Lecture 6- transport across membranes
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
major component of cellular membranes
phospholipids
hydrophobic transmembrane domains interact with
fatty acid what of membrane lipids
tails
many membrane proteins have # transmembrane domains
multiple
an enzyme that breaks proteins into very small pieces, too small (generally) to see in an SDS-PAGE ge
trypsin
rypsin can or can not get into a cell – thus transmembrane
and internal proteins are protected
can not
some molecules penetrate the lipid
bilayer:
oil-soluble (partition coefficient) or very # molecules (O2)
small
Large uncharged polar molecules like glucose, sucrose, amino acids or IONS are not permeable and must be transported by what
proteins
from area of high concentration to low concentration
Passive Transport
from area of low concentration to high concentration
Active Transport
movement of H2O from an area of low solute
concentration to an area of higher solute concentration
Osmosis
In passive transport H2O can diffuse what through membrane
quickly
H2O enters/exits cells through specialized pores called what
aquaporins
H2O molecules pass through aquaporins how
one by one
Aquaporins’ Channel wall is positively charged and binds to negatively charged what; thereby disrupting H bonds that link H2O molecules together
Oxygen
facilitated diffusion (transport) of what through membranes via transporter
glucose
Most cells contain a glucose transporter that facilitates the diffusion of glucose from the blood stream into the cell to be used for what
energy
hormone produced by endocrine cells of the pancreas -
it maintains blood sugar levels
Insulin
at what insulin levels few transporters are on the cell surface. (limits uptake)
low
Insulin stimulates the what of the glucose transporters
exocytosis
small ions (K+, Na+, Ca2+, Cl-) can or can’t diffuse through lipid bilayers
can’t
most ion channels are what for specific ions
selective
determined by the concentration difference of the substance on the two sides of the membrane
chemical gradient
determined by the charge difference between the two sides of the membrane
electro-potential gradient
pen based on differences in ionic charge between the inside and outside of the cell
(membrane potential)
voltage-gated channels
open based on a “ligand”
binding to the channel (conformational change)
can bind to either inside or outside of membrane
ligand-gated channels
open in response to force or other stimuli
mechanosensory gated channels
K+ channel of bacteria: only permits K+ ions to bind
selectivity filter
channel (alpha helices), selectivity filter, and the gate (M1-M2 helices ~ S5-S6 helices)
Pore domain
Senses the voltage across the membrane
Voltage-sensor domain
resting
negative membrane potential
S4 (+ charges)move from cytoplasmic exposure to extracellular
exposure
positive membrane potential
conformational changes does what the channel
close
genetic diseases linked to ion channels
channelopathies
Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid (TRPV) is gated by
ligands or by what (& pain)
heat
you discovered a new channel!
• you name your new channel “Ch 303 - HD”
• your observation: it multimerizes and folds in such a way that there is a very small pore lined with amino acids with a positive or partially positive charge
predict what most likely travels through this channel:
anions (negatively charged ions)
you try a “patch clamp” experiment
• measures ion flow by measuring electrical current
• you find that your channels is specific for Cl-
• but, you only observe current flow when you add cAMP into your cell, not when you apply a voltage
what kind of channel is this?
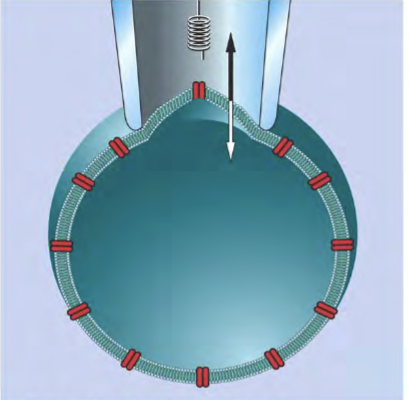
ligand-gated ion channel
more about channel 303…
given that the Cl- concentration is 110 mM outside
the cell, and 10mM within the cell, what direction do
you expect Cl- ions to flow in the presence of ligand?
you make a mutant form of your channel that deletes the
C-terminal region:
How to you expect this to alter ion flow?
makes it constitutive (ie, unregulated and constant)
(pumps) use ATP for energy
primary active transporters
use stored energy (gradients of other molecules) to move a substance against its gradient
secondary active transporters
movement against a concentration gradient occurs by what
active transport
what mediate active transport – drive a given ion in only one
direction
pumps
Pumps are critical:
• maintain what pH inside lysosomes
• maintain what pH inside the stomach
• store ionic energy
low
pumps move substances how a concentration gradient (active transport)
against
This pump creates the big difference in the concentrations of Na+ and K+ inside vs outside the cell
he Na+/K+ ATPase pump
what binds to the transport protein on the inside of the cell with high affinity
Na+
what is hydrolyzed and the released P binds to the transport protein
ATP
binding of P changes the transporter’s
configuration and affinity for what
released to the outside of the membrane
Na+
most of the time proteins are associated with something else in the cell in a complex (C) via which bonds
non-covalent
If the protein and ligand have what affinity, very little ligand is required to get a complex
high
K+ binds to the pump
P dissociates causing the pump resumes its original conformation
this does what to K+ binding affinity
lowers
K+ diffuses into the what
cytoplasm
must have a higher binding affinity for what inside the cell and a lower binding affinity for what outside of the cell
Na+
must have a higher binding affinity for what outside of the cell and a
lower binding affinity for what inside the cell
K+
different affinities are achieved by phosphorylating the what protein
transport
Na+/K+ pump is only in which cells
animal
H+/K+ pump in the what (pumps acid into; pump translocates to plasma membrane after eating)
stomach
H+ proton pump in what is important for import of solutes and
control of pH
plants
superfamily of pumps
• present in bacteria through mammals
• pump ions, sugars, peptides, polysaccharides, proteins!
ATP-binding cassette (ABC)
Defects in pumps, transporters, or channels often lead to
what
disease
tumor cells become resistant to chemotherapy
multi-drug resistance (MDR)
MDR-1 protein is part of a pump (ABC transporter) that pumps
what materials out of cells
toxic
MDR-1 expressed in normal liver and what to export
toxic molecules
kidney
BUT in cancer cells: MDR-1 gene is amplified and over-
expressed so chemotherapy drugs that diffuse through the which cell membrane are pumped out
cancer
what (secondary) transport takes advantage of stored energy
coupled
gradients created by what ion pumping store energy that can be coupled to other transport processes
active