Unit 3: DNA & RNA
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Why DBA replication is needed
production of gametes - sex cells during meiosis
Growth + repair of tissue - mitosis
Semi - conservative
Replication of DNA - one old + one new strand
When cell = ready to divide - 2 strands of double helix = seperate
Each of original strands acts as template for the creation of a new strand
new strands = assembled through complimentary base pairing
DNA Replication
Unwinding + unzip double helix with enzyme HELICASE
Unzips to position called replication fork
Nucleotides base pair through complementary base pairing
DNA Polymerase joins together nucleotides - strong phosphodiester bonds
DNA polymerase only adds nucleotides in 5’ to 3’ direction
Double strand reforms a double helix
Polymerase chain reaction
Used for making copies of DNA artificially
Used to amplify/make millions of DNA copies
Taq polymerase = heat resistant version of DNA polymerase
PCR = Cloning DNA at rapid speed
Temperature used instead of enzymes to break H bonds - 95 degrees
Gel Electrophoresis
Fragments of DNA move in electrical field and are separated
Separation = based on size/mass
Sample of DNA = placed on wells ong el
Electrical current = passed across gel
DNA = negatively charges - when electrical current is passed through
DNA fragments move to positive electrodes
Large Fragments move slow
Small fragments move quicker
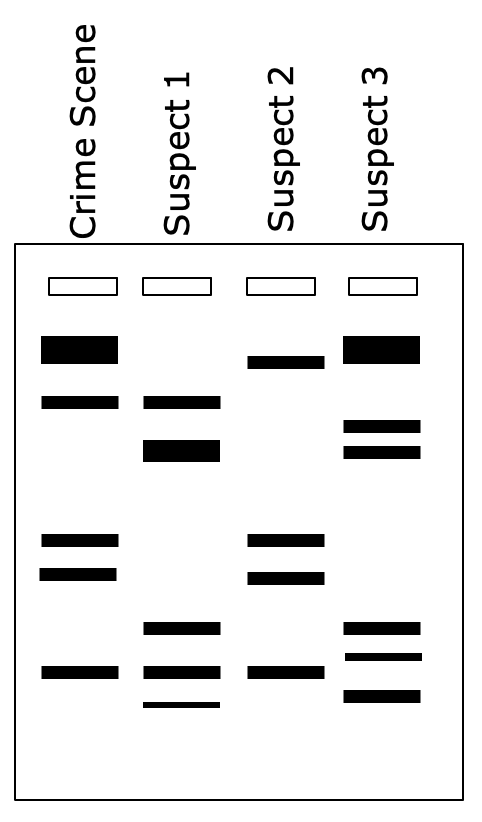
Gel electrophoresis used in DNA profiling
Used to differentiate between individuals
Technique can be used for:
Forensic crime investigations - see if suspects DNA match DNA on scene
Parentage issues
Animal breeding
Disease detection
HL - DNA replication
Takes place during S section of interphase
5’ to 3’
Antiparallel strands
Replication begins at sites ‘origin of replication’
Helicase attaches + unzips and unwinds - breaks hydrogen bonds
Gyrae keeps DNA strands separated
RNA Primase synthesises small amount of RNA primer (will be changed to DNA)
DNA polymerase III can only join Nucleotides in 5’ to 3’
only nucleotides can join to 3’ end called leading strand
On other side DNA polymerase works away from replication fork
Create small fragments - Okazaki fragments - Lagging strand
Several primers - one between each fragment
Enzyme Ligase joins okazaki fragments to form one continuous DNA molecule
DNA polymerase I replaces RNA primer with DNA
DNA polymerase 3 can check its work and repair mismatched bases
What is the full name of DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
What does DNA carry?
the genetic code for all living organisms
What is the genetic code said to be?
Universal
Where is DNA usually found?
In the nucleus
Apart from the nucleus, where else could DNA be found?
in the chloroplasts or the mitochondria
What is the full name for RNA?
Ribonucleic Acid
What is RNA the main component of?
Ribosomes
Apart from ribosomes, where else is RNA found?
in the cytoplasm and the nucleus
Are viruses considered living?
No
What are RNA and DNA?
Polymers
What are the subunits of DNA and RNA?
Nucleotides
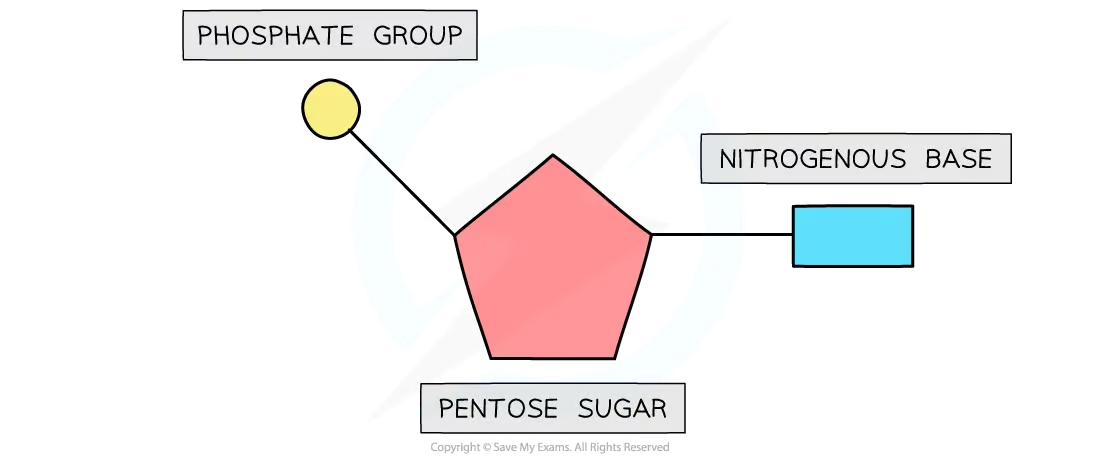
What are the components of nucleotides?
A pentose sugar, nitrogenous bases, and a phosphate group
What are the two type of pentose sugars?
ribose and deoxyribose
What pentose sugar does RNA have?
ribose
What pentose sugar does DNA have?
deoxyribose
What are the two types of nitrogenous bases?
Purines and Pyrimidines
What are the purines?
A and G
What are the pyrimidines?
T and C
What distinguishes purines and pyrimidines?
purines have two rings, pyrimidines have one
What are the nitrogenous bases for DNA?
A, G, C, T
What are the nitrogenous bases for RNA?
A, G, C, U
What are the full names of all the bases?
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
What is the chemical formula for a phosphate group?
PO₄⁻
What are the complimentary bases in DNA
A and T are complimentary, G and C are complimentary
Draw a Nucleotide
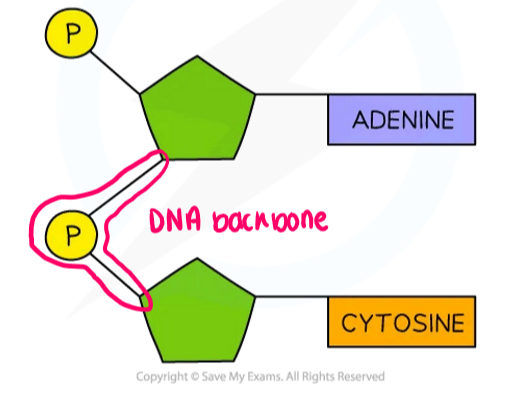
What is the DNA backbone (show on diagram)
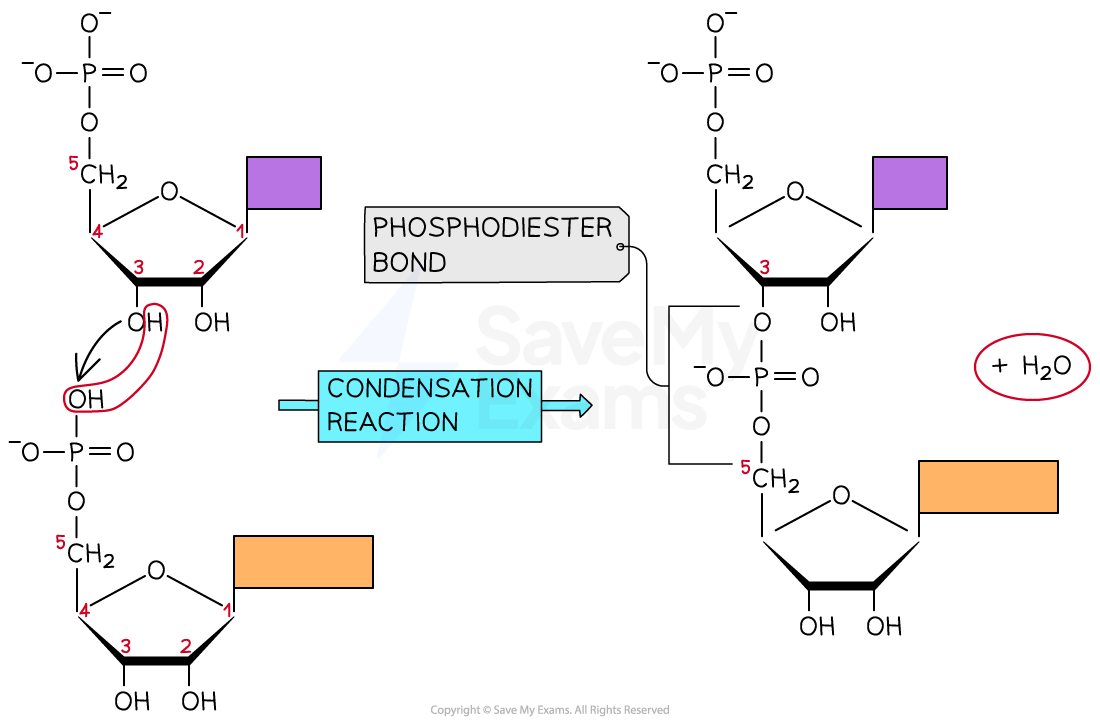
How is the bond between the phosphate group and carbon 3 on the pentose sugar made?
Condensation
What is a polymer of nucleotides (forming a nucleic acid) known as?
a strand
Describe the structure of ribonucleic acid
Relatively short, a single-stranded polynucleotide, with ribose as the pentose sugar
What is the name of the bond between a carbon atom of a pentose sugar and the phosphate group?
A phosphodiester bond
Draw the formation of a phosphodiester bond
What are the three types of RNA?
messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRna)
What is the role of tRNA?
transports amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis
Define mRNA
formed in the nucleus and transported to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
What is the use of rRNA?
forms part of ribosomes
Define the structure of DNA
A double helix made of two anti-parrallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonds between complimentary nitrogenous base pairs.
How many hydrogen bonds are between A and T?
2
How many hydrogen bonds are between G and C?
3
What are the three main differences between DNA and RNA?
in RNA the pentose sugar is ribose, in DNA the pentose sugar is deoxyribose
In RNA there’s no base thymine, instead there’s uracid, in DNA there’s no base uracil, instead there’s thymine
RNA is single stranded, DNA is double stranded
What are the three roles of bases pairing?
DNA replication, transcription, and translation
Define briefly the role of base sequences in DNA replication
the base sequences in DNA can be accurately copied so the genetic information of a cell can be passed on to daughter cells
Define briefly the role of base sequences in DNA transcription
RNA can be made of the same base sequence as 1 of the DNA strands, mRNA carries the sequence of a the protein coding gene to the ribosome
Explain (in detail) translation using complimentary base pairs and codons
A base sequence can be used to determine the the amino acid sequence in a polypeptide. mRNA has a three-base codon, tRNA carries a three-base anticodon and 1 amino acid. Ribosomes link condons to anti-codons by complimentary base pairing
What is the formula for the number of base pairs?
4ⁿ
How much information can be stored in DNA?
A limitless amount
how many codons are there?
64
How do codons provide proof of LUCA?
There are billions of ways to assign meaning to codons, but all living organisms do the same way (with slight variation)
What is the use of codons?
They can indicate any one of the amino acids
Where does the phosphate group form a bridge between when linking nucleotides?
Carbon 3 and Carbon 5
What is the name of the ends of nucleotides?
3’ and 5’
What molecule is at each end of the nucleotide?
OH
Draw a single strand nucleotide showing 3’ and 5’
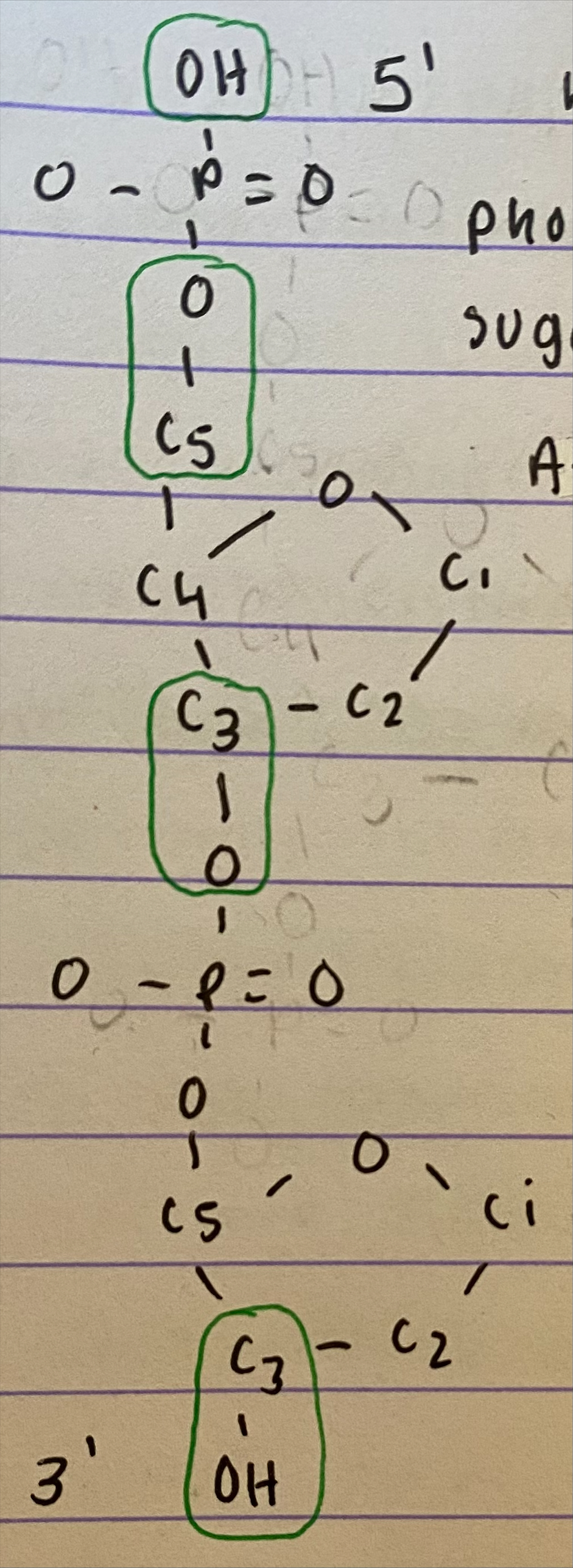
Explain the advantages of having a purine attach to a pyrimidine?
The width is always the same creating a stable molecule
explain the role of a nucleosome
A disc-like structure which packages DNA into a condensed chromosome which allows the control of replication and transcription
Define the structure of a nucleosome
8 histone proteins in it’s core with DNA wound twice around it and held together by an additional histone protein.
What is the name of the experiment that found that genes came from DNA and not proteins?
the Hershey-Chase experiment
What radioactive isotopes were used in the Hershey-Chase experiment?
³⁵S and ³²P
What bacteria was used during the Hershey-Chase experiment?
E. Coli
What element does DNA contain that proteins don’t?
Phosphur
What element does protein contain that DNA doesn’t?
Sulfur
What is the supernatant?
The liquid
What is the relationship between the percentages of bases A and G?
Their sum equals 50%
What is the relationship between the percentages of bases T and C?
Their sum equals 50%
What is the relationship between the percentages of bases G and C?
They’re equal
What is the relationship between the percentages of bases A and T?
They’re equal