Chemistry Quiz 2
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Blackbody Radiation
Planch
Photoclentric effect
Eistein
Atomic Line Spectra
Bohr
Heisenberg’s uncertainty Principal
It is not possible to know the position and energy if a moving particle at the same time.
Atomic Orbital
Where an electrons spends most of its time e- of a specific E
Energy (n)
Size of atomic orbital and distance from nucleus
Shape (L)
Angular Momentum
Orientation (ml)
spatial orbital orientation
L
=Integer from 0 to (n-1)
Which n=# is the closest to the nucleus
n=1
How to find L numbers
L→0→(n-1)
Magnetic Quantium # (ml)
-L→0→+L
Value of L=0
S
Value of L=1
P
Value of L=2
d
Value of L=3
f
Value of L=4
g
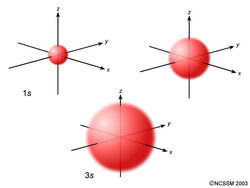
L=O (s orbital)
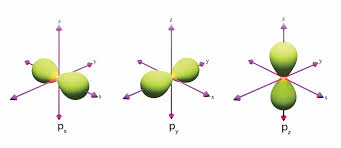
L=1 (p orbital)
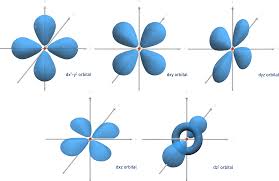
L=2 (d orbital)
Ms
Electron spin quantum # (+1/2 or -1/2)
Paulis exclusion Principle
No two electrons in the same atoms can have the same 4 quantum numbers.
Aufbau Principle
Electrons frill orbitals start at lowest possible energy before filling higher stats.
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
Max two Electron with opposite spins
Hunds Rule
When orbitals of equal energy are avaliable the electron configuration of the lowest energy has max # of unpaired electrons with parallel spin.
Condensed Configuration
Has the same symbol of the previous noble gas in square brackets
Exceptions to 4s & 3d Sublevels
Chromium (Cr; z=24) → [Ar] 4s13d5
Copper (Cu; z=29) → [Ar] 4s13d10
Inner (Core) Electrons
Electrons that are closer to the nucleus, Subtract the number of valence electrons from the atomic number.
Outer electrons
Highest energy Value/Level and spend most of their time away from the nucleus
Valence electrons
The electrons in the outermost shell.
Main group: Valence electrons are outer electrons
Transitional: Valence electrons include outer ns electrons and any (n-1)d electrons
paramagnetism
attracted by a magnetic field
Diamagnetism
not attracted and slightly repellent magnetic field
The three atomic properties
Atomic Size, Ionization energy, electron affinity
Metallic Radius
Metals, ½ shortest distance between nuclei
Covalent Radius
Non metals, ½ shortest distance but bonded atoms
Trends in atomic size (Main group)
Increases down a group and decreases across a period.
Ionic Radius
Measure of the size of an Ion and is obtained from the distance between the nuclei of adjacent ions in a crystalline ionic compound.
Trends in Ionic compounds (Parent atoms)
Cations are smaller while anions are bigger
Trends in Ionic Compounds (Ionic Radius)
Increases down a group, generally decreases except from the last cation to the first anion
Trends in Ionic compounds (Cation)
Cation size decreases as charge increases
isoelectronic series
Atoms that have the same electron configuration, ion size decreases as nuclear charges.
Ionization energy (IE)
Energy required for the complete removal of 1 mole
Ionization Energy Trends (Group)
N value increases
atomic size increases
distance increases
attraction lessens
Ionization energy Trends (Period)
Zeff increases
atomic size decreases
attraction increases
Low IE
Cations
High IE
Anions
Electron Affinity
Energy change that occurs when 1 mol of electrons is added to 1 mol of gaseous atoms or ions
Low EA
Cations
High EA
Anions
Reactive Non-Metals
High IE, Highly negative EA and form negative ions
Reactive Metals
Low IE, Slightly negative EAs and form positive ions
Nobel gases
Very High IE, Slightly positive EAs
Metallic Bonding
Electrons pooling with a metal to another metal
Bonding capacity
Number of Covalent bonds an atoms forms to have an octet of electrons in a valence shell
Coulombs Laws
Electrostatic potental Energy
Energy = (Charge 1 x Charge 2)/Distance (Size)
Lattice Energy
Enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mole of ionic solid separated into gaseous Ions
Lattice energy trends
As ionic charge increases, Lattice Energy Increases
As Ionic size decreases, Lattice Energy Increases
Ionic Compounds (Physical Behavior)
Hard, Rigid, Brittle
Ionic Compounds (Electrical Conductivity)
Do not conduct in a solid state but do if melted or dissolved
Ionic Compounds (Thermal Conductivity)
High melting points and a much higher boiling point
Bond Energy
Bond Enthalpy or bond strength
Endothermic
Bond Breakage
Exothermic
Bond forming
Bond Length
Distance between the nuclei of the bond atoms
Trends in Bond Order (Length)
Higher bond oder results in shorter bond length and higher bond energy
Increases down a group and decreases across the period
Shorter bond
Stronger bond
Molecular Covalent Substances
Individual molecules
strong intramolecular forces
Much weaker intramolecular forces (IF)
Network Covalent Solids
No separate molecules
Strong Intramolecular forces
Molecular Covalent Compound (Physical Properties)
Soft, low melting, and low boiling
Network Covalent solid (Physical Properties)
Hard, high melting point
Covalent Electric Conductivity
Most are poor conductors whether melted or not
Polar Covalent Bonds
Unequal Sharing of bonding pair, uneven distribution of charge (Much more common)
Electronegativity Trends
Down a group energy decreases as size increases
Across a period (Main group) it increases.
Nonmetal are more Electronegative than Metals