Honors Chemistry Unit 2 (Classifying Matter)
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
matter
substance and mixture
substance
elements and compounds
extensive properties
depend on amount
extensive properties examples
mass, volume, length
intensive properties
depends on the TYPE of matter (not amount)
intensive properties examples
density, melting point, boiling point
physical property
condition of a substance that can be observed without changing the substance
physical property examples
mass, volume, length, density, melting point, boiling point
chemical property
how one substance reacts with another
chemical property examples
CH4 (methane) reacts with O2
solis (s) or (cr)
fixed shape and fixed volume
liquid (l)
takes shape of container, fixed volume
gas (g)
takes shape and volume of container
elements
atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons, cannot be broken down by chemical reactions
compounds
combinations of atoms, can only be broken down by a chemical reaction
atomic number
number of protons an atom has
how to find the number of neutrons
mass = number of protons + number of neutrons
relationship between number of protons and neutrons in atoms
number of protons = number of neutrons
isotopes
same element with different number of neutrons
quantum mechanics
used for very small pieces of matter moving very quickly such as PHOTONS
newtonian mechanics
used for matter under usual conditions such as PROTONS
what are chemical reactions based on?
electrons
heisenberg uncertainty principle
it is impossible to know both the location and direction of an electron, the bohr model was dead
schroedinger’s equations
modern atomic theory; mathematical model that describes 90% probability orbitals, the best we can do is use probability to describe where electrons are likely to be found
aufbau principle
electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first
pauli exclusion principle
an atomic orbital can only hold two electrons each with a different spin
hund’s rule
with orbitals of the same energy, a single electron must occupy each orbital before they pair up
orbital
a pair of electrons
principal quantum number (n)
-tells you the energy level of the electron
-distance from the nucleus
-size of the electron cloud
second quantum number (l) —> (lowercase L)
-tells you the sublevels of the electron
sublevel s
can hold 2 electrons, shape is a sphere
sublevel p
can hold 6 electrons, shape is a dumbell
sublevel d
can hold 10 electrons, don’t worry about shape
sublevel f
can hold 14 electrons, don’t worry about shape
third quantum number (m)
-the space occupied by one pair of electrons is called an orbital
-describes the orientation in space of this orbital
fourth quantum number (spun quantum number) (s)
-no two electrons can live in the same space, in other words, occupy the same spot so this quantum, number designates the “spin” of the electron
valence electrons
electrons that are located in the outermost electron shell of an atom (highest energy level)
electron configuration chart
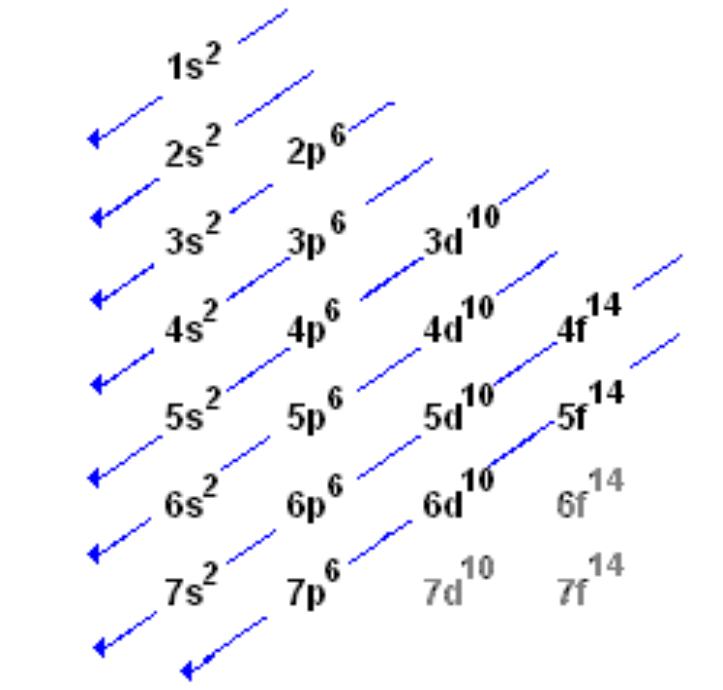
what determines the order of the elements on the periodic table?
the number of protons
what determines the shape of the periodic table?
electron configuration
s block
groups 1 and 2
p block
groups 13 through 18
d block
groups 3 through 12
f block
lanthanide series and actinide series
what do atoms become when they gain or lose electrons?
ions
noble gases
group 18
octet rule
to become stable, atoms want 8 electrons in their outer shell (hydrogen and helium want 2)
oxidation number (charges)
the most common charge that an element uas after it has
group 1 oxidation number
+1
group 2 oxidation number
+2
aluminum oxidation number
+3
zinc oxidation number
+2
silver oxidation number
+1
group 15 (N as P) oxidation number
-3
group 16 oxidation number
-2
group 17 oxidation number
-1
atomic radii (trend: increasing from top to bottom)
size of the atom
first ionization energy (trend: increasing from left to right, increasing from bottom to top)
amount of energy needed to pull the highest energy level electron off of the atom
cation (metals)
positive ion
anion (non-metals)
negative ion
group 1 name
alkali metals
group 2 name
alkaline earth metals
groups 3-12 name
transition metals
groups 17
halogens
group 18 name
noble gases
wavelength
the distance from one crest to another, usually measured in m, cm, nanometers

wavelength symbol
frequency
how many waves pass a point per second, measured in hertz
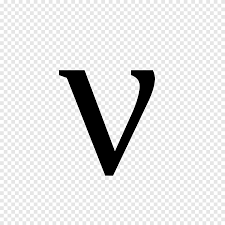
symbol for frequency
the speed of light
3.0 × 10^8
planck’s hypothesis- energy is quantized
energy is given off in little packets called quanta/quantum/PHOTON, energy of a wavelength was related to its frequency