TV4101 - Avian 13 - Guinea Pigs
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
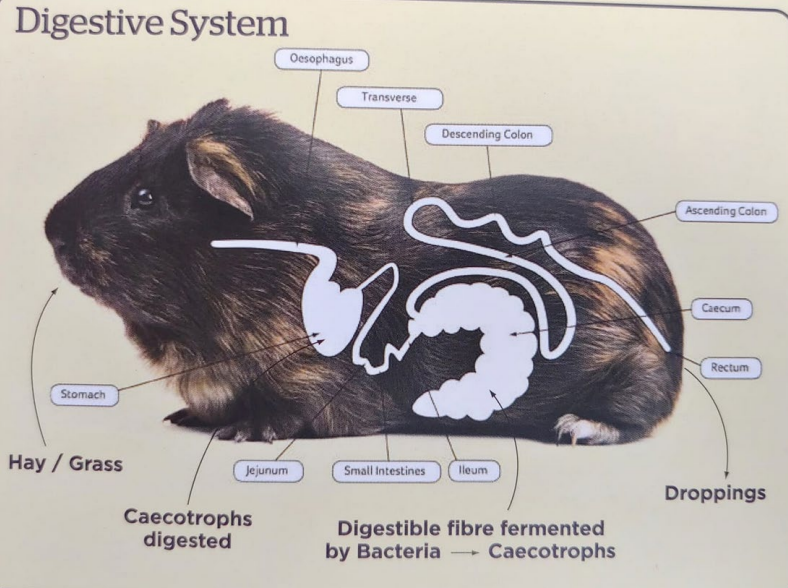
Guinea Pig Anatomy - Features?
Monogastric hind gut fermeters
Requires finely tuned flora for perfect function
Has large cecum, up to 65% of GIT volume
Obligate nasal breather
Very small thoracic area
Guinea Reproductive Aspects?
• Very advanced offspring
• Must be bred or desexed early to avoid future dystocia issues due to
pelvic size
Guinea Pigs can start breeding at?
When can they be desexed?
4-8 weeks of age and may be
desexed at 5-6mths of age for a female and 3-4 mths for a male
A female guinea pig should have her first litter before?
Why?
6 months of age.
After this age the pelvic bones become fused and can cause problems during labour.
Desexing reduces the incidence of?
Sterilised guinea pigs and behaviour?
Ovarian cysts and reproductive tumours in females and faecal impaction in males
In almost all cases sterilised guinea pigs will bond better with
their owners and other guinea pigs
Signs of illness in Guinea pigs
• Weight loss
• Eating less
• Only eating soft foods, no longer eating hay
• Drooling
• Diarrhoea
• Less active than normal, lethargic
• Unkempt coat, not grooming
• Lumps or bumps anywhere on body
• Hair loss
• Scratching all the time
• Coughing
• Sores on their feet
Large percentage of guinea pigs are presented as?
Collapsed, moribund and severely hypothermic (<35 C) - End stage
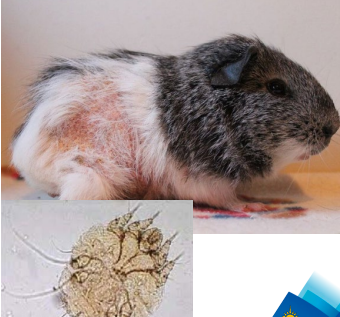
What this?
CS?
DX?
TX?
Guinea pig mites
CX
Oft presented “seizuring” as pruritis is so intense
Hair loss, flaking skin, self excoriation - back, thighs, shoulders and neck
DX - clinical signs and skin scrapings
Treatment – mectins – ivermectin, selamectin – 2-3 treatments , 10 days
apart, antibiotics if infection • Treat all in contact animals
Vit C deficiency
Why does it occur?
Predisposed in?
Other features?
Guinea pigs cannot produce vitamin C independently and must obtain it from their diet
Young growing, pregnant, elderly, and/or sick guinea pigs are at a higher risk of vitamin C deficiency
Complete vitamin C deficiency generally leads to a more rapidly progressing form of the disease
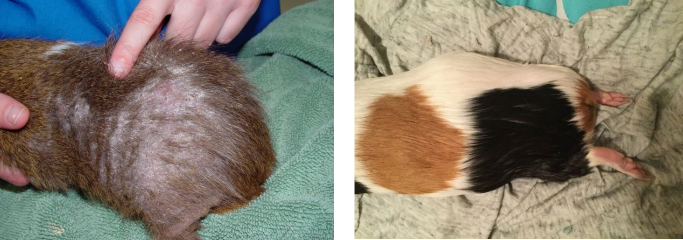
Clinical symptoms of chronic Vit C deficiency including
Behaviour?
External appearance?
Other features
Behaviour
Lameness, decreased mobility , partic hind legs
Teeth grinding, vocalising from pain
Anorexia or difficulty eating
External appearance
Flaky, rough coat
Painful swollen joints
Bruising
Bloody urine or diarrhoea
Other
• Delayed wound healing
• Secondary bacterial infections
• Gastrointestinal stasis
• Death
Vit C def TX?
Supplements and stuff
• Vitamin C supplementation via injection or oral medication is
often administered in the first instance.
• Oxbow Vitamin C supplement tablets
• Vitamin C may be added to drinking water, but the vitamin is
unstable in light and is most likely inactivated quickly.
Vit C def TX
Dietary requirements?
A good quality guinea pig food pellet should provide at least?
Fresh fruits and vegetables that are high invitamin C, such as ? should be given daily
Storage aspects?
Most guinea pigs require a daily vitamin C requirement of around
10-50mg/kg.
10-30 mg of vitamin C per day
Red or green capsicum, kale, broccoli, parsley and spinach
Vitamin C is easily destroyed by heat, light, and oxygen, so it's essential to store guinea pig food in a cool, dark place
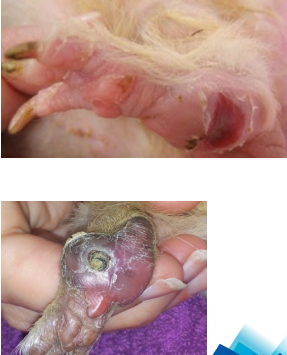
What this? Describe it
CS?
Pododermatitis
Pressure sores on feet, usually on heels of hind but front can also be affected
CS
Early signs - inflammation/redness of the exposed skin
As condition worsens:
lameness, swelling, ulcers, bleeding and
infection
Pododermatitis
A combination of factors may cause this, including?
Husbandry problems:
Small cages,
Hard floor surface
Dirty/damp bedding
Poor diet
Inactivity
Conformation:
Overweight animals,
Very thin body condition
Pregnancy
Deformed leg
Physical:
Trauma causing inflammation or lameness,
Chronic joint (arthritis) or back pain resulting in inactivity or poor grooming
Scalding of the feet by urine or faeces
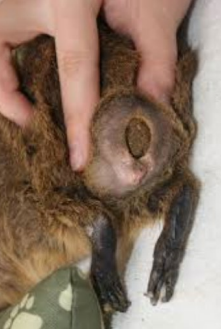
What is this?
Seen in who
Why?
CS?
TX?
Faecal impaction
• Entire males, >2-3 years
Increased size of the testicles and fat deposit in the scrotal sac prevents faeces from falling out of the rectum. This ‘dilates’ this area causing more faeces to accumulate
Still pass normal faeces but usually show symptoms of straining to defecate or an unusual odour
• Prevented by early castration
• Manual cleaning 1-10 times weekly, depending on the boar

What is this?
CS?
Caused by?
DX?
Vestibular disease
CSX – head tilt, rolling, “seizures”, nystagmus
Common causes of Vestibular disease are bacterial infections, ear infections, protozoal infections, and trauma
Often secondary to dental or respiratory disease tracking into middle ear
DX – ear examination, radiographs
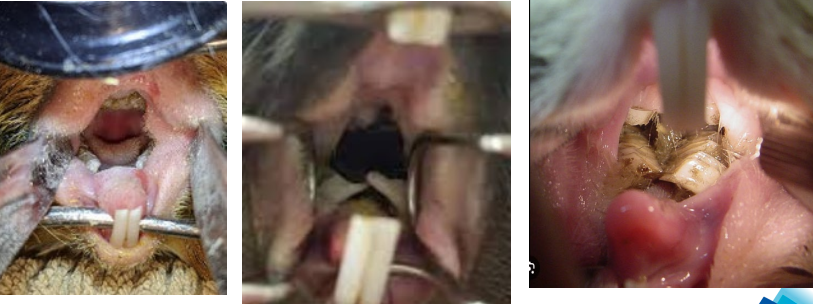
Dental Disease
Why does it occur?
Result?
Guinea pigs fed mainly on pellets or guinea pig mixes lack the high fibre need for normal teeth wear
Curved inward lower cheek teeth aren’t worn down and eventually entrapping the tongue
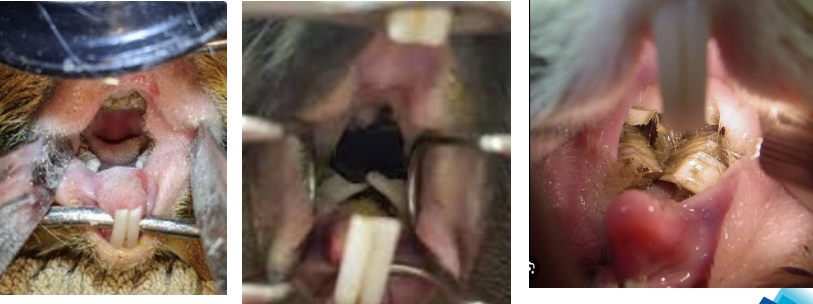
Dental Disease
CSX
stops eating certain types of food or any food at all. Weight loss common, start producing fewer or smaller droppings, excessive saliva (drooling) leading to fur matting under the jaw.
Dental Disease
DX
Diagnosis
• Oral exam, difficult without appropriate equipment – nasal speculum attachment on otoscope
• Radiographs to confirm degree of overgrowth
Dental Disease
TX?
• Surgery to grind down teeth
• Requires special dental jigs to open mouth as oral cavity very
small
• Grind teeth back with dremel/dental burrs
• May need to be carried out as often as 6 weekly if chronic changes
Dental Disease Prevention
Feeding a diet that includes at least :
70% grass and good quality hay (oat, timothy or orchard hay)
20-30% fruit and vegetables
No more than 5-10% pellets
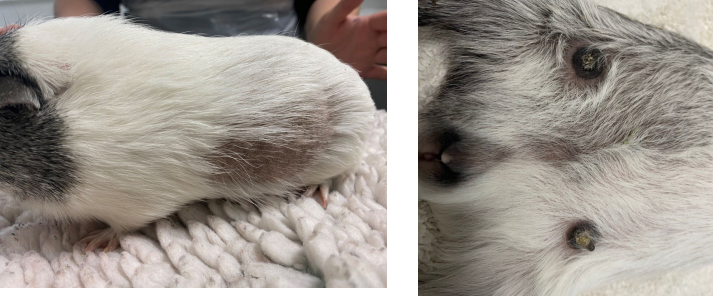
What is this?
How can we tell?
Other signs?
Functional ovarian cyst (secreting hormones)
Bilateral symmetric hair loss in the flank region, crusty nipples
Being irritable or seeming uncomfortable in their abdomen
With large cysts may show signs of anorexia, depression and lethargy
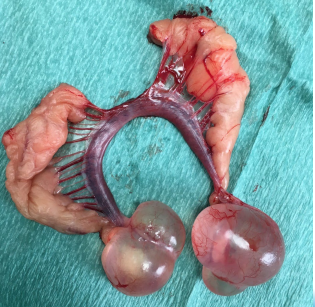
Ovarian Cysts
Signalment?
Ovarian cysts may be associated with?
Female entire guinea pigs aged 2-4 years
Uterine disease and can become significant space-occupying masses if left untreated
Ovarian cysts often increase in size
with time, and the pressure of the cyst
on other organs may cause ?
What else can form?
DX?
Pain and gut stasis
Adhesions can also form, which can cause problems at a later date
Confirmed by palpation, an abdominal ultrasound or radiographs
Ovarian Cyst TX?
Exploratory abdominal surgery to remove the cyst and perform
an ovariohysterectomy or ovariectomy (completely removes ovaries so better option)
Ultrasound-guided aspiration of the cysts under sedation -
provides a temporary solution however carries some risk
Gut Stasis
Caused by what?
Give explicit examples that should be avoided
Typically antibiotic induced
Explicitly avoided: clindamycin, lincomycin, ampicillin, amoxicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, cephalosporins, erythromycin, and penicillin if given orally
Gut Stasis
SAFE OPTIONS to prevent this shit?
Penicillin (SC or IM only), trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole, chloramphenicol, metronidazole, and fluoroquinolones
Pododermatitis TX
Address underlying issue - flooring, wt, RG for OA/spinal issues
Treat lesions → debriding surgery to remove dead tissue and then appropriate dressings up to 6 months
Infections may lead to osteomyelitis - ABs and pain relief
Clinical symptoms of antibiotic associated enterotoxemia begin?
Signs include?
DX?
If overgrowth of Clostridia - can be confirmed with?
1 to 5 days after antibiotic administration
Anorexia, dehydration, and hypothermia
Diarrhoea sometimes
Based on clinical history and clinical signs
PCR or ELISA for C. difficile toxin
Routine GI stasis
TX?
comprehensive supportive care (aggressive fluid hydration, pain management, and assisted nutrition)
Warmed fluids 25-35ml/kg every 8 hours orally or SC
More severe hydration may require IV
Minimise anxiety with injectable midazolam (0.25–0.5 mg/kg
IV/IM)
Pain controlled with analgesics, buprenorphine then to meloxicam after adequate hydration (0.2 mg/kg IM/SC/by mouth every 24 hours
in guinea pigs).
Routine GI stasis
Once obstruction has been ruled out, what next?
Prokinetic agents can be used
Including metoclopramide (0.5 mg/kg SC/by mouth every 8–12
hours) and/or cisapride (0.5 mg/kg by mouth every 8–12 hours)
Routine GI stasis - TX?
Reducing Gas Distension?
Simethicone (20 mg/kg by mouth every 8–12 hours) can be
used
Routine GI stasis
If Gastric ulcers are likely, what use?
Ranitidine (2 mg/kg IV every 24 hours, 2–5 mg/kg by mouth every 12 hours) used in cases with prolonged anorexia
Routine GI stasis - Nutrition?
Syringe feeding (15 mL/kg every 8 hours) of an herbivore critical care formulation
Prolonged nutritional support can be provided by nasogastric tube
Routine GI Stasis - ABs?
Antibiotics should only be used in cases complicated by
enterotoxemia and bacterial enteritis
For cases of enteritis caused by bacterial overgrowth, fecal
bacterial culture and sensitivity can be helpful to guide
antiobiotic therapy such as?
broad-spectrum agents, including
trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (30 mg/kg by mouth every 12 hours)
or enrofloxacin (15 mg/kg by mouth every 24 hours)
Enteritis from bacterial overgrowth?
Dysbiosis?
What can help suppress Clostridial Overgrowth?
Attempts to correct the dysbiosis including transfaunation and commercial probiotics containing Lactobacillus spp (anecdotal success)
Chloramphenicol (50 mg/kg by mouth every 8 hours)