bio230 L10 protein sorting
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
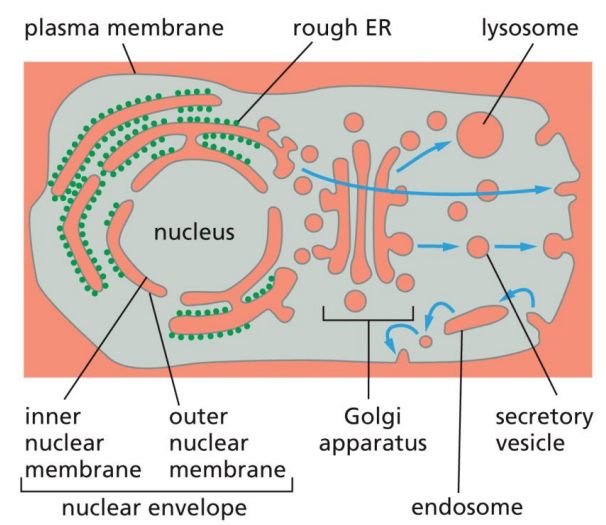
major functions of the ER
synthesis and modifications of proteins
synthesis of lipids
what proteins get sorted to the ER
soluble proteins, transmembrane proteins, proteins destined for golgi, secretion, lysosomes
topological equivalence in terms of vesicular transport
the inside of the ER and the Golgi apparatus are topologically equivalent to the extracellular space
proteins will maintain topological equivalence during vesicular transport — cytosolic segments/proteins in the cytosol, and extracellular segments/proteins in the vesicle
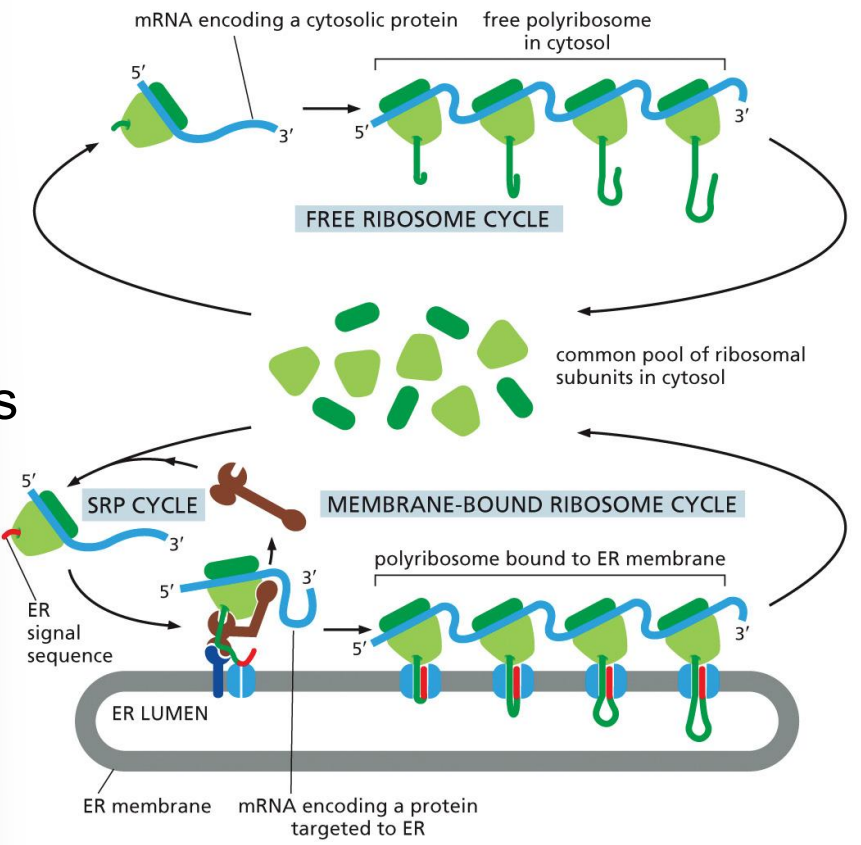
protein sorting to the endoplasmic reticulum
mRNA + ribosomes
translation starts, ER signal sequence emerges first
ribosomes directed to ER membrane
co-translational translocation
ER signal sequence
N-terminal, internal, and stop-transfer sequences that direct growing polypeptide chains to the ER
specific hydrophobic sequences, predicted by stretches of hydrophobic amino acids
signal recognition particle (SRP)
a protein that brings ribosome-amino acid chain complexes to the SRP receptor for protein translocation into the ER
has low affinity for ribosome, hovers outside the exit site until it detects signal sequence
has a high affinity for the ER signal sequence
has a GTPase domain that binds GTP
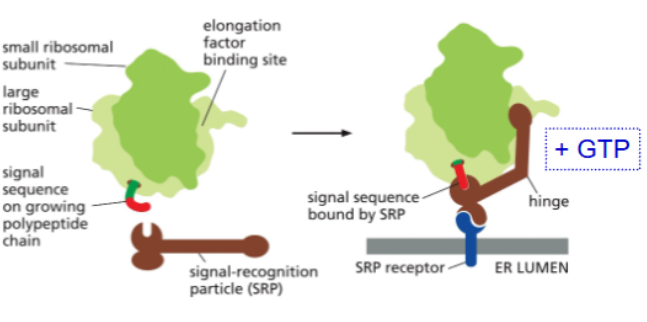
SRP receptor
a protein that accepts helps the SRP bring the target protein to the translocator
has a GTPase domain that binds GTP
SRP process
ribosome → protein translocator channel (translocon, a gated channel)
ribosome forms a tight seal with the translocator (prevents diffusion of ions, small molecules)
SRP + SRP receptor undergo GTP hydrolysis and complex dissociates
SRP released
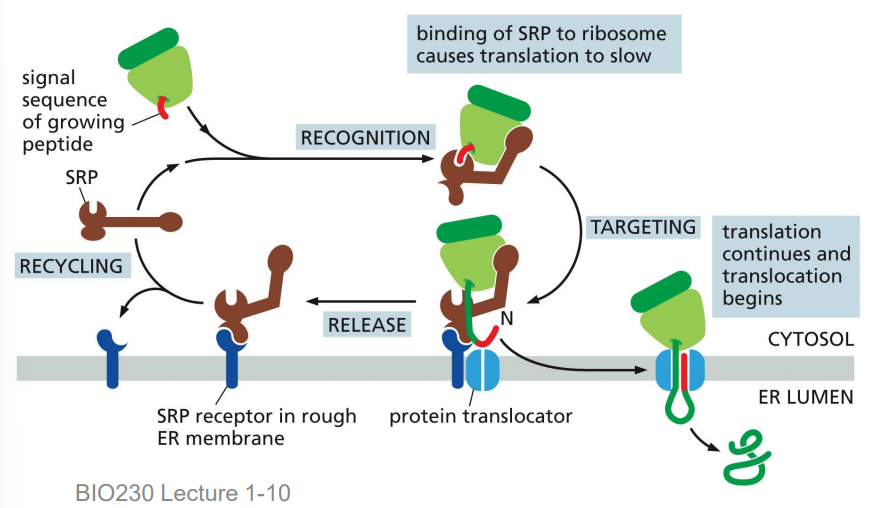
protein sorting to the ER: soluble proteins
N-terminal start-transfer sequence binds to the translocator
a signal peptidase cleaves the ER signal sequence
the ER signal sequence laterally diffuses into the lipid bilayer, not seen again. translocator is gated in a 2nd direction
translocated protein is released into the ER
signal peptidase
membrane bound protein that cleaves the ER signal sequence
soluble proteins
a protein that is not associated with the membrane
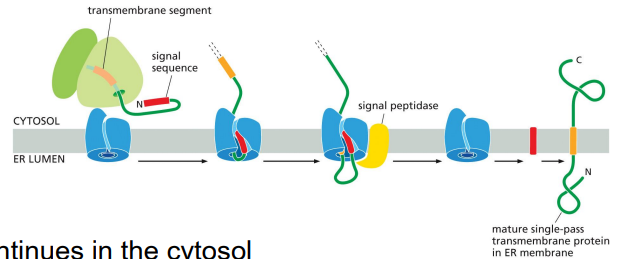
protein sorting to the ER: transmembrane proteins
single-pass & multi-pass transmembrane (TM) proteins
N and C terminal ends are sorted during translocation
single-pass TM proteins have 3 types of insertions
protein sorting to the ER: transmembrane proteins, singlepass, COOH in cytosol
ER signal sequence: NH2 start-transfer
TM domain is a stop-transfer signal that is cleaved and laterally diffuses into lipid bilayer
protein synthesis continues in the cytosol
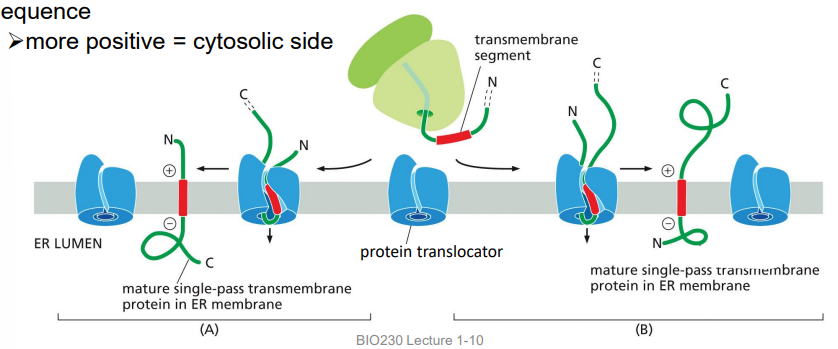
protein sorting to the ER: transmembrane proteins, singlepass, positive side in cytosol
TM domain is an internal start-transfer sequence and is not cleaved, laterally diffuses into the lipid bilayer
orientation is determined by the amino acids adjacent to the internal start-transfer sequence
more positive = cytosolic side
membrane protein types
integral (including transmembrane)
lipid anchored
peripheral
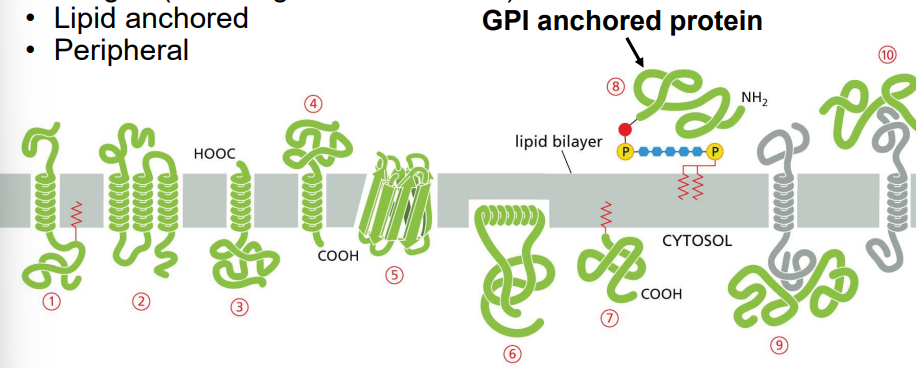
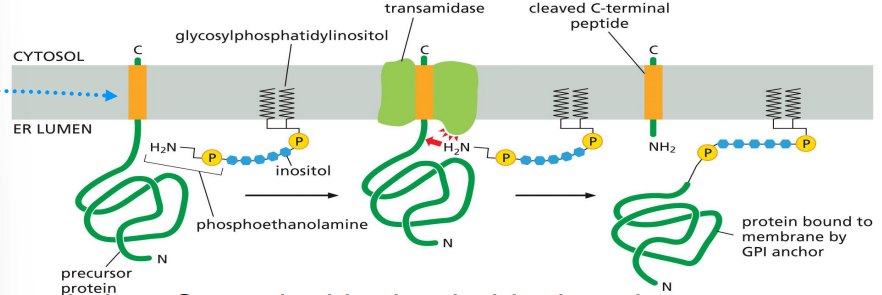
formation of glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein
target protein has c-terminal hydrophobic domain with signal for GPI anchor
GPI anchor is pre-formed in membrane
ER enzyme transfers protein to GPI anchor
GPI-anchored protein ends up on ER luminal side and can go to cell exterior surface