Chp 18: Esters, Epoxides, Thiols and Sulfides
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
preparation of ethers:
Williamson ether synthesis requires..
an alcohol
primary alkyl halide or primary tosylate
a strong base (ex: NaOH, NaNH2)
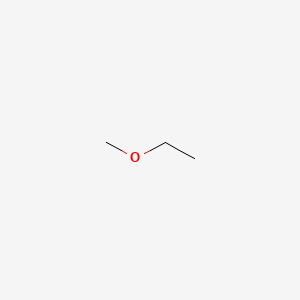
classification
IUPAC
Common name
unsymmetrical
ethyl methyl ether
1- methoxy ethane
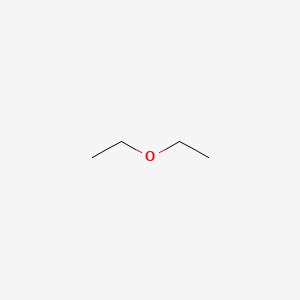
classification
IUPAC
Common name
symmetrical
diethyl ether
1- ethoxy ethan
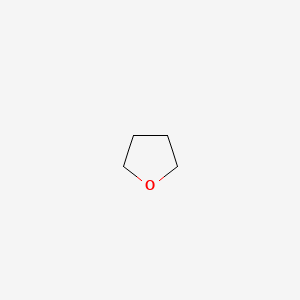
classification
Common name
cyclic
Tetrahydrofuran (THF)
Reaction of ethers: Using HBr or HI
HCl does not cleave ethers because
Bromine and Iodine are larger than Chlorine and therefore can stabilize the negative charge much better than leaving groups
ether mechanisms:
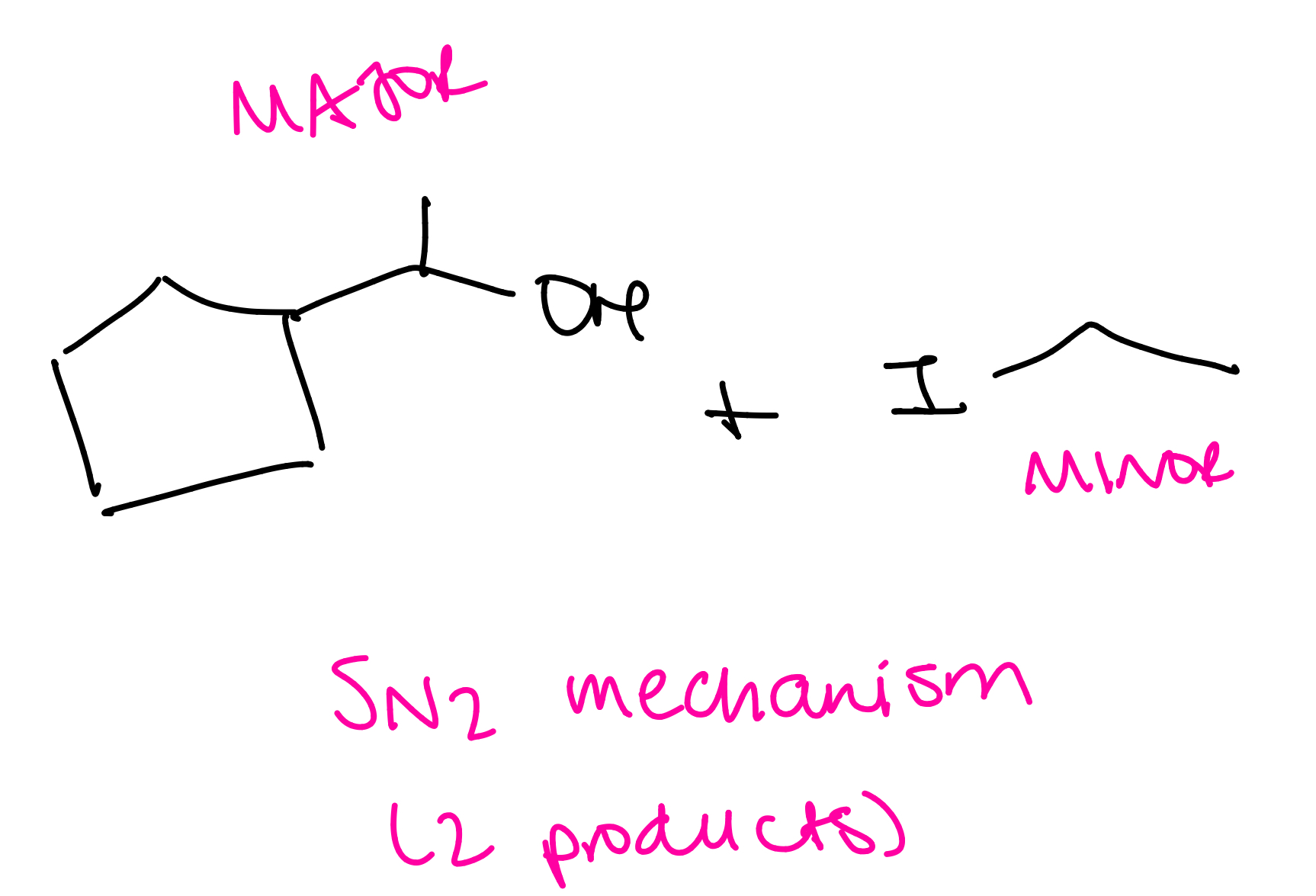
ethers with primary or secondary alkyl groups (SN2)
nucleophile attacks the least sterically hindered carbon
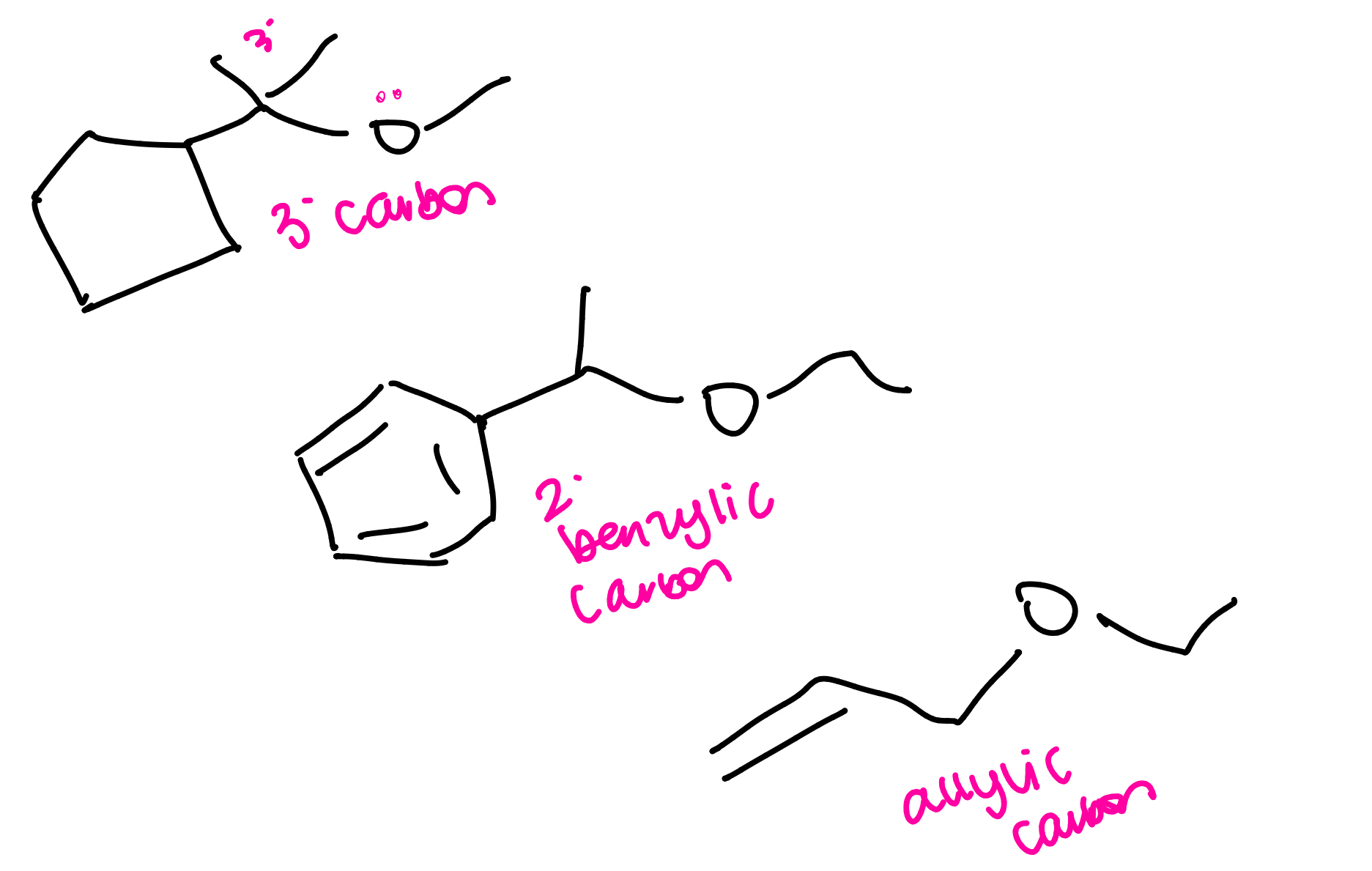
ether mechanisms: (benzylic or allylic)
ethers with tertiary alkyl groups (SN2 or E1)
a protonated epoxide can form a stable tertiary carbocation intermediate that is then attacked by a weak nucleophile (halide)
4 product reaction
reactions of epoxides: ring opening
base catalyzed epoxide ring opening is ALWAYS…
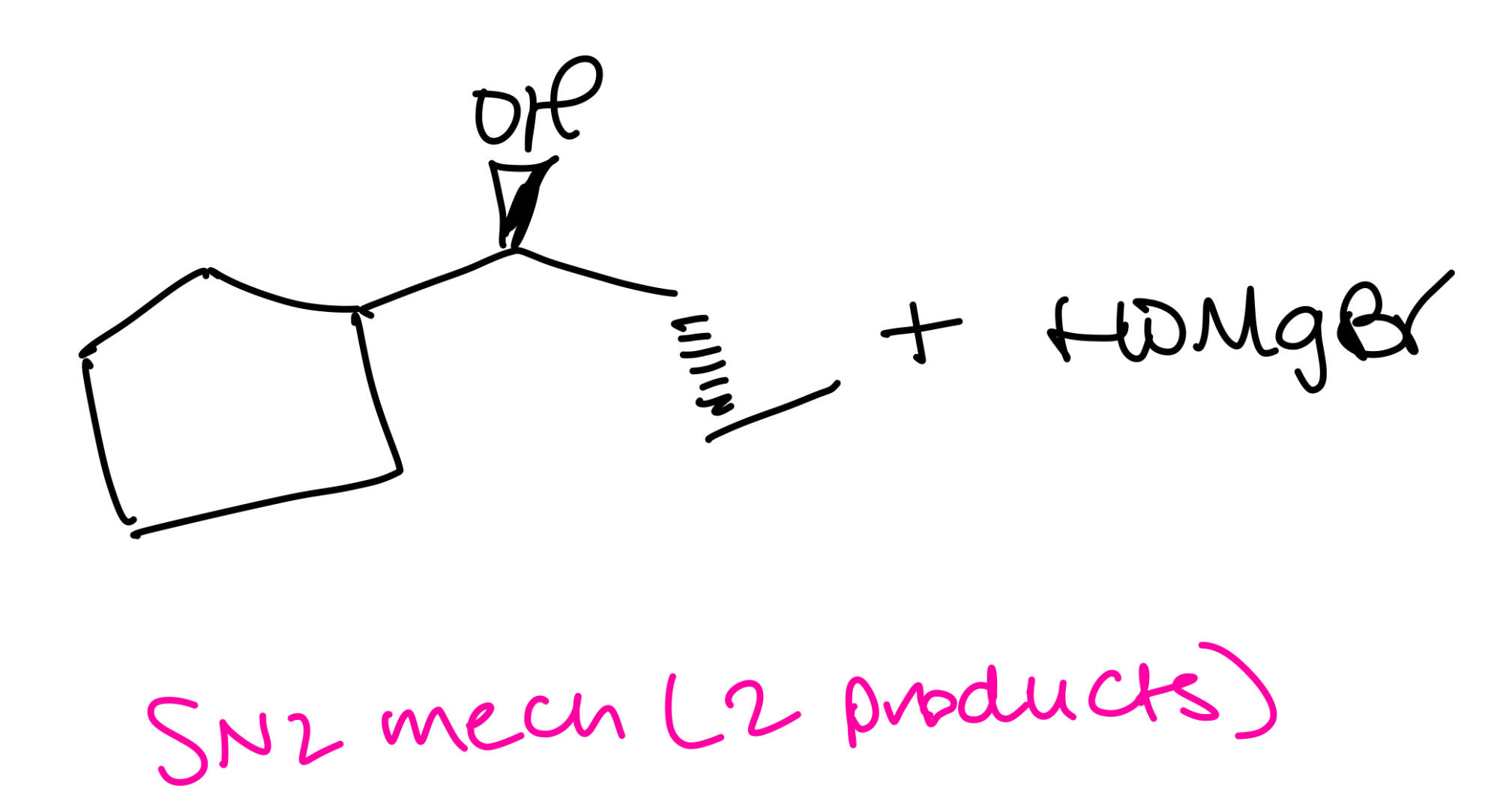
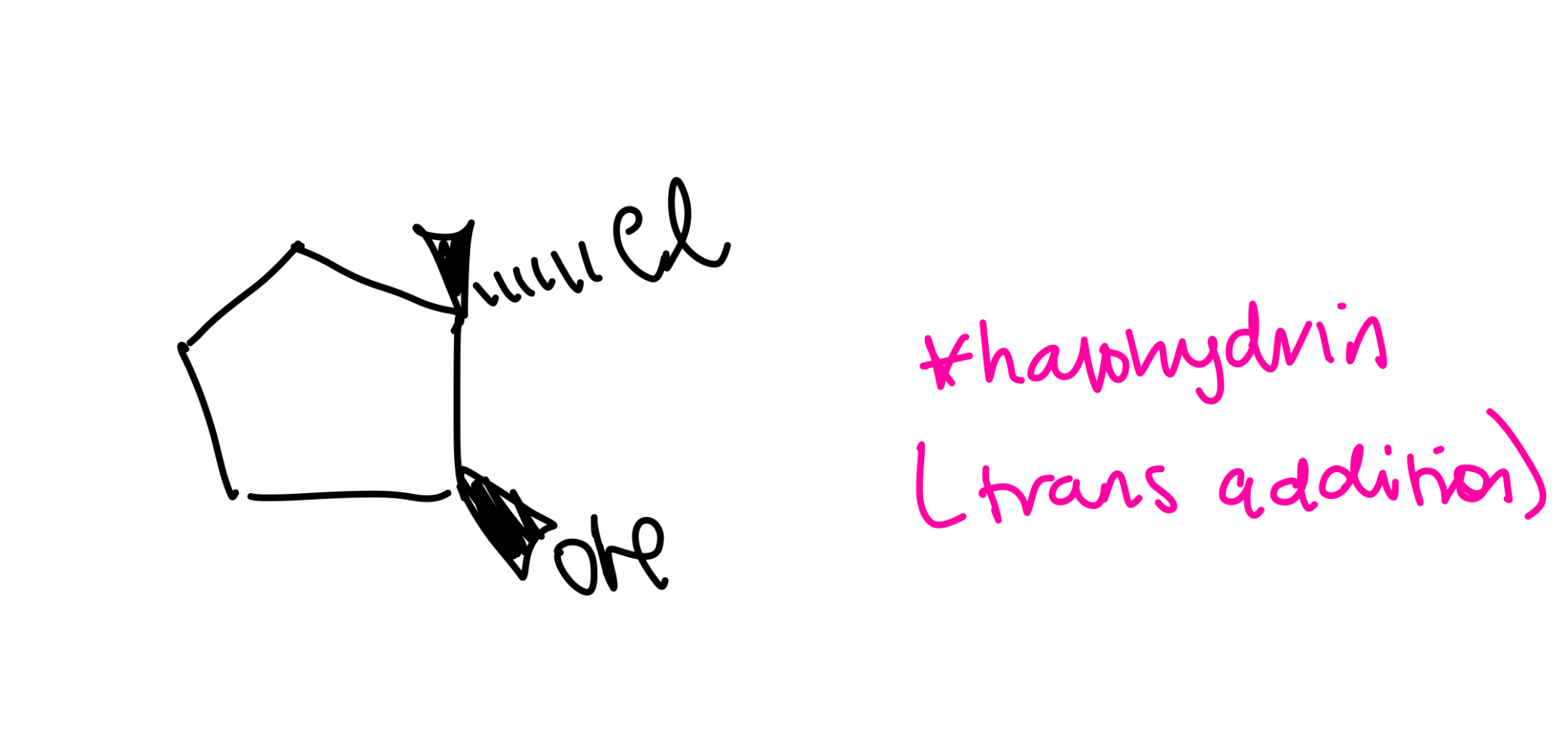
SN2 mechanism: Nucleophile attacks the less hindered carbon
if the epoxide has a primary or secondary carbon…
the mechanism will be SN2
if epoxide has a tertiary, benzylic or allylic carbon…
the mechanism will be SN1

Williamson ether synthesis
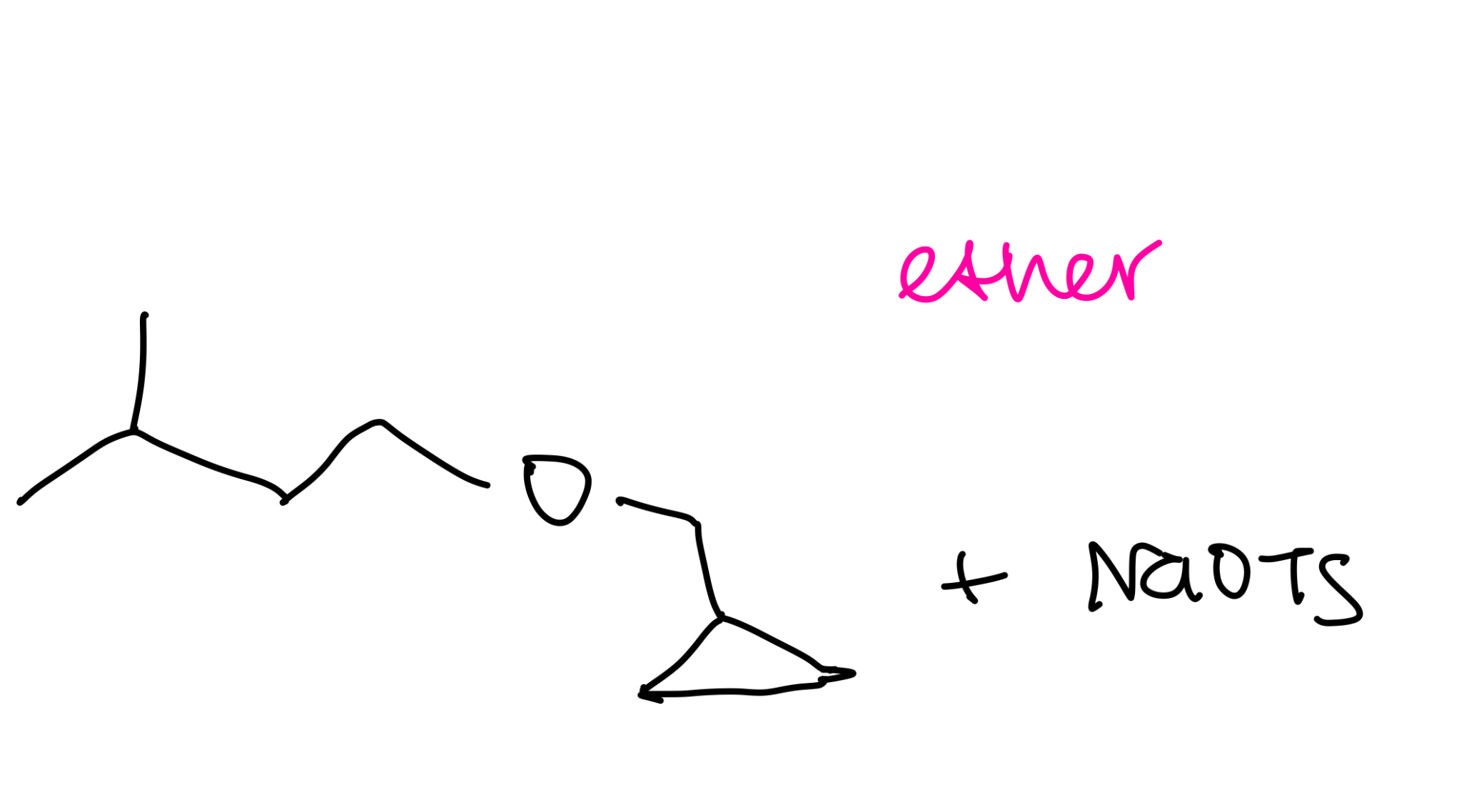

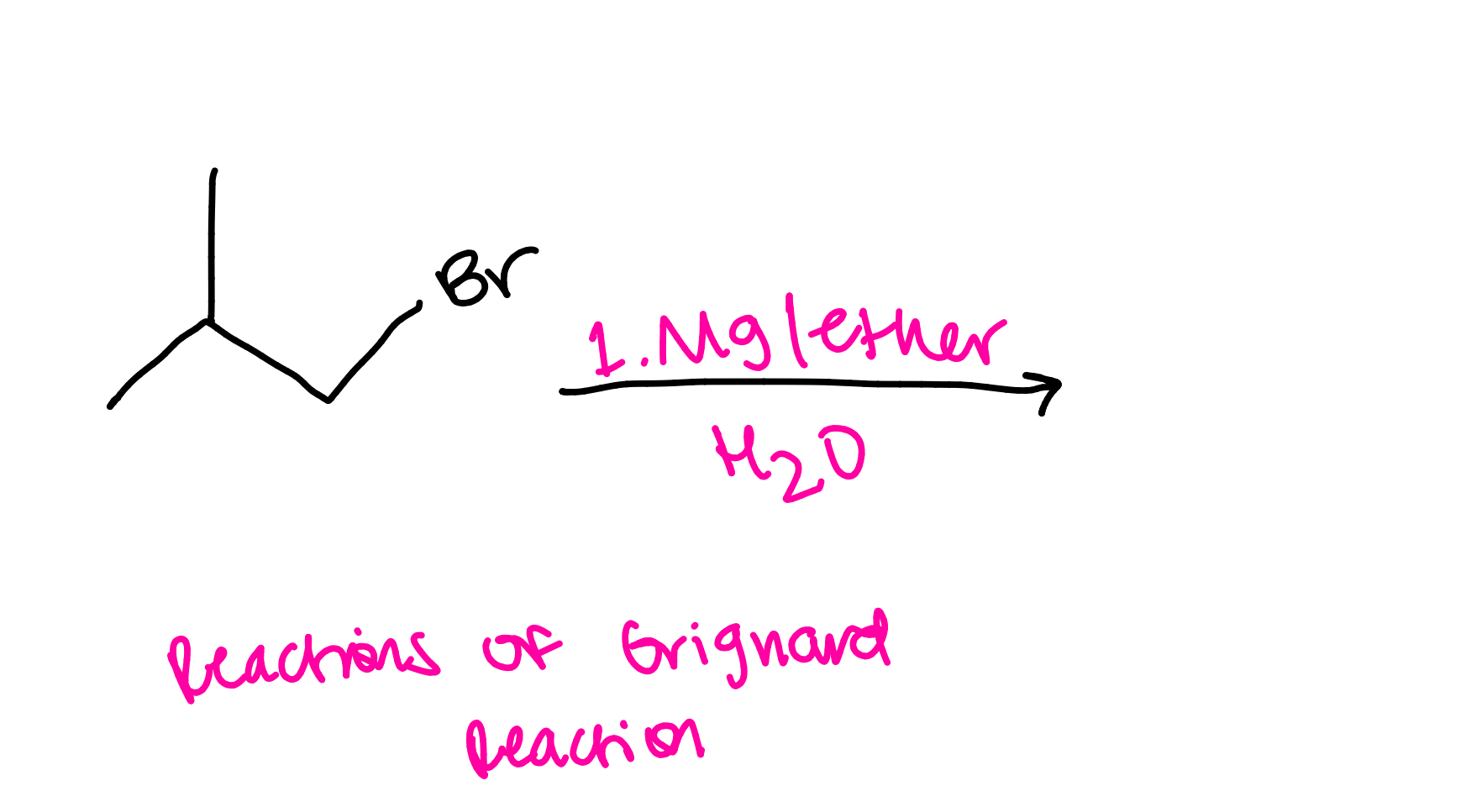
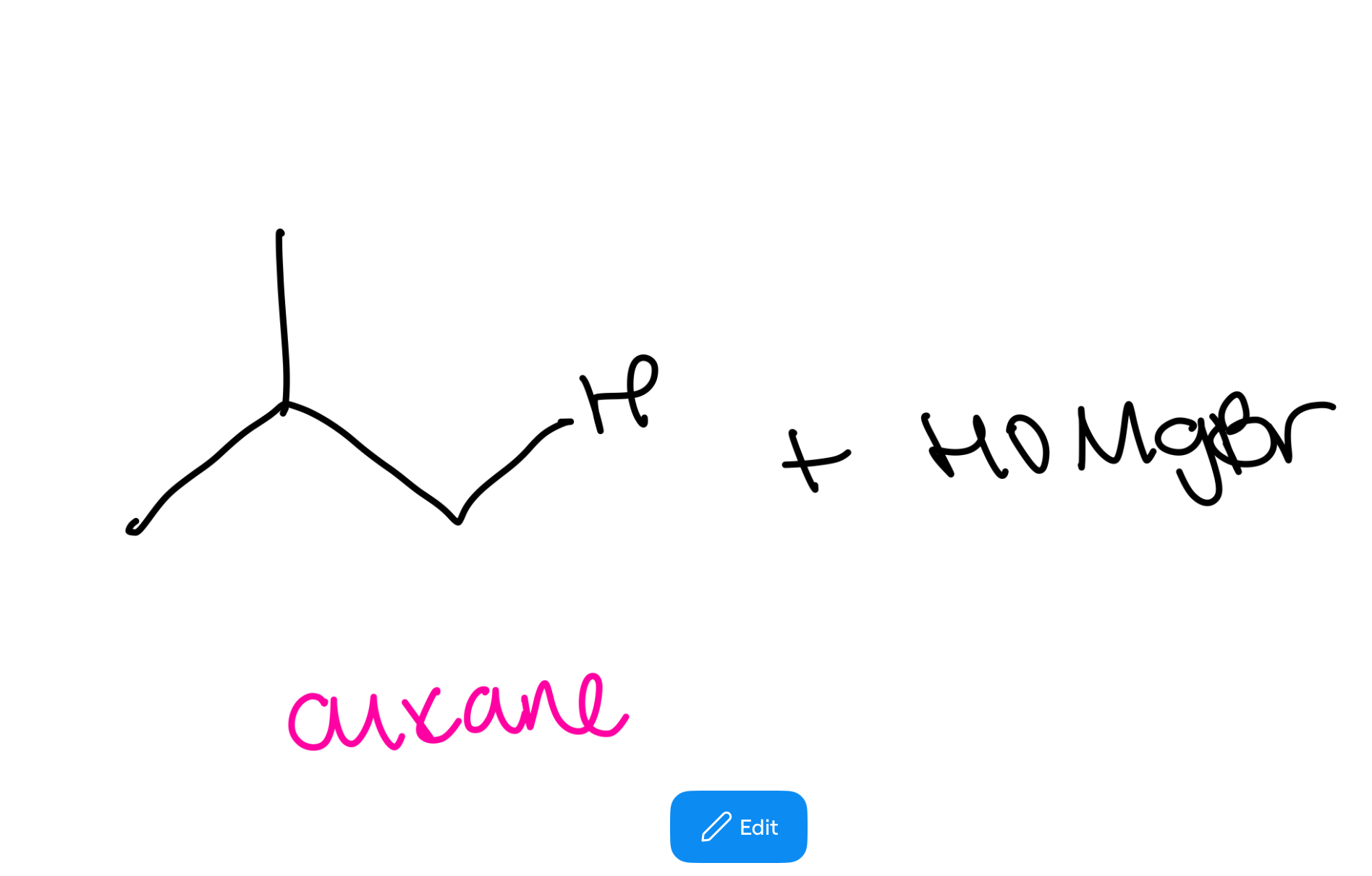
Alkoxymercuration-demurcuration ether synthesis
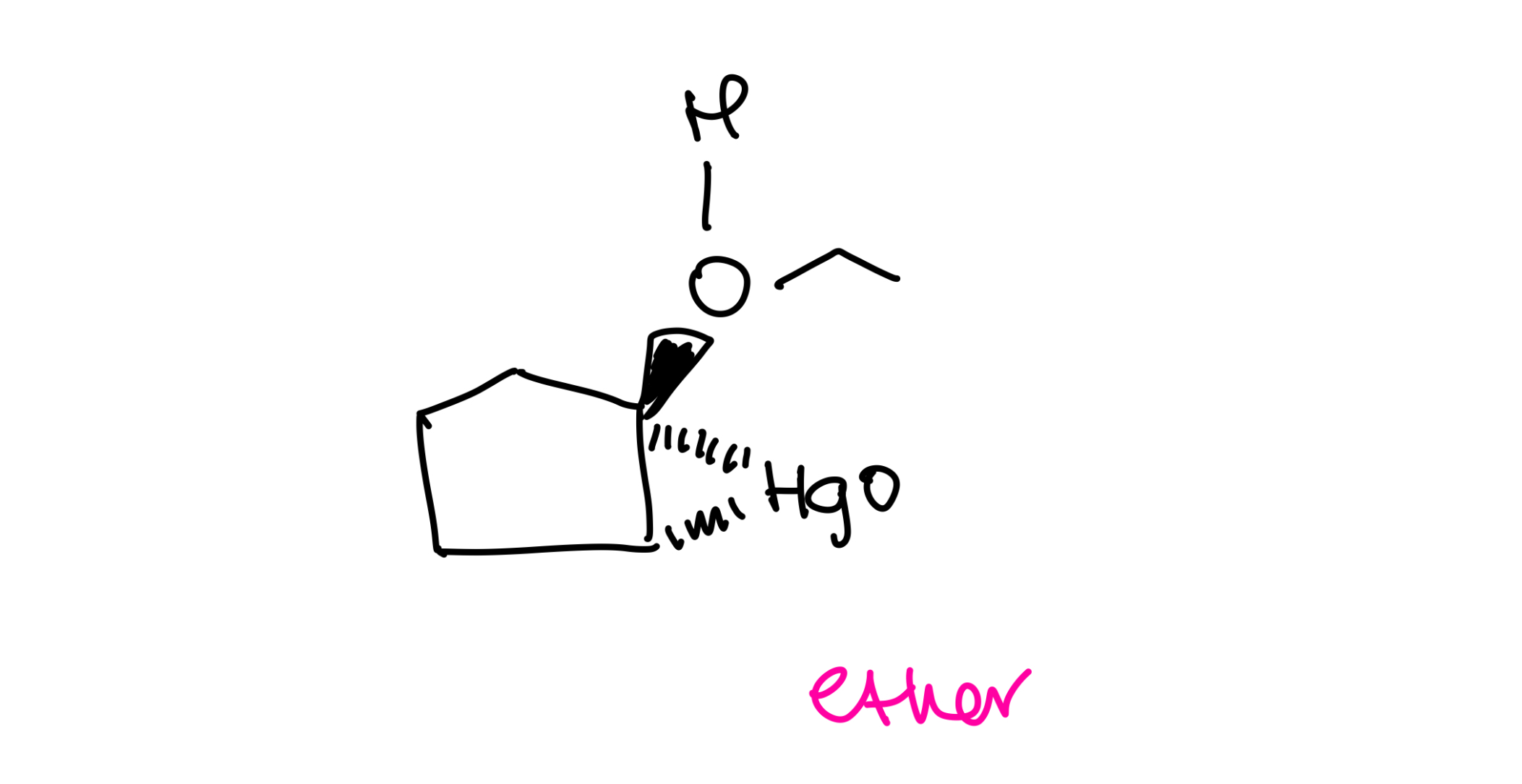

Ethers with secondary alkyl groups
SN2 mechanism (2 products)


Reactions of epoxides: ring opening
Base-catalyzed epoxied ring opening is ALWAYS SN2
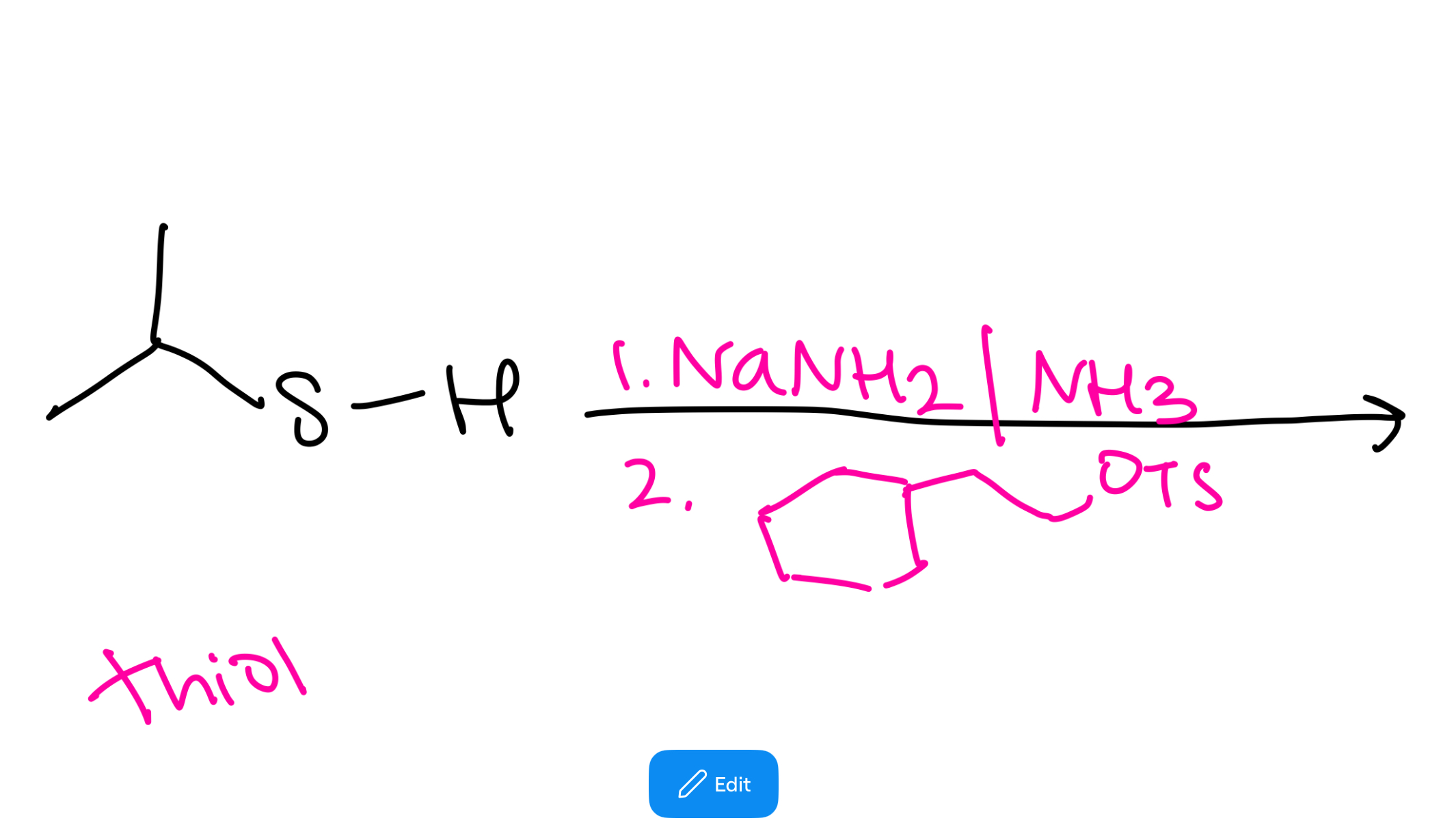
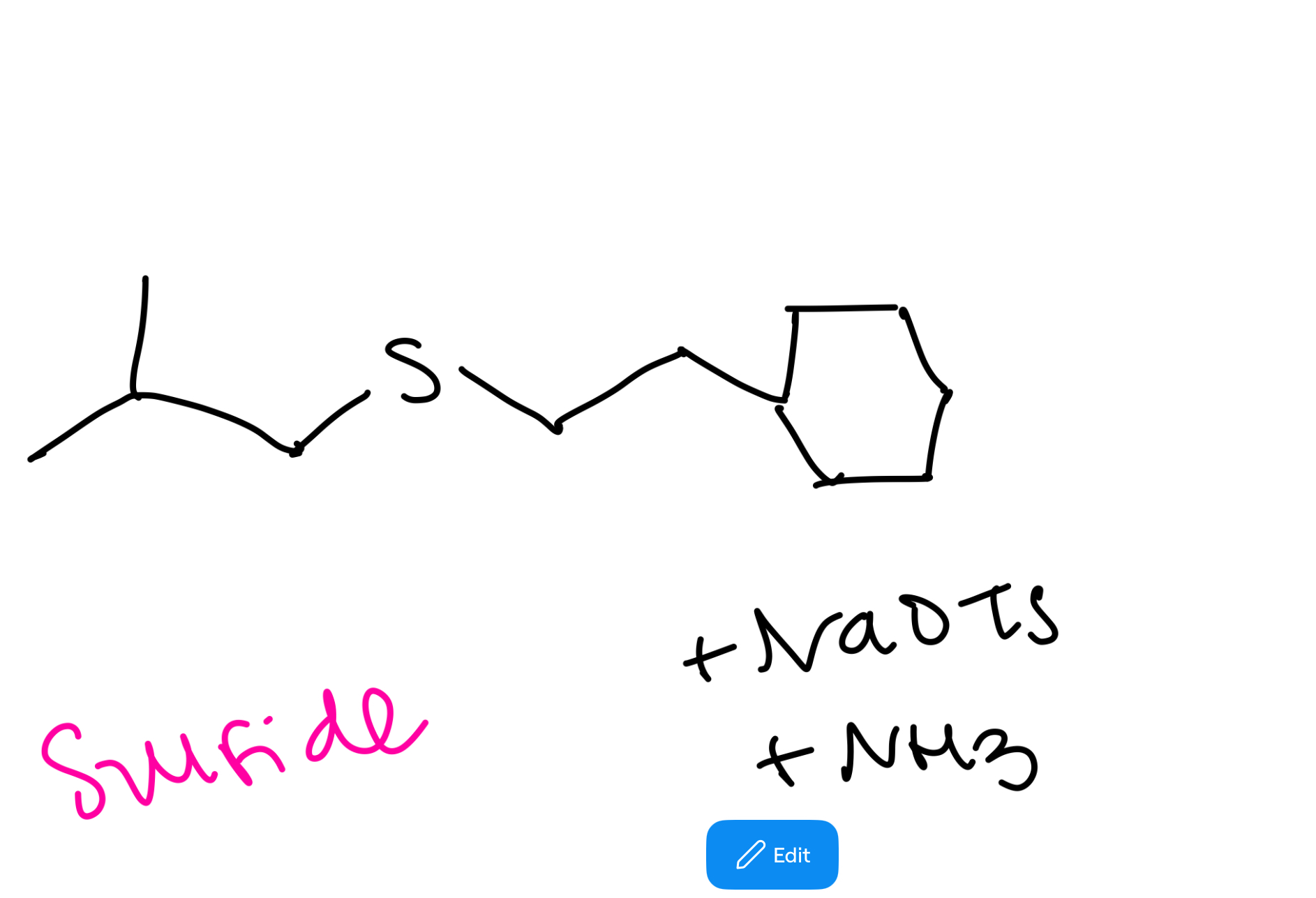
Thiol to sulfide synthesis
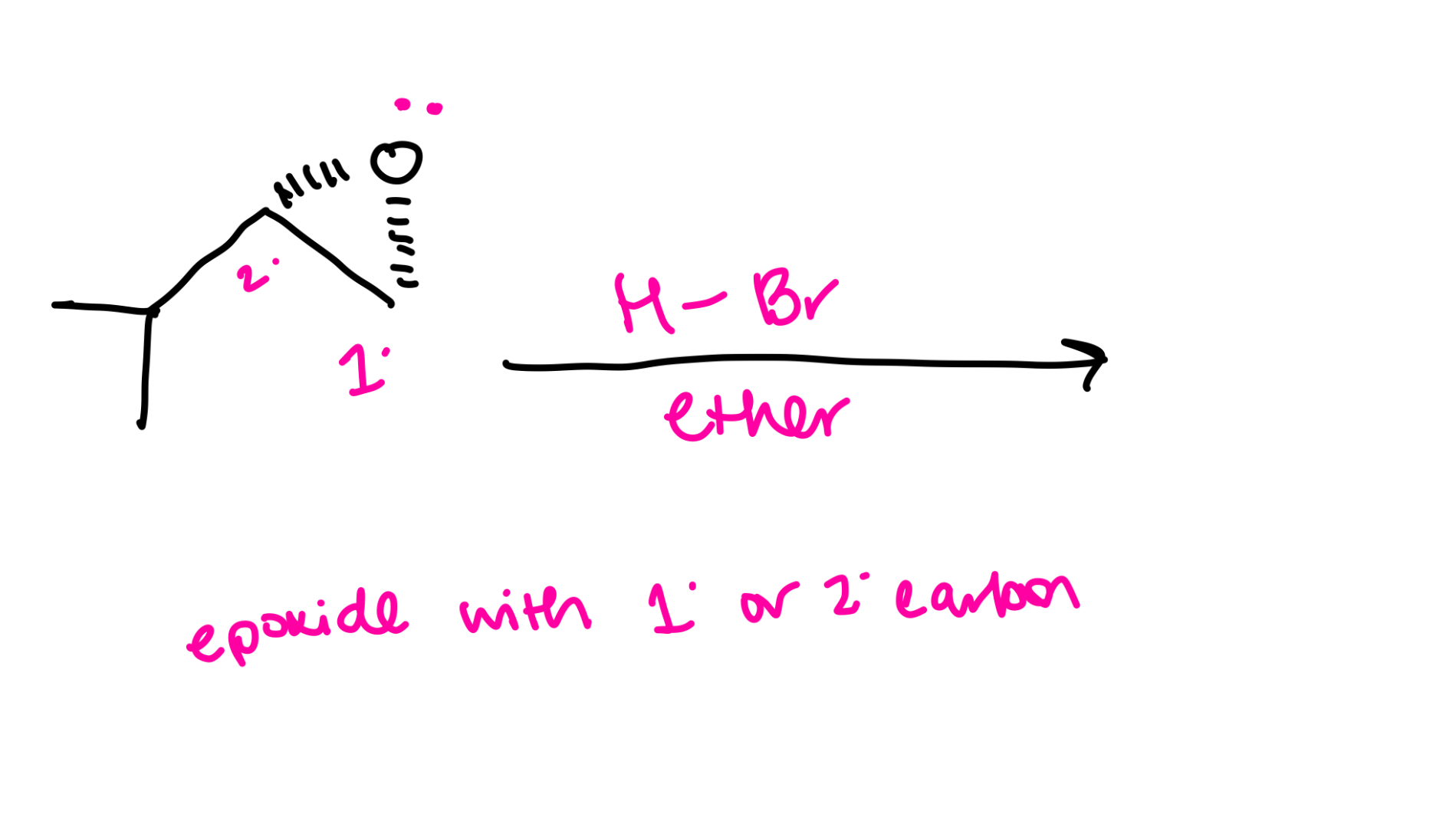
Epoxied with primary or secondary carbon
SN2 mechanism

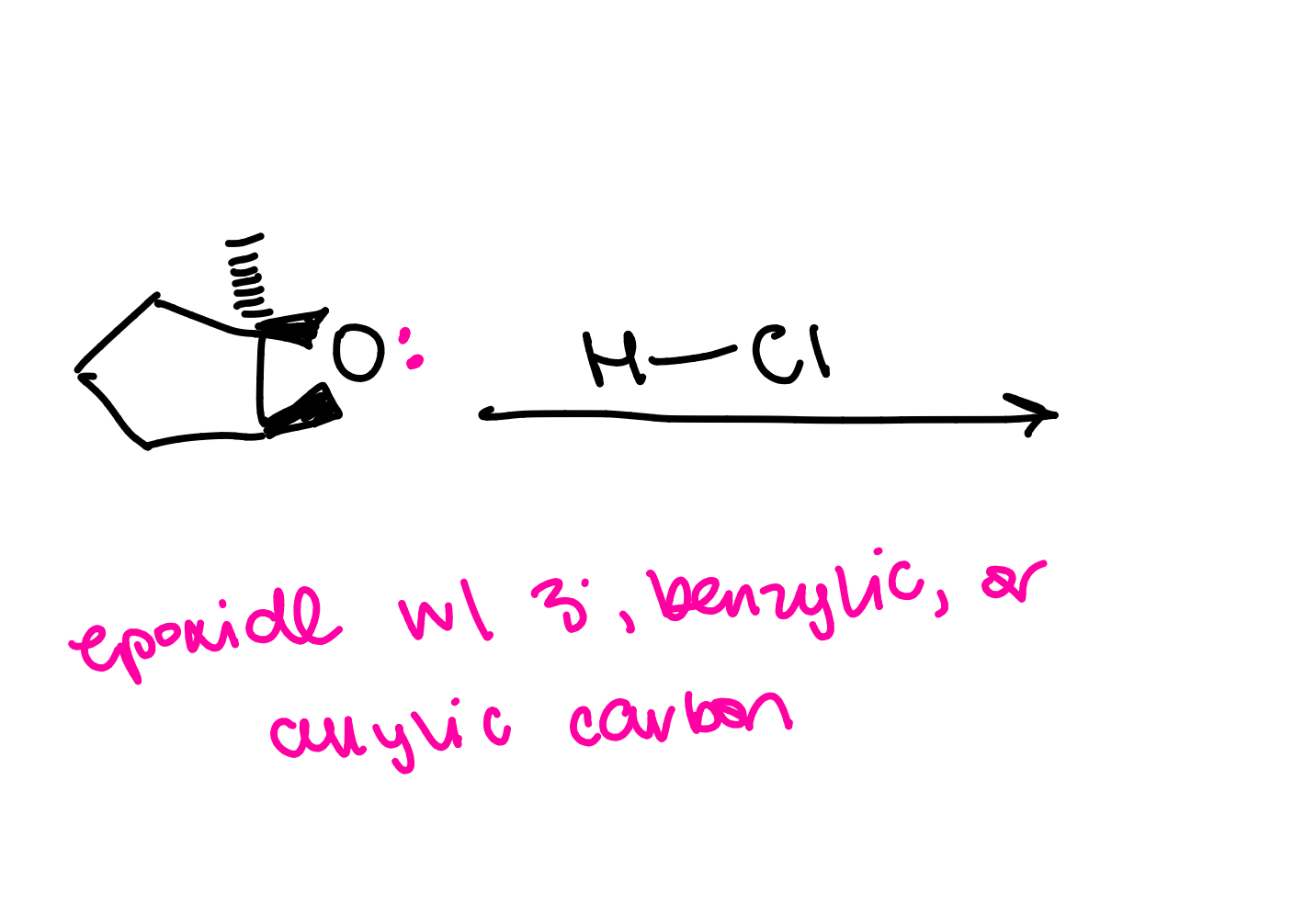
SN1 mechanism

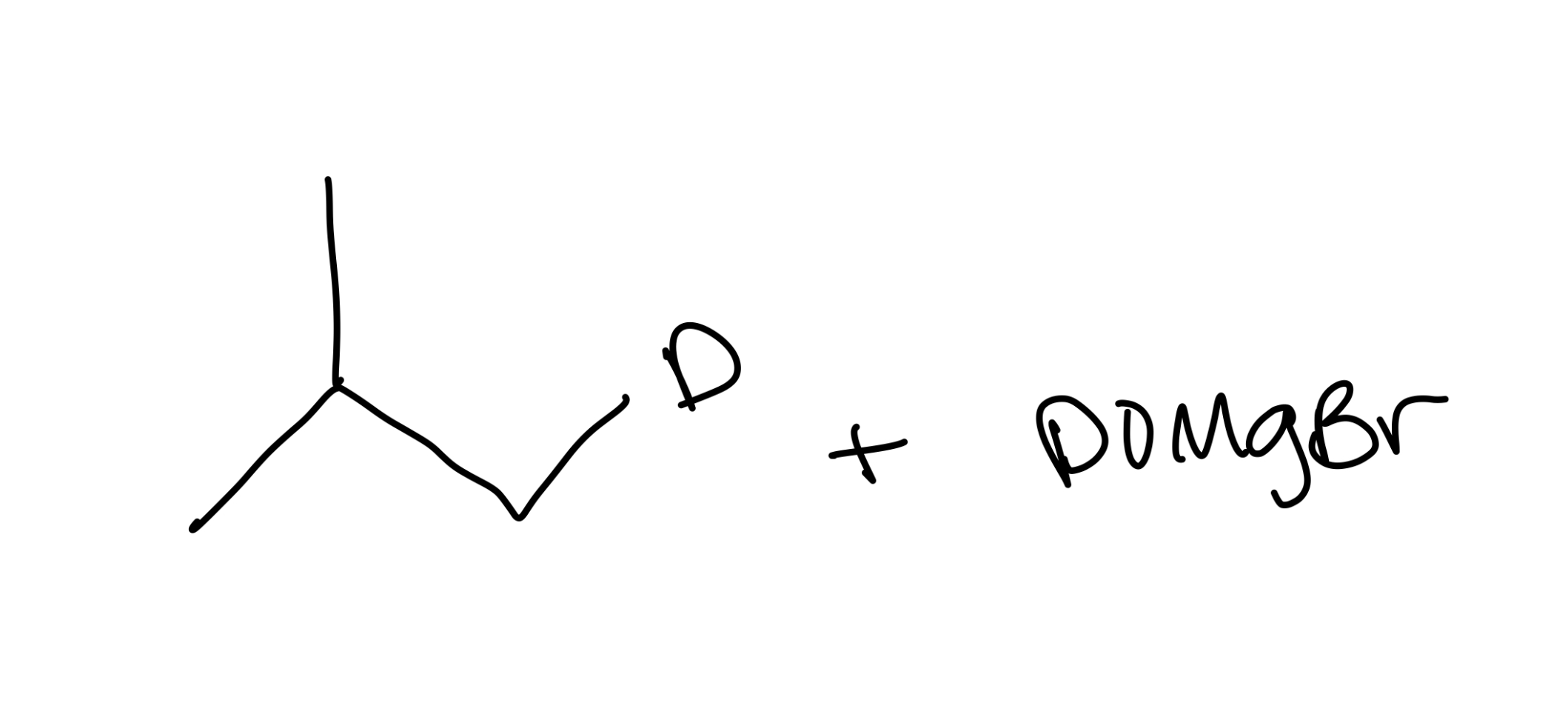


Naming ethers
Alphabetize the alkyl groups -ether