C1 The science of cognition
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What is cogsci?
The science of how the mind is organized to produce intelligent thought and how the mind is realized in the brain
brief history of cogsci
Modern psychology begins 1879'
1st psychology lab in Germany
Wilhelm Wundt
Method: introspection
no clear results duh
America: action oriented psychology, functionalism
theory of learning, reward&punishment; Edward Thorndike ~1890
behaviorist revolution: 1920s-50s
John Watson
not dominant in Europe
Germany: gestalt psych
how the brain perceives experiences and processes patterns, not individual components
Cognitive revolution 1950-1970
behaviorism (1920s at least)
psych should only be concerned with external behaviour, consciousness is not a usable concept
let’s not talk about perception, image, desire, emotion etc
= external behavior is the concern, not the mind
created methods for experimental study
3 main influences of the cognitive revolution
information theory
computer science & AI
linguistics
Cognition
information processing
great feats of intelligence are the result of…
basic cognitive processes
introspection
analyzing thought into its components through self-analysis; examination on one’s own thoughts, feelings and behaviors
information processing approach
attempts to analyze cognition as a set of steps for processing info
=way to describe a cognitive process into components
abstract
aka component process approach
Sternberg’s abstract information processing account
not always to be taken literally; more abstract
information theory
abstract analyzing of information processing; the mathematical study of the coding of information
Cognitive neuroscience
how cognition is realised in the brain
biological processes
Neuron
a cell that accumulates and transmits electrochemical activity in the brain
key part of the makeup of the brain
neuron parts
dendrites, nucleus, soma (cell body), axon hillock, axon, myelin sheath, axon terminals (terminal boutons), synapses
+neurotransmitters, action potential, arborization
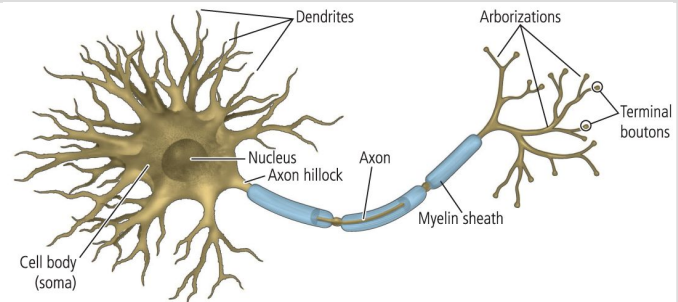
what is a myelin sheath comprised of
myelin, schwann cells and nodes of ranvier
central nervous system CNS
brain + spinal cord
cerebral cortex
aka cortex
most recently evolved
gyri (gyrus)
sulci (sulcus)
divided (brodman areas, major sulci (lobes))
subcortical structures
under the neocortex
generally associated with low-level, primitive functions
breathing, heartbeat, basic drives (cerebellum), memory (hippocampus), basic emotions and threat responses (amygdala)
topographical organization
adjacent areas of the body (or visual field) are represented in adjacent brain areas
Neural imaging techniques
single-cell recording
EEG
Magnetoencephalography MEG
Positron emission tomography PET
fMRI
TMS
the methods differ in e.g. spatial and temporal accuracy
MEG
magnetoencephalography
PET
positron emission tomography