AQA Psychology - Memory (Paper 1)
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
1
New cards
What is memory?
The ability to **preserve** and recover information
2
New cards
What is coding?
The way in which information is **stored**
3
New cards
What are the three ways in which information can be coded?
**Visually, semantically, or acoustically**
4
New cards
**Baddely** (1996) found that the STM and LTM are coded in which way?
STM - acoustically
LTM - semantically
LTM - semantically
5
New cards
What is capacity?
How much **data** can be **held** in a memory store
6
New cards
What is the capacity of the STM?
7 ± 2
7
New cards
What is the capacity of the LTM?
Potentially infinite
8
New cards
What is duration?
The length of time information can be remembered before being forgotten
9
New cards
What is the duration of LTM?
Infinite
10
New cards
What is the duration of STM?
Short - around **18 Seconds**
11
New cards
How is capacity tested?
### @@**Milner (1956) Digit Span**@@
⤷ Participants are to repeat back a string of numbers or letters in the same order and the number of digits/letters gradually increased, until they can’t recall it anymore
⤷ Participants are to repeat back a string of numbers or letters in the same order and the number of digits/letters gradually increased, until they can’t recall it anymore
12
New cards
Give an example of **research** into the **Duration of STM**
### ==Peterson & Peterson (1959) trigram retention experiment==
* Peterson and Peterson (1959) conducted an experiment on short-term memory duration.
* Participants were presented with **trigrams** (e.g WZT) and asked to recall them after different retention intervals (3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18)
* The longer the retention interval, the lower the recall accuracy.
* **Short-term memory has a limited duration of around** ***18 seconds***.
* Peterson and Peterson (1959) conducted an experiment on short-term memory duration.
* Participants were presented with **trigrams** (e.g WZT) and asked to recall them after different retention intervals (3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18)
* The longer the retention interval, the lower the recall accuracy.
* **Short-term memory has a limited duration of around** ***18 seconds***.
13
New cards
Give an example of **research** into the **coding of the LTM**
### ==**Baddely’s (1966) Cat/Mat Experiment**==
* Baddely's (1966) Cat/Mat experiment was a study on the effects of acoustic and semantic similarity on short-term memory.
* Participants were presented with lists of words that were either **acoustically similar** (e.g. cat, mat, sat) or **semantically similar** (e.g. big, large, huge).
* They were then asked to recall the words in the correct order.
* The results showed that participants had **more difficulty recalling acoustically similar words** than **semantically similar words**, suggesting that short-term memory is affected more by sound than meaning
* Baddely's (1966) Cat/Mat experiment was a study on the effects of acoustic and semantic similarity on short-term memory.
* Participants were presented with lists of words that were either **acoustically similar** (e.g. cat, mat, sat) or **semantically similar** (e.g. big, large, huge).
* They were then asked to recall the words in the correct order.
* The results showed that participants had **more difficulty recalling acoustically similar words** than **semantically similar words**, suggesting that short-term memory is affected more by sound than meaning
14
New cards
Give an example of **research** into the **duration of LTM**
### ==Bahrick (1975)==
* He conducted a study on **high school yearbooks.**
* The study aimed to investigate the **long-term memory retention of high school graduates.**
* Participants were asked to recall the names and faces of their classmates from their yearbook.
* The results showed that participants were able to recognise their classmates' faces and names up to **34 years after graduation**.
* However, the **accuracy** of recall **declined over time**, with participants being more accurate in recognising **faces** than **names**
* He conducted a study on **high school yearbooks.**
* The study aimed to investigate the **long-term memory retention of high school graduates.**
* Participants were asked to recall the names and faces of their classmates from their yearbook.
* The results showed that participants were able to recognise their classmates' faces and names up to **34 years after graduation**.
* However, the **accuracy** of recall **declined over time**, with participants being more accurate in recognising **faces** than **names**
15
New cards
What is the **Multi Store Model** (MSM)?
==Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968)== developed a store of memory that has 3 stores. It describes flow between three different stores: ***sensory register, long term memory and short term memory***
16
New cards
What is the **sensory register**?
Where **information from the senses** is stored but only for a **duration** of approximately **a half second** before it is forgotten
17
New cards
Draw the MSM
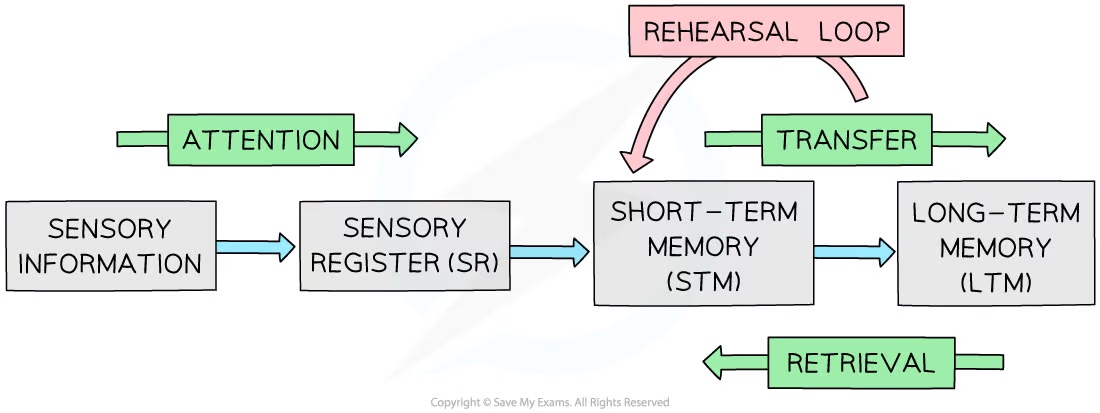
18
New cards
Describe the process of committing data to LTM, as per MSM
1. Information must first be **encoded** through **rehearsal** and **attention**
2. The information is then stored in the short-term memory store, where it can be further **rehearsed** to prevent **decay**.
3. If the information is deemed important, it is transferred to the long-term memory store through storage
4. Once the information is fully stored, it can be retrieved from long-term memory for later use
5. It may also be forgotten as the result of **retrieval failure** or **interference**
19
New cards
Give a **limitation** of the MSM
One limitation of the MSM is that research on the **duration** of short-term memory has **low ecological validity**. Peterson and Peterson (1959) used **meaningless stimuli** like trigrams such as 'XQF' that do not resemble items learned in real-life situations.
20
New cards
Give a **strength** of the MSM
Research supports the idea of **distinct STM and LTM systems** (e.g. brain-damaged case study patient KF’s STM was impaired following a motorcycle accident, but his LTM remained intact)
21
New cards
Give an **issue/debate** of the MSM
**Too simplistic**
↳ The MSM is too simple and it’s depiction of the STM has since been replaced by the WMM
↳ The MSM is too simple and it’s depiction of the STM has since been replaced by the WMM
22
New cards
What is the Working Memory Model?
**Baddely and Hitch (1974)** argued that the STM should be replaced by a Working Memory Model meaning information could be processed and interrelated and can flow from LTM to STM
23
New cards
Draw the WMM
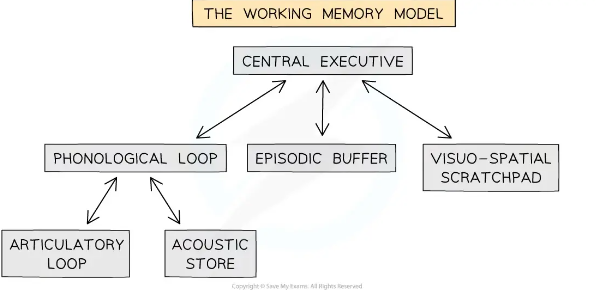
24
New cards
What is the **Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad?**
* The Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad is a component of working memory.
* It processes visual and spatial information.
* It is responsible for mental imagery and relationships between objects.
* It processes visual and spatial information.
* It is responsible for mental imagery and relationships between objects.
25
New cards
What is the **Phonological Loop?**
A **temporary acoustic** strange system for auditory and verbal information - contains the **inner voice** and the **inner ear**
26
New cards
What is the **Central Executive?**
The central executive is a key part of working memory, per Baddeley and Hitch's model. It manages attention, coordinates data from the phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad, and integrates info from long-term memory.
27
New cards
What is the **Phonological Store**?
Phonological Store is in the **working memory model** and **stores auditory info temporarily**. It's called "inner ear" and holds up to 2 seconds of info.
28
New cards
What is the **Episodic Buffer**?
Transfers information to the Long Term Memory
29
New cards
Give **research** support for the WMM
### ==Hitch and Baddeley (1975)==
* They conducted a **dual task experiment.**
* Participants completed a digit span task and a verbal reasoning task simultaneously.
* The difficulty of the verbal reasoning task was varied by changing the length and complexity of the sentences.
* Results showed that as the verbal reasoning task became more difficult, participants made more errors on the digit span task.
* ==**This supports the working memory model.**==
* **The working memory model suggests that both tasks were competing for the same cognitive resources.**
* They conducted a **dual task experiment.**
* Participants completed a digit span task and a verbal reasoning task simultaneously.
* The difficulty of the verbal reasoning task was varied by changing the length and complexity of the sentences.
* Results showed that as the verbal reasoning task became more difficult, participants made more errors on the digit span task.
* ==**This supports the working memory model.**==
* **The working memory model suggests that both tasks were competing for the same cognitive resources.**
30
New cards
Give **research** criticism for the WMM
### @@**Paulescu (1993)**@@
* Criticized the Working Memory Model (WMM) for not accounting for the prefrontal cortex's role in working memory.
* He argued that the prefrontal cortex is responsible for executive functions like attentional control and information manipulation.
* There is alsio no evidence for the Central Executive or Episodic buffer
* Paulescu's criticisms highlight limitations of the WMM
* Criticized the Working Memory Model (WMM) for not accounting for the prefrontal cortex's role in working memory.
* He argued that the prefrontal cortex is responsible for executive functions like attentional control and information manipulation.
* There is alsio no evidence for the Central Executive or Episodic buffer
* Paulescu's criticisms highlight limitations of the WMM
31
New cards
Give an **issue** with the working memory model
Much of the research into WMM is based on lab experiments which mean that they **lack ecological validity**
32
New cards
What is **Episodic Memory?**
Memory about **personal experiences** - @@declarative@@
ex. *first day of school*
ex. *first day of school*
33
New cards
What is **Semantic Memory**?
Knowledge about the world shared by **everyone** - ==declarative==
ex. *The Captal of England is London*
ex. *The Captal of England is London*
34
New cards
What is **Prodecural Memory**?
Procedural memory is concerned with **skills** - ==undeclarative (unable to be explained)==
ex. *Tying a shoelace*
ex. *Tying a shoelace*
35
New cards
How do **Brain scans** support evidence for types of LTM?
LTM is active at different point of the brain and Episodic memory is associated with **activity in the frontal lobe**
36
New cards
How does the case study of **Clive Wearing** support evidence for types of LTM?
He has no semantic memory; he remembers **how to play the piano** (procedural) and **recognises his wife** (episodic)
37
New cards
How does the case study of **HM** support evidence for types of LTM?
He has no episodic and procedural memory but could do hand-eye co-ordination skills such as mirror drawing
38
New cards
Give an **Issue/debate** with types of long term memory
**Using reserach from patients w/ brain damage**
↳ Its difficult to be cerain of which part of the brain has been affected after the person has died + damage to a part of the brain doesn’t mean that part is responsible for the behaviour
↳ Its difficult to be cerain of which part of the brain has been affected after the person has died + damage to a part of the brain doesn’t mean that part is responsible for the behaviour
39
New cards
What are the **two** key factors in **explanations of forgetting**?
**Accessibility** - whether information can be retrieved
**Availability** - whether the information has been stored in the first place
**Availability** - whether the information has been stored in the first place
40
New cards
What is **interference**?
When **one memory** disrupts the ability to **recall another**
41
New cards
What is **retroactive interference**?
When **new information** affects the ability to store **recall new information**
42
New cards
Give an example of **retroactive interference**
When you learn the lyrics to a new song and forget the old one
43
New cards
What is **proactive interference?**
When **old information** affects the ability to **recall new information**
44
New cards
Give an example of **proactive interference**
Calling a current partner by a former partner’s name
45
New cards
Give **research support** for **Interference**
### @@**McGeoch and McDonald (1931)**@@
↳ *Lab Experiment into interference*
* Participants were split into **three** groups.
* Groups had to remember a list of words
* Group 1 had to learn just adj. list 1, Group 2 had to learn a adj. list and no. group, and recall 1. Group three had to recall 1,2 and 3
* **Group 1 had 70% accurate recall and** Group 3 the least
* **Similarity between old and new information exacerbates interference.**
↳ *Lab Experiment into interference*
* Participants were split into **three** groups.
* Groups had to remember a list of words
* Group 1 had to learn just adj. list 1, Group 2 had to learn a adj. list and no. group, and recall 1. Group three had to recall 1,2 and 3
* **Group 1 had 70% accurate recall and** Group 3 the least
* **Similarity between old and new information exacerbates interference.**
46
New cards
Give **limitations** of **interference** as an explanation of forgetting
* Lab experiment research means **low ecological validity**
* Too simplistic - **doesn’t tell us about cognitive processes**
* Too simplistic - **doesn’t tell us about cognitive processes**
47
New cards
What is **retrieval failure**?
When the **memory is available** but not **accessible** until the appropriate cue is presented
48
New cards
What is a **cue?**
**Information trigger** that **allows us access to a memory.** They may be **external** or **internal** (personal, mood etc)
49
New cards
What is **Context Dependent Forgetting**?
Forgetting due to **a lack of the correct environmental** (or external) **cues**
50
New cards
Give **research support** for context dependent forgetting
### @@**Godden and Baddely's (1975)**@@
* Godden and Baddeley's (1975) experiment studied context-dependent memory.
* Divers learned and recalled a list of words on land or underwater.
* Participants who learned and recalled in the same environment had better recall.
* **Memory is context-dependent and the environment can affect recall**
* Godden and Baddeley's (1975) experiment studied context-dependent memory.
* Divers learned and recalled a list of words on land or underwater.
* Participants who learned and recalled in the same environment had better recall.
* **Memory is context-dependent and the environment can affect recall**
51
New cards
What is **State Dependent Forgetting**?
Forgetting due to a **lack of internal cues**
52
New cards
Give an example of **research support** for **State Dependent Forgetting**
### @@**Goodwin et al. (1969)**@@
* A study on male volunteers to investigate memory recall when drunk or sober.
* Participants were asked to remember lists of words when they were either drunk or sober.
* After 24 hours, participants were asked to recall the words in either a drunk or sober state.
* The results showed that **words learned when drunk were better recalled when drunk, and words learned when sober were better recalled when sober**
* The study provides evidence for **state-dependent forgetting**, where the physical and mental state of an individual at the time of learning affects their ability to recall information later on.
* A study on male volunteers to investigate memory recall when drunk or sober.
* Participants were asked to remember lists of words when they were either drunk or sober.
* After 24 hours, participants were asked to recall the words in either a drunk or sober state.
* The results showed that **words learned when drunk were better recalled when drunk, and words learned when sober were better recalled when sober**
* The study provides evidence for **state-dependent forgetting**, where the physical and mental state of an individual at the time of learning affects their ability to recall information later on.
53
New cards
Give a **strength** of **retrieval failure** as an explanation of forgetting
**Real World Application**
↳ **Abernathy (1940)** found that students performed **better** if they took exams in the **same place** they learned the information
↳ **Abernathy (1940)** found that students performed **better** if they took exams in the **same place** they learned the information
54
New cards
Give a **limitation** of **retrieval failure** as an explanation of forgetting
==**Limited Ecological Validity**==
↳ A majority of studies are lab experiments which do not reflect the way people actually learn
↳ A majority of studies are lab experiments which do not reflect the way people actually learn
55
New cards
What is **eyewitness testimony**?
The **evidence** provided in court by a person who **witnessed a crime** regarding the perpetrator of the crime
56
New cards
What are **Leading Questions**?
A question that is **phrased** in a way that makes the participants **more likely** to give the **desired answer**
57
New cards
What is **Misleading Information**?
**Supplying information** that may lead a witness’ memory of an incident **to be altered**
58
New cards
What is **post-event discussion**?
A discussion between co-witnesses or an interviewer *after* an incident - contaminate a memory
59
New cards
Give an **example** of **research** into **leading questions**
### @@**Loftus and Palmer's (1974)**@@
* A study examined the accuracy of eyewitness testimony.
* Participants watched a video of a car accident and were asked about the speed of the cars.
* The wording of the question influenced participants' estimates.
* Those asked about the cars "**smashing**" gave higher estimates than those asked about the cars "**hitting**".
* The study shows that **leading questions can distort eyewitness testimony**.
* A study examined the accuracy of eyewitness testimony.
* Participants watched a video of a car accident and were asked about the speed of the cars.
* The wording of the question influenced participants' estimates.
* Those asked about the cars "**smashing**" gave higher estimates than those asked about the cars "**hitting**".
* The study shows that **leading questions can distort eyewitness testimony**.
60
New cards
Evaluate **Loftus and Palmer’s research** into **Accuracy of Eye-witness testimony**
* **Low Ecological Validity**
* **Only University students - small sample pod**
* **Only University students - small sample pod**
61
New cards
Give an **example** of **research** into **misleading information**
### @@**Loftus & Palmer (1975)**@@
* Loftus and Palmer’’ (1975) study examined the impact of misleading information on eyewitness testimony.
* Participants watched a video of a car accident and were asked whether they saw **broken glass**.
* Some were given misleading information about the speed of the cars involved.
* Those who had been told the car was going **faster** were more likely to say there was **broken glass** whereas those who’d believed it was slower said there was not.
* The study shows how misleading information can distort eyewitness testimony.
* Loftus and Palmer’’ (1975) study examined the impact of misleading information on eyewitness testimony.
* Participants watched a video of a car accident and were asked whether they saw **broken glass**.
* Some were given misleading information about the speed of the cars involved.
* Those who had been told the car was going **faster** were more likely to say there was **broken glass** whereas those who’d believed it was slower said there was not.
* The study shows how misleading information can distort eyewitness testimony.
62
New cards
What is **Yerkes-Dodson Inverted U Hypothesis?**
* Anxiety has a **negative effect** on the accuracy of **EWT** at **very high or very low levels**
* **Moderate levels** of anxiety are actually **beneficial** to accuracy of recall as adrenaline can **sharpen senses** and **create clearer memories**
* **Moderate levels** of anxiety are actually **beneficial** to accuracy of recall as adrenaline can **sharpen senses** and **create clearer memories**
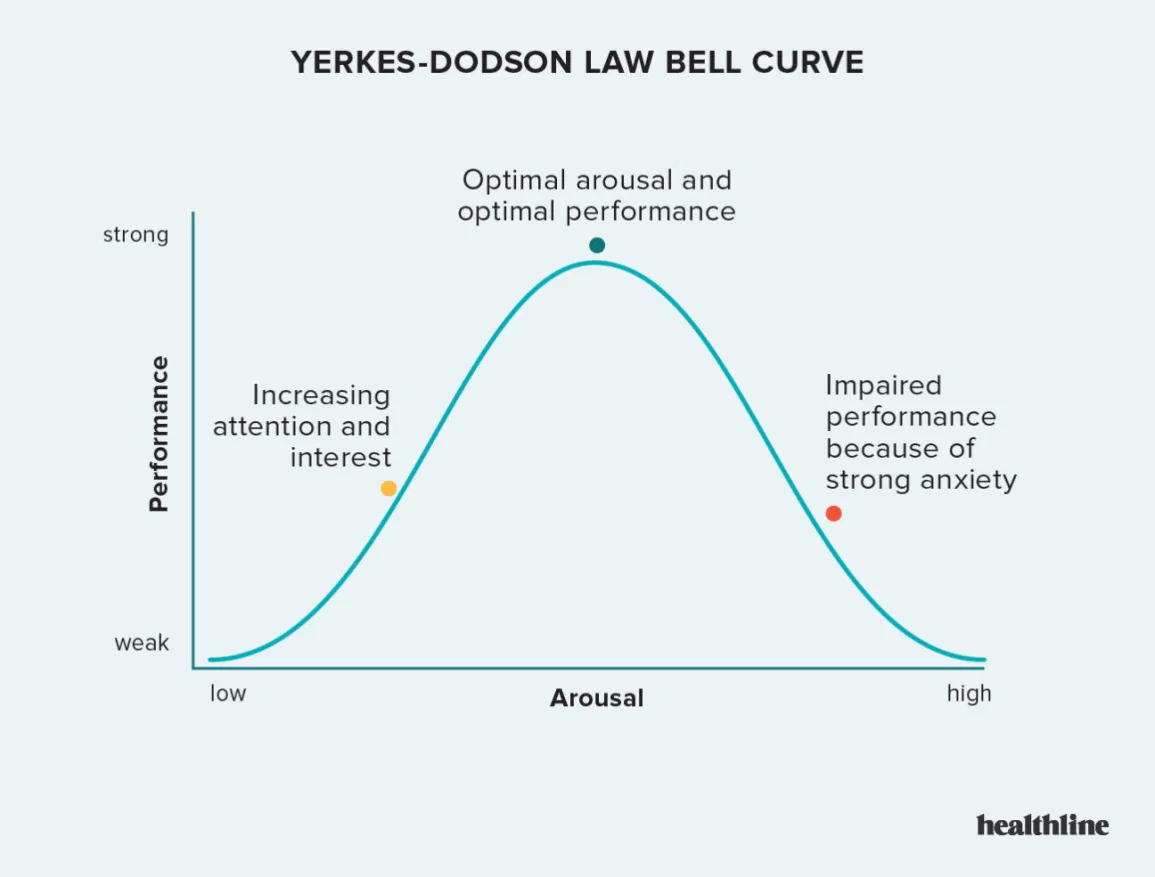
63
New cards
What is the **effect** of **anxiety** on **EWT**?
Crimes tend to cause **high levels of anxiety** which inn turn can cause **memories to distort**
64
New cards
What are the the **negative effects of anxiety?**
* Low confidence
* Poorer memory
* ‘Weapon Effect’
* Poorer memory
* ‘Weapon Effect’
65
New cards
What are the the **positive effects of anxiety?**
* More attention to detail
* More aware of surroundings
* More aware of surroundings
66
New cards
What is **The Weapon Effect?**
When a weapon is present, it causes **high levels of anxiety** and **poorer recall** as the focus is on the weapon
67
New cards
Outline research into **The Weapon Effect**
### @@**Johnson and Scott (1976)**@@
* Their Weapon Effect Experiment demonstrated that the presence of a weapon can **impair** eyewitness memory.
* Participants who saw a man holding a bloody knife were less accurate in identifying him and recalled fewer details.
* Those who saw the man holding a pen had **better accuracy** in identifying him and recalled more details.
* **The study suggests that the presence of a weapon can distract and overwhelm an eyewitness's attention, leading to poorer memory recall.**
* Their Weapon Effect Experiment demonstrated that the presence of a weapon can **impair** eyewitness memory.
* Participants who saw a man holding a bloody knife were less accurate in identifying him and recalled fewer details.
* Those who saw the man holding a pen had **better accuracy** in identifying him and recalled more details.
* **The study suggests that the presence of a weapon can distract and overwhelm an eyewitness's attention, leading to poorer memory recall.**
68
New cards
What is the **Cognitive Interview?**
**Geiselman and colleagues (1985)** identified that standard police interviews could negatively affect eye witnesses’ recall accuracy of crimes so developed a new interview
69
New cards
What are the **4 main techniques used in the cognitive interview?**
1. Change the order of events
2. Change the perspective - victims POV
3. Reinstatement of context - **return to the place**
4. Report Everything - recall even the most trivial details
70
New cards
Give a **limitation of The Cognitive Interview**
**Individual Differences**
↳ Loftus et al. found that **old people** tend to be worse at **EWT** than **middle aged people**
↳ Loftus et al. found that **old people** tend to be worse at **EWT** than **middle aged people**
71
New cards
Give an example of research into the use of the **Cognitive Interview**
* Fisher and Geiselman (1989) studied the Cognitive Interview technique.
* The technique improved eyewitness testimony accuracy.
* Open-ended questions, mental reinstatement of context, and changing the order of recall helped retrieve more information.
* The cognitive interviewers obtained **47%** more information comoared to no inc. from the Standard interview
* The technique improved eyewitness testimony accuracy.
* Open-ended questions, mental reinstatement of context, and changing the order of recall helped retrieve more information.
* The cognitive interviewers obtained **47%** more information comoared to no inc. from the Standard interview