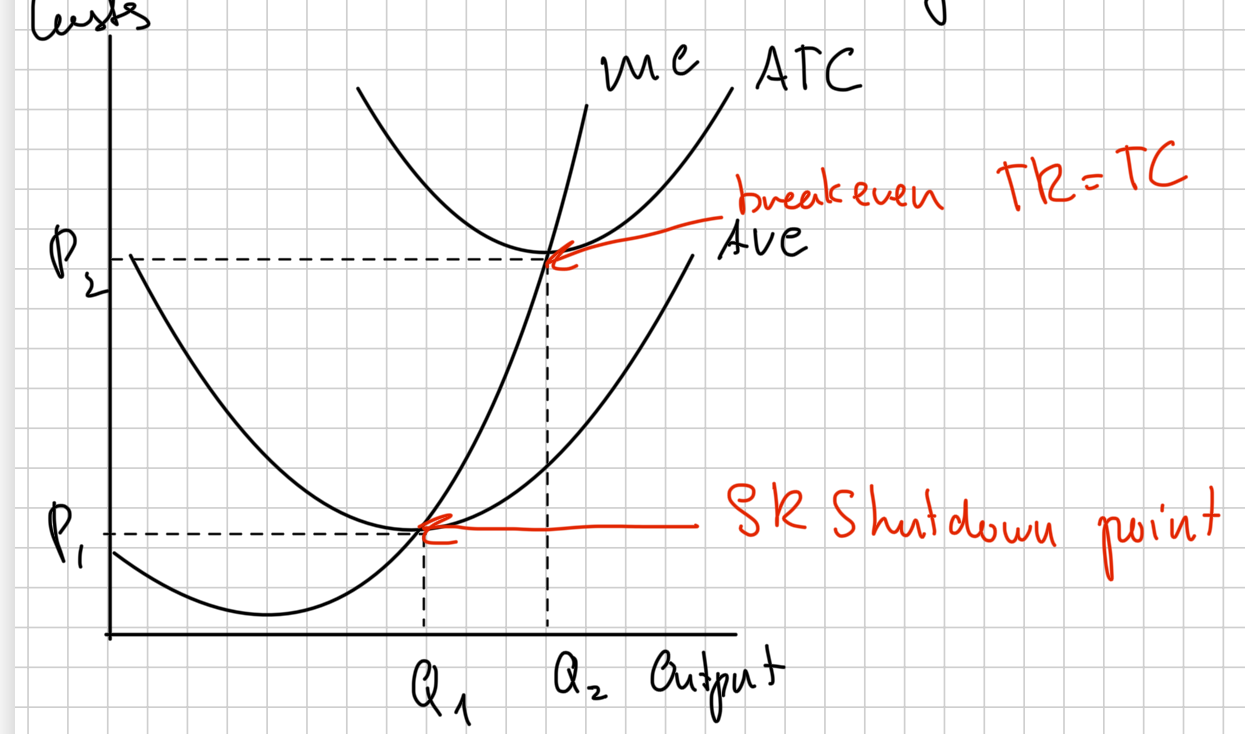
reasons why loss-making firms keep operating in SR (if they cover vc)
the reason for the losses is likely to improve soon by recession
to keep loyal customers
to keep highly trained workers
to avoid the cost of redundancy
if they have reserves of cash they can use to pay costs
machinery in a factory may be damaged if shut down for long
specialisation
using resources for the activity they are best suited to
division of labour
specialisation of each individual worker
2 methods of dividing labour
by product
by process
optimum output
the output where ATC is at its minimum
law of diminishing returns
if you keep increasing one factor in the production of goods (such as your workforce) while keeping all other factors the same, you'll reach a point beyond which additional increases will result in a progressive decline in output.