Details of Carbohydrates
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What elements do carbs consist of?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
What are the three types of monosaccharides?
glucose, fructose, galactose
What do all three monosaccharides have in common?
All monosaccharides have the same formula (C6H12O6). However, since they all have different functions, they are considered isomers.
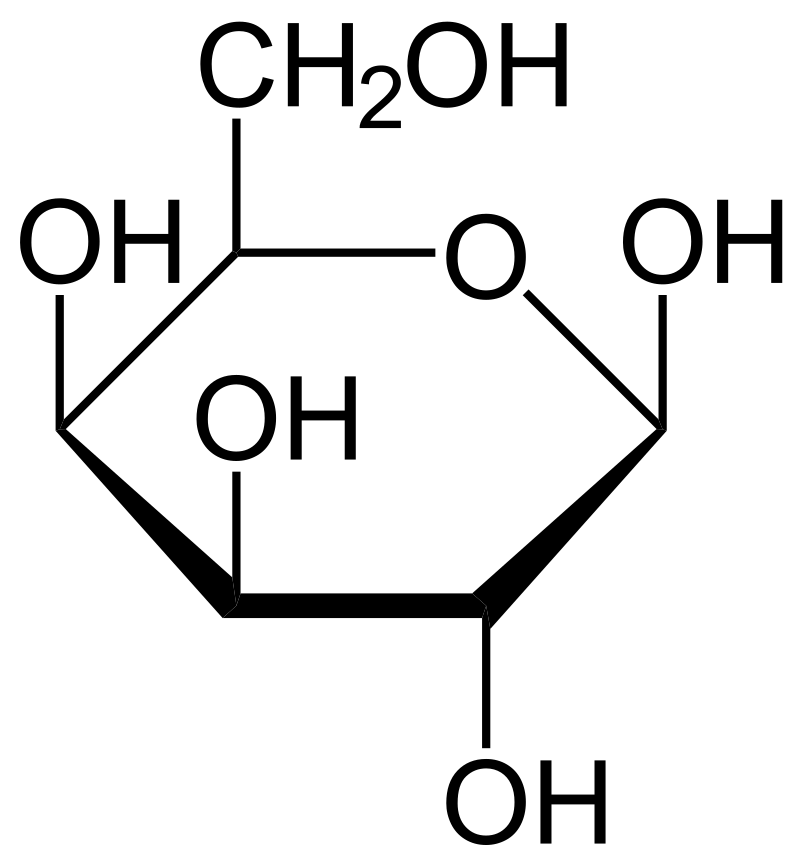
Glucose
A simple sugar whose primary source is to fuel cells in the body. It's a key product of photosynthesis and plays a crucial role in both cellular respiration and the production of ATP and NADH
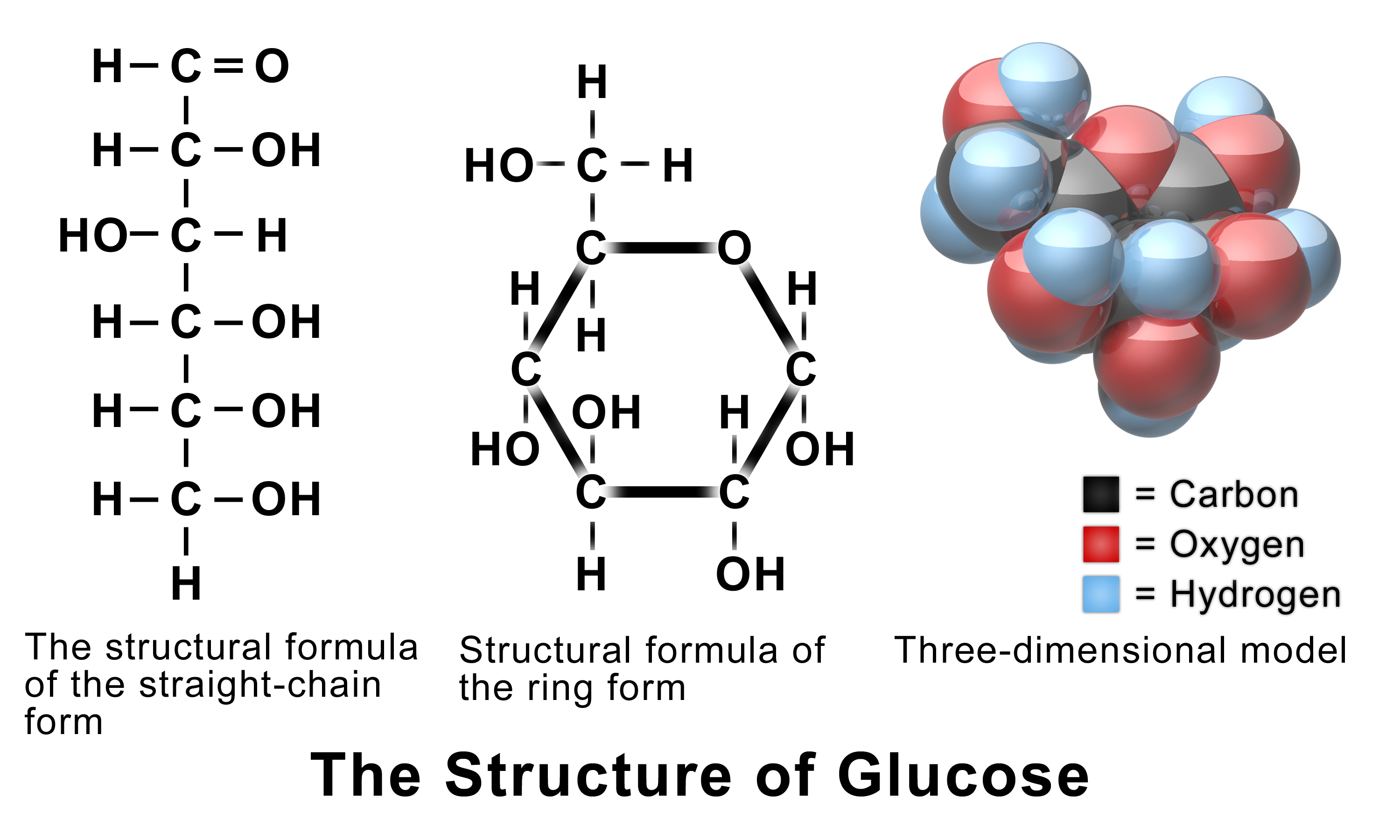
Fructose
a simple sugar known for its sweetness found naturally in fruits, vegetables, and honey. It's known as a component of sucrose (table sugar), glucose, and is a key player in carbohydrate metabolism within the body
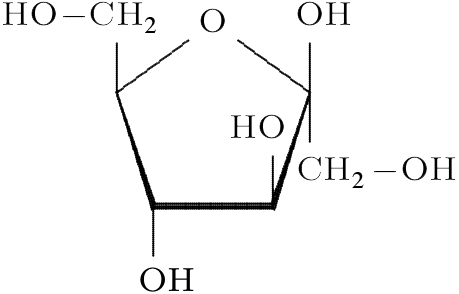
Galactose
a simple sugar that, along with glucose, makes up the disaccharide lactose (milk sugar). It's found in dairy products and some fruits and vegetables
Disaccharide
a type of sugar composed of two monosaccharides (simple sugars) joined together after going through dehydration synthesis. Common examples include sucrose (table sugar), lactose (milk sugar), and maltose
Dehydration Synthesis
a chemical process where two molecules are joined together to form a larger molecule, with the simultaneous removal of a water molecule. This reaction is crucial in the synthesis of larger biological molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids from their monomers
When determining the atomic number of a monosaccharide, what is one rule we can follow?
Oxygen is always half of Hydrogen
Polysaccarides
a large molecule (polymer) made up of many smaller sugar molecules (monosaccharides) linked together.
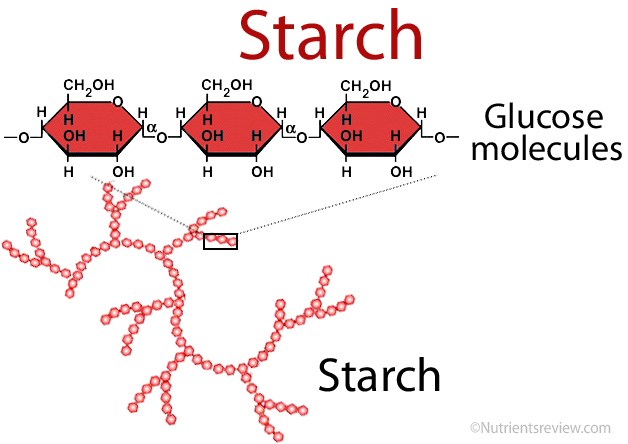
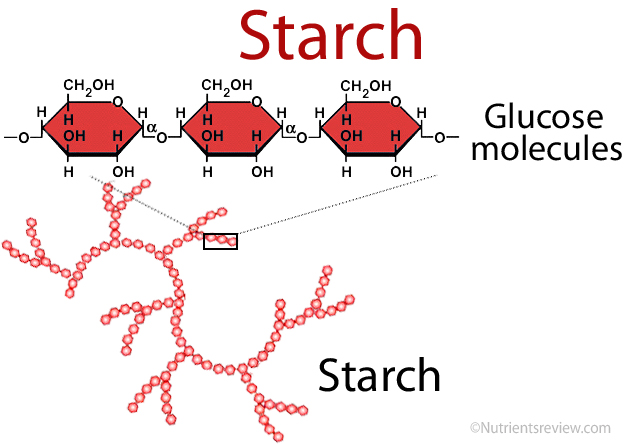
Starch
Carbs stored in plants
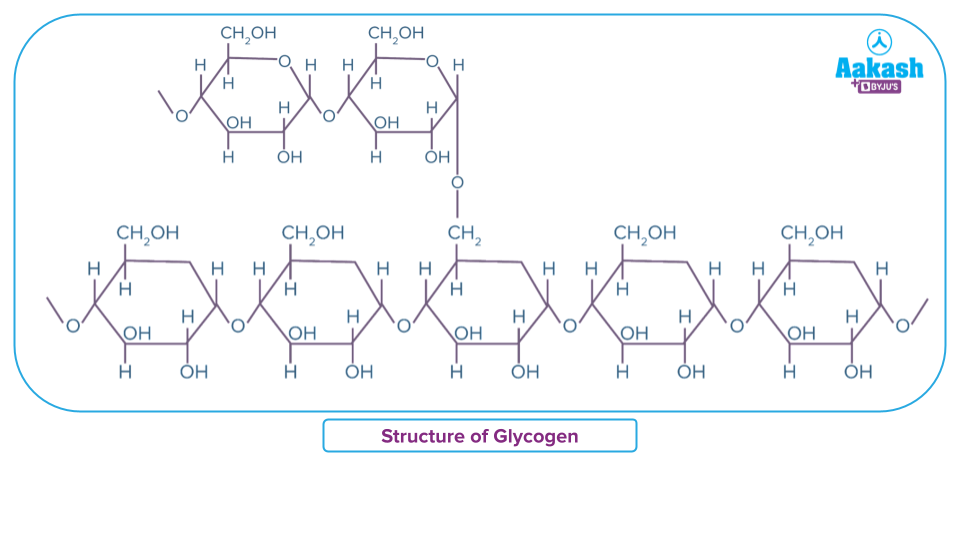
Glycogen
Carbs stored in the animals (liver and muscle) and fungi
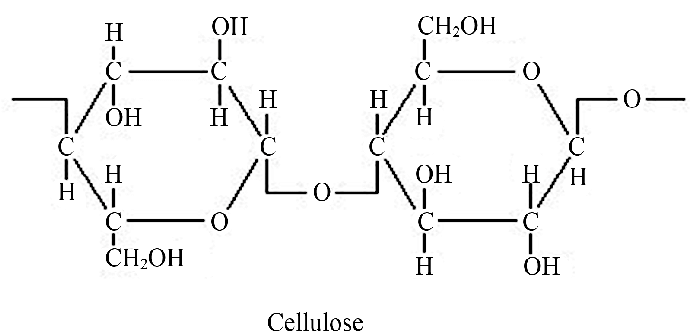
Cellulose
Main component of the plant cell wall, giving them strength and rigidty
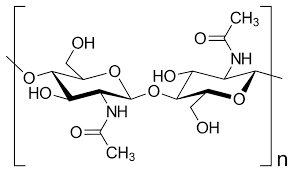
Chitin
a tough, protective substance found in the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans, and the cell walls of fungi
Hydrolysis
The process of using H2O to break bonds b/w monomers
aka, digestion