Genes, Cell Divison ans Genetics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Briefly describe the structure of DNA
genetic material of an organism
Codes for all the proteins needed within an organism
Double helix
2 helices held by complimentary hydrogen bonding
It is a polynucleotide chain
Nitrogenous Base (adenine,thymine,guanine,cytosine)
Phosphate group
Sugar (deoxyribose sugar)
What does a chromosome consist of?
DNA
Histones (proteins)
and trace amounts for chromosomal RNA
How are chromosomes organized ?
DNA is wound around 8 globular proteins called histones - this is known as a nucleosome
Nucleosome pack together forming a chromatin fiber of about 6 nucleosome per turn taking thr shape of a solenoid
Further supercoiling occurs and a tightly packed structure - chromosome arises
Karyotype
complete set of chromosomes, differs by species
Eg humans usually have around 46 chromosomes
Karyogram
visual image where the chromosomes of an organism are neatly organized by length and centromere location.
This allows for one to determine the species type, or any genetic defects
DNA replication
occurs during s phase of interphase before meiosis and mitosis
This is when a chromosome replicates itself
These then join to form sister chromatids
Cohesion proteins
Keep sister chromatids together
Kinetochore
DNA- Protein complex serving as an attachment for micro tubules
Microtubules
Made of tubulin dimers, form the spindle during meiosis and mitosis
Centromere
Region where kinetochore and cohesion proteins are located, serving to keep sister chromatids together
Sister chromatids
2 identical DNA molecules
homologous chromosomes
a pair of chromosomes with similar but not identical genetic information (Have different alleles)
cells with pairs of homologous chromosomes are called diploid.
Advantages of more than 1 set of chromosomes
More likely to survive a mutation → chromosomes usually have similar genes so in the case of a mutation the unaffected gene can act as a backup
Polyploidy - 3 or more sets of chromosomes associated with advantageous features such as increased size, resistance to disease/env conditions
Genetic Variation → mixture of genes and characteristics from both parents
Meselson and Stahl Experiment - Describe
bacteria was grown on a medium containing N15
→ lowest density after centrifugation with caesium chloride
then after one generation transferred to an N14 containing medium and allowed to replicate
→ one band of intermediate density bcs of N14 and N15
the sample was then again transferred to an N14 medium and allowed to replicate
→ one light band bcs of n14 and N14 and one intermediate n15 n14
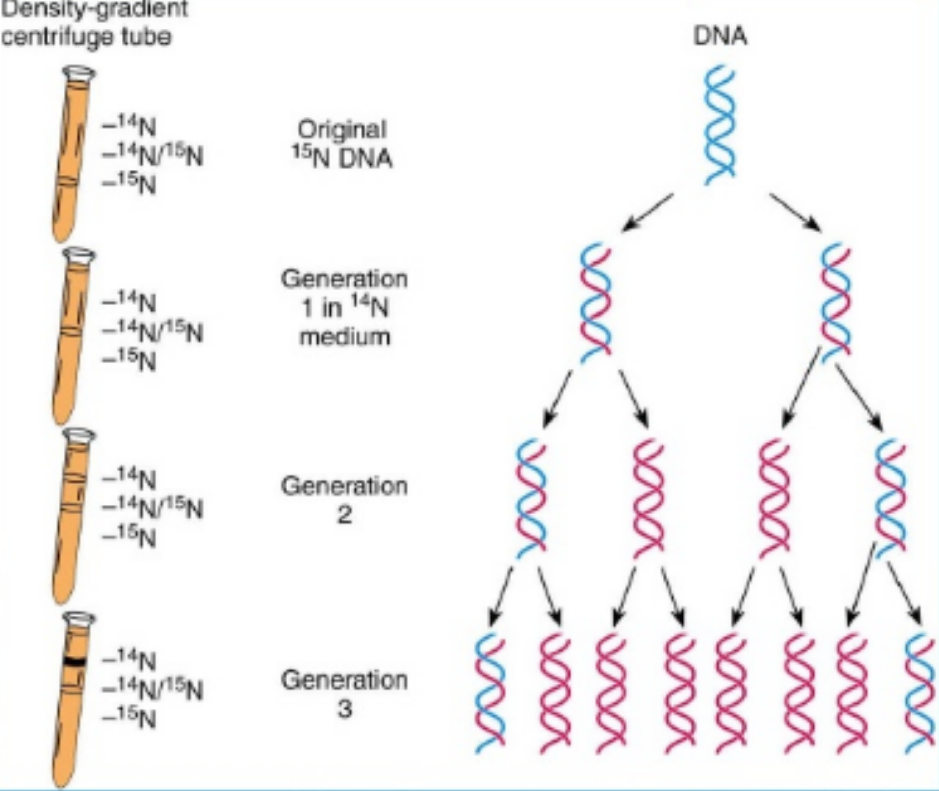
why does this prove semi-conservative replication
if it was conservative there would be no intermediate strands only one light vs one heavy
if it was dispersive it would have been HALF the density of parental DNA
Steps of DNA replication
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Initiation
Helicase unwinds the two complimentary strands at the origins of replication producing a replication fork
Single stranded binding proteins stabilize the newly separated Strands (due to their complimentary nature they want to rejoin)
Gyrase prevents the supercooling of double stranded dna outside the replication fork
Elongation
RNA primase → rna primer from which dna polymerase III begins to synthesize DNA from (operates in 5’ to 3’ direction)
Two strands are synthesized at the same time one is the leading strand the other the lagging
Leading strand - Continuous replication
3’ - 5’ parent strand (therefore the daughter strand is 5’ - 3’)
Phosphate is removed from dnTPs and the energy released is used for dna replication
Lagging strand - Discontinuous replication
Occurs on the 5-3 parents strand (hence replicated strand will be 3 - 5)
because dna polymerase III only works in 5-3 it needs to complete replication in short segments called Okazaki fragments - here several rna primers are required at the start of each Okazaki fragment
Termination
end of replication DnA polymerase I removed rna and replaced it w dna
DNA ligase joins the Okazaki fragments and seals gaps by forming phosphodiester bonds
DNA polymerase III proofreads.
Proofreading Mechanism
DNA polymerase I and III proofread. When recognize a mispairing of bases, it removes the incorrect nucleotide and tries again
Mismatch Repair Mechanism
a second set of enzymes post replication survey the newly replicated molecules and looks for remaining mismatched base pairs
detects wrong base bcs dna strand is chemically modified after replication - methylation. The new strand would not be methylated yet so the enzyme knows which strand to check and which base is incorrect (the A or the G)
mismatch repair enzymes cut mismatched base/adjacent bases
DNA polymerase and ligase synthesize and seal up a new base sequence
Excision Repair Mechanism
this is when the dna of the cell is damaged by radiation/chemicals
enzymes constantly inspect DNA and cut any defective bases and a few other adjacent bases.
DNA polymerase and ligase synthesize and seal up a new base sequence