Biochemistry Chapter 2; Nucleic Acids
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nucleic Acids and PCr
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is the structure of ribonucleotides?
Ribonucleotides contain a nitrogenous base (A, G, U, C), a carbohydrate sugar, and a phosphate.
The 5 carbon sugar contains an OH group.
What is the structure of deoxyribonucleotides?
Deoxyribonucleotides contain a nitrogenous base (A, G, C, T), a carbohydrate sugar, and a phosphate.
The 5 carbon sugar only contains H, no OH.
What are the properties of nitrogenous bases?
They are heterocyclic; containing 1 or 2 rings (pyrimidine:purine).
They contain ketone, amine, or methyl groups to participate in H-bonding).
They’re never found in an ionized state - are nonpolar.
They’re aromatic and have resonance; can absorb UV.
Resonance stabilizes the compound.
What are the purines?
Heterocyclic n-bases with 2 rings;
Adenine
Has an amino bonded to a ring C.
Guanine
Has an amino and double bonded oxygen bonded to ring C’s.
*Used in DNA, RNA, metabolism, signalling.
What are the pyrimidines?
Heterocyclic n-bases with 1 ring;
Cytosine
Has an amino group bonded to a ring C, and a double bonded oxygen.
Bonds to Guanine.
Thymine
Has two double bonded oxygens and a methyl group.
Bonds to Adenine (DNA).
Uracil
Has two double bonded oxygens.
Bonds to Adenine (RNA).
What is tautomerism?
When a compound can migrate protons, which results in manipulated functional groups in the enol form.
NH2 → C=NH
Amino → Imino
C=O → C — OH
Ketone → Hydroxyl
**Usually less favored in biochemistry and is pH dependent.
Enols manipulate H-bond ability and catalstic centers.
Why is tautomerism bad?
It can modify hydrogen bonding properties, and alter catalytic centers.
DNA vs deoxyribonucleotide?
DNA is made of multiple deoxyribonucleotides.
What is a nucleoside?
A 5 carbon sugar linked to a nitrogenous base through a glycosidic bond at the 1’C.
DNA; A, G, C, or T glycosidically bonded to the 1st carbon of the sugar ring.
RNA; A, G, C, or U glycosidically bonded to the 1st carbon of the sugar ring.
What is a nucleotide?
A nucleoside bound to a phosphate group through a phosphoester link to the OH group on the 5’C.
Nucleoside monophosphate.
Additional phosphate groups can be added through phosphoanhydride links.
Nucleoside di/tri=phosphates.
Characteristics of nucleotides?
The phosphate group produces a negative charge at neutral pH.
Triphosphates can donate 3 protons - polyprotic; ATP.
They can link with divalent metal ions.
They hydrolyze with negative ΔG; they can be used in coupling to drive non-spontaneous reactions.
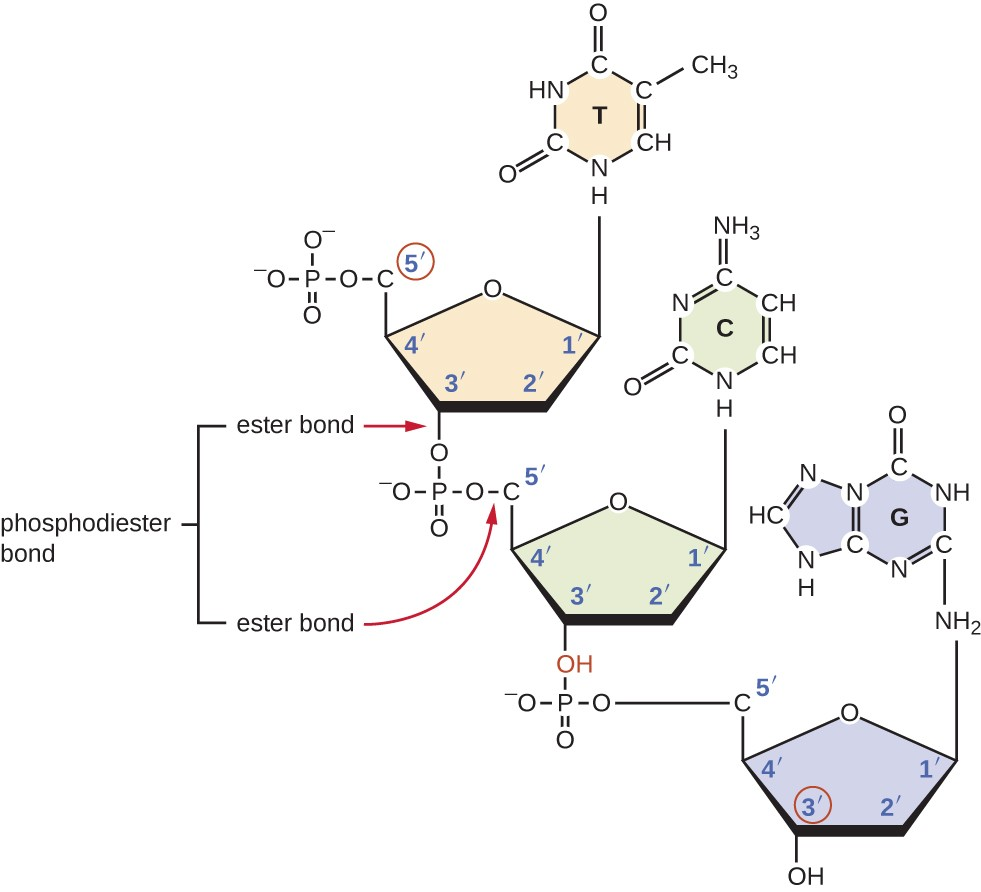
How do nucleotides come together to form DNA or RNA? What type of bond and where?
A phosphodiester bond is created between the phosphate of one nucleotide (at the 5’ C), and the hydroxyl on the 3’C of another.
Water is released as a byproduct.
Where is the code of life stored, and transferred, according to the central dogma?
In purine and pyrimidine base matching, through hydrogen bonds.
What base pairs are harder to denature?
G-C base pairs, because they have 3 sites of H-bonding, increasing the melting point. Therefore they are harder to break compared to A-T/A-U.
G-C dense areas are harder to denature.
DNA vs RNA?
DNA:
Two antiparallel strands of deoxyribonucleotides, twisted into a double helix.
T pyrimidine.
Deoxy.
RNA:
A single strand of ribonucleotides bound together by phosphodiester bonds, folded into complex figures.
U pyrimidine.
Ribo.
How do proteins interact with DNA?
Through the major and minor grooves formed by the double helix.
What forces stabilize the DNA double helix?
Stacking of n-bases in the hydrophobic core of the helix.
Due to dipole-dipole, pi-pi, and London dispersion forces.
Exhibits the hydrophobic effect, allows water to be less ordered and have higher entropy.
Charge-charge repulsion of phosphate groups.
Coulombic effect.
Backbone interactions with water.
Three types of DNA helixes? Most common one in cells?
A, B, and Z DNA.
B DNA is most common cells; wider major groove and narrower minor groove.
A DNA is common in labs.
Z DNA is a left-handed twist common in complexes.
Ratios of purines:pyrimidines and their pairs?
The ratio of purine:pyrimidine pairing is 1:1 in any strand; if 30% of my DNA strand contains A, then 30% of it must also contain T (its base pair).
40% is left, split between G:C; so 20% each.
What forces fold the RNA strand?
RNA forms helical sections of 3-12 nucleotides using a single strand. Stabilizes by the;
Hydrophobic effect.
3D shape.
Same week forces as DNA.
RNA is more diverse than DNA but less stable than DNA (d/t 2’C OH attacking backbone).
Why does replication occur from 5’-3’?
Because the OH on the 3’C is capable of nucleophilic attack, allowing the formation of a new phosphodiester bond with another nucleotide (via their phosphate group). Replicating from 5’-3’ leaves this site open for new polymerization.
Binding at the phosphate end (3’-5’) would make proofreading impossible due to the loss of energy needed for coupling.
Structural features of DNA replication? What keeps it at a low error rate?
DNA is organized into chromosomes, containing all the genetic material of the cell.
The antiparallel double strand formation allows for two template strands.
A daughter cell receives one parent and one synthesized — semi-conservative.
Replication forks make leading and lagging strands; okazaki fragments have to be ligated on the lagging strand.
DNA pol can only synthesize 5’-3’.
What is the rate-determining step in eukaryotic cell division?
DNA replication.
What is bidirectional replication and why is it helpful?
It refers to the idea that DNA pol can only add nucleotides to the 3’ end OH of the strand. This means that in a replication fork both a leading and lagging strand are synthesized, bidirectionally and outwards..
Allows for multiple replication forks to be working on a chromosome simultaneously.
What is the pathway to synthesizing proteins?
DNA is first transcribed into mature mRNA, which is translated into protein by ribosomes and tRNA.
Key features of transcription?
Eukaryotic genes coded in DNA are separated into introns (non-coding) and exons (coding).
Transcription factors bind to the 5’ end promoter region, to elicit RNA pol to make a premature mRNA.
Introns are spliced out to form a mature mRNA.
A 7-meth.guan cap and poly-A-tail are placed on the 5’ and 3’ end to prevent degradation and stabilize.
Key features of translation?
Ribosomes catalyze the reaction.
tRNA reads the mRNA code in 3’s, and transfers a specific amino acid to the chain.
There is 1 code for 1 AA.
How can we regulate gene expression ?
Transcription factors can up or downregulate gene expression and mRNA synthesis.
mRNA riboswitches fold it into a complex shape, disabling translation.
RNAi forms a dsmRNA.
Virus vs Retrovirus?
A virus contains DNA or RNA as they genetic material.
A retrovirus has RNA genes, but uses a DNA intermediate at some point.
Both infiltrate host cells to survive and replicate.
How do mutations affect the central dogma?
Chemical degradation via UV light or heating can denature or mutate DNA
Chemical damage can invoke crosslinks in bases, altering the transcription pathway.
What is the central dogma?
The flow of genetic material; how information is expressed in the genome.
DNA→RNA→Protein.
Name the three steps of PCr?
Denature; heat to break h-bonds and separate strands (90c).
Anneal; to create forward and reverse sites through primers (cool temp).
Extension; Heat to synthesize via taq (72c).
Amplify and repeat.
What are the properties of PCr? What are the 5 components?
In vitro.
Amplifies specific DNA fragments.
Only replicates selected pieces.
Creates an unmodified DNA copy.
DNA primers to target each end.
Taq polymerase to bind and add.
dNTP’s to create new strand.
Buffers
Target DNA
What amount/ratio does PCr amplify?
It doubles the number of double-stranded pairs of DNA each cycle.
Quadruples the number of single DNA strands.
Amplified 10^6 times after 25 cycles.
What enzymes can manipulate DNA?
Restriction enzymes; cut sequences.
Ligase; joins fragments.
Polymerase; generates a copy.
Topoisomerase; unwinds DNA.
Reverse transcriptase; converts RNA→DNA.
How does DNA cloning occur?
Occurs in vivo (a living organism), using plasmids, target DNA, and a carrier host.
Restriction enzymes cut a fragment of target DNA and a plasmid.
Plasmids (short bacterial loops, cloning vectors) are capable of inserting and replicating in a host.
The target DNA is ligated to the plasmid, forming recombinant DNA.
The recombinant DNA is inserted into a bacterial host through transformation, transfection, or infection.
Host cells replicate the recombinant DNA.
What does cloning mean?
To generate copies of DNA by inserting a fragment into another living host, and propagating it through growth and replication.
How can we verify successful cloning transformations?
Antibiotic resistance; plasmid contains AB gene and is placed on media containing the antibiotic. Only bacteria that took up plasmid will grow.
Markers (lacZ → X-gal); colonies turn blue in the presence of X-gal. Gene ligation disrupts lacZ on the plasmid, so colonies appear white. White = recombinant DNA.
Gene sequencing; checking to make sure genes were inserted with no mutations and the correct orientation.
What is qPCr?
qPCr allows the detection of PCr product after each individual cycle.
Real-time quantification of DNA present.
Allows the comparison of specific nucleotides, gene expression, and present copies from different samples.
How does Taqman qPCr work?
Taqman qPCr is a probe bound to fluorophore on one end and a quencher on the other.
The probe is bound to the target sequence of DNA.
As Taq pol synthesizes the strand, its exonuclease activity cleaves the probe into single nucleotides.
The fluorophore is separated from the quencher.
Fluorophore emits a signal when a specific DNA sequence is amplified, and it’s intensity increases as more DNA is amplified.
**The threshold is set by researcher, to determine when a detectable amount of nucleotides have been created.
What enzyme cleaves hydrogen bonds of nitrogenous base pairs?
Helicase.
What does DNAa do in prokaryotes?
It binds to ATP when ATP is high, forming a DNAa-ATP complex. The complex binds to the DNA box and promotes replication.
What triggers DNA replication in eukaryotes?
DNA replication occurs as part of the cell cycle;
A signalling cascade where kinase action forms pre-replication complexes.