BUSFIN- WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Working capital management
Refers to the set of activities performed by a company to make sure it got enough resources for day-to-day operating expenses while keeping resources invested in a productive way.
Working capital = Current Assets- Current Liabilitites
To measure a company’s short term financial health and ability to cover day to-day operating expenses
Current Assets
Cash, Account Receivable, Inventories
Current Liabilitites
Accounts Payable , Short Term Debt
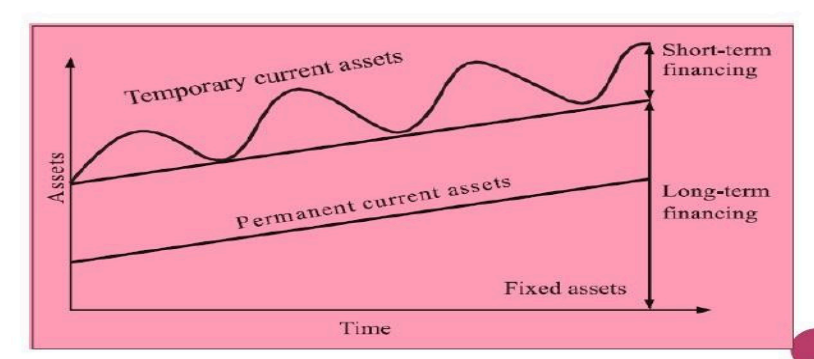
Maturity-matching
Aggressive
Conservative
Three Types of Working Capital Financing Policies Management:
Aggressive Financing
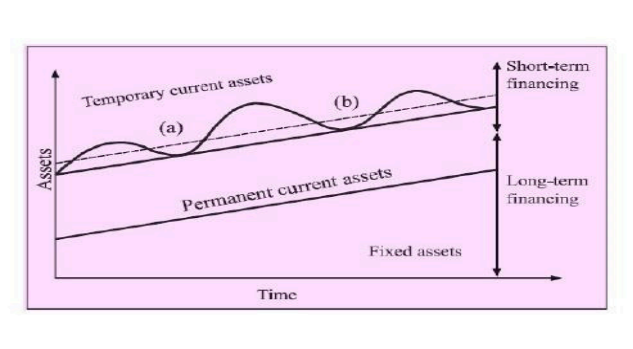
Conservative Approach
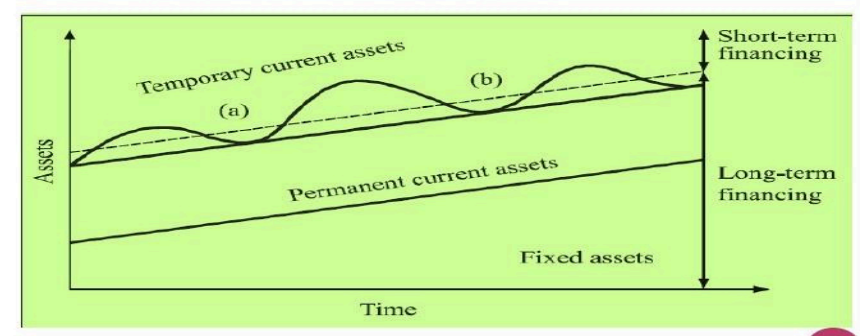
Matching Plan (Hedging Approach)
1) Cash
2)Accounts Receivable
3) Inventories
4)Accounts Payable
Management of Working Capital Accounts
Cash
Is the most liquid assets of a company.
•There must be proper controls over cash that need
•The most vulnerable to theft. to be observed to safeguard the asset.
1.Separate cashiering function from the recording or accounting function.
2.Issuing official receipts for collections and report.
3.Depositing collections
4.Adopting the check voucher system for payments.
Internal Controls over cash
Cash Budget
• for a year. Shows the expected cash receipts and disbursements for an accounting period.
•It can be prepared on a monthly or quarterly basis
It allows management to see if there will be funding requirements or excess cash during a budget period and when these are expected to happen.
Cash Reciepts
Cash Disbursements
Net cash flow for the period
Target cash balance
Cumulative excess cash or funding requirements
Parts of a cash budget
Cash Receipts
(receivables,loans,sharesof stocks and advances to stockholders)
Cash Disbursements
suppliers,service providers,loans and cash dividends
Net cash flow for the period
amount of excess cash or cash deficit for the period
Target cash balance
maintain at all times
Cumulative excess cash or funding requirements
can identify the possible sources of cash
For transaction
Compensating balance purposes
Primary Reasons for Holding Cash
For Transaction
A company needs to pay for the ff. such as purchase inventories, salaries, utility services,loans,dividends, and other transactions affecting the business.
Compensating balance purposes
Having deposit accounts and loans with a bank requiring a minimum amount maintained with the bank.
Precautionary Purposes
Speculative Purposes
Secondary Reasons forHolding Cash
Precautionary Purposes
In case of economic crisis, management want to maintain a higher level of cash emergencies and to serve a buffer for any slowdown in business activities.
Character
Capacity
Collateral
Condition
Capital
FIve C’s of Credit
Character
this refers to the integrity and reputation of the customer.
Capacity
This refers to the ability to pay
Capital
This refers to the amount of capital invested by the owner or into his company.
Collateral
This guarantees provided by the customer to support his exposure with the company.
Condition
Describes the environment where the company operates which may affect the ability of a customer to pay.