Chapter 21 Biochem - Prokaryotic transcription
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Gene
the basic physical and functional unit of heredity.
what are chromatins made of
Euchromatin (light color, active genes (being transcribed)
Heterochromatin (dark color, inactive genes)
What is chromatin
DNA plus protein
Histone
The protein that DNA wraps around when being compressed
Nucleosome
Histone proteins + DNA
Linker DNA
between nucleosomes, more vulnerable to degradation.
What does the write function do on a histone tail
adds modification
What does the erase function do on a histone tail
removes modification
What does the read function do on a histone tail
binds to modification to
Three most common modifiers
Acetylation
Methylation
Phosphorylation
Histone Acetylation
An acetyl group is added to a lysine amino acid
in the histone, neutralizing its positive charge. Reduces the negative DNA’s affinity for the
histone. Compacting the DNA
is Histone Acetylation on active or inactive
active
Acetyl groups are written by
Histone Acetyl Transferases
Acetyl groups are erased by
Histone DeACetylases
Acetyl reader
bromodomain
Histone Methylation
A methyl group is added to an arginine or lysine amino
acid in the histone
is Histone Methylation work on active or inactive dna
Context dependent
Methyl groups are written by
Histone Methyl
Transferases
Methyl groups are erased by
Histone DeMethylases
Methyl reader domain
chromodomain
Histone Phosphorylation
A phosphate group is added to a serine, threonine, or tyrosine amino acid in the histone. Opens up the DNA by making it more negatively charged. Used for gene repair
is Histone Phosphorylation on active or inactive DNA
active
Phosphate groups are added by
Histone Kinases
Phosphate groups are removed by
Histone Phosphatases
Phosphate reader domain
14-3-3 domain
DNA Methylation
Adds a methyl group to cytosine to deactivate genes
is DNA Methylation active or inactive?
inactive
Promoter
Site where the RNA polymerase and other transcription factors bind – controls when
and how much the gene is expressed
RNA-coding region
Part of the gene that is actually transcribed into RNA.
Terminator
Site where transcription finishes
Upstream
towards the promoter
Downstream
towards the terminator
Transcription Factor
Binds the promoter, basic machinery needed for RNA polymerase to bind
TATA box
consensus sequence recognized by transcription factors
Transcriptional activators and co-activators
Bind Promoters and Enhancers. Activators stimulate transcription but are not required like
Transcription Factors.
Transcriptional Repressors
Binds to silencers
Enhancer
DNA sequence stimulating transcription from a distance away from promoter
Insulator
DNA sequence that blocks or insulates the effect of enhancers
Mediators
Scaffolding proteins that hold the complex together
TFIID
recognizes TATA box
TFIIH
Helicase
activity aids
in creating
transcription
bubble
The Lac (lactose) operon structural genes (prok)
lacZ, lacY, and lacA
The Lac (lactose) operon regulatory genes (prok)
lacI
The Lac (lactose) operon regulatory elements (prok)
lacO and lacP
The LacZ gene encodes β-galactosidase
Enzyme converts
disaccharide lactose to monosaccharides glucose and
galactose.
The LacY gene encodes permease
which transports lactose into the bacterial cell
The LacA gene encodes the enzyme transacetylase
its exact function is unknown, but it may be involved in removal of toxic by-products of lactose digestion from the cell
repression loop
Binding of repressor to operators O1 & O3 or O2 & O3
what does a repression loop do
Prevents RNA polymerase access to the promoter
• Represses transcription of the structural genes
When lactose binds an allosteric site on the repressor
it loses the ability to bind the operator and repress
transcription
if no lactose is present with lac operon
Enzymes not needed expression of
genes encoding enzymes repressed.
if lactose is present with lac operon
Indirectly induces activation of
genes by binding repressor.
if all lactose is metabolized with lac operon
none available to bind to
repressor—transcription repressed.
Activator
exerts positive control over lac operon
What does cap do
binds to a cap binding site and facilitates transcription
What happens to CAP if high levels of glucose are present
Diminishes expression of operon when glucose is
present
What does cAMP do
helps bind CAP to a promoter
what type of relationship does glucose and cAMP have
inverse
Low lactose, low glucose
No expression
Low lactose, high glucose
No expression
High lactose, high glucose
Some expression
High lactose, low glucose
High expression
what are the three major requirements for transcription
DNA template, raw materials, and a transcription aperatace
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme that directs the synthesis of RNA using DNA template
promotor
Specific D NA sequences in the 5′ region upstream of the
initial transcription point.
RNA polymerase σ factor
responsible for promoter recognition.
Cis-acting DNA elements
elements are adjacent parts of the same DNA molecule.
Trans-acting RNA & protein factors
factors bind to cis-acting DNA elements to influence gene expression
What is the first step of transcription
Initiation
what is initation?
DNA double helix is denatured at the transcription
start site
• The DNA unwound to make the template strand
accessible for RNA polymerase
• Interaction of promoters and RNA polymerase
regulates efficiency of transcription
• RNA polymerase and other DNA binding proteins
often bind to specific consensus sequences
consensus sequences
The average strand that gets bonded to
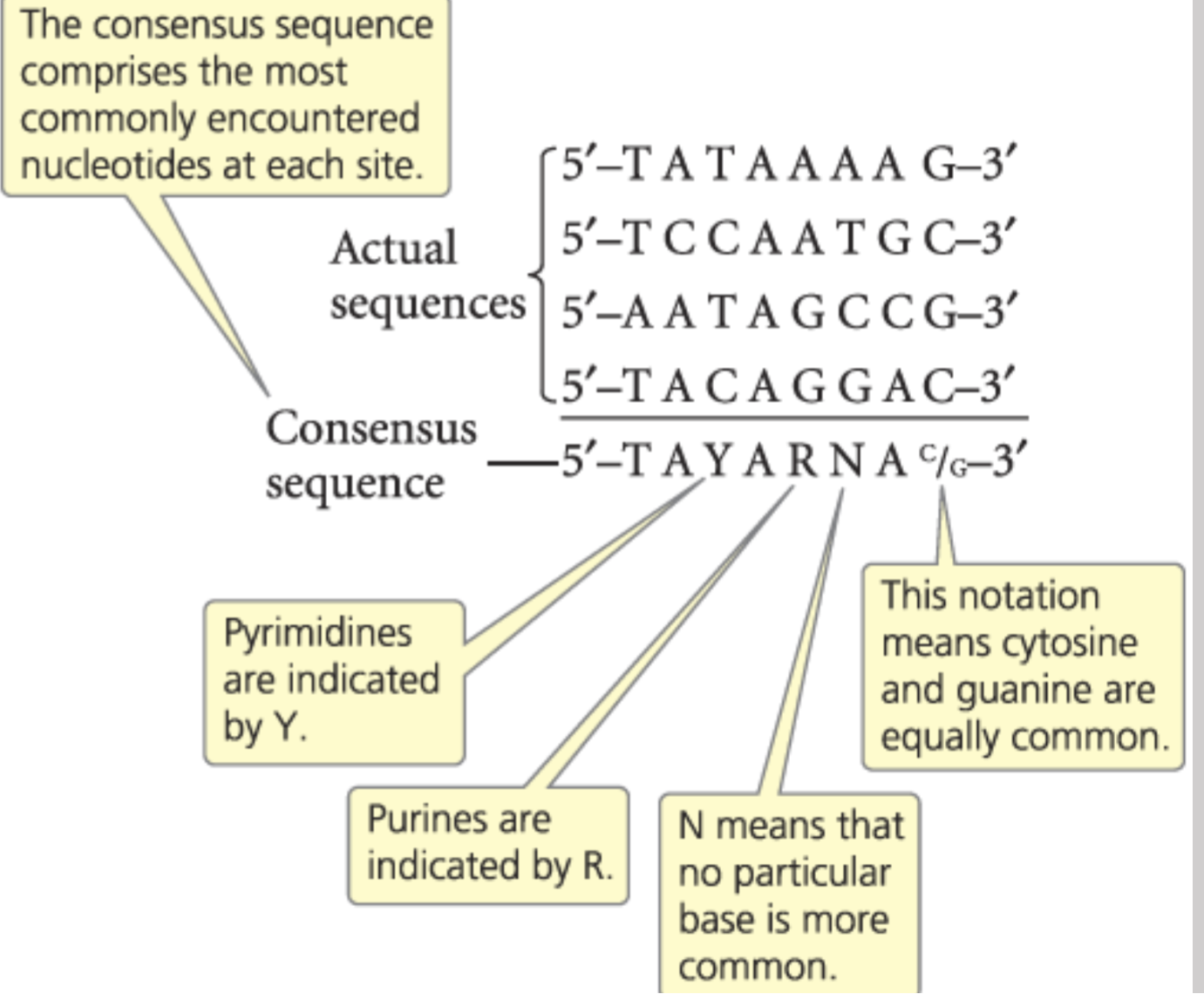
what is step 2 of transcription
elongation
Elongation
σ subunit dissociates from the RNA polymerase
holoenzyme one initiation is complete and
elongation starts
• Elongation proceeds under direction of the core
enzyme
• As mRNA emerges from the RNA polymerase
ribosomes bind to it and begin translation
what is step 3 of transcription
RNA Polymerase traverses the entire gene until a
termination nucleotide sequence is encountered
Intrinsic (Rho Independent)
Hairpin and UA repeats
destabilize the polymerase and cause it to release the
RNA & DNA
Rho Dependent
the Rho protein separates the RNA &
DNA and removes the polymerase
Polycistronic Transcription
Multiple genes are transcribed together