Diagnostic imaging exam 1 ( chest and abdomen)
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
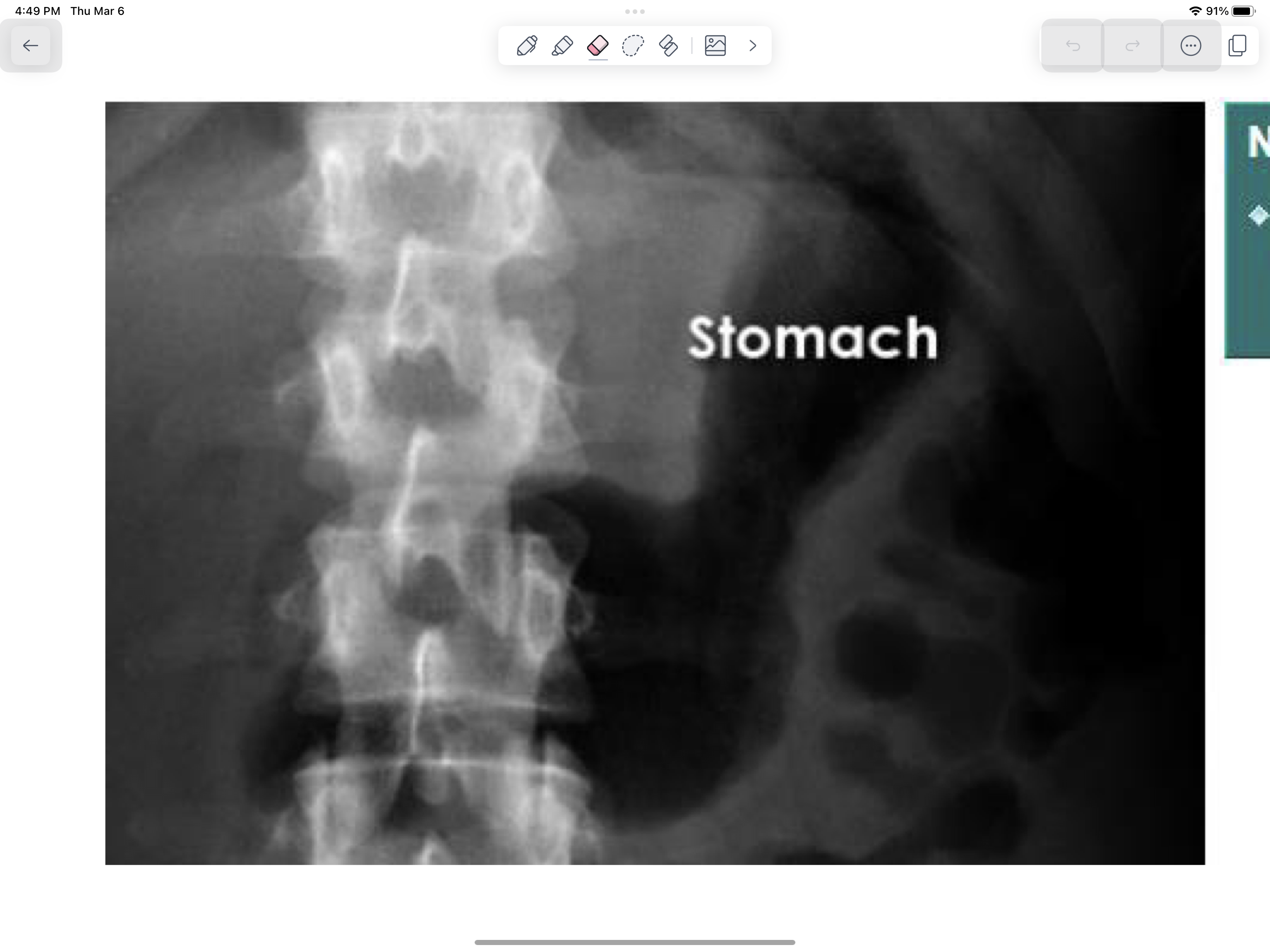
Normal stomach
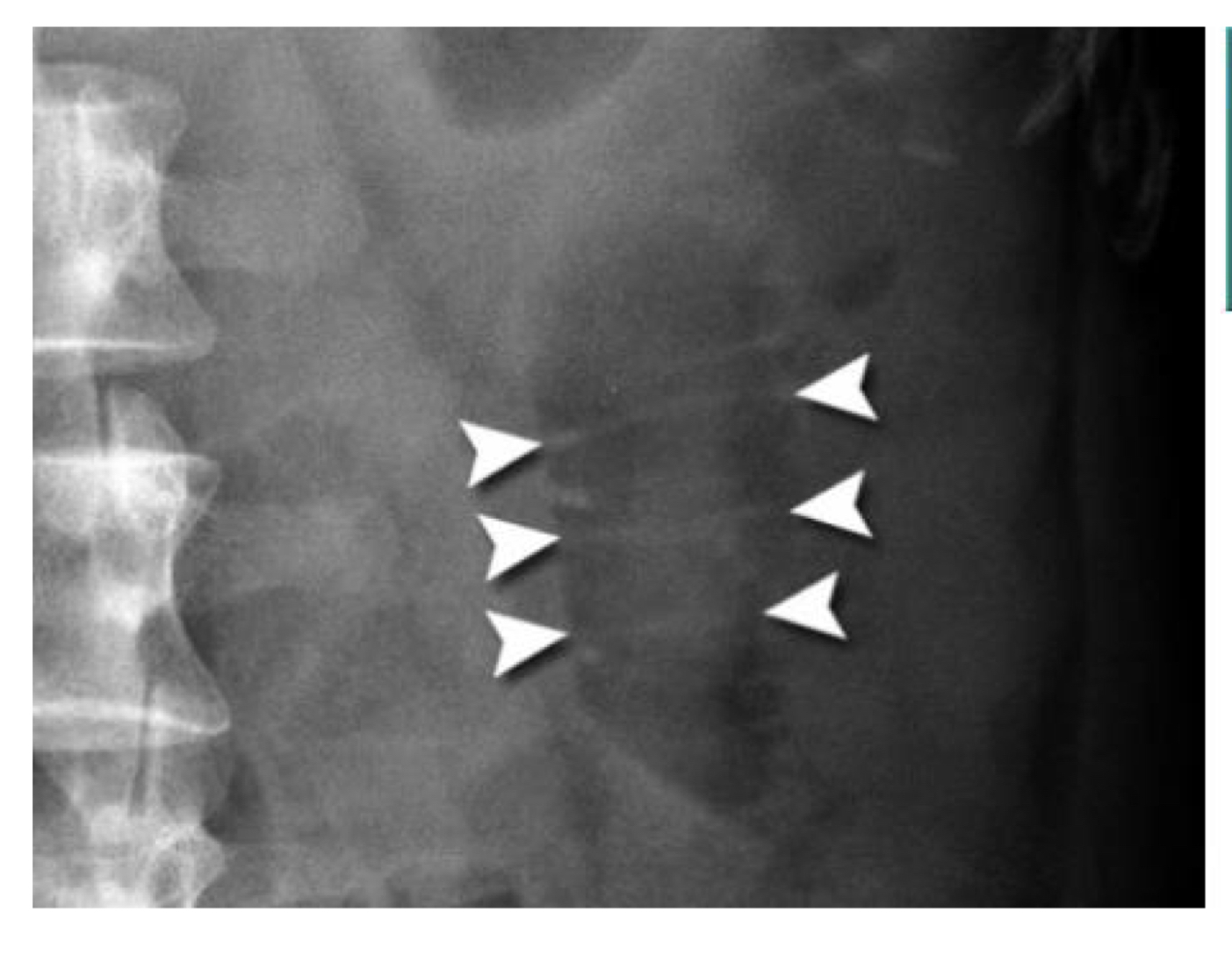
Valvae connivents - bowel gas patterns
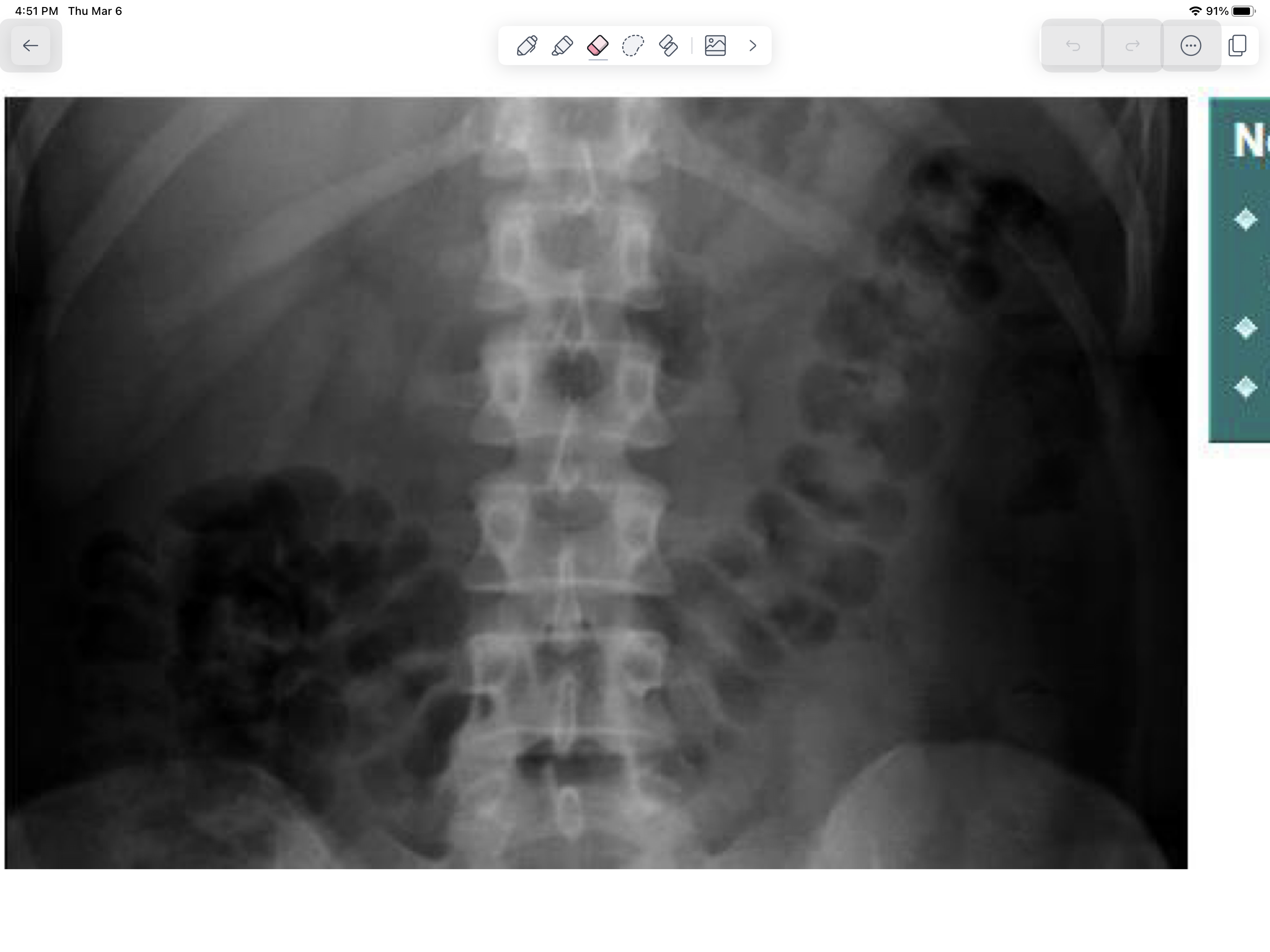
Normal large bowel
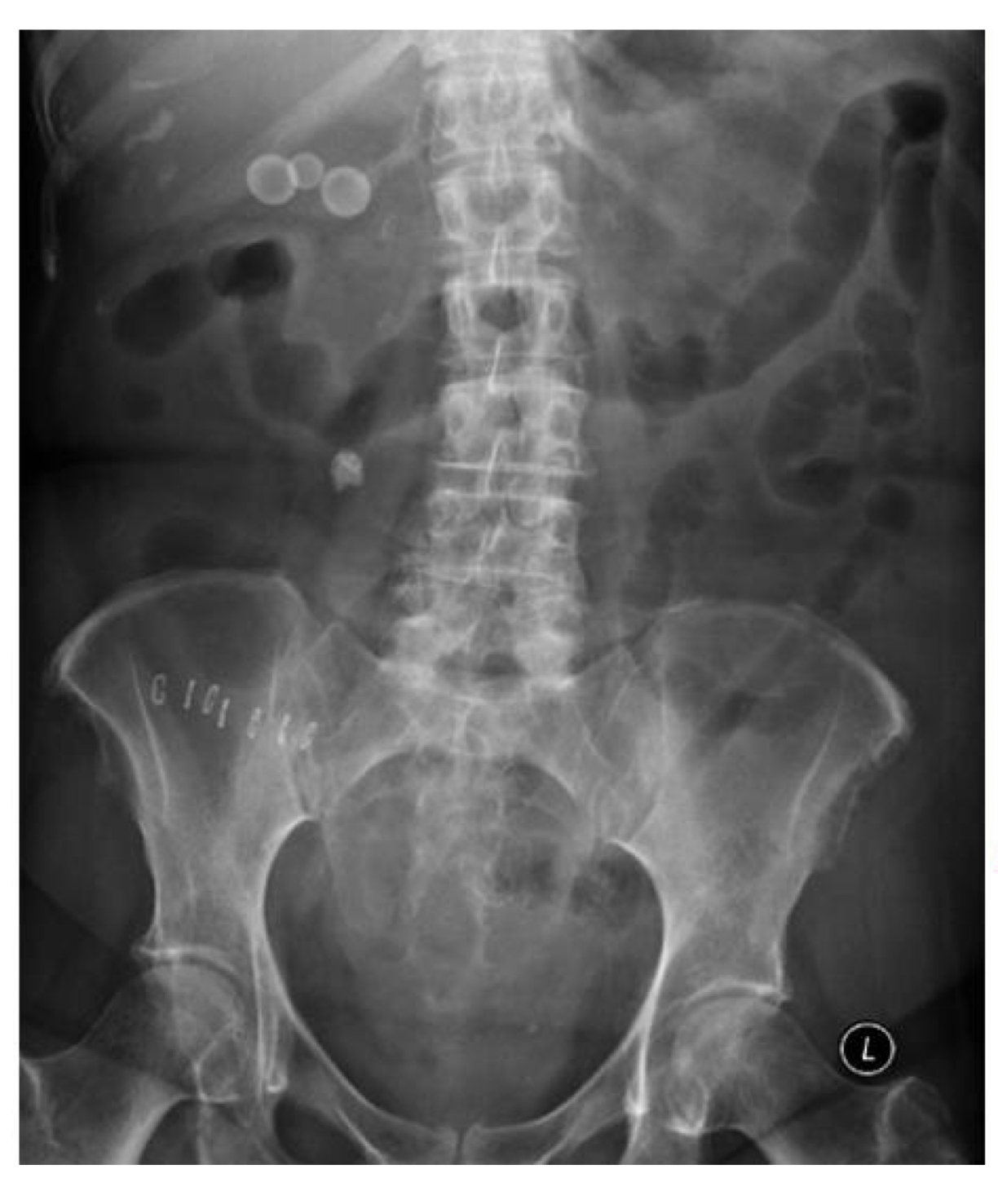
Pt recovering from appendectomy
Calcification
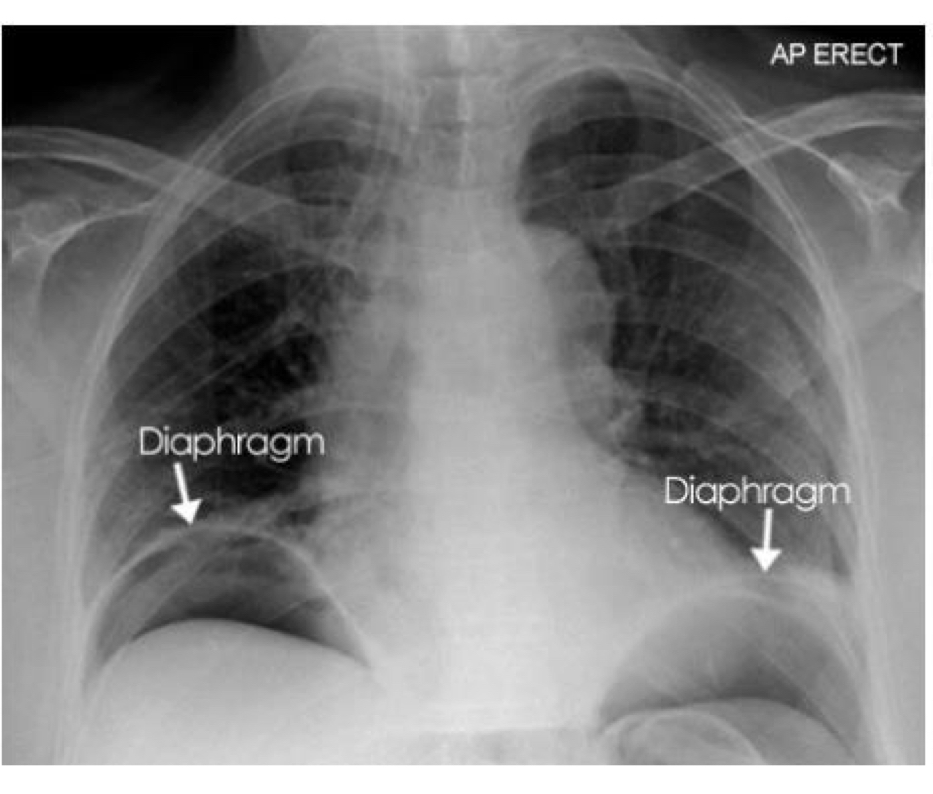
Free air due to duodenal ulcer
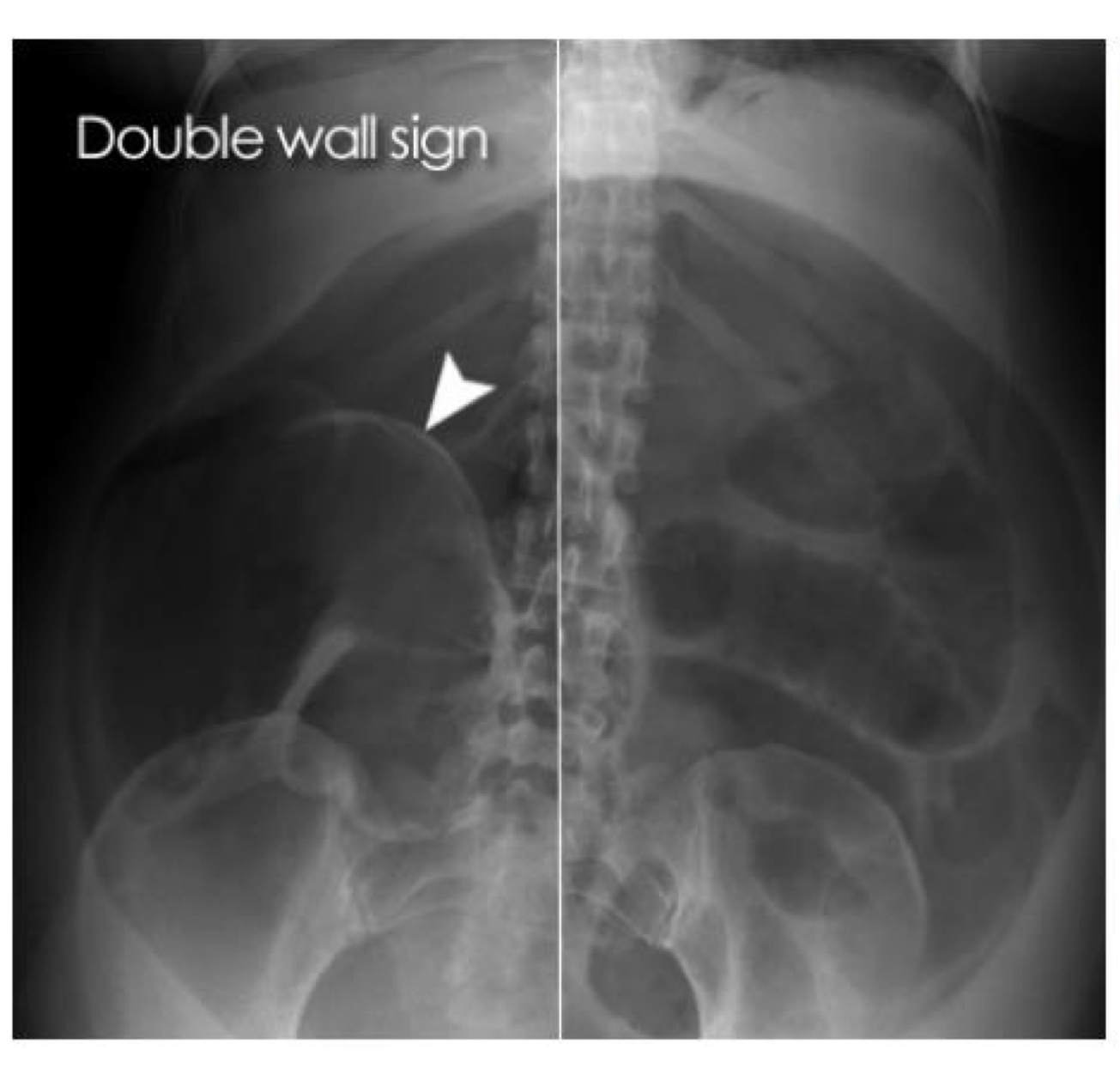
Free air due to perforated bowel
Football sign
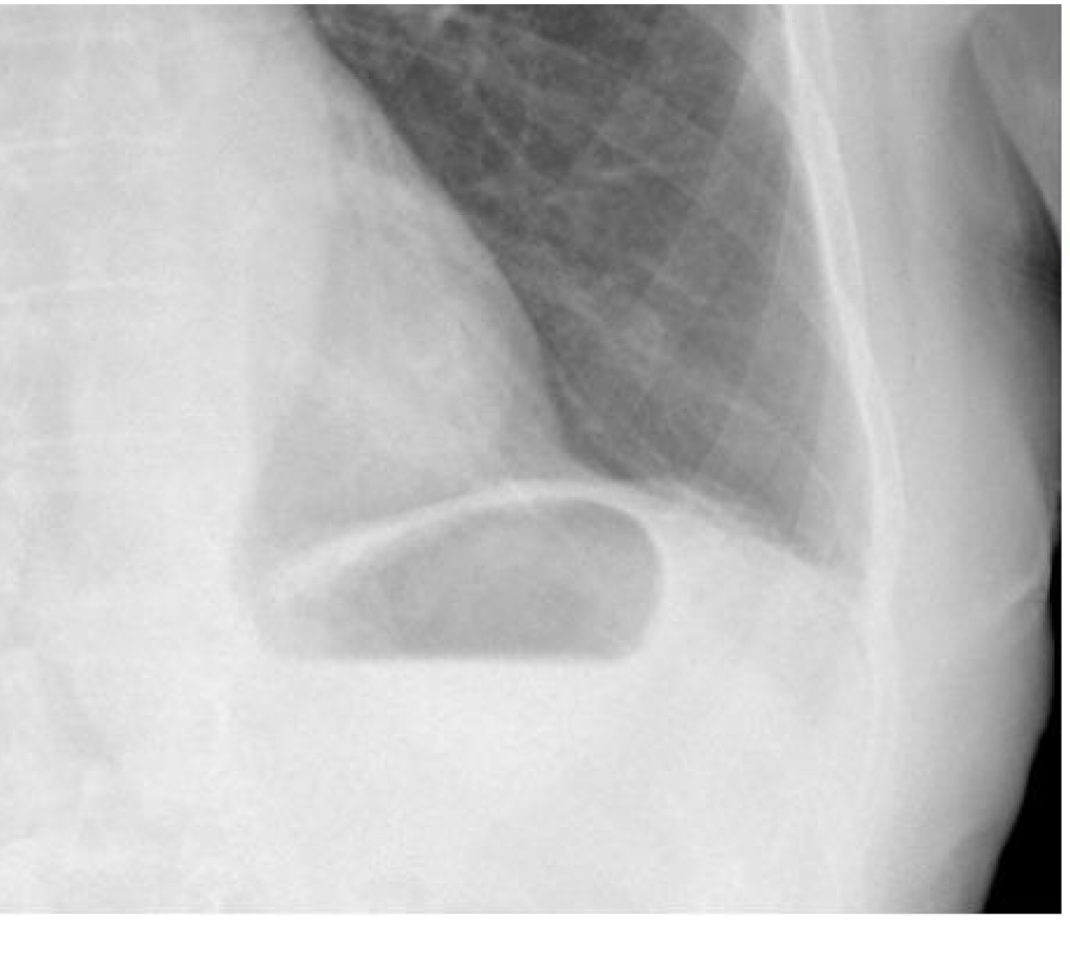
Bubble shape
Thick upper wall
Normal stomach bubble
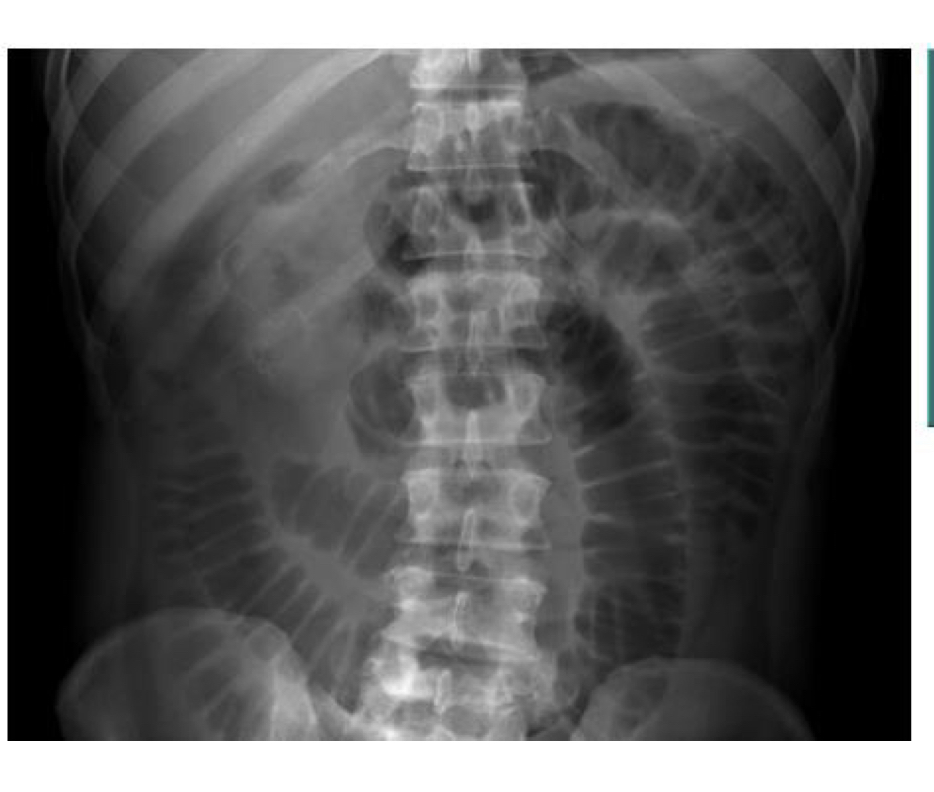
Small bowel obstruction/illeus
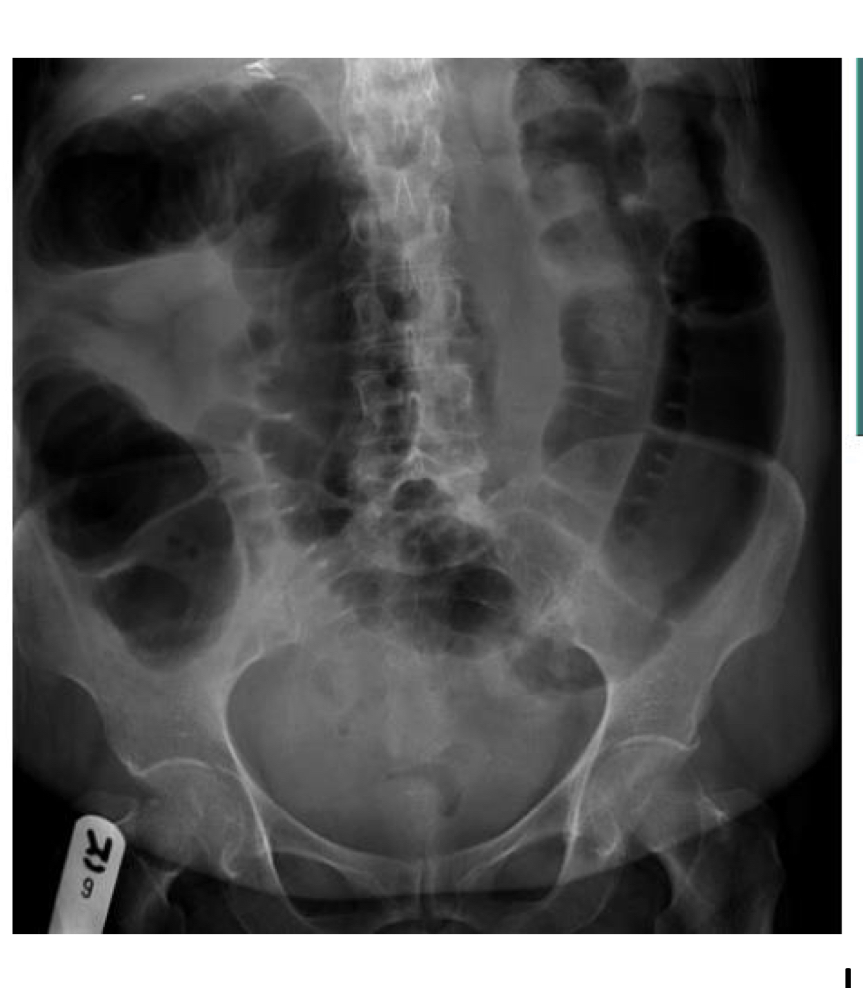
Large bowel obstruction
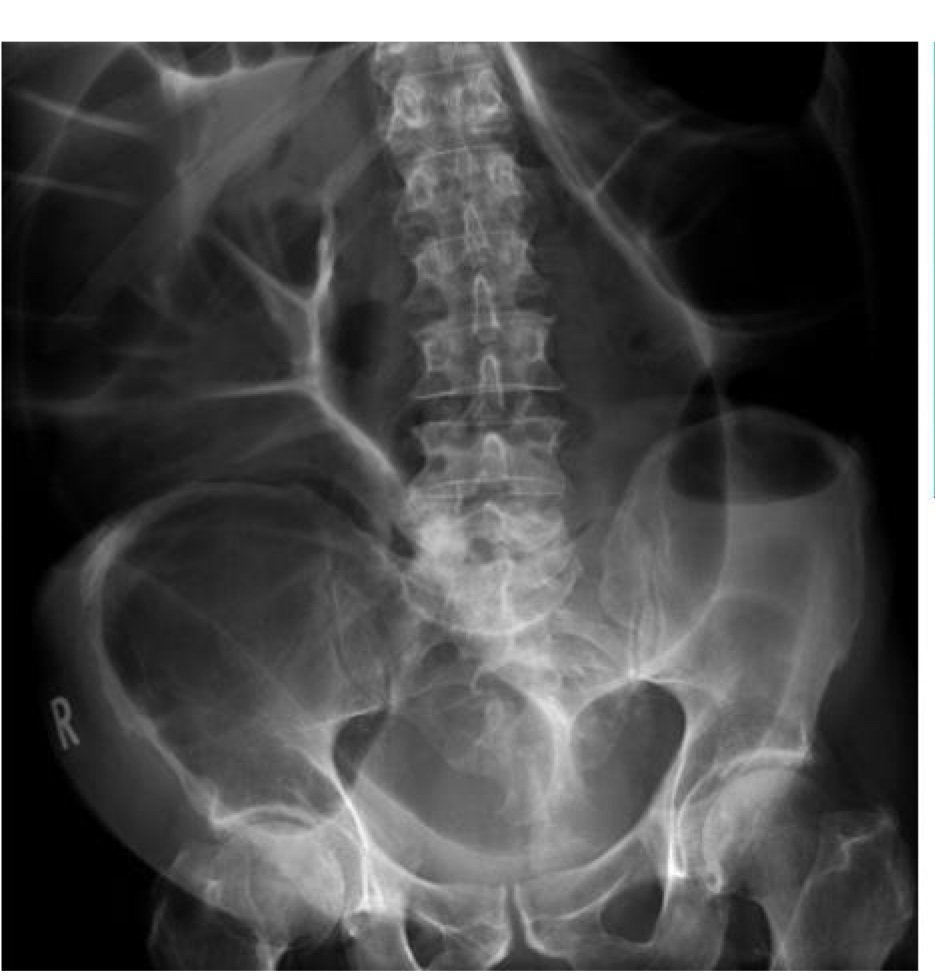
Sigmoid volvulus (coffee bean or bird beak sign)
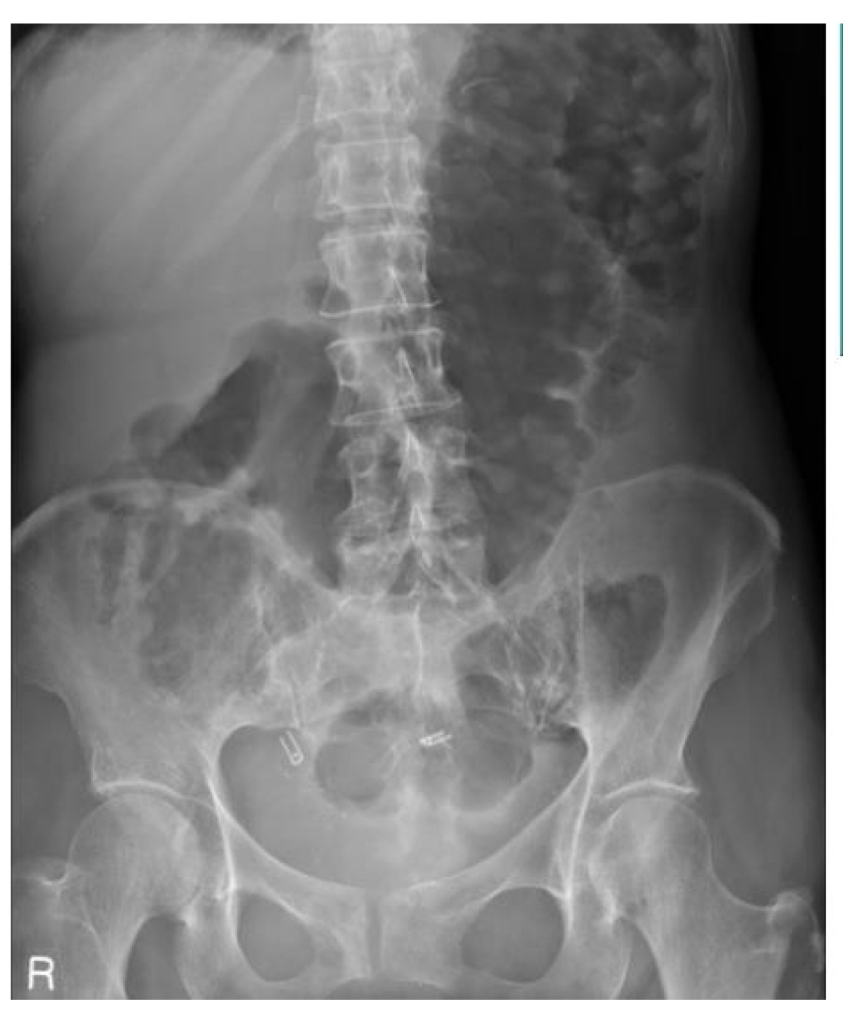
Pt has acute abd pain, sepsis, and hx of ulcerative colitis
evidence of: thumb printing and mucosal islands
abnormal bowel gas fracture:
Bowel wall inflammation - toxic mega colon
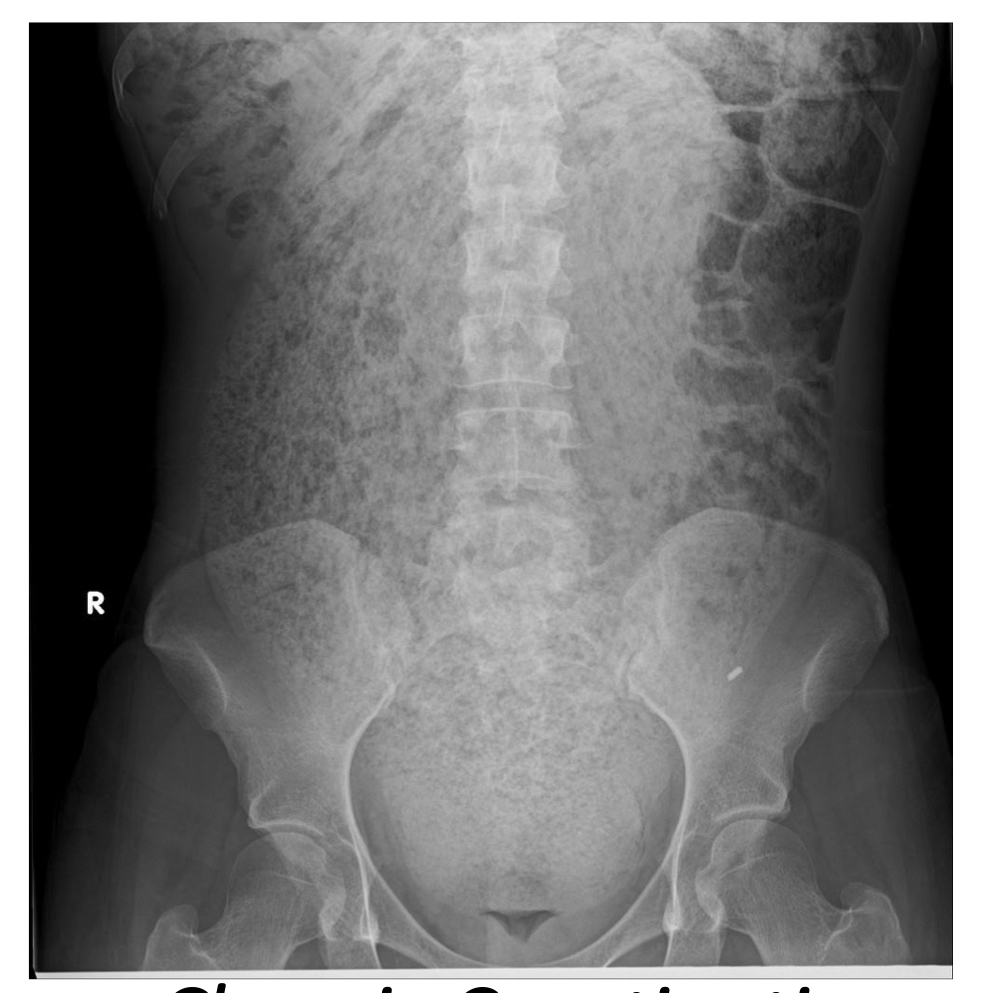
Chronic constipation
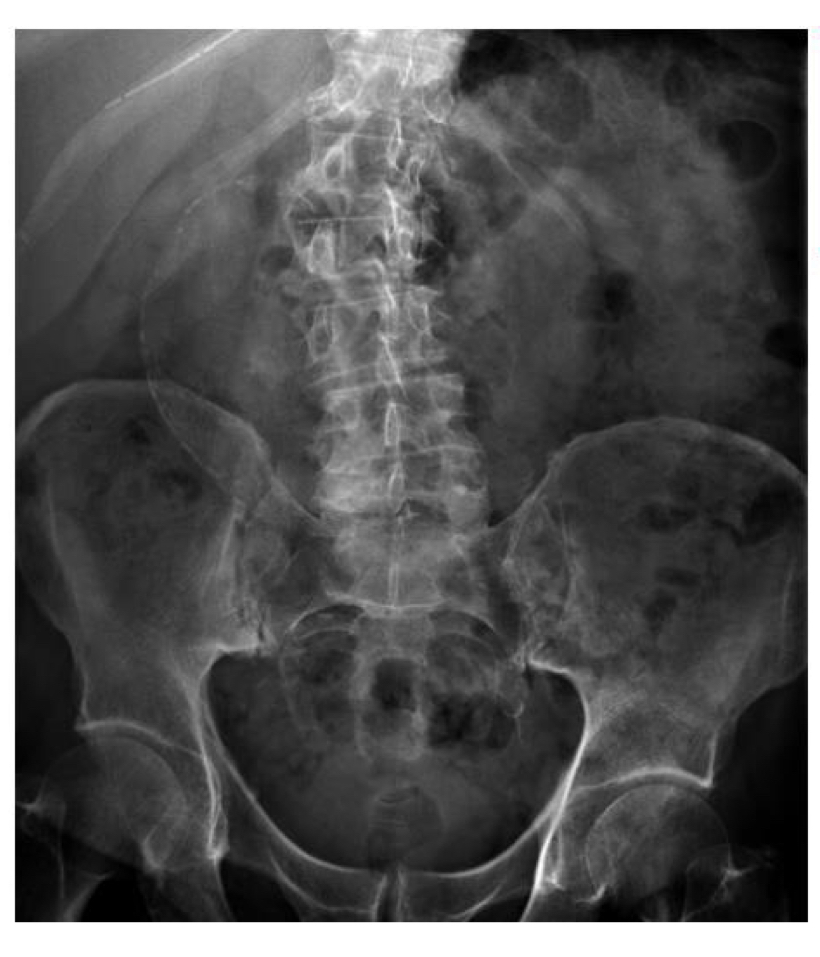
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
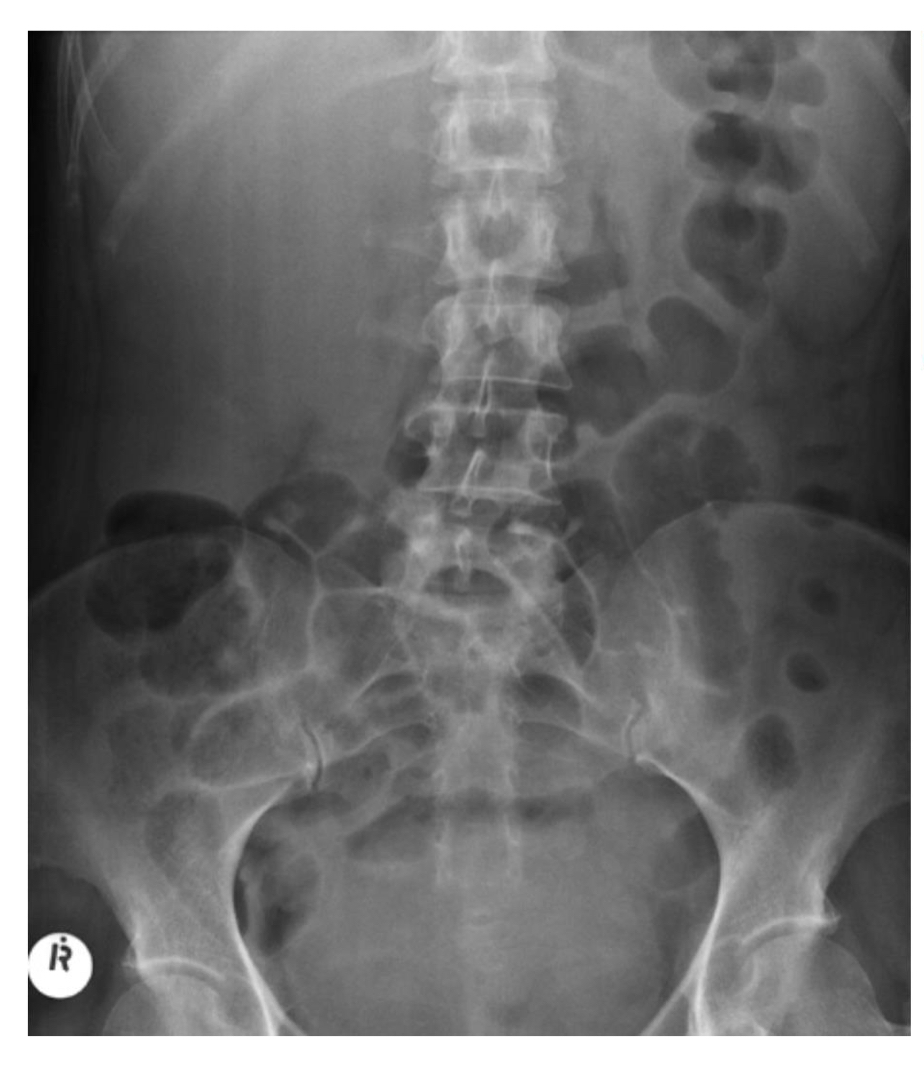
Diffuse soft tissue density shadowing in RUQ
Hepatomegaly
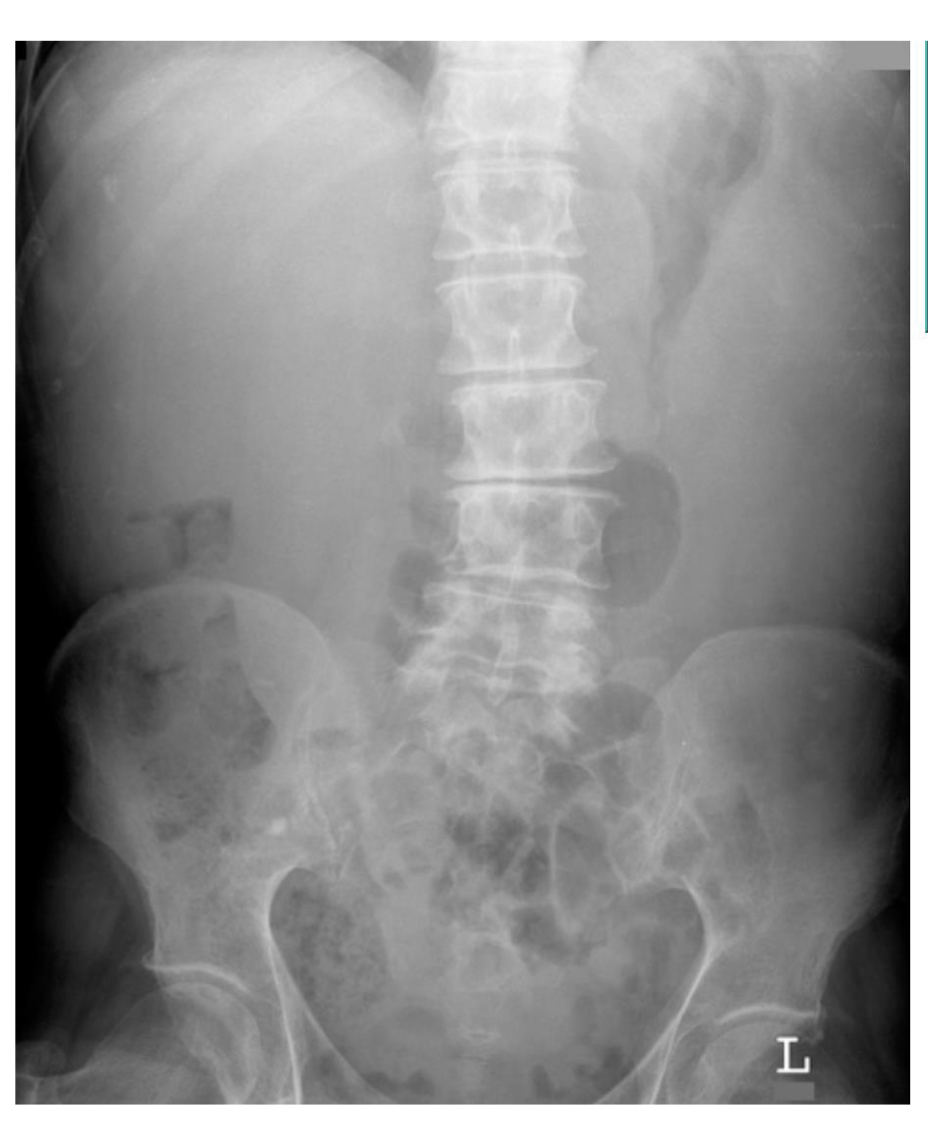
Patient has myeloproliferation disorder
Increase in soft tissue density but bowel appears pushed away by thr edge of the spleen
Splenomegaly
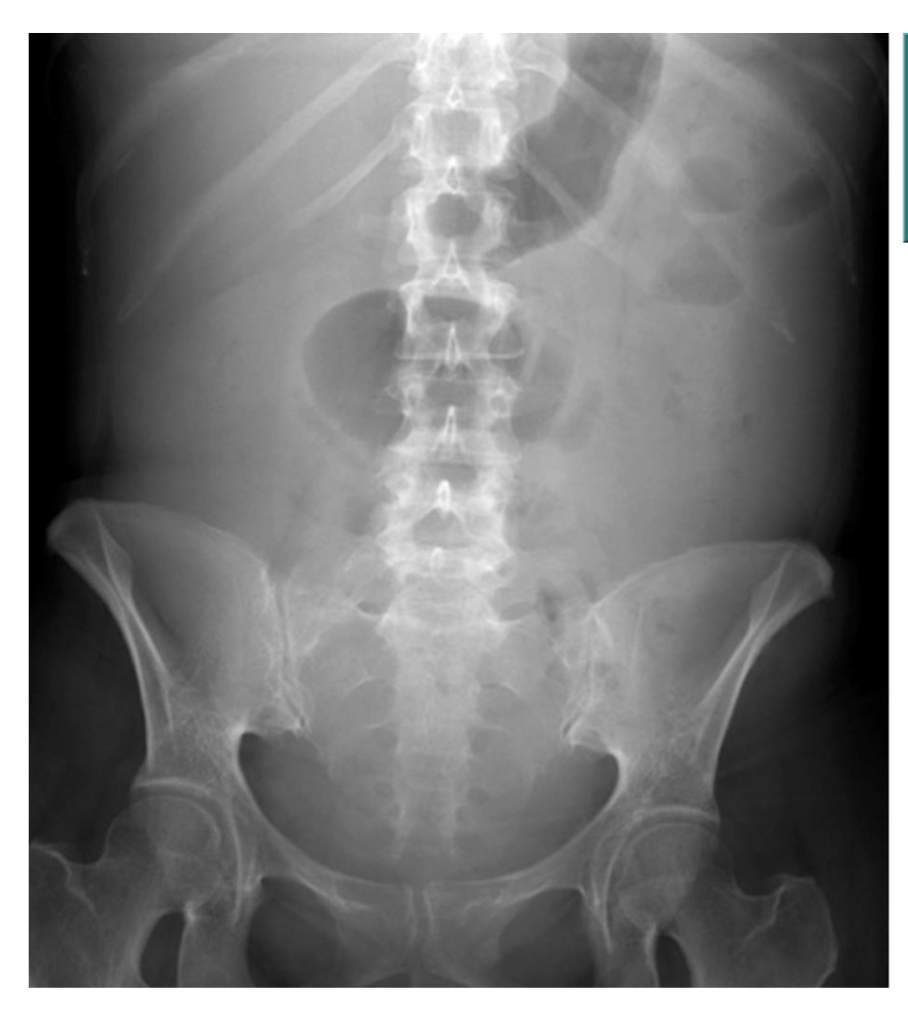
Hazy density of entire abdomen
A loop of gas filled bowel lies centrally in the abdomen
Ascites
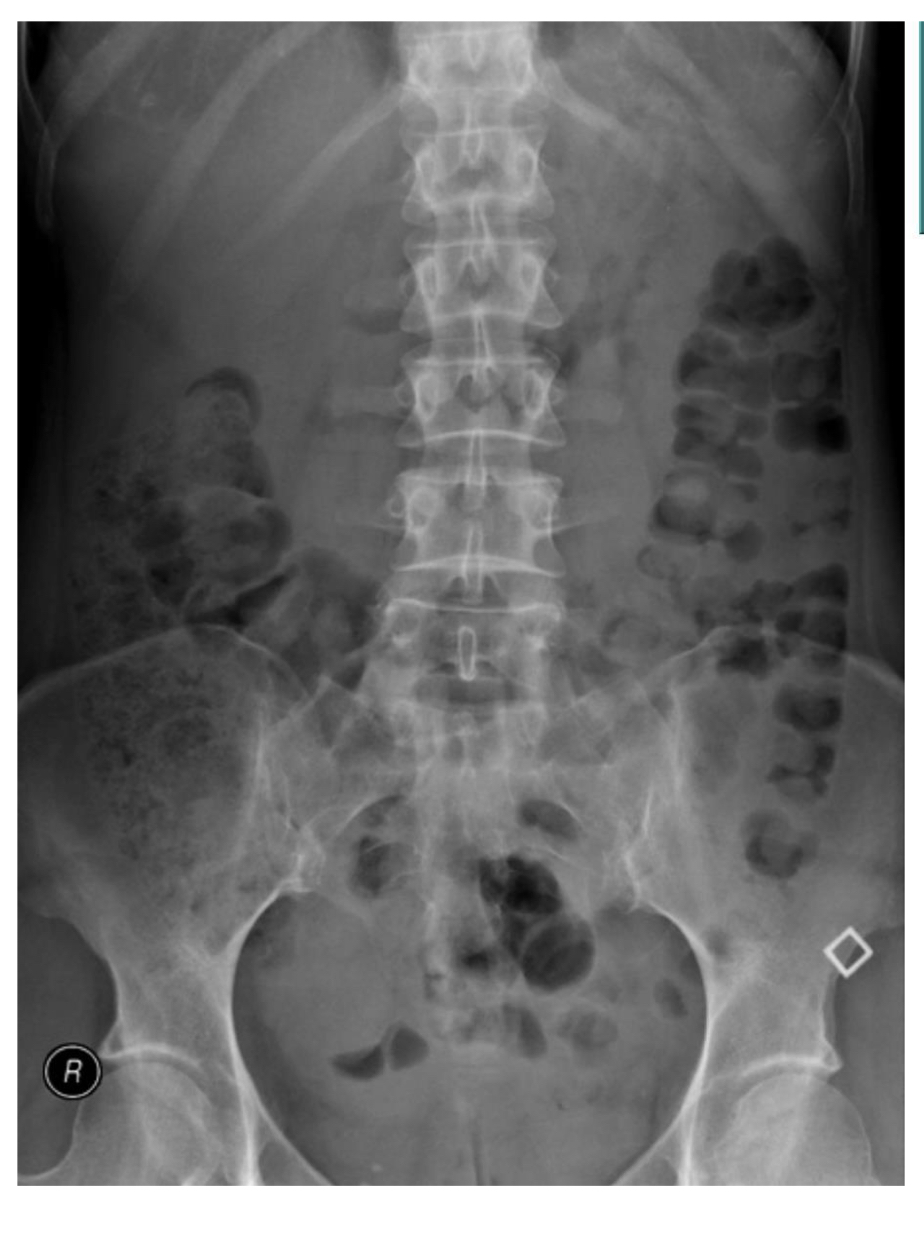
Small pelvic mass
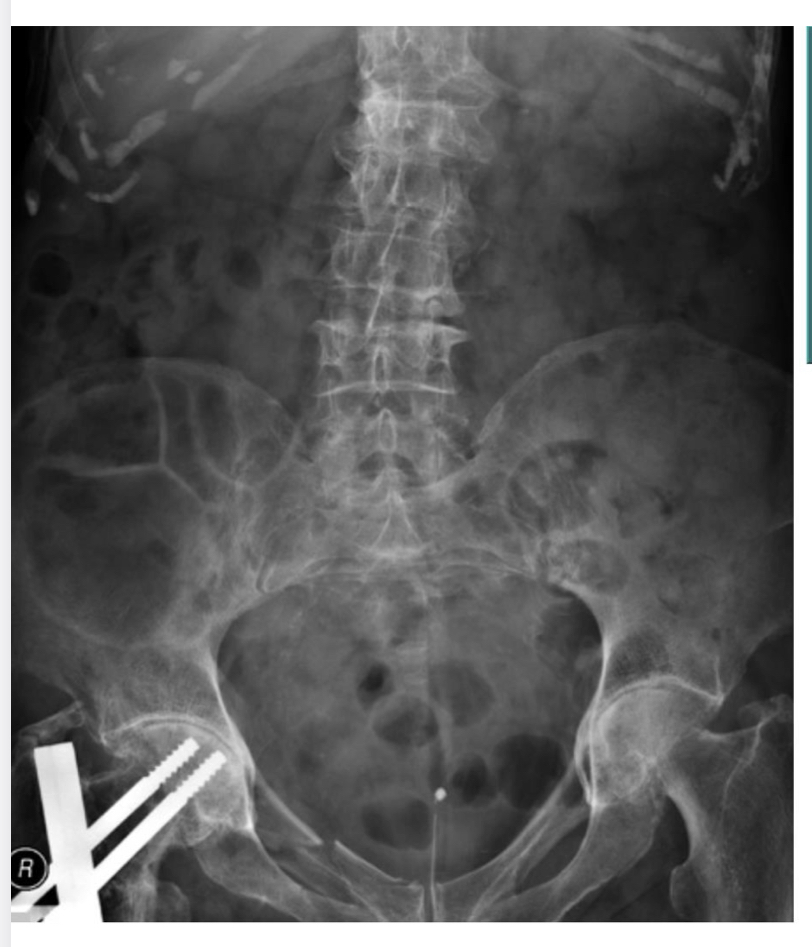
Elderly pt presents with abd pain and no clear history of trauma
Tenderness I’m the suprapubic region due to intraabdominal pathology
Fracture and osteoarthritis
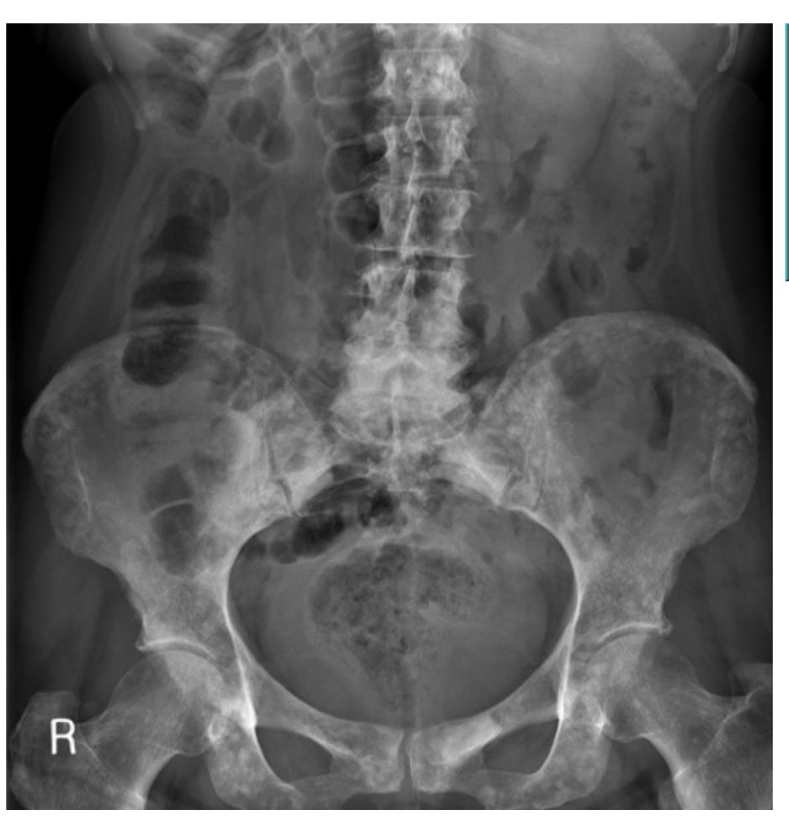
Hx of breast cancer
Abd pain
Bone Mets
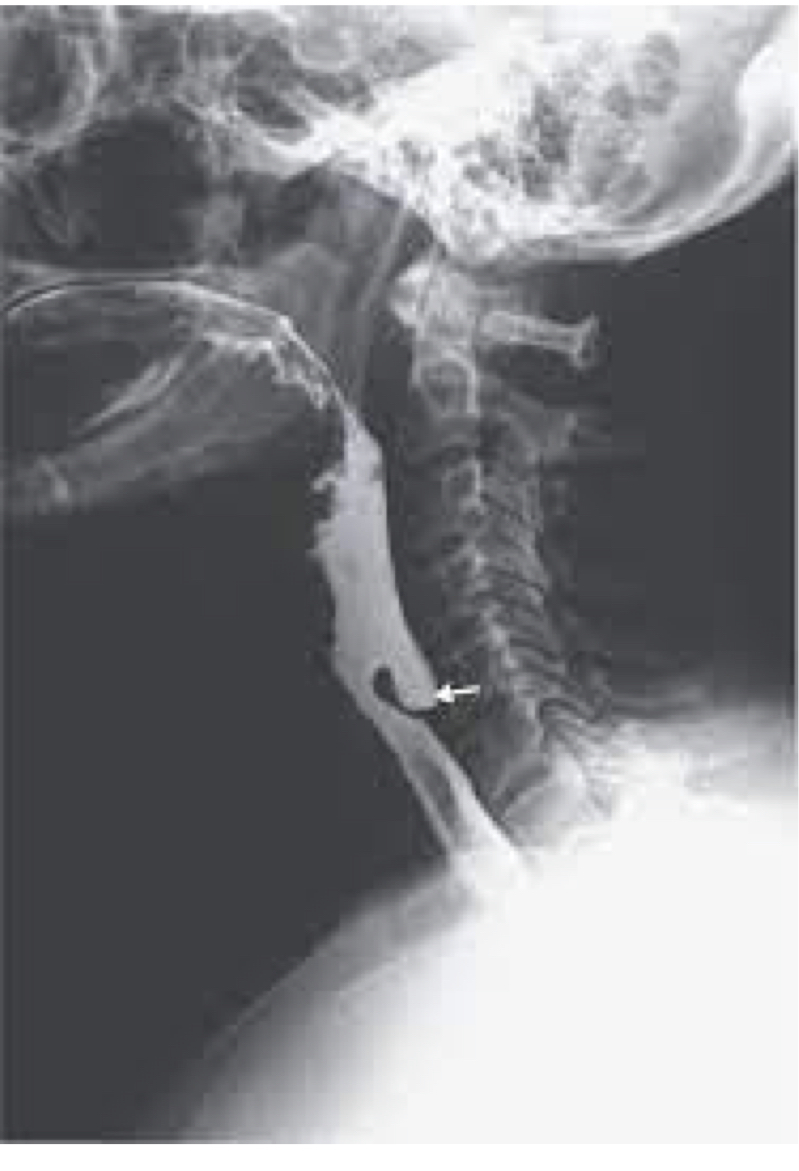
Pt experiences dysphagia
Zenkers diverticulum
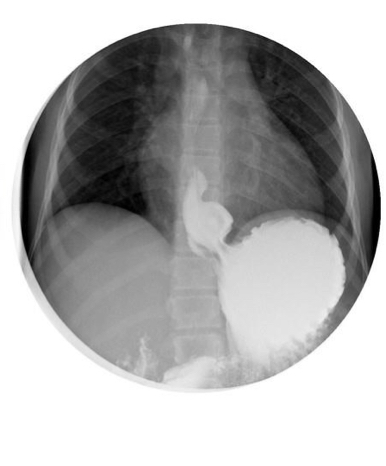
Pt has heartburn, dysphagia, regurgitation
Hiatal hernia
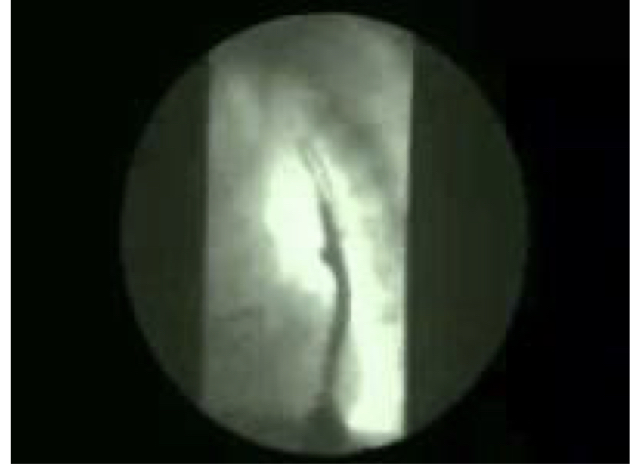
Pt has heartburn
GERD - hx and PE sufficient to diagnose
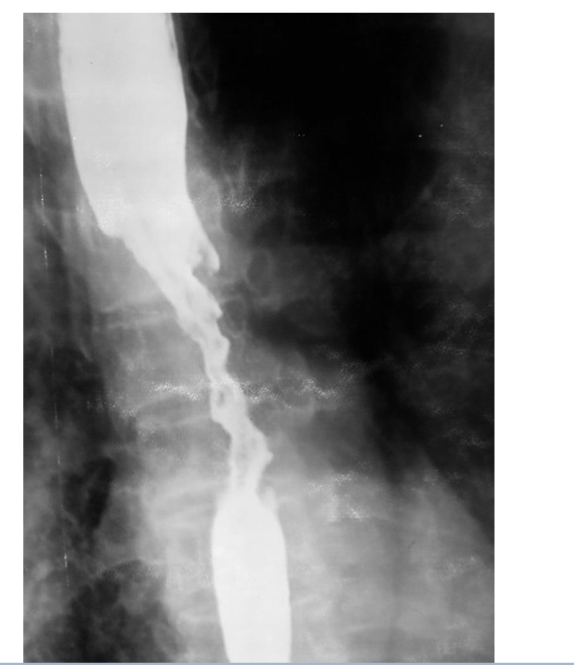
Pt has dysphagia
Esophageal cancer
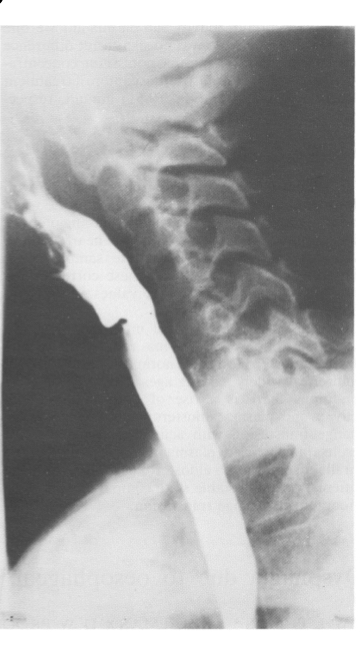
asx
Pt has Plummer Vinson syndrome
Esophageal web
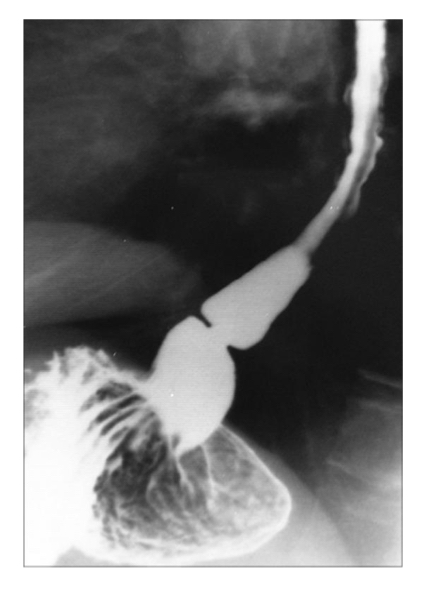
Dysphagia
Schatzki’s ring
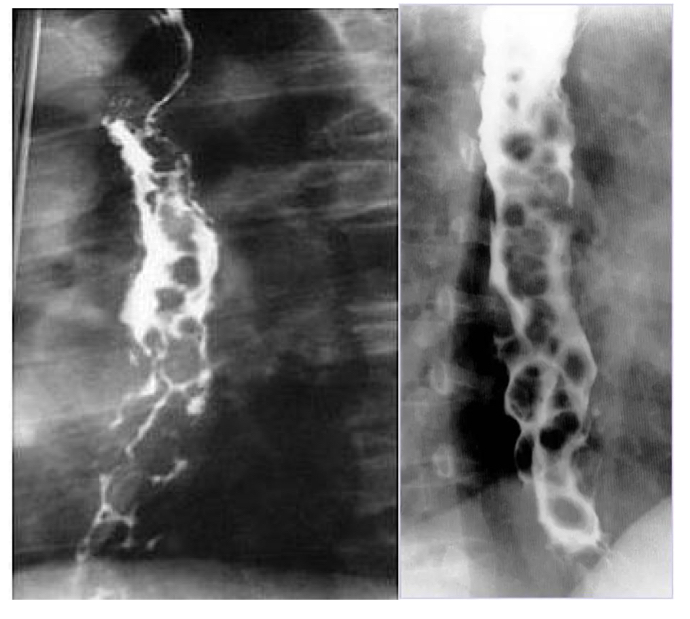
Pt has portal HTN and is an alcoholic
Varices
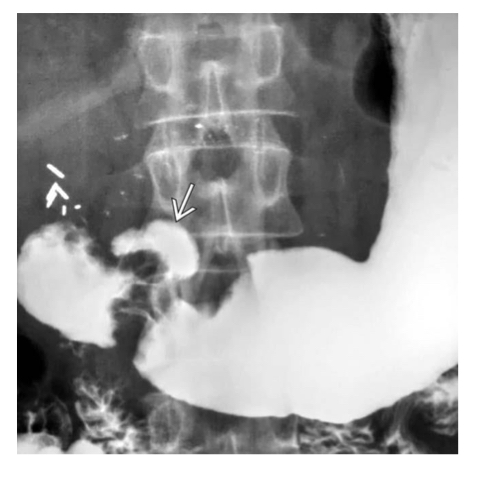
Peptic ulcer disease
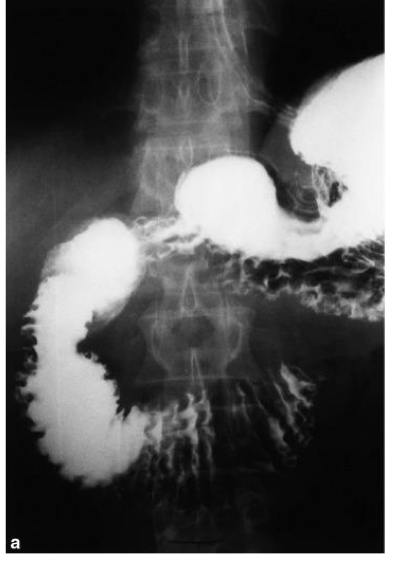
Pancreatic cancer
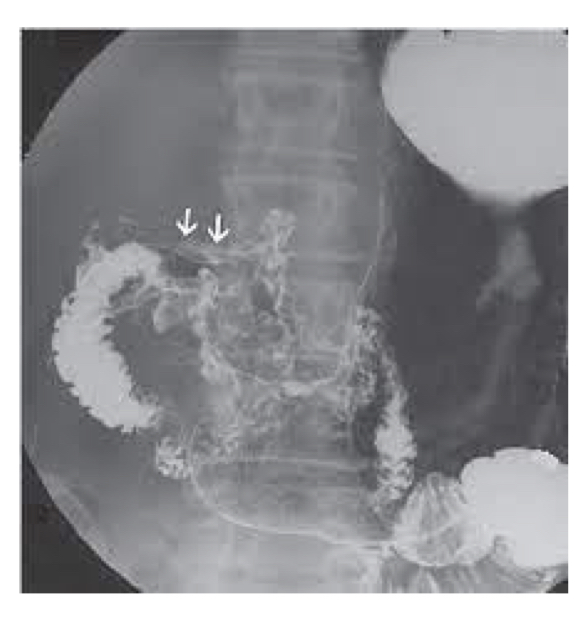
Duodenal cancer
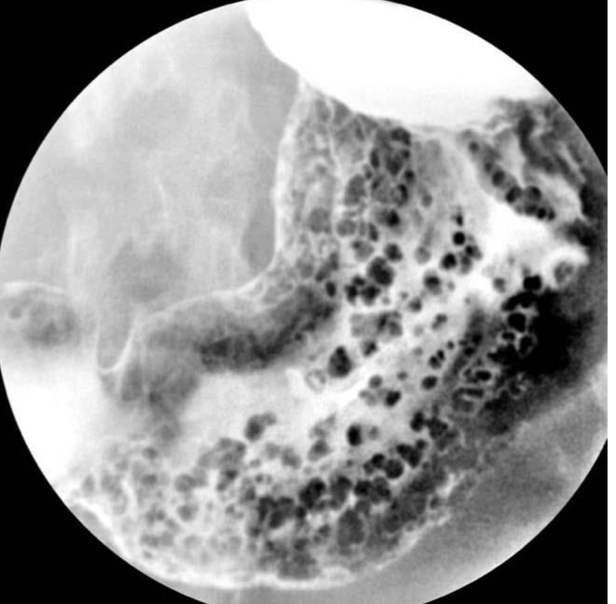
Gastric polyps
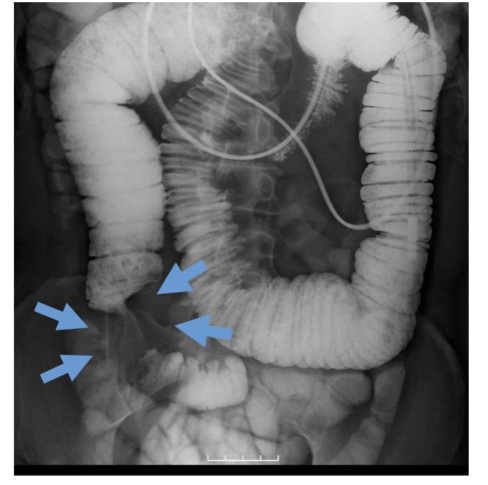
Small bowel obstruction
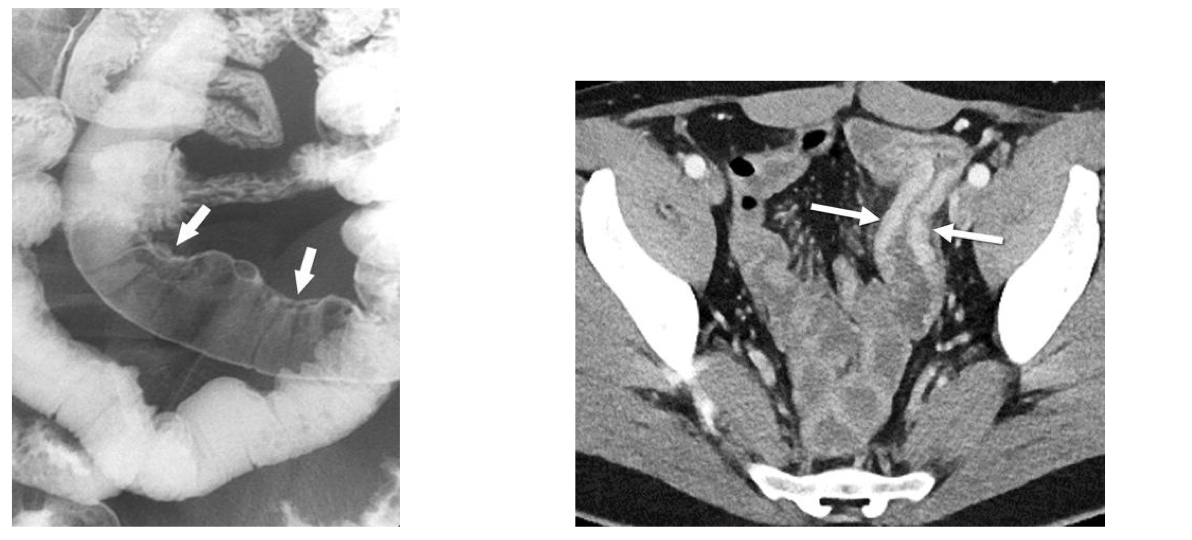
Crohn’s disease
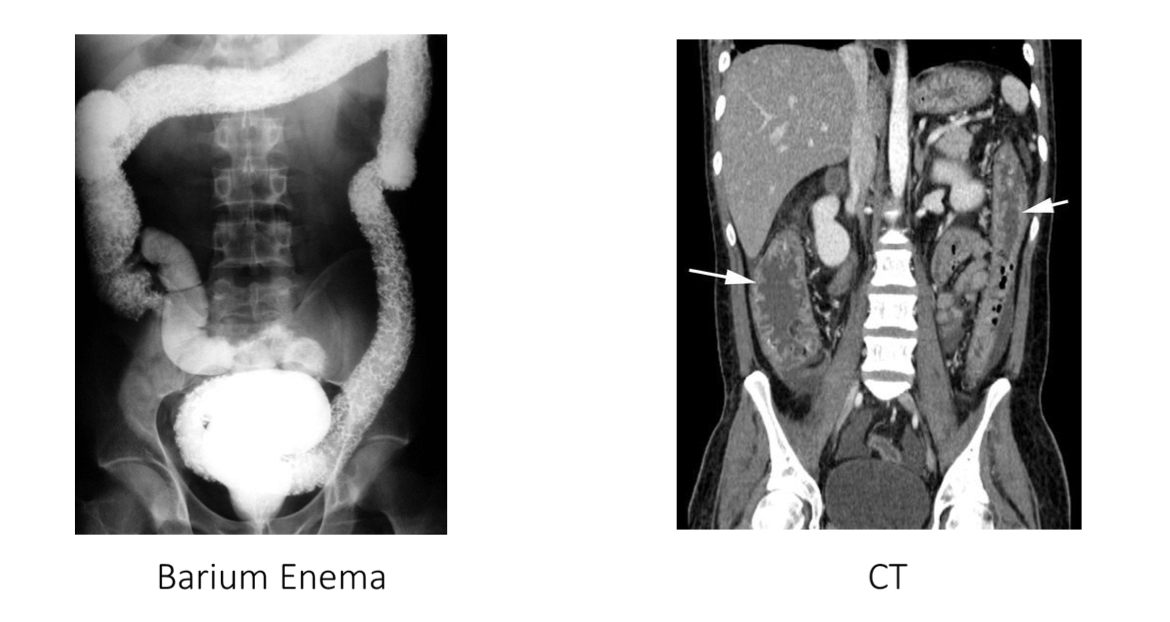
Ulcerative colitis
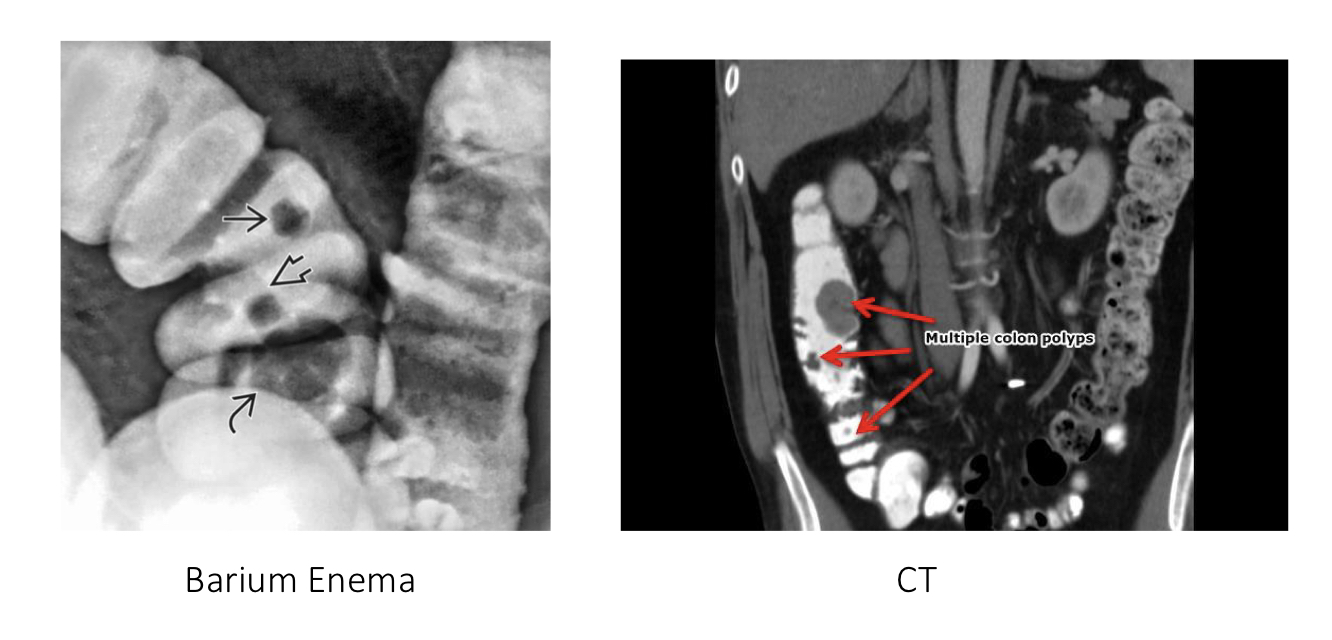
Colon polyps
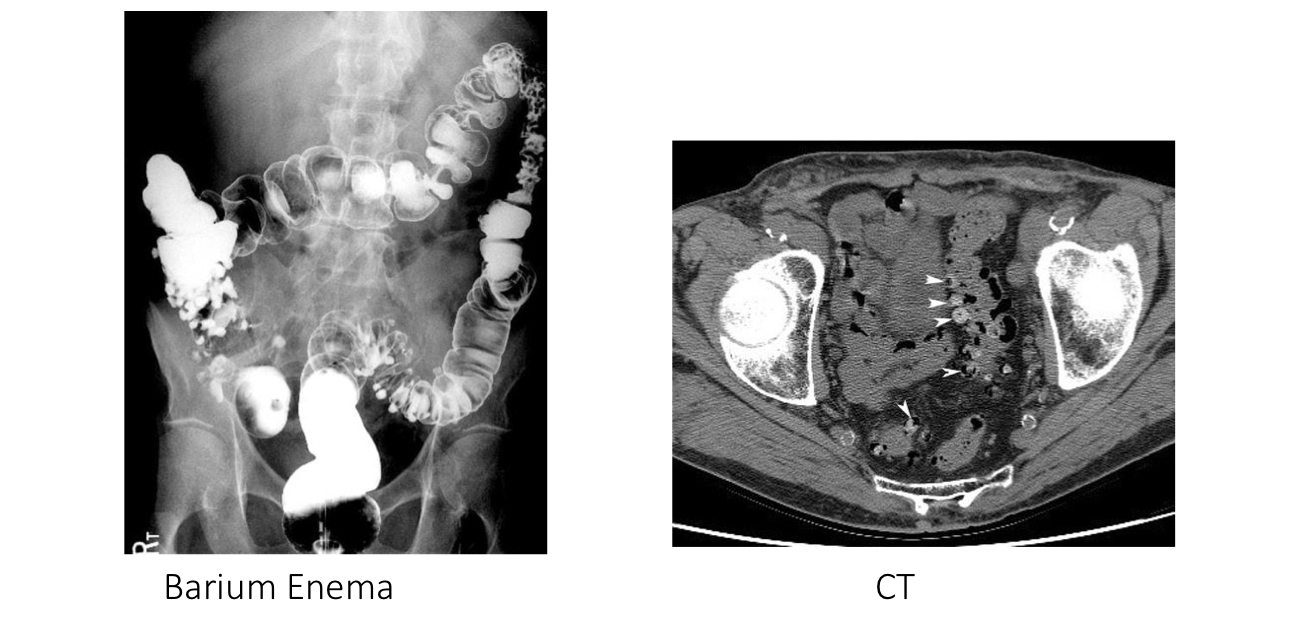
Diverticulosis
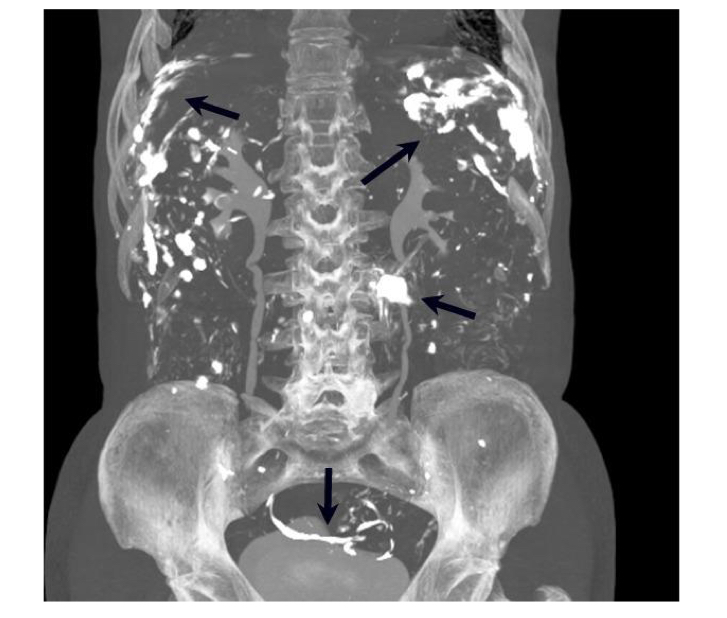
Perforation
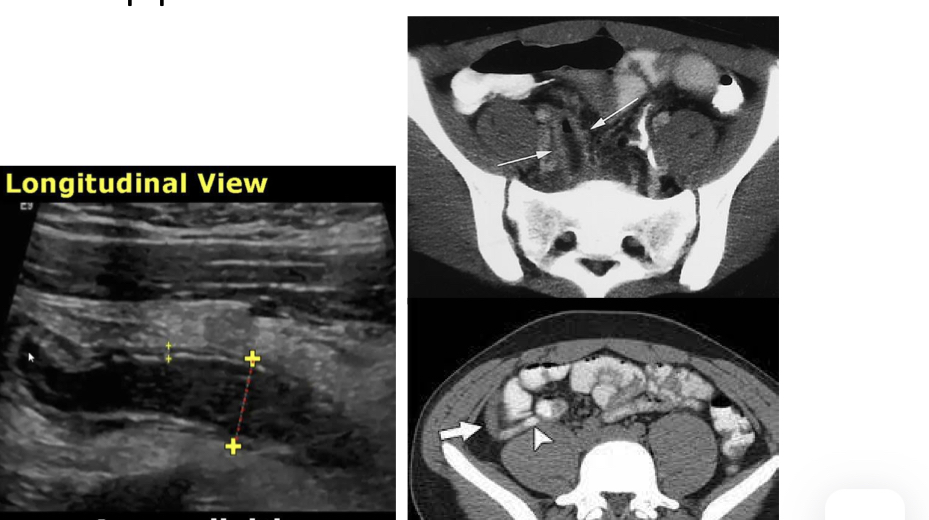
Appendicitis
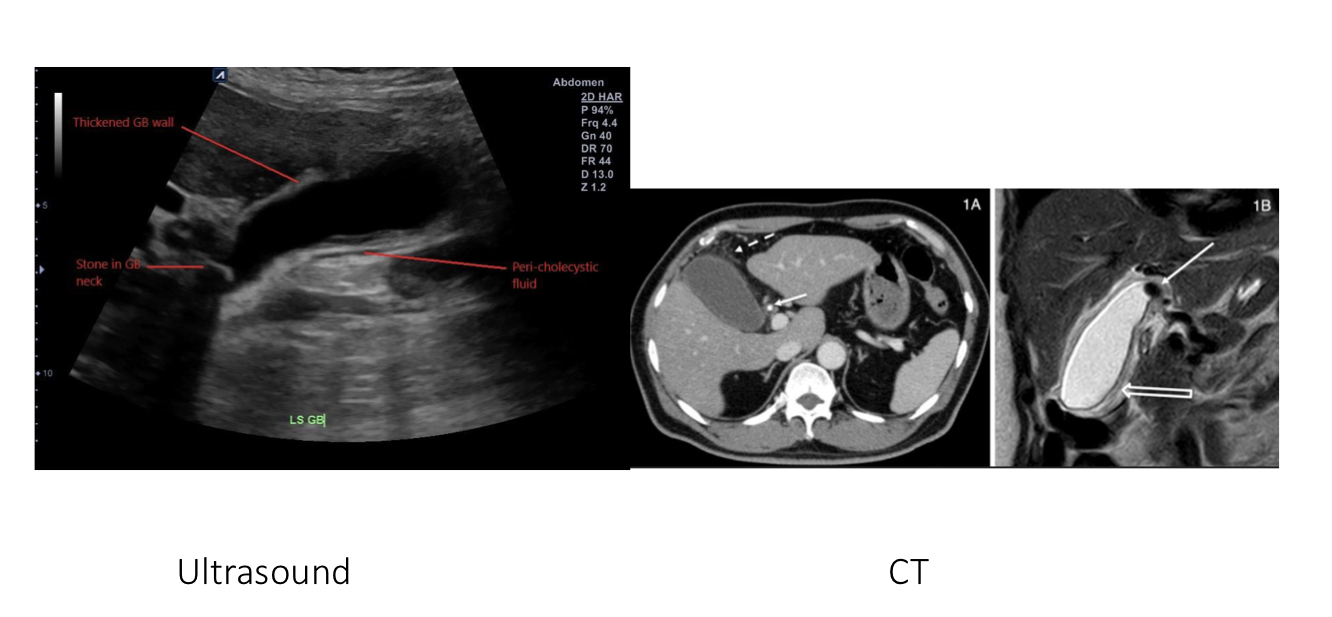
Cholysistitis
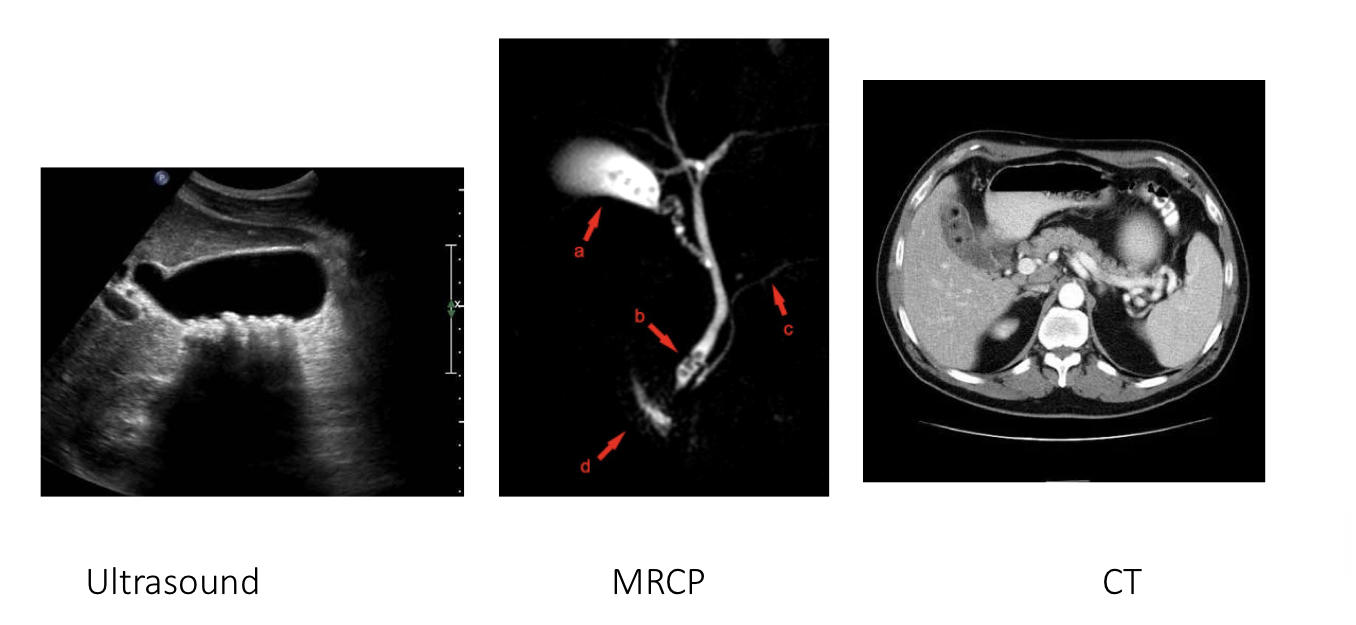
Cholelithiasis
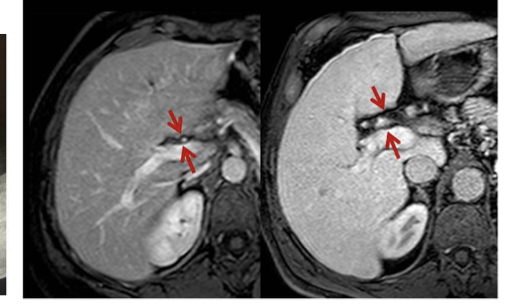
Cirrotic liver
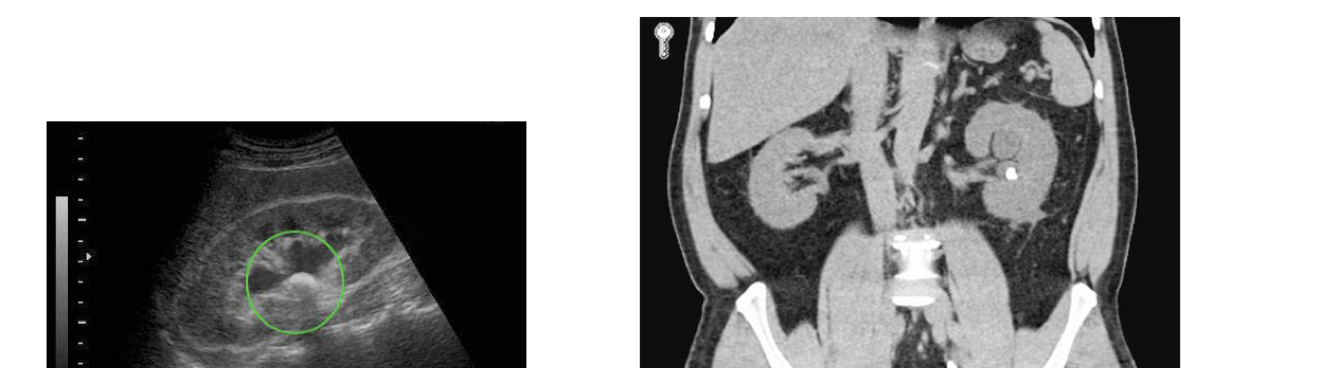
Kidney stone
Renal calculi
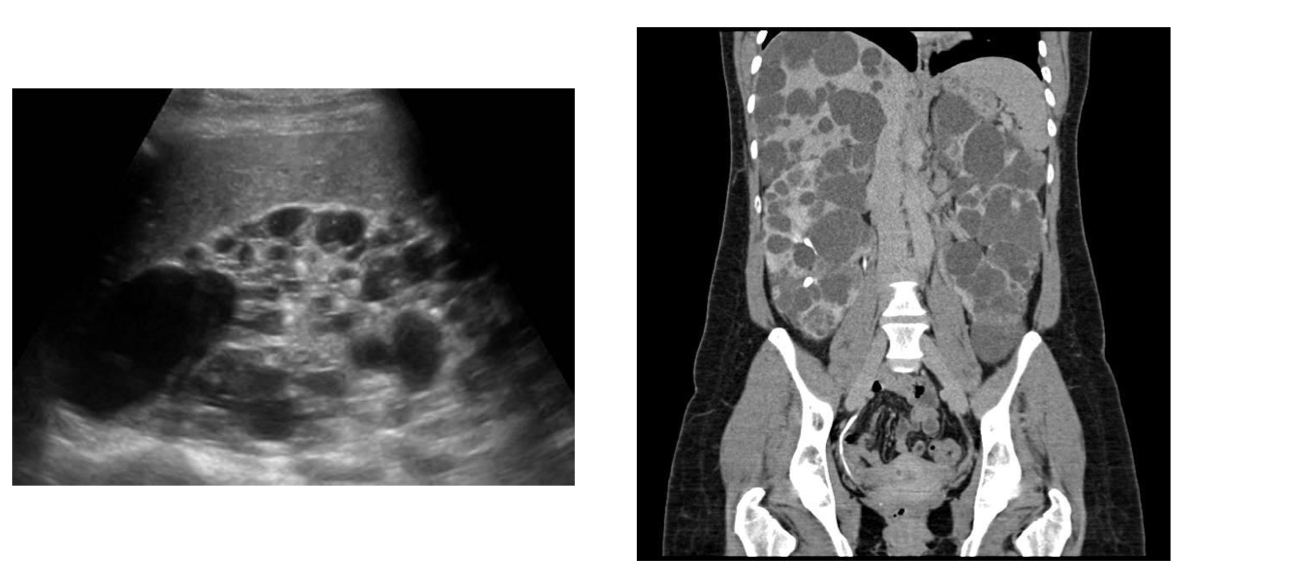
Polycystic kidney disease
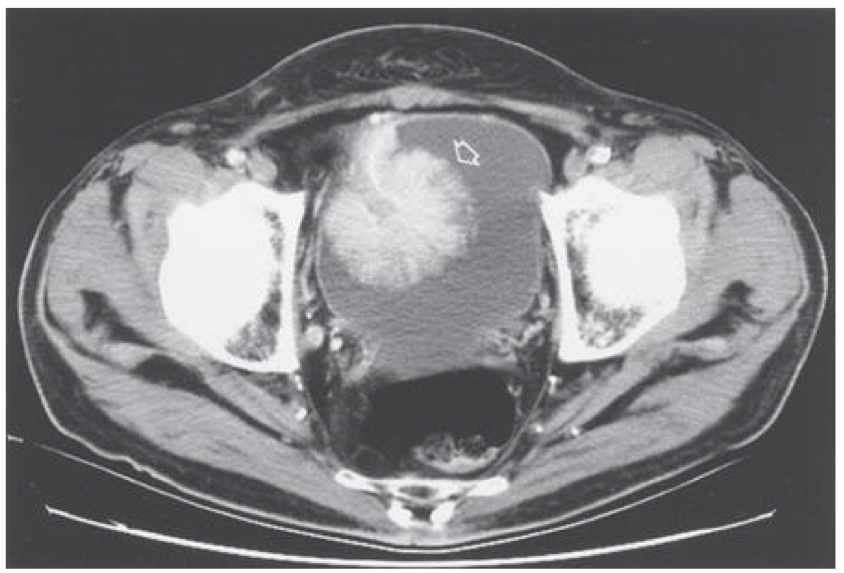
Bladder cancer
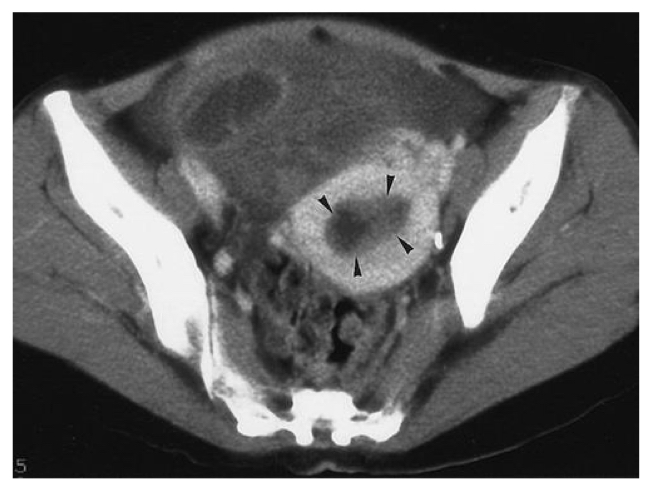
Ovarian cancer
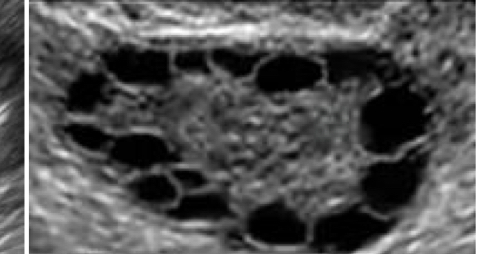
Polycystic ovary
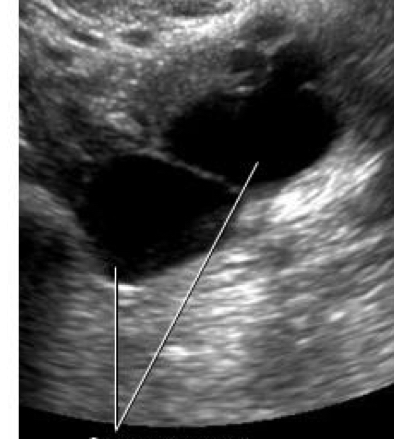
Ovarian cyst

Fibroid - vaginal
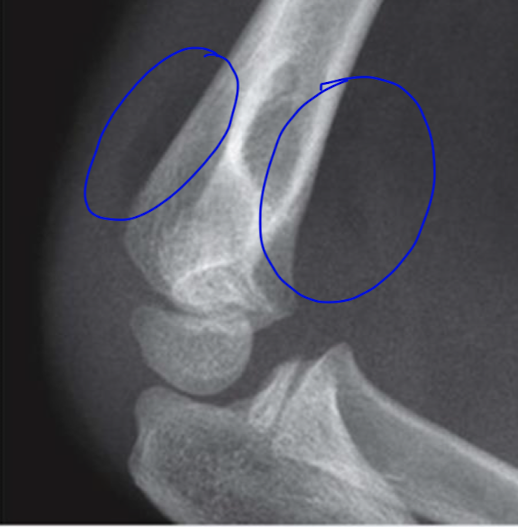
posterior and anterior fat pad ( sail sign)
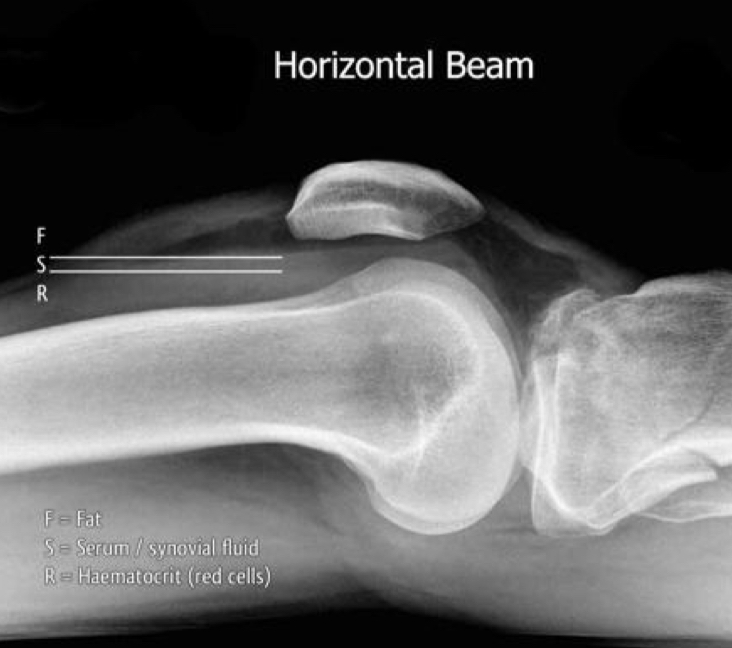
fat fluid level of the knee
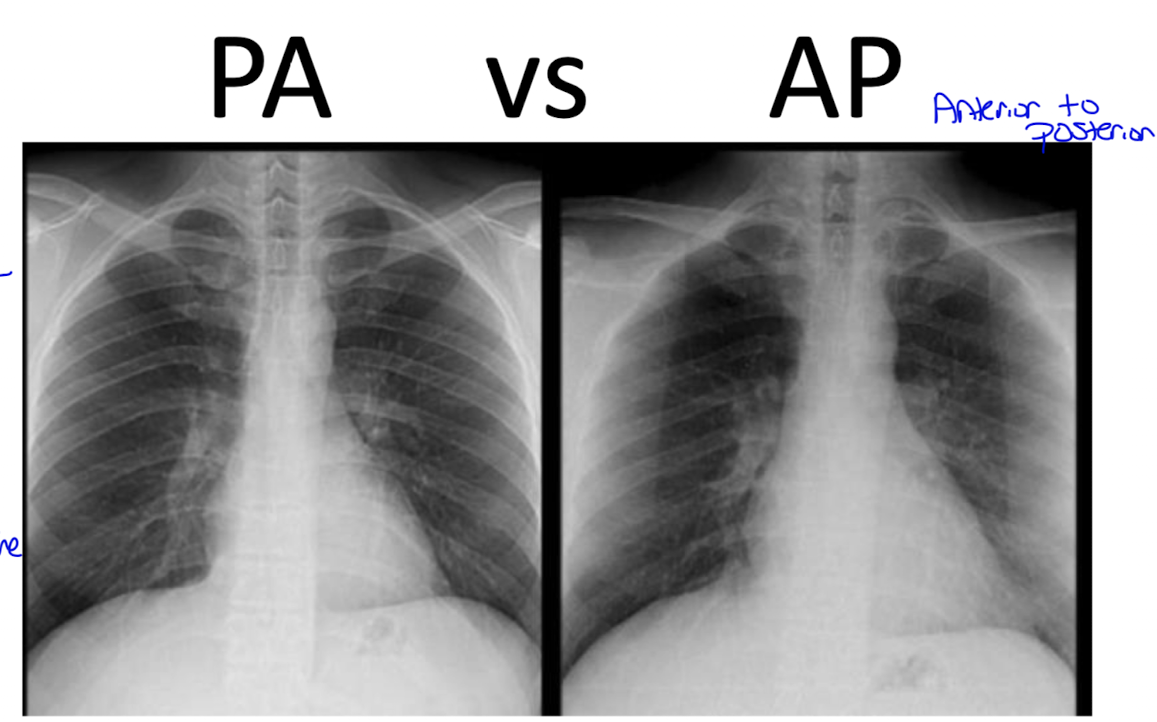
what’s the difference?
PA: because the beam is shot posterior to anterior the heart will look smaller since its farther away
AP: because the beam is from ant to post the heart will appear larger because its closer to the beam
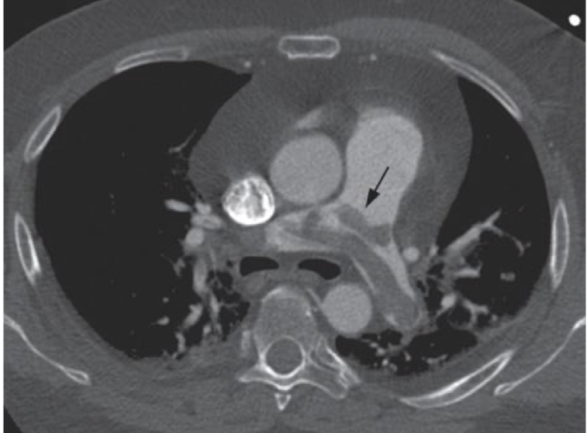
saddle embolus on CT
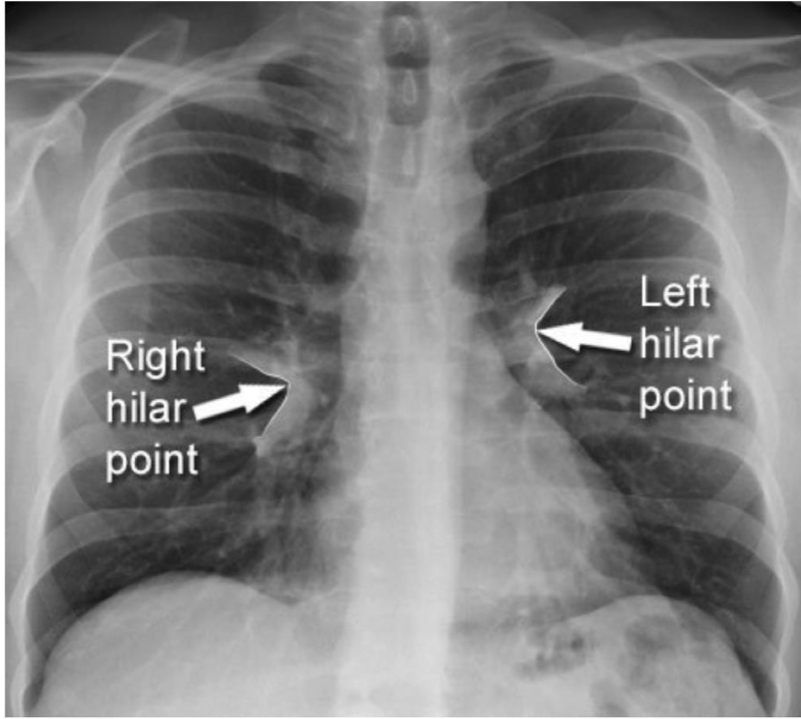
hailer points are where the upper and Lowe lobe meat the pulmonary vessels
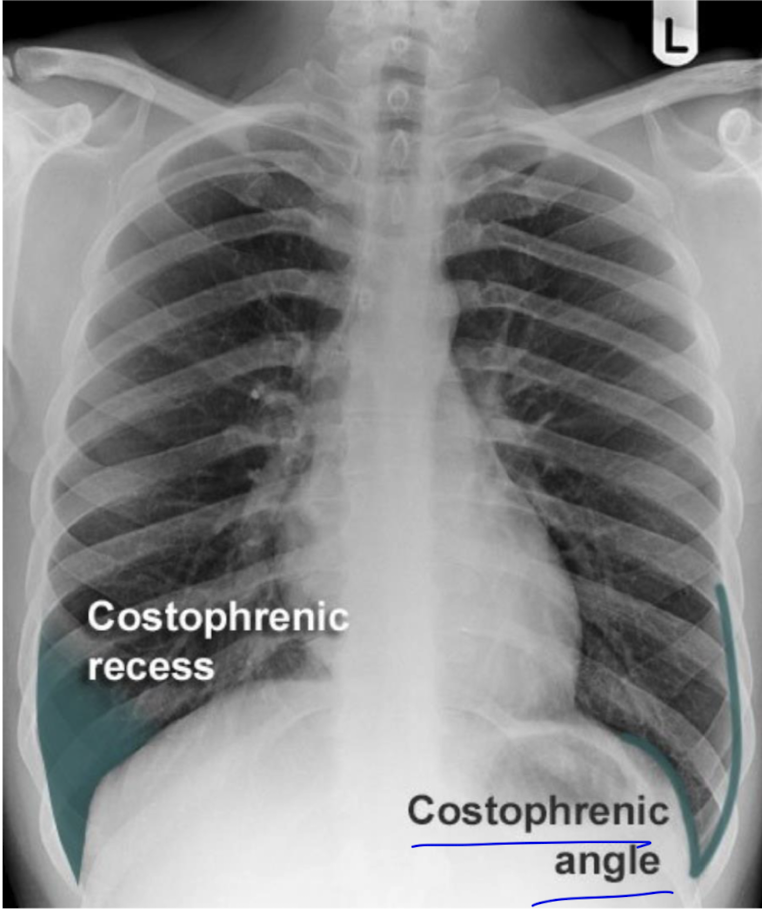
costo phrenic angles are formed by the lateral chest wall and the dome of the hemidiaphram
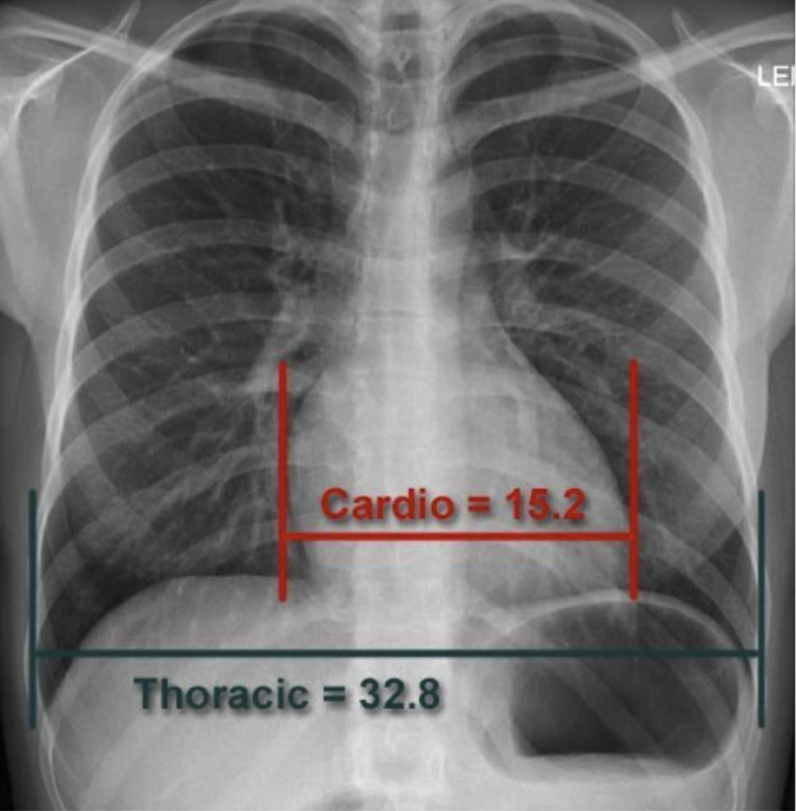
only to be used in the PA view, the cardiothoracic ratio is a measure used to assess cardiac size in relation to thoracic diameter, helping to identify cardiomegaly.
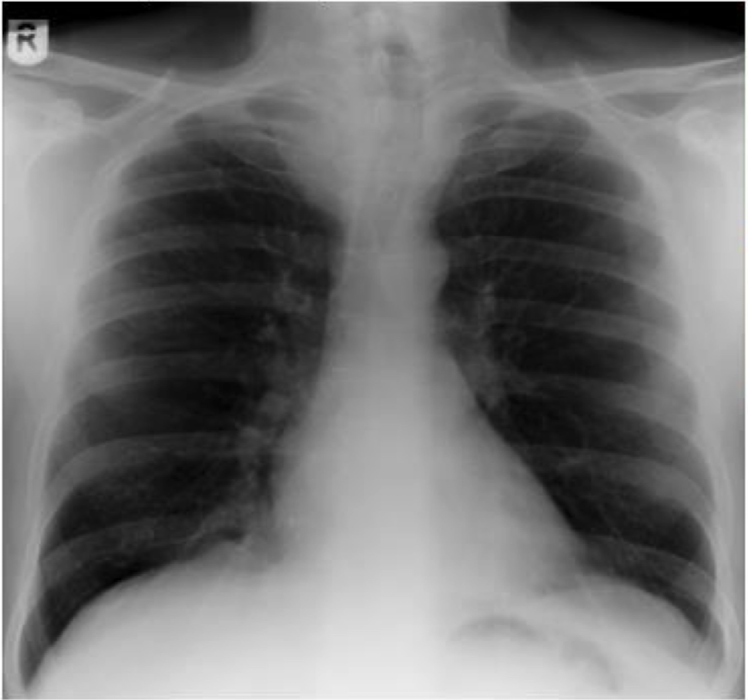
tracheal deviation
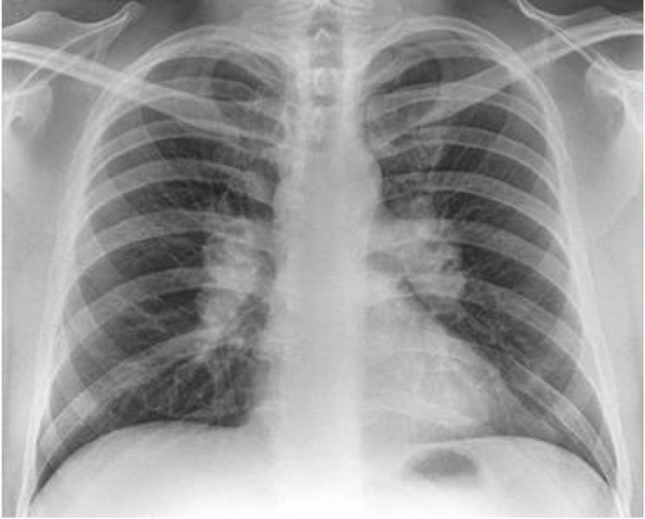
bilateral hilar enlargement
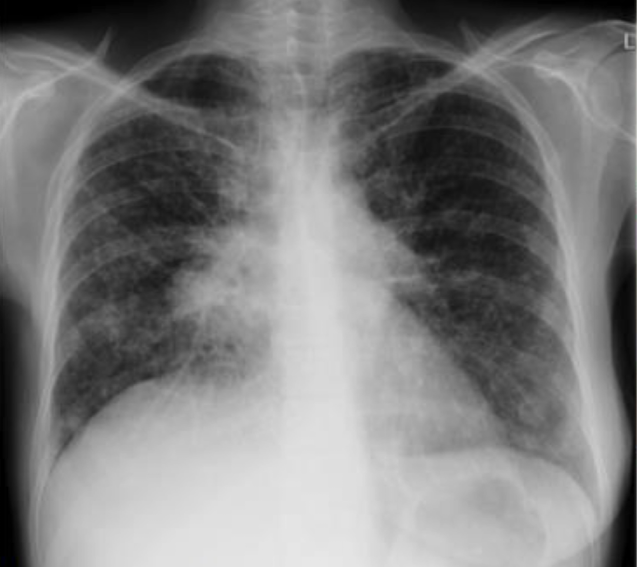
asymmetrical hilar enlargement
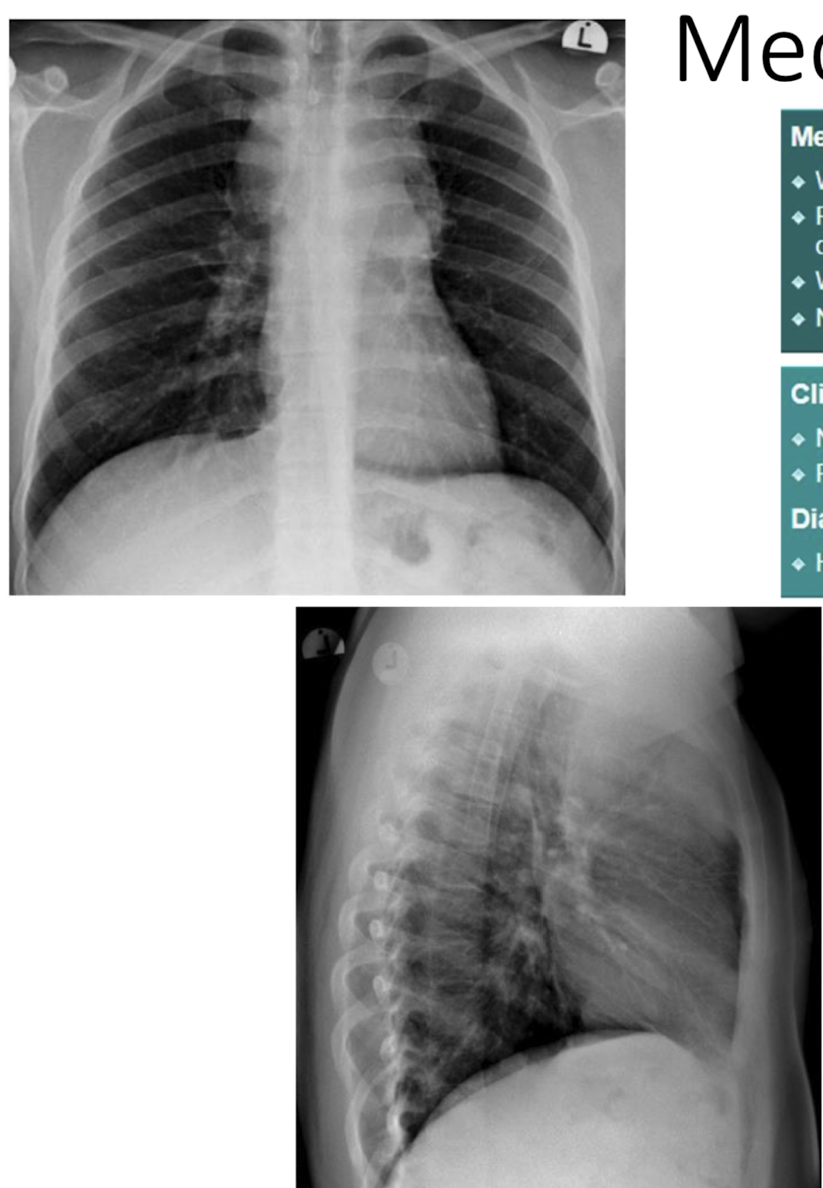
mediastinal mass 2 views
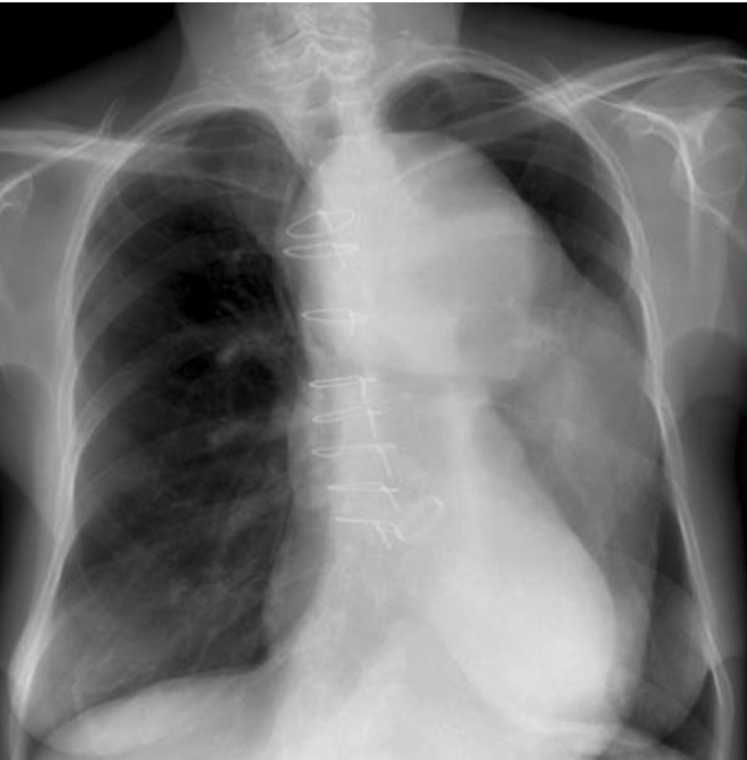
thoracic aortic aneuyurism
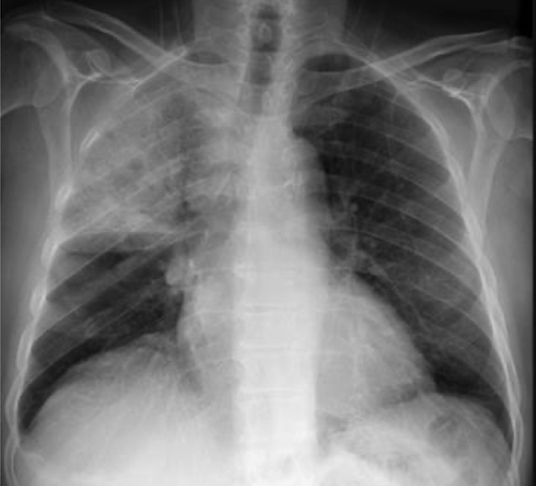
lobar pneumonia
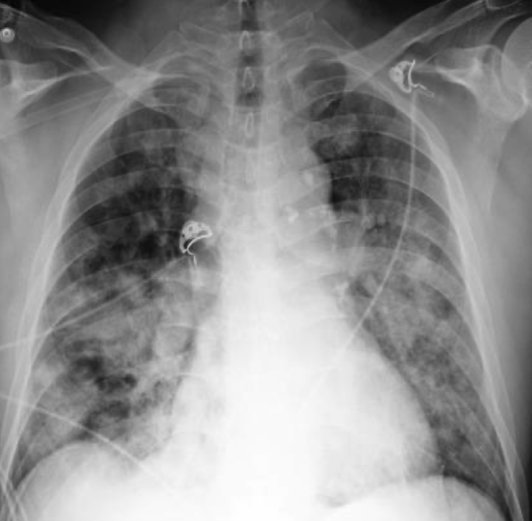
multifocal pnumonia
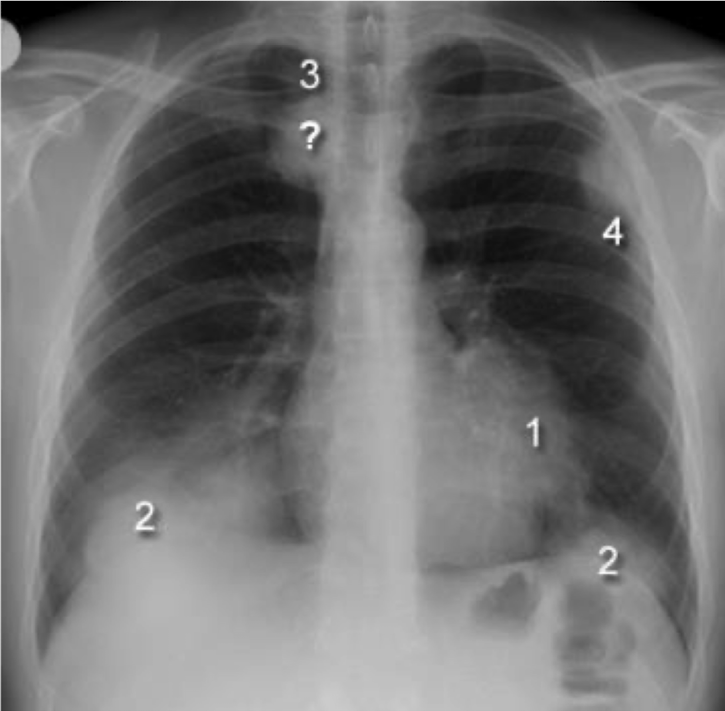
loss of silhouette sign
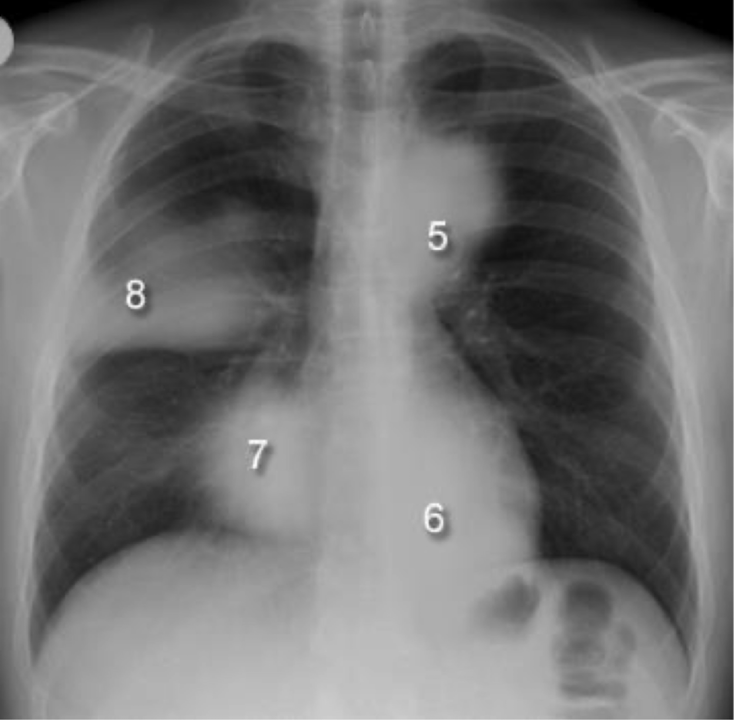
loss of silhouette sign
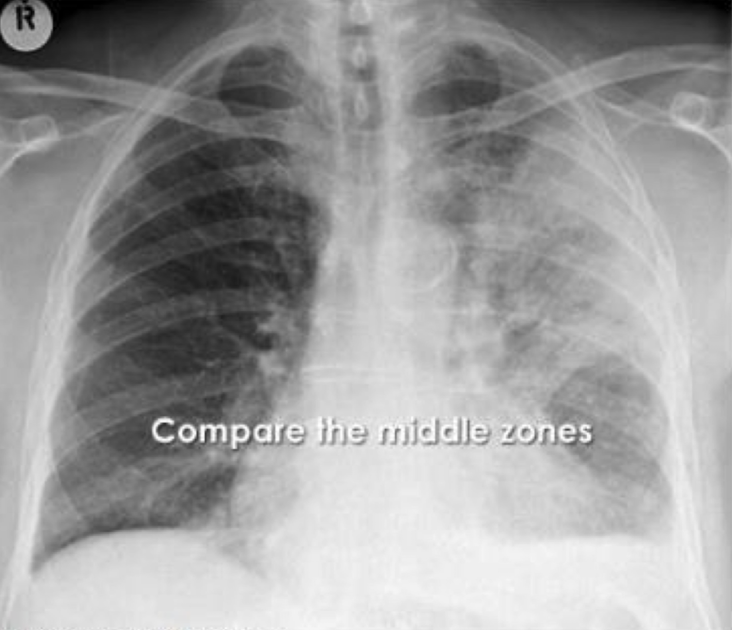
consolidation with the air bronchogram: Pneumonia
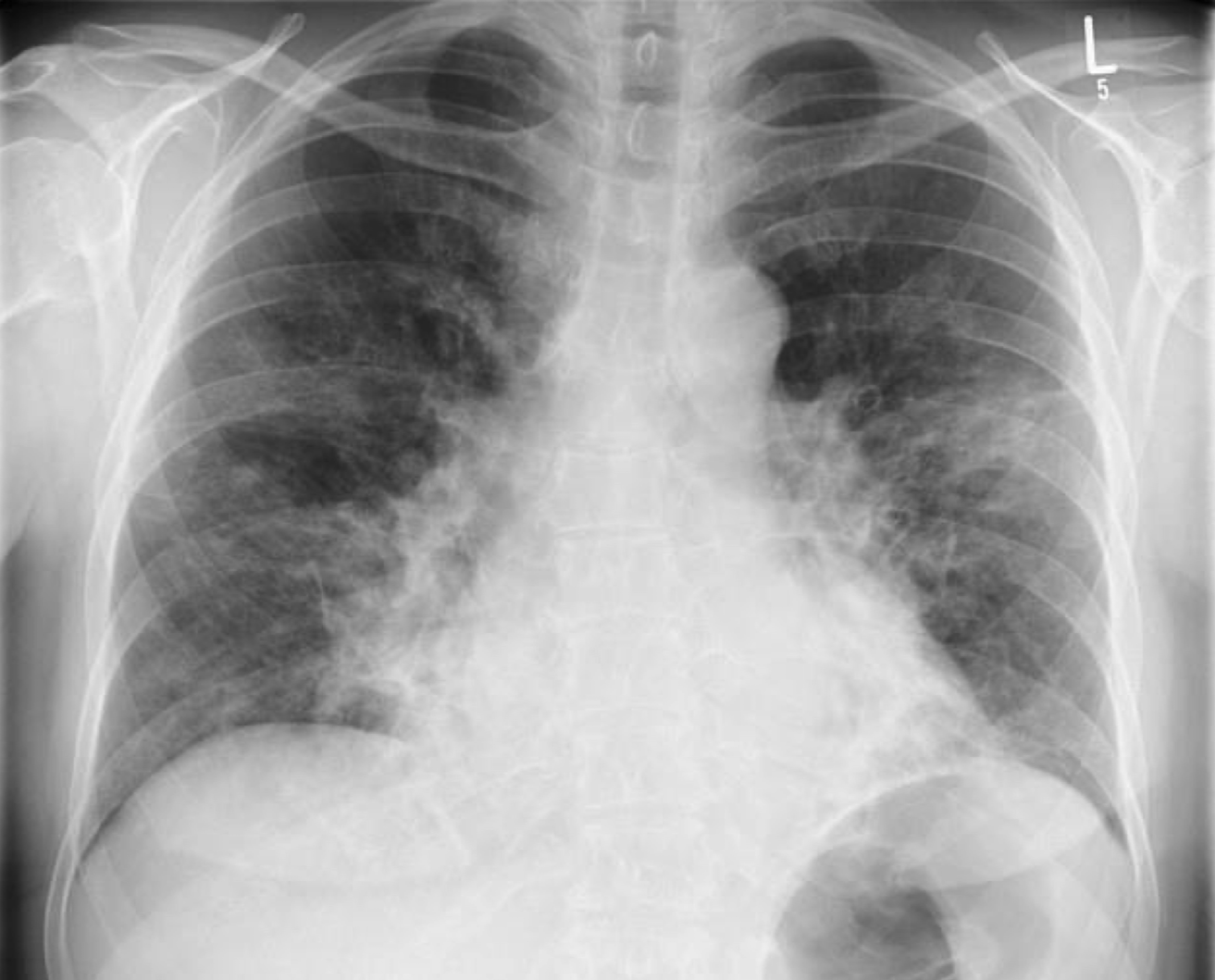
fine reticular pattern seen with viral pneumonia
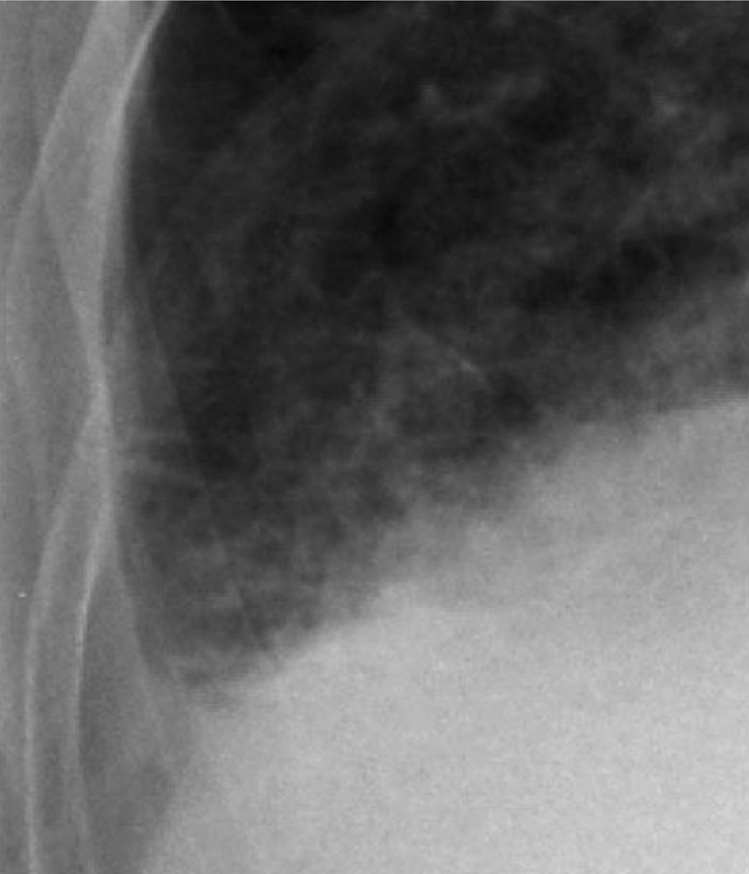
close up of Kelley b lines consistent with CHF
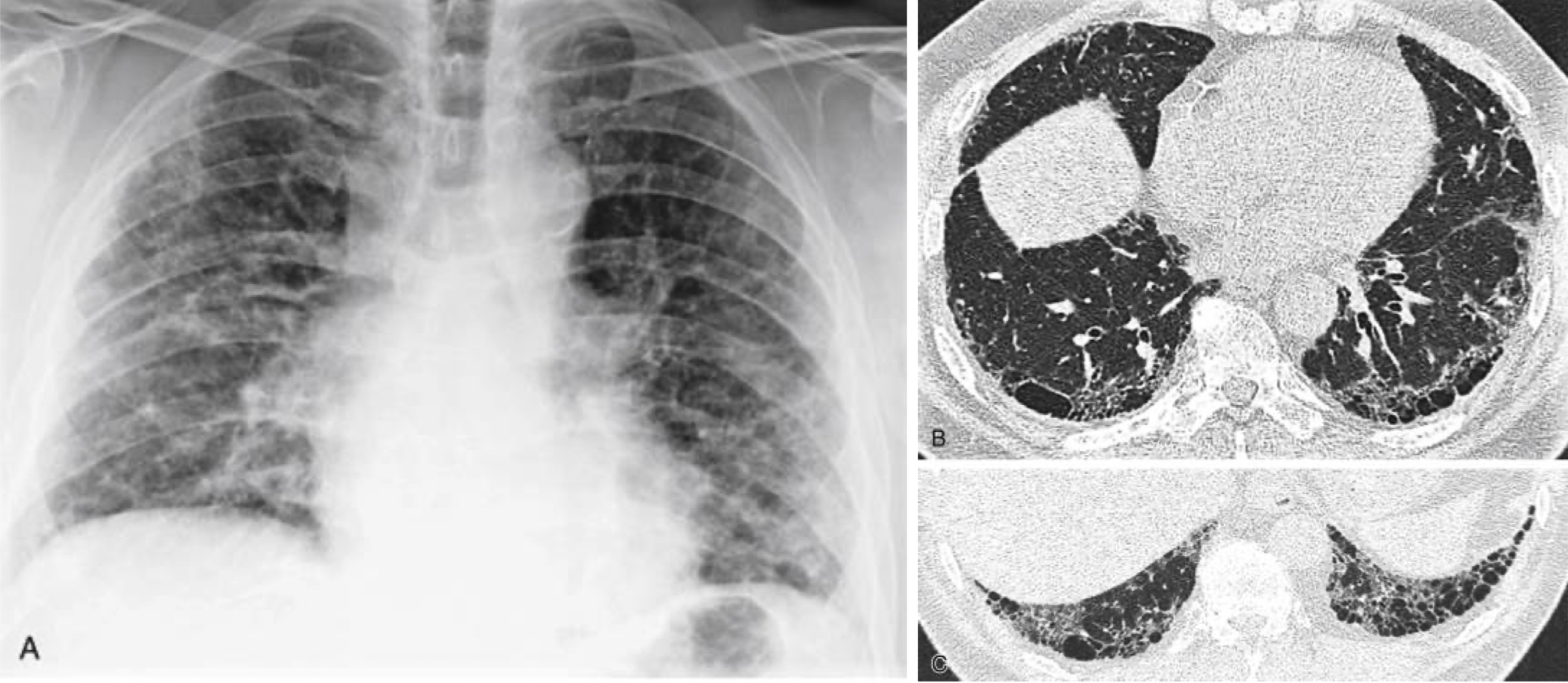
course reticular pattern seen with end stage pulmonary fibrosis ( honeycomb lung)
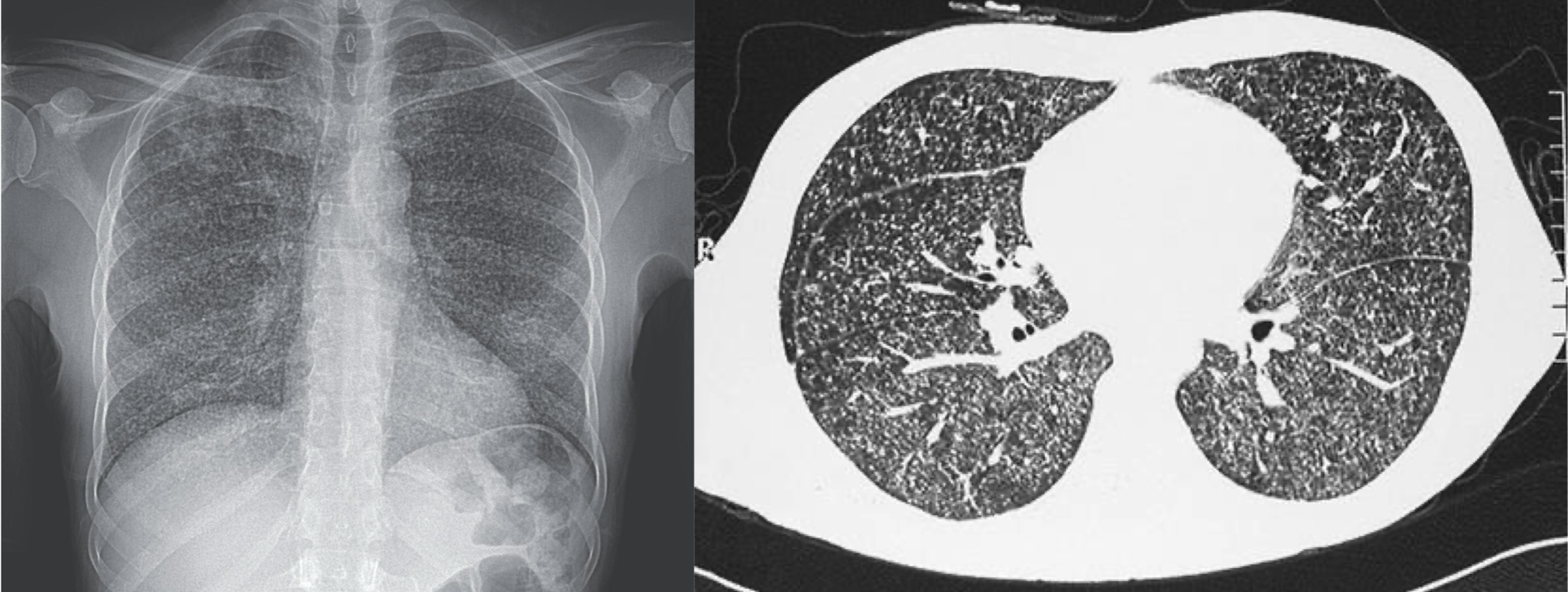
military tuberculosis
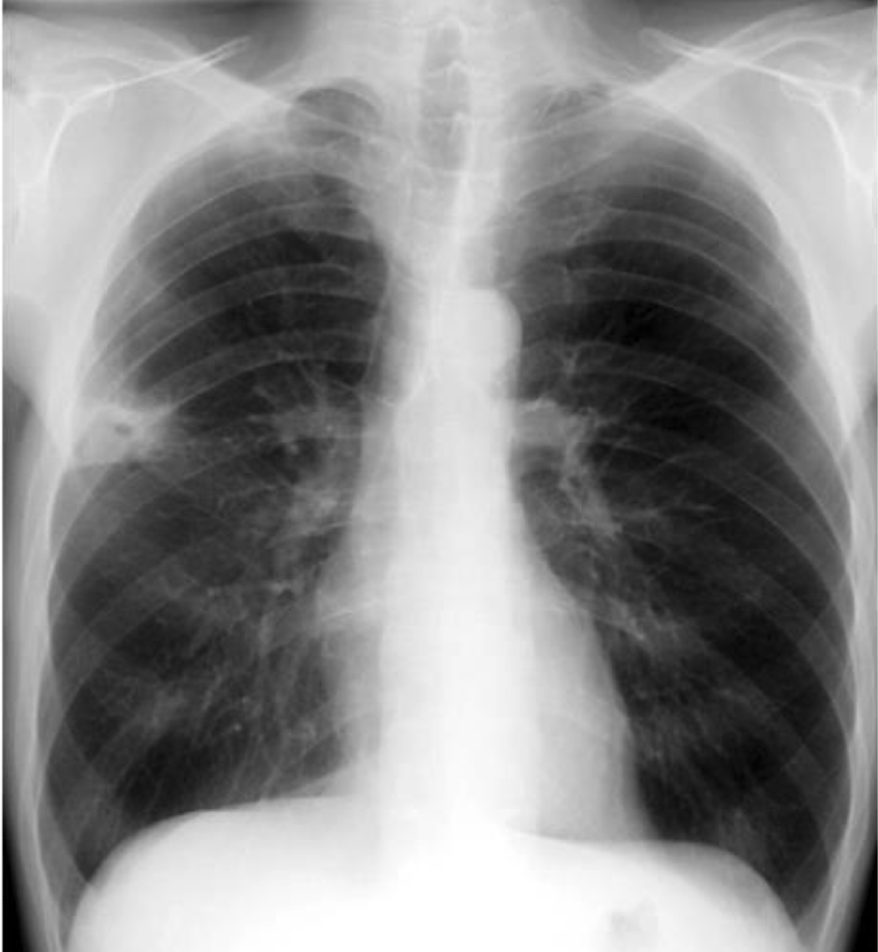
septic embolus
atelectasis
pneumothorax
pleural thickening from mesothelioma
non cancerous asbestos pleural plaques
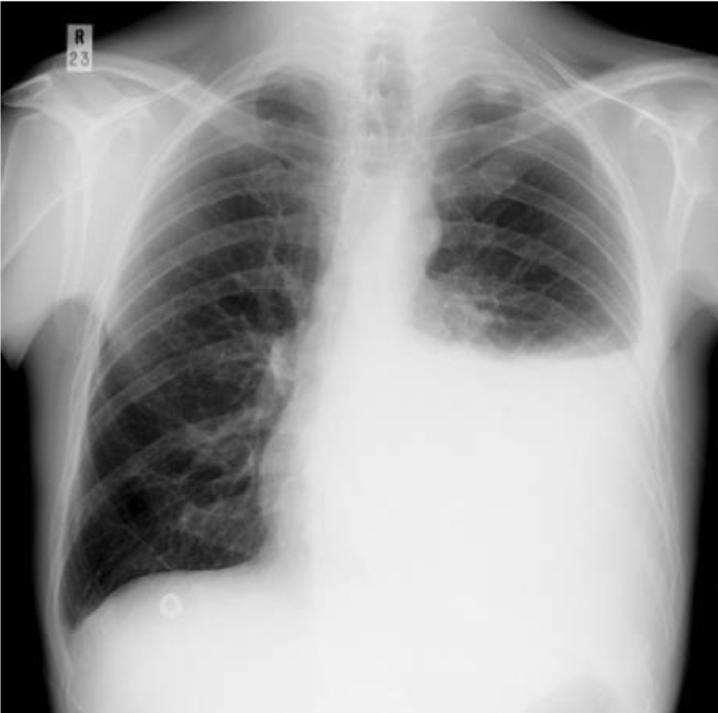
pleaural effusion
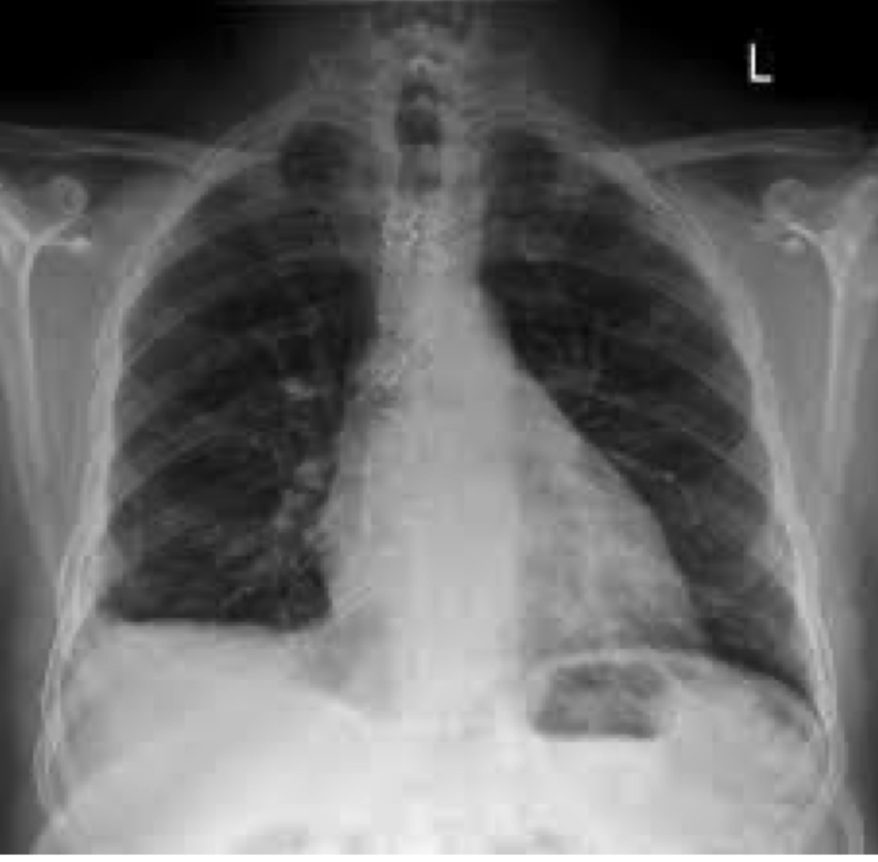
costophrenic angle blunting indicating a R side PE
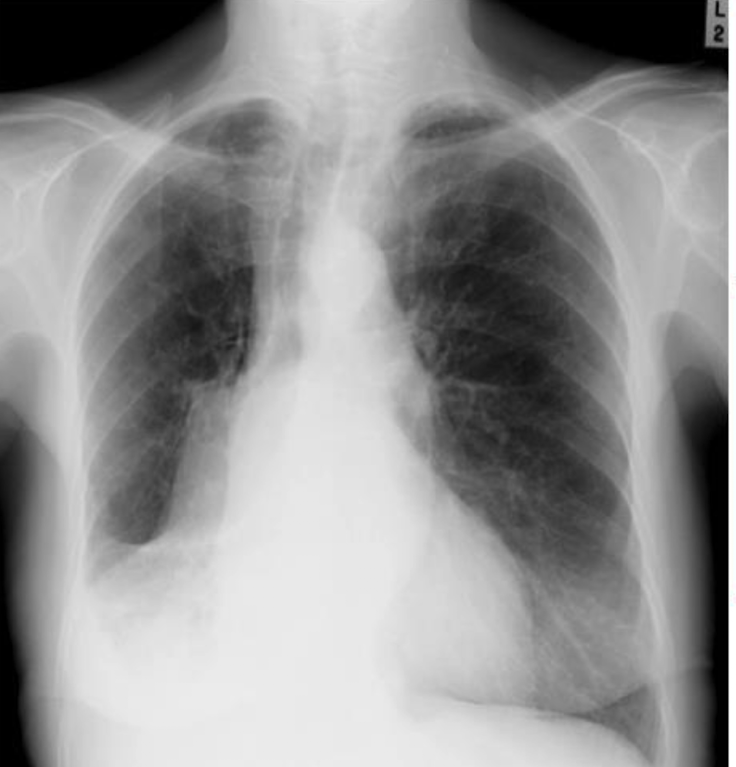
costophrenic angle blunting of the right middle and lower lobe atelactasis
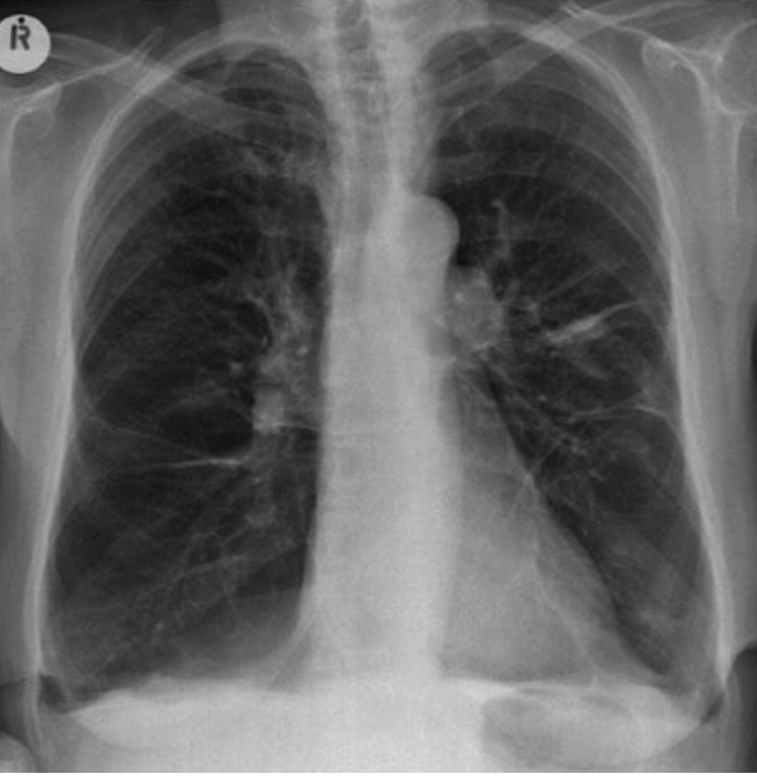
costophrenic angle blunting with COPD
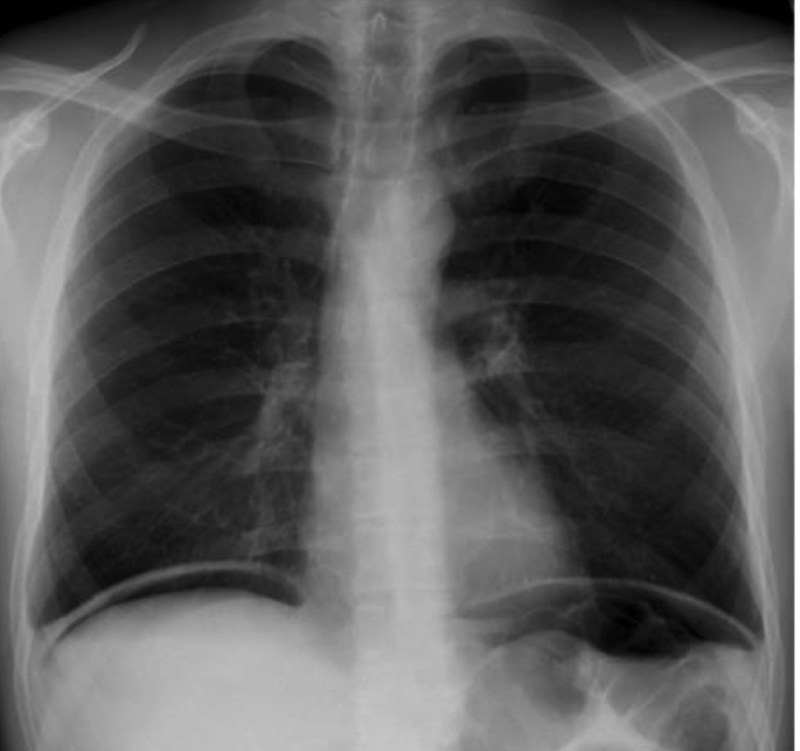
pneumoperitoneum secondary to a perforated duodenal ulcer
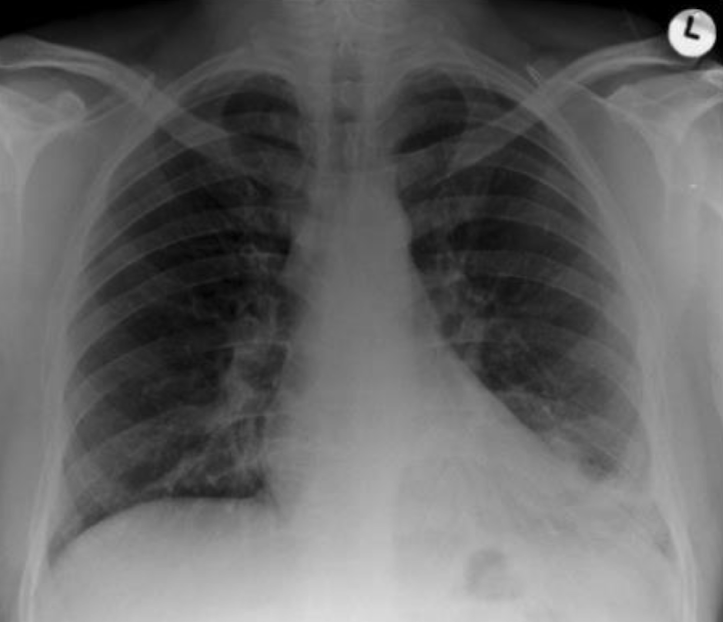
,left lower lobe pneumonia
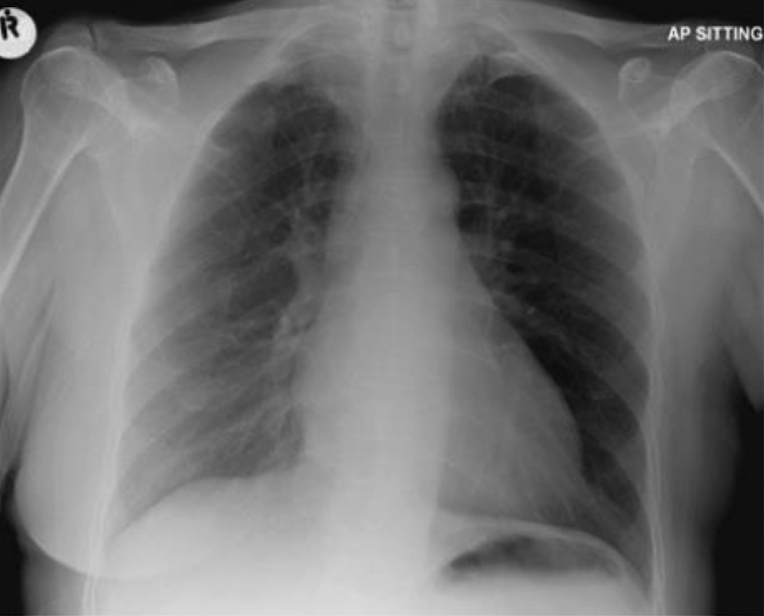
loss of soft tissue due to mastectomy
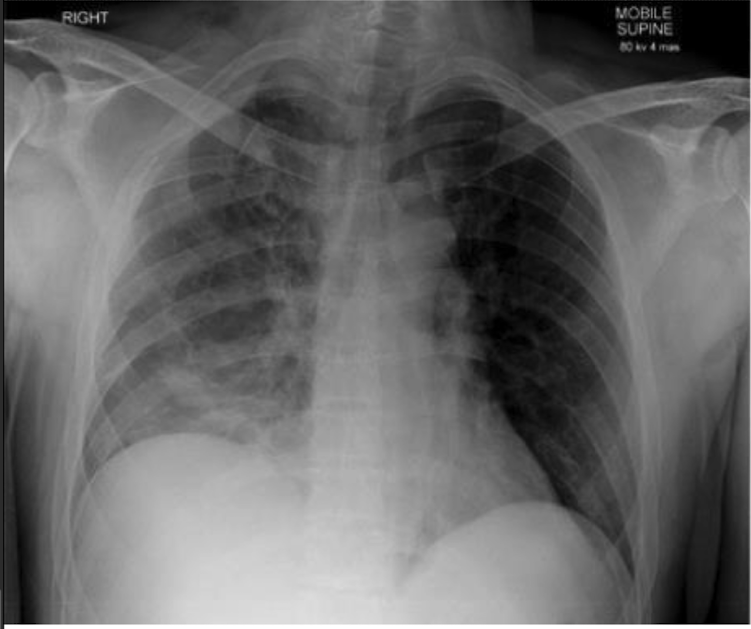
rib fracture
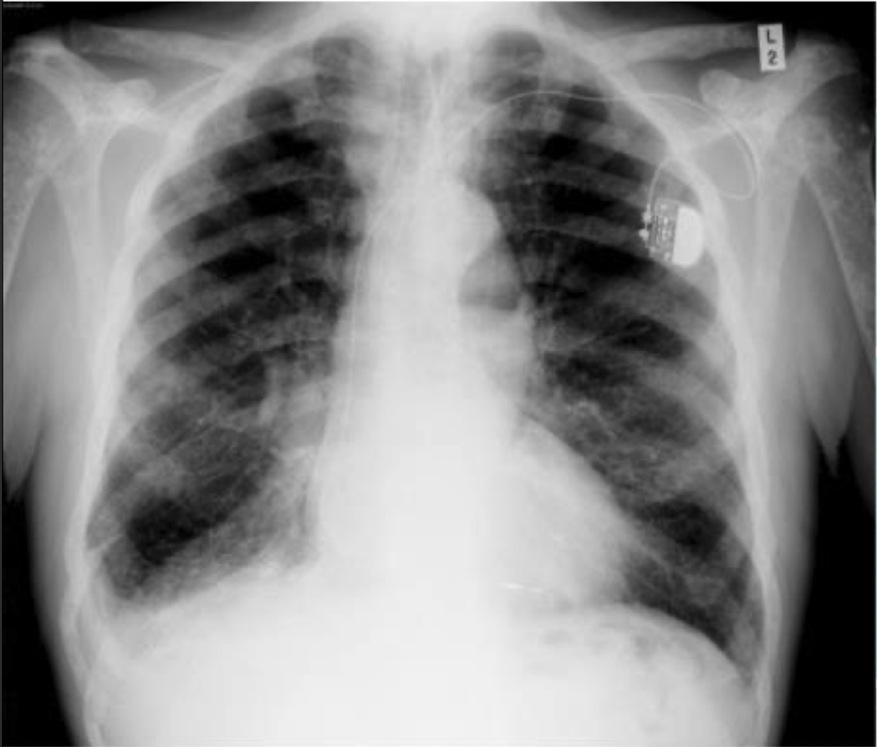
bone metastasis with a pace maker
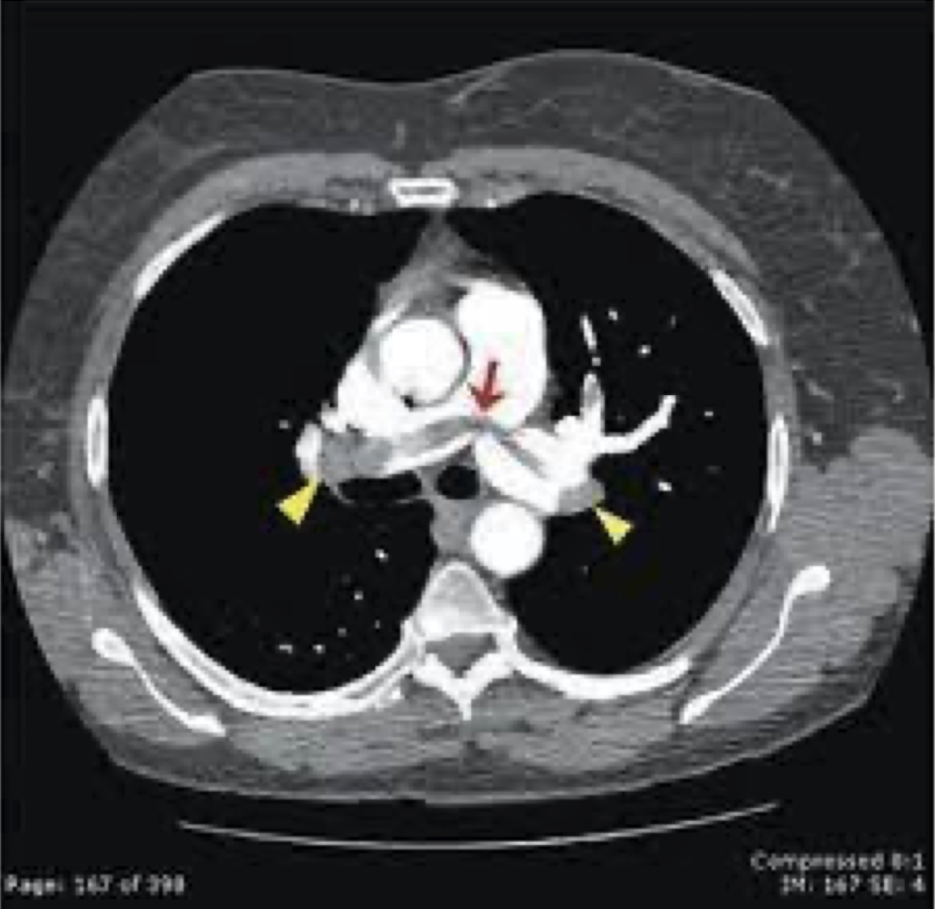
pulmonary embolism ( saddle embolus)
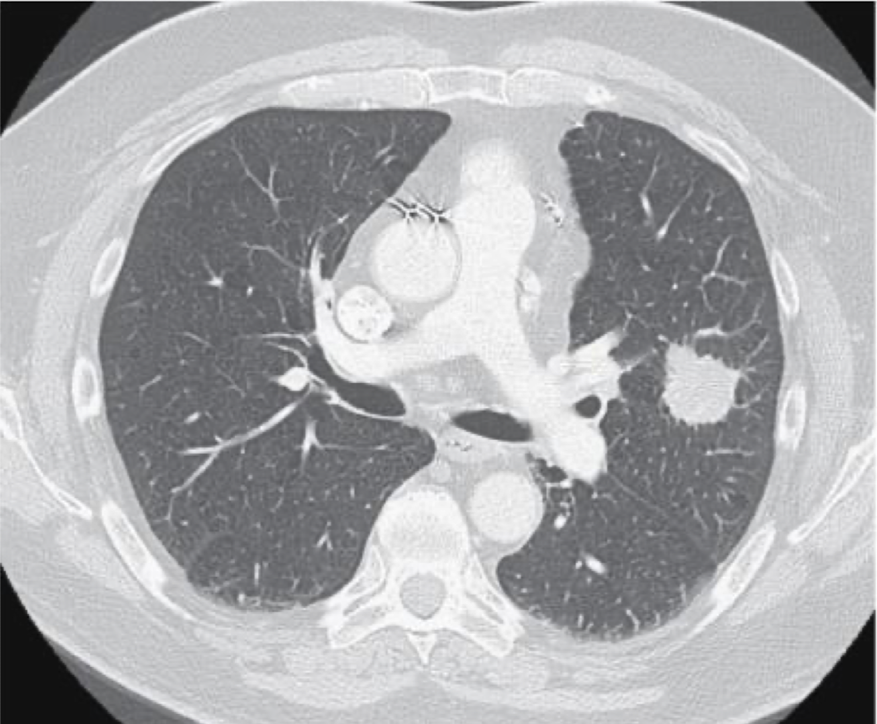
lung mass on CT
how do x rays work?
electrons areboiled off of a hot filament toward a tungsten anode, those then coiled with negative electrons to create an x ray photon beam, the beam is directed through a window and shot at the patient who has a receiving film behind them which then processes higher/lower density structures due to electron absorption
black: air, white: bone
radiolucent
black structures in an image showing things that are less dense
radiopaque
white structures in an image that indicate denser materials, such as bone. These areas absorb more x-rays, preventing them from reaching the film.
fracture lines on x ray
mostly black but sometimes white with impaction
what do visible fat pads tell us
soft tissue signs indicate a likely fracture
how many views of an x ray should you have
always more than one
r rules of assessing radiographs
1) always analyze all veiws
2) develop a systematic approach to checking radiographs even if something is obvious
3) check if prior radiographs exist
oral contrast
bariu swallows allow for enhanced bowel imaging
how does artifact happen
patient moving
can pregnant patient get imaging
Xray and CT should be assessed for risk benefit can have major contraindications in the first trimester
how do MRI work
powerful magnet produces a strong magnetic field that forces protons to align with its field, then the protons are stimulated to pull against the field. lastly the field is turned off and the MRI senses the energy release as the protons realign which forms an image based on time it takes to realign
T!: longitudinal relaxation
enhances fatty tissue and suppresses water
T2: transverse relaxation
enhances the signal of water
how does US work
piezoelectric transducer is used to emit and receive high frequency sound waves, shade of grey is assigned to each amptitude
strong echos: white, weak echos : black nechouca
anechoic
no reflection, appears black ( ex: water)
hypoechoic
dpoes not reflect as well as the structures around it and appears darker than its surroundings (soft tissue)