BIOL215 Final
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Ecosystem ecology
Study of communities (groups of populations) interactions with their environment (& abiotic factors)
Energy pathway
Flows from one end to another- isn’t “recycled”
Nutrient pathway (general)
Is cycled and recycled throughout communities
How is energy lost from one trophic level to another
heat, respiration
Where does free energy come from
the sun, chemical energy. very little is converted into usable forms
What transforms free energy into usable energy
Autotrophs/primary producers
Primary productivity
rate of capture of energy by ecosystems
Respiration
Oxidation rxn, process of converting carbohydrates into CO2
Photosynthesis
Reduction, CO2 into carbohydrates
How is primary productivity measured
by rate of e capture
kcal/unit area/unit time
watts/m2
biomass promused
biomass
renewable organic material from plants and animals that can be used to generate energy
Relationship between biomass and primary productivity
Biomass is a standing amount, whereas primary productivity is a rate. The biomass of two communities could be the same, while the rate of primary productivity could differ.
Gross primary production GPP
total E fixed by plants per unit time. Some of this energy is used for respiration
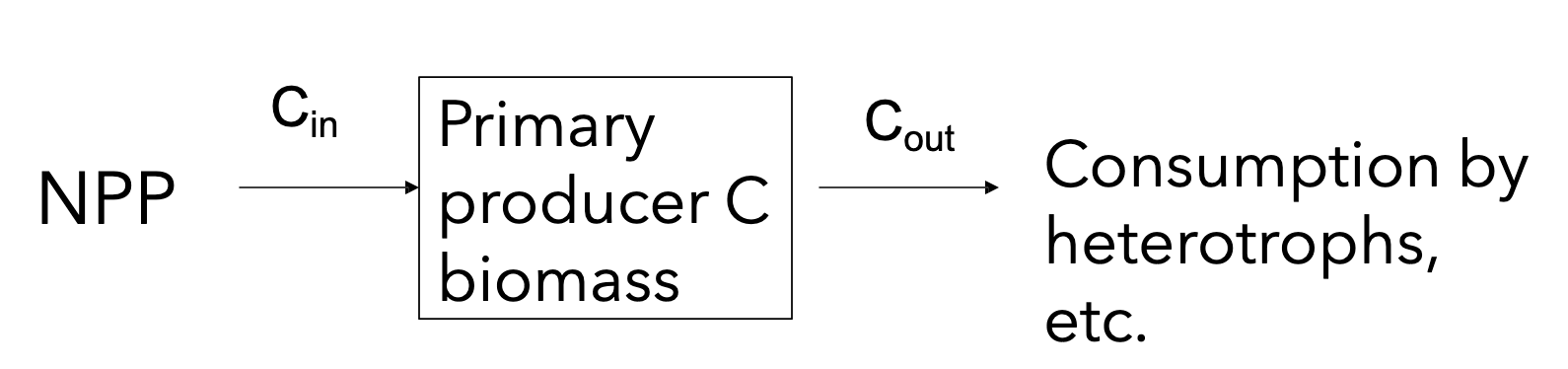
Net primary production (NPP)
Energy fixed by photosynthesis- Energy lost from respiration
Methods of measuring productivity
Harvest method, Gas exchange
Method of measuring productivity over long intervals
Harvest method
Method of measuring productivity over short intervals
Gas exchange
Harvest method
Way of measuring productivity via change in biomass. Equation is (B1-B2)/t
Gas exchange method
Way of measuring productivity, typically in aquatic environments. Equation is (rate of gas production) - (rate of gas consumption)
Difference between calculating GPP v. NPP
GPP= change in biomass + other ways + energy lost to respiration
NPP= change in biomass + other ways
Liebig’s law of the minimum
the rate of any biological process is limited by the factor that is in least amount relative to the organism’s requirement, yield limited by single resource
Evapotranspiration
the amount of water that evaporates off of and is transpired by plants off a landscape, positive rls. between evapotranspiration and NPP
Nutrients limiting ability
Terrestrial: soil fertility can account for some variation in terrestrial fertility, particularly due to the limiting amounts of N and P
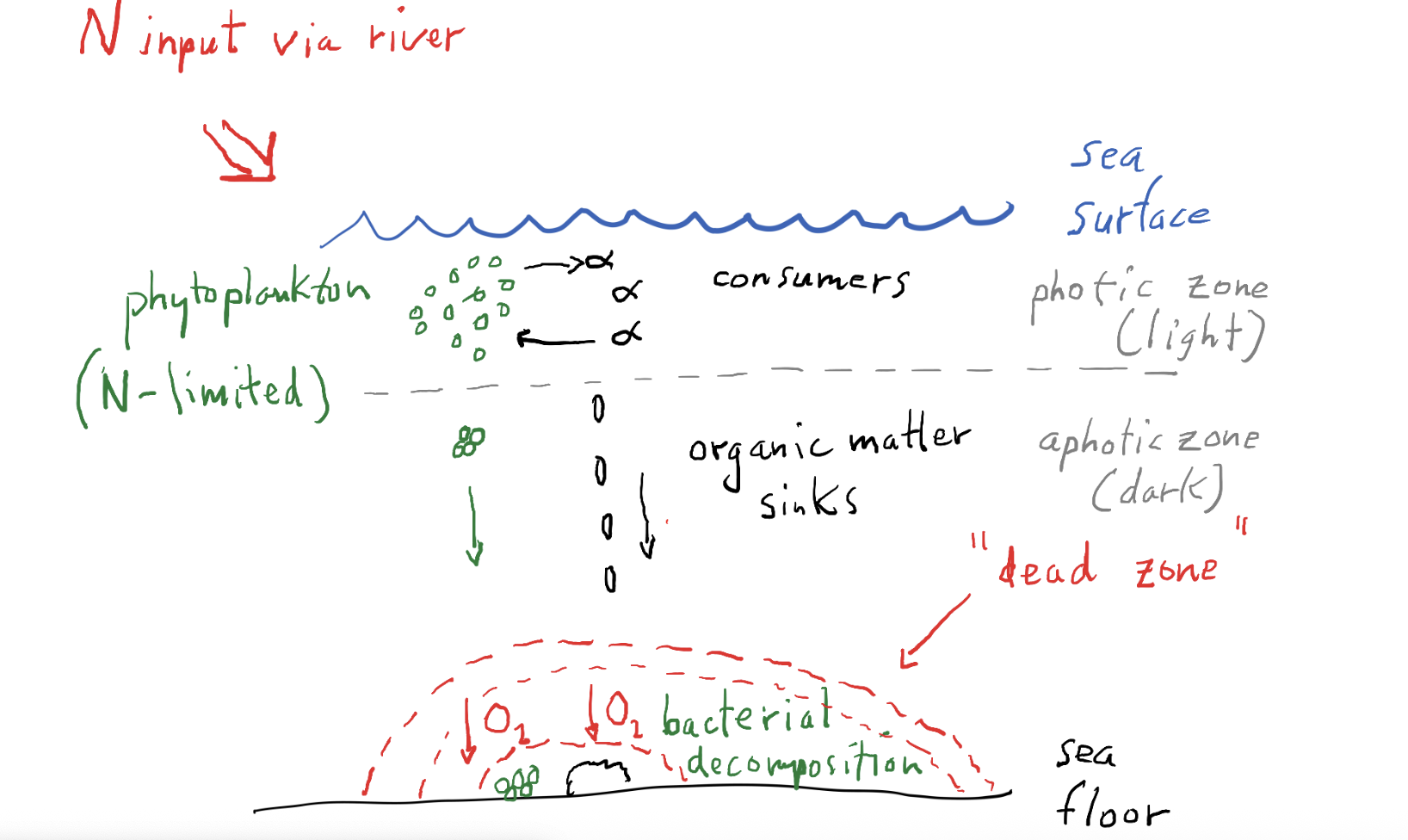
Aquatic: light is NOT the primary limiting factor for NPP, but rather nutrients.
eg. Phytoplankton biomass controlled by P concentration in lakes, in ocean N
Secondary production
the biomass created by consumer organisms (heterotrophs) by consuming other organisms
Detritus pathway
a food chain that begins with dead organic matter (detritus), which is broken down by decomposers like bacteria and fungi. This decomposition process is followed by detritivores (like earthworms and snails) that consume the detritus and decomposers, which are then consumed by predators, completing the flow of energy and nutrients through the ecosystem
Trophic efficiency
= (net productivity at trophic level i + 1)/ (net productivity at trophic level i)
Nutrients
chemical forms of elements used for the growth of all organisms
Chemical forms of N
NO2, NO3, NH4, N2, etc
How can nitrogen forms that are not usable to plants and animals be pumped into the environment
Cycling- plants that fix nitrogen and animals that dispense nitrogen
Where do nutrients used by autotrophs come from
Outside the ecosystem
Through the atmosphere
Earth’s crust
deep ocean
Within the ecosystem
recycling consumers/decomposers
Detrital food chain
detritus going to microbes, microbes eaten by microbivores/detrivores, which are in turn consumed by invertebrates
Factors that affect the rate of decomp
temperature ex) understory detritus in Panama decomposing quicker than in montreal
Reservoir
the amount of a specific material in a certain environment
eg. the amount of N in the atmosphere
Fluxes
the movement of one reservoir to another, measured in units time
Steady state
reservoir size constant and input = output
Mean residence time
mass of material in reservoir/input or output
Non steady state
Reservoir size changes , input or output is greater
Nitrogen fixation
Adds N to the biosphere
Denitrification
Removes N from the atmosphere
2 major reservoirs of N
Atmosphere and Rocks, biosphere cont. much less N than the nature biomes
Oxygen depletion in the aquatic ecosystem (draw)
Carbon cycle greatly affected
by human activity, reservoirs in sedimentary rocks and kerogen
Greenhouse effect
“blanket effect” that warms the earth
source
Adds a gas to the atmosphere, Rtotal/GPP>1
sink
removes a gas from the atmosphere, Rtotal/GPP <1
Net ecosystem production
NEP= GPP- Rtotal
Population ecology
One to two species and how they interact
Community ecology
3 + species, evaluating the value of biodiversity
community
group of all the different living organisms that live and interact in a specific area, typically only the biotic factors
succession
the process of change in ecological communities over time
dispersal & probability of arrival
closer plants will grow
Space-for-time replacement
Looking around at patches of a community that have been more recently disturbed to get a better idea of succession
Primary succession
All biotic factors wiped out. eg. volcano
Factors which affect the rate of primary succession
soil nutrients, precipitation, spread of disaster, faciliation, availability of colonizers
the abiotic environment: nutrient availability soil formation
processes among the initial species can help or hinder primary succession
typical order of succession
shorter shrubs or grasses that need sunlight
quicker growing plants that spread seeds more quickly - those that can float through the air
forensic entomology
Forensic entomologists focus on the types of insects that colonize a dead body, the order in which they appear, and how their life cycles progress over time. can be used to determine time of death among other factors