Genética y receptores NBME
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Cystic Fibrosis
Gene: CFTR (ΔF508 deletion), Chromosome 7
Inheritance: Autosomal recessive
Pathophysiology:
Mutation → misfolded CFTR protein → retained in RER, not transported to cell membrane.
Defective Cl⁻ channel →↑ Na⁺ and H₂O reabsorption→ thickened mucus → lung, pancreatic, GI dysfunction
Clinical Features:
Neonatal: Meconium ileus
Pancreatic insufficiency: steatorrhea
Azoospermia (no vas deferens)
Recurrent infections: S. aureus (kids), Pseudomonas (adults)
Diagnosis:
↑ Cl⁻ in sweat test, immunoreactive trypsinogen (newborn screening)
Treatment: CFTR modulators (ivacaftor, lumacaftor), Chest physiotherapy, pancreatic enzyme replacement,
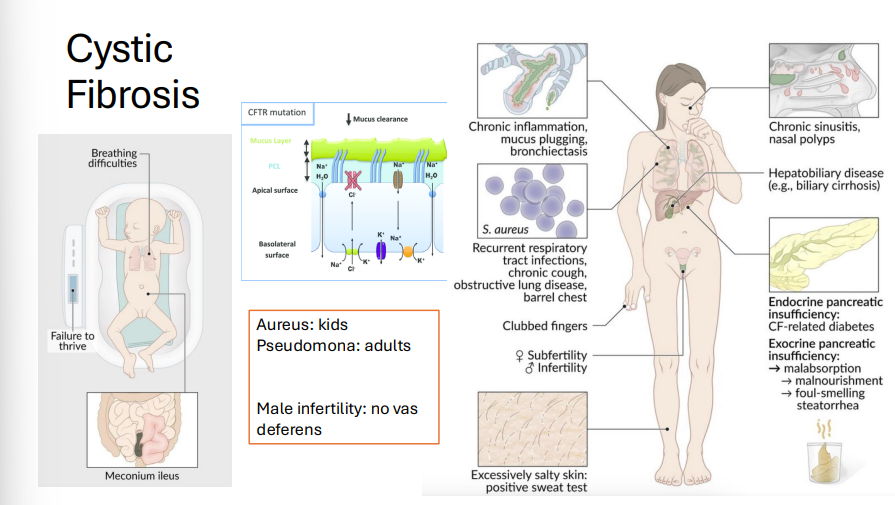
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Gene: PAH (phenylalanine hydroxylase); cofactor: tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)
Inheritance: Autosomal recessive
Pathophysiology:
Deficiency of PAH or BH4 → accumulation of phenylalanine → neurotoxic
Clinical features:
Intellectual disability
Musty body odor
Hypopigmentation: fair skin, blue eyes
Seizures, eczema
Treatment: ↓ phenylalanine (avoid aspartame), ↑ tyrosine, BH4 supplements
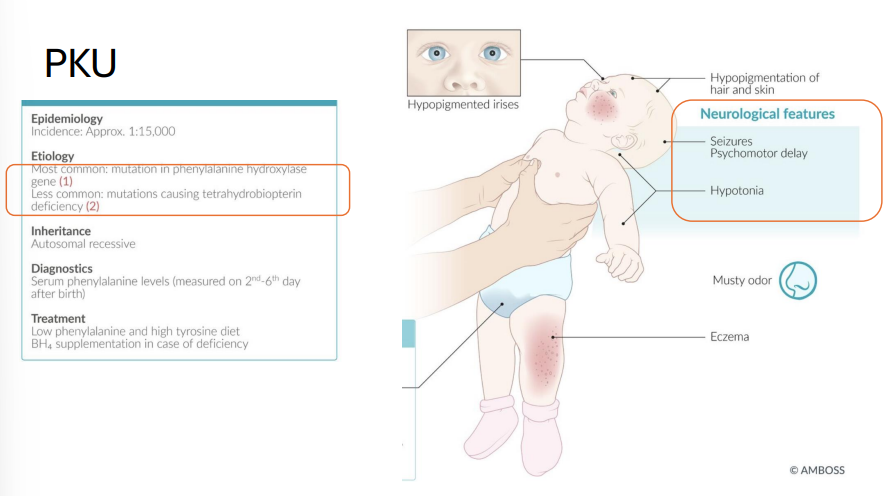
Friedreich Ataxia
Gene: FXN (frataxin), Chromosome 9
Mutation: GAA trinucleotide repeat (autosomal recessive)
Pathophysiology:
↓ Frataxin → mitochondrial dysfunction → oxidative stress and degeneration of neurons (dorsal columns, spinocerebellar tract)
Clinical Features:
Childhood-onset progressive ataxia
Pes cavus, kyphoscoliosis
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (cause of death)
Diabetes mellitus
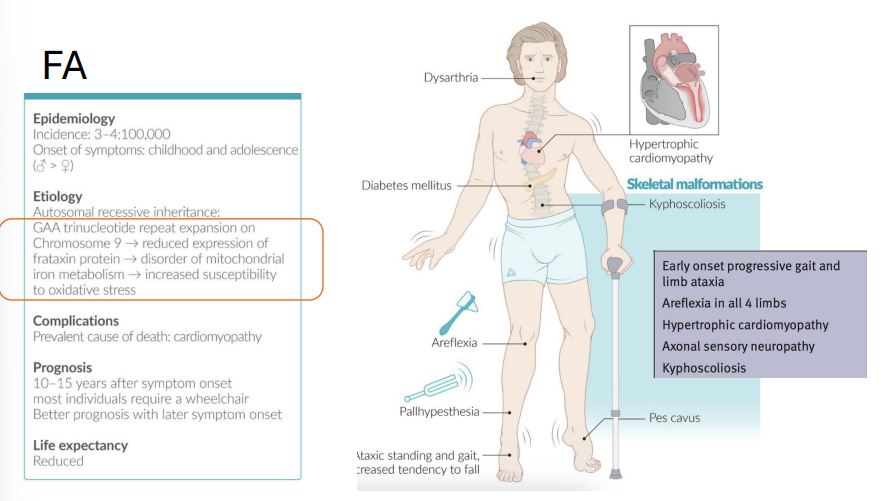
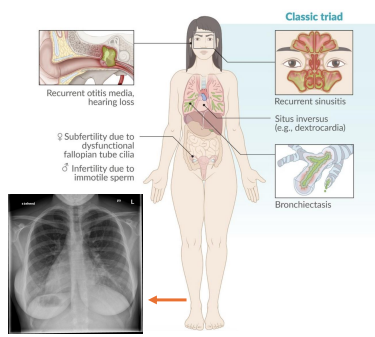
Kartagener Syndrome (Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia)
Gene: DNAI1, DNAH5
Inheritance: Autosomal recessive
Pathophysiology:
Immotile cilia due to dynein arm defect
Clinical features:
Chronic sinusitis, bronchiectasis
Situs inversus (50%)
Male infertility (immotile sperm), recurrent otitis media
Oculocutaneous Albinism (OCA)
Genes:
TYR (type I), OCA2 (type II), TYRP1 (type III), SLC45A2 (type IV)
Inheritance: Autosomal recessive
Pathophysiology:
Deficient melanin biosynthesis in melanocytes
Clinical features:
Reduced visual acuity, photophobia, nystagmus
↑ risk of squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma
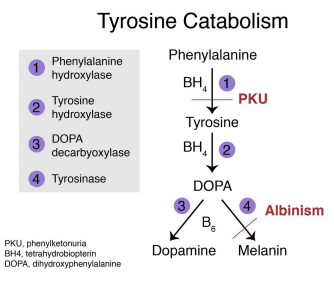
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
Gene: PKD1 (Chr 16, ~85%), PKD2 (Chr 4, ~15%)
Inheritance: Autosomal dominant
Pathophysiology:
Cyst development in renal tubules → progressive kidney failure
Clinical features:
Bilateral enlarged kidneys, hematuria, flank pain
Associated: berry aneurysms, mitral valve prolapse, hepatic cysts
ESRD usually by 50–60 y/o
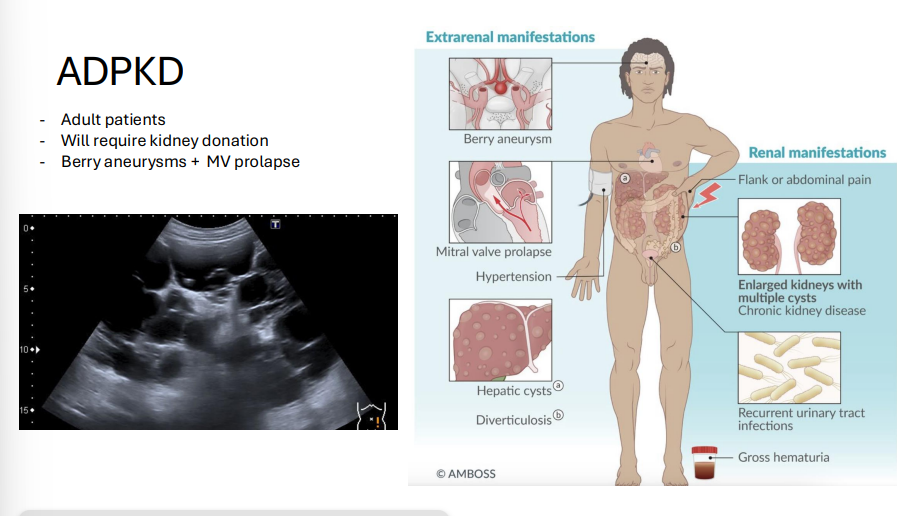
Huntington Disease
Gene: HTT (Huntingtin gene)
Chromosome: 4
Inheritance: Autosomal dominant, trinucleotide repeat (CAG)n with paternal anticipation
Pathophysiology:
Accumulation of mutant huntingtin protein → neurotoxicity, especially in caudate nucleus and putamen (neostriatum)
↓ GABA and ACh
Clinical Features:
Chorea (involuntary movements)
Dementia and psychiatric changes (depression, aggression)
Atrophy of caudate and putamen (MRI: enlarged lateral ventricles)
Onset usually 30–50 y/o; progressive and fatal
Mnemonic: “CAG = Caudate loses ACh and GABA”
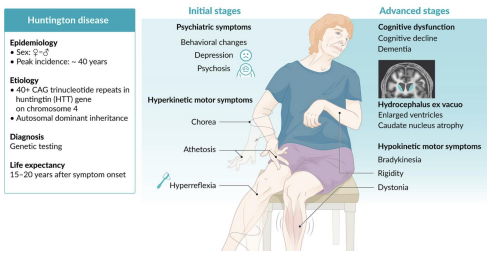
Fragile X Syndrome
Gene: FMR1 (fragile X mental retardation 1)
Mutation: CGG trinucleotide repeat expansion → gene silencing by methylation
Inheritance: X-linked dominant
Pathophysiology:
Hypermethylation → ↓ expression of FMR1 → impaired synaptic plasticity
Clinical Features:
2ND Most common inherited cause of intellectual disability (1ST = DOWN SYNDROME)
Long face, large ears, macroorchidism
Autism spectrum behaviors, mitral valve prolapse
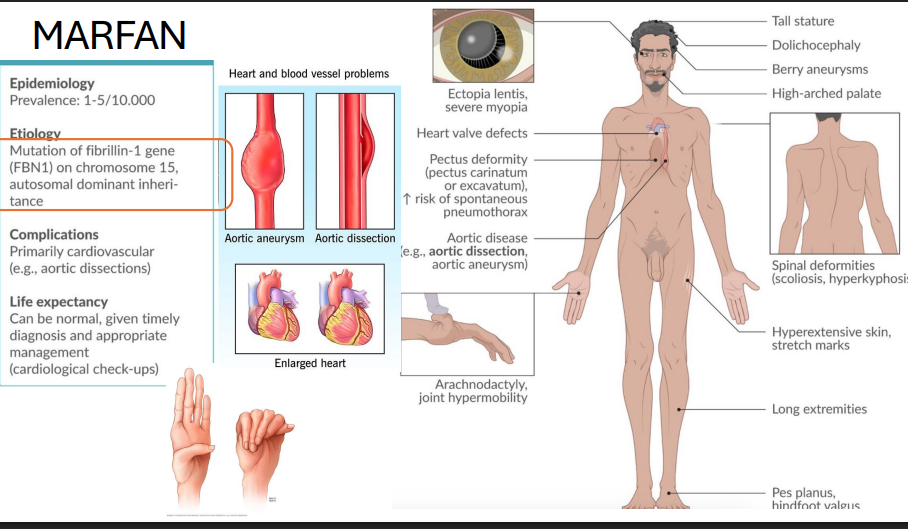
Marfan Syndrome
Gene: FBN1 (Fibrillin-1), Chromosome 15
Inheritance: Autosomal dominant
Pathophysiology:
Defective microfibrils in connective tissue → Defective fibrillin → abnormal elastic fibers + ↑ TGF-β activity
Clinical Features:
Tall stature, long limbs, arachnodactyly
Aortic root dilation → dissection, MVP
Ectopia lentis (lens dislocation upwards)
pectus deformities
Rett Syndrome
Gene: MECP2 (X-linked mutation, de novo)
Inheritance: Sporadic (girls only; lethal in males)
Pathophysiology:
Loss of transcriptional repression during development
Clinical Features:
Normal development then regression at 6–18 months
Hand-wringing, seizures, intellectual disability, scoliosis

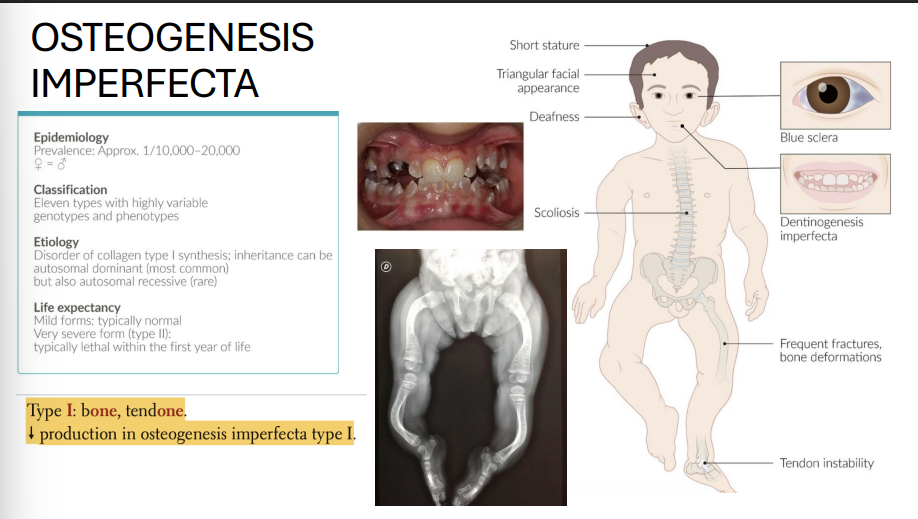
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (Type I)
Genes: COL1A1, COL1A2
Inheritance: Autosomal dominant
Pathophysiology:
↓ type I collagen synthesis
Clinical features:
Bone fractures with minimal trauma
Blue sclerae (translucent connective tissue)
Hearing loss (ossicle damage)
Dental imperfections
Mitochondrial Myopathies
Genes: Mutations in mtDNA (maternal inheritance)
Pathophysiology:
Defective oxidative phosphorylation → CNS + muscle symptoms
Diseases:
MELAS (mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, stroke-like episodes)
MERRF (myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers)
LHON (Leber hereditary optic neuropathy): subacute vision loss in males
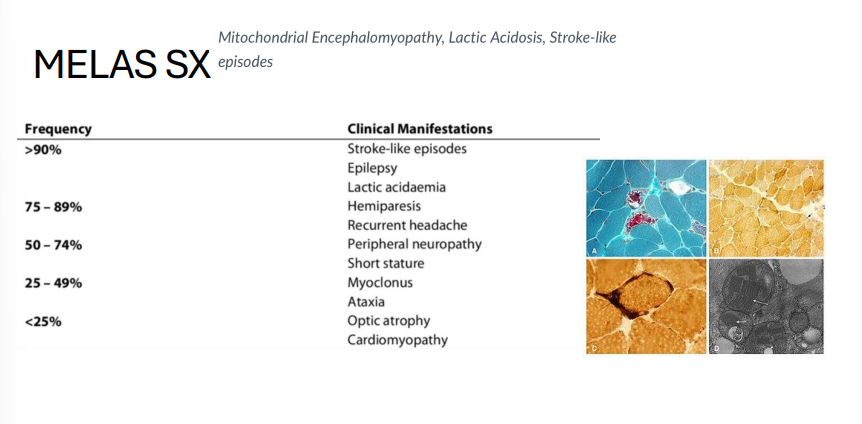
MELAS
Gene: mtDNA (heteroplasmic mutation)
Inheritance: Mitochondrial (maternal)
Pathophysiology:
Defective oxidative phosphorylation
Clinical features:
Myopathy
Encephalopathy
Lactic acidosis
Stroke-like episodes in young patients
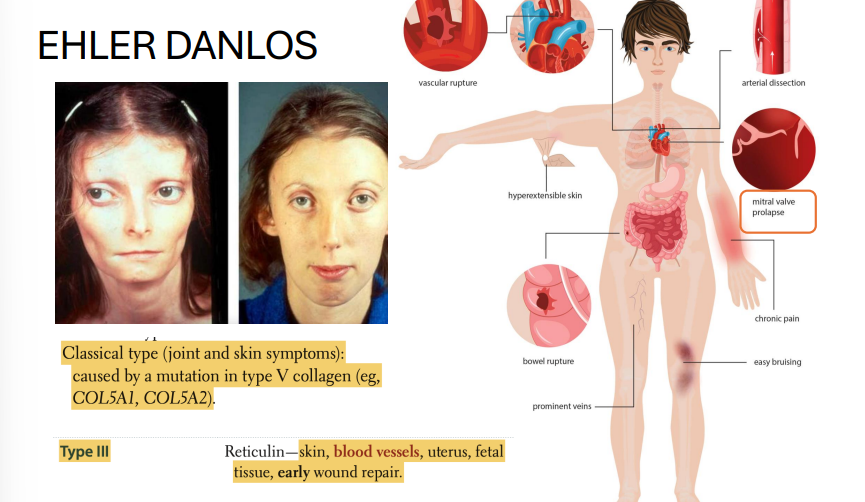
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS)
Genes: Multiple, depending on subtype:
COL5A1, COL5A2 (classic type, AD)
COL3A1 (vascular type, AD)
Inheritance: Autosomal dominant (some forms AR)
Pathophysiology: Defects in collagen synthesis (mainly types III and V)
Clinical features:
Hyperextensible skin
Joint hypermobility
Easy bruising, poor wound healing
Vascular type: risk of arterial rupture, organ rupture (esp. uterus, colon)
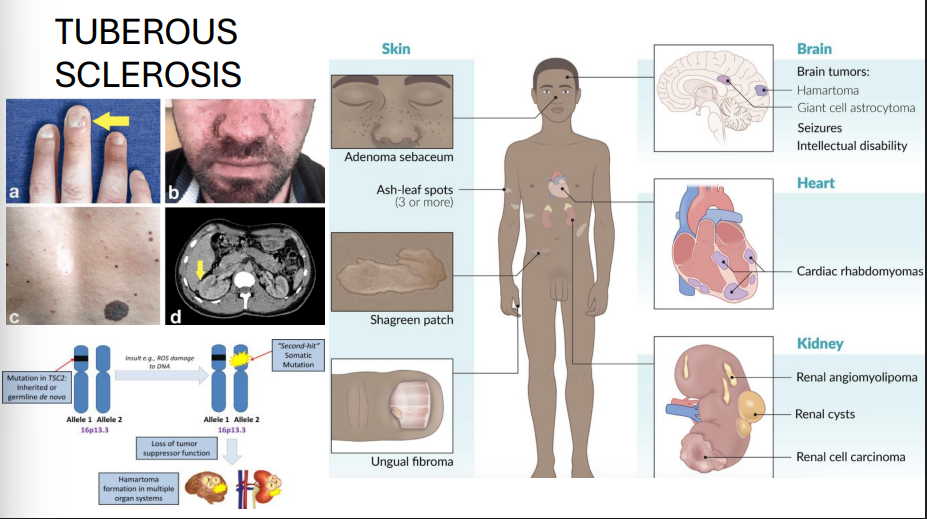
Tuberous Sclerosis
Genes: TSC1 (hamartin, Chr 9), TSC2 (tuberin, Chr 16)
Inheritance: Autosomal dominant with variable expressivity
Pathophysiology: Tumor suppressor gene loss → ↑ mTOR signaling → hamartoma formation
Clinical features:
Seizures, intellectual disability
Facial angiofibromas (adenoma sebaceum)
Shagreen patches, ash-leaf spots (hypopigmentation)
Renal angiomyolipomas
Cardiac rhabdomyomas
Subependymal giant cell astrocytomas (SEGAs)
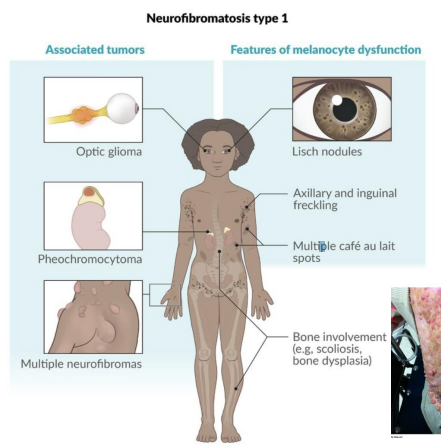
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1 / von Recklinghausen disease)
Gene: NF1 (neurofibromin, Chr 17)
Inheritance: Autosomal dominant, 100% penetrance, variable expression
Pathophysiology: Tumor suppressor gene → negative regulator of RAS
Clinical features:
Café-au-lait macules
Neurofibromas (cutaneous and plexiform)
Axillary/inguinal freckling
Optic gliomas
Lisch nodules (iris hamartomas)
Risk of pheochromocytoma
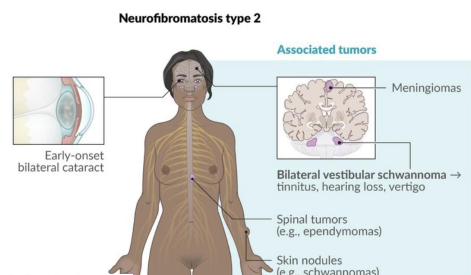
Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2)
Gene: NF2 (merlin/schwannomin, Chr 22)
Inheritance: Autosomal dominant
Pathophysiology: Loss of tumor suppressor → CNS tumors
Clinical features:
Bilateral vestibular schwannomas (hallmark)
Juvenile cataracts
Meningiomas, ependymomas
Hearing loss, balance dysfunction
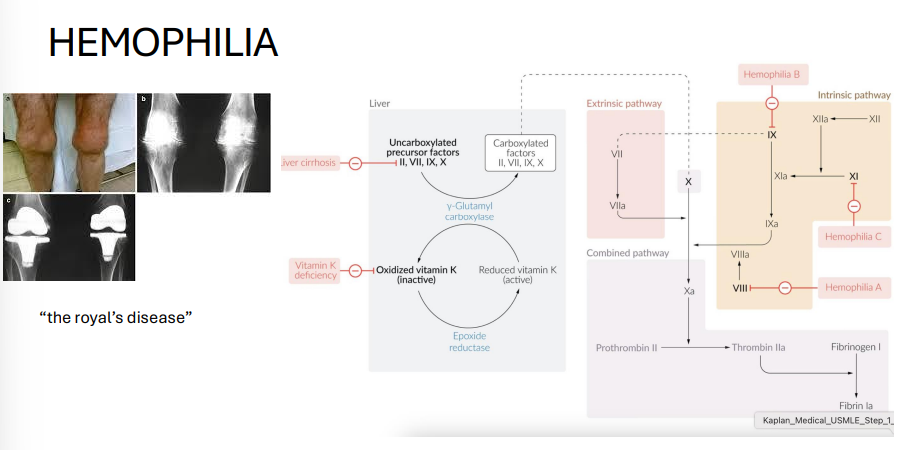
Hemophilia A and B
Genes:
A: F8 (Factor VIII)
B: F9 (Factor IX)
Inheritance: X-linked recessive
Pathophysiology: Coagulation factor deficiency → impaired intrinsic pathway
Clinical features:
Hemarthroses (joint bleeding)
Easy bruising
Prolonged aPTT, normal PT/bleeding time
Treatment: Factor replacement therapy
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Gene: DMD (dystrophin); frameshift or nonsense mutation
Inheritance: X-linked recessive
Pathophysiology: Absence of dystrophin → sarcolemma instability → myonecrosis
Clinical features:
Onset <5 y/o, rapid progression
Gowers sign (climb up legs)
Calf pseudohypertrophy (fat/fibrosis)
Elevated CK and aldolase
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Death: by early adulthood (respiratory/cardiac failure)
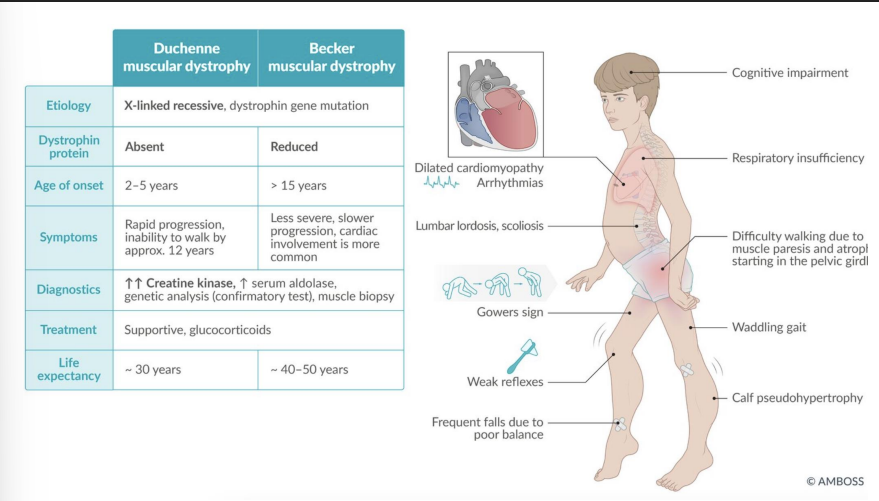
Becker Muscular Dystrophy
Gene: DMD (in-frame mutation)
Inheritance: X-linked recessive
Pathophysiology: Partially functional dystrophin protein
Clinical features:
Later onset (adolescence/adulthood)
Milder weakness
Slower progression
Preserved lifespan relative to DMD
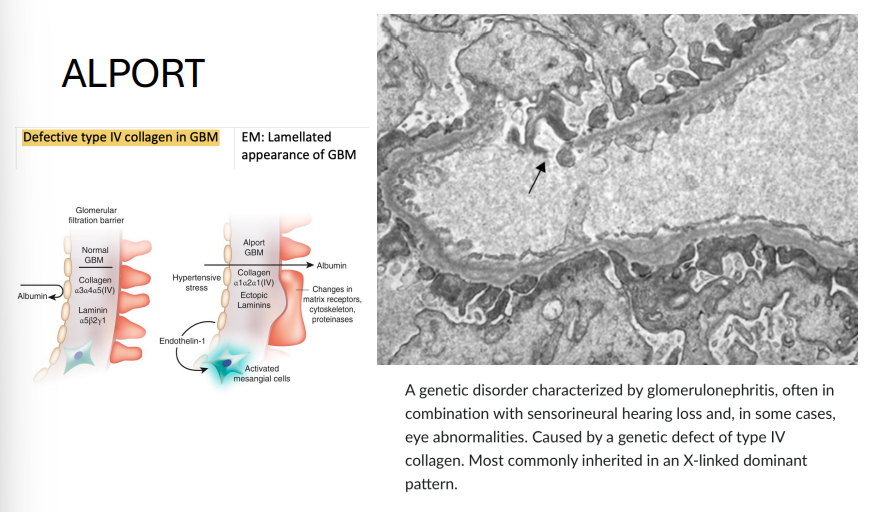
Alport Syndrome
Gene: COL4A5 (most common, X-linked); less commonly COL4A3/4 (AR/AD)
Inheritance:
X-linked dominant (classic)
Some forms AR/AD
Pathophysiology: Defective type IV collagen in basement membranes
Clinical features:
Glomerulonephritis → hematuria, progressive renal failure
Sensorineural deafness
Ocular findings (e.g., anterior lenticonus)
EM: “Basket-weave” appearance of GBM
Polygenic Inheritance
Definition: Traits/diseases influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors; no single mutation explains causation.
Inheritance pattern: Does not follow Mendelian rules; risk ↑ with more affected family members.
Mechanism: Combined effect of multiple genetic loci with small individual effect sizes
Examples:
Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hypertension
Coronary artery disease
Schizophrenia
Bipolar disorder
Autism spectrum disorders
Psoriasis
Multiple sclerosis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Alopecia areata
Alzheimer’s disease
Obesity
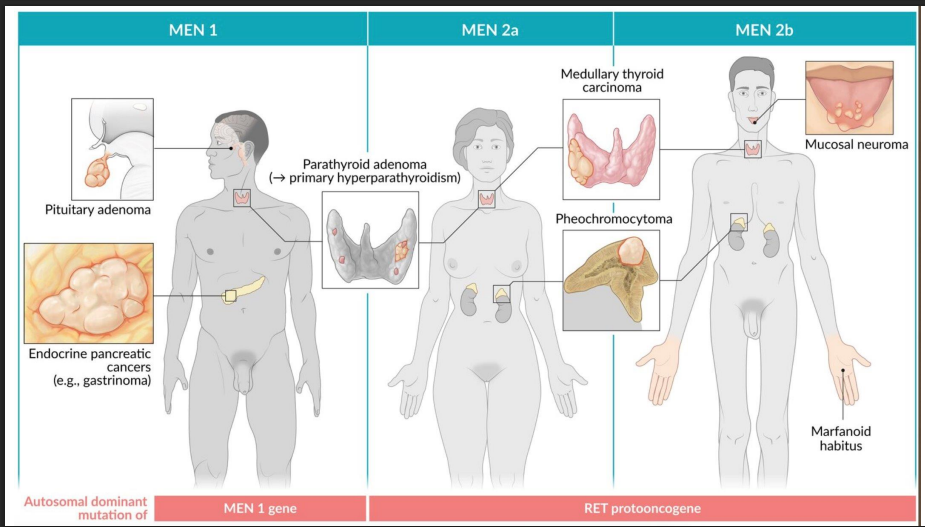
MEN 1, 2A, 2B
ALL: AD
MEN 1 = 3 P's: Parathyroid, Pituitary, Pancreas
Mutation: MEN1 (tumor suppressor)
Watch for kidney stones, ulcers, hypoglycemia
MEN 2A = 2 P's + T: Parathyroid, Pheochromocytoma, Thyroid (medullary)
Mutation: RET (proto-oncogene)
Prophylactic thyroidectomy often in childhood
RET testing is mandatory in families
MEN 2B = 1 P + T + M: Pheochromocytoma, Thyroid, Mucosal neuromas + Marfanoid
Mutation: RET (different codon)
No parathyroid involvement
Oral/intestinal neuromas + tall habitus
Intracellular Receptors
Ligands:
Steroid hormones: cortisol, aldosterone, estrogen, progesterone, testosterone
T₃
Vitamin D (calcitriol)
Retinoic acid (vitamin A)
Location: Cytoplasm or nucleus
Mechanism:
Lipophilic hormone crosses the cell membrane.
Binds to a receptor in cytoplasm or nucleus.
Hormone-receptor complex acts as a transcription factor → binds hormone response elements (HREs) in DNA → modulates gene expression.
Example conditions:
Glucocorticoids modulate anti-inflammatory gene transcription.
Thyroid hormone upregulates metabolic gene expression.
Tyrosine Kinase Receptor
Ligands:
Insulin
Growth factors: IGF-1, EGF, FGF, PDGF, VEGF
Structure:
Single-pass transmembrane protein with intrinsic kinase activity.
Mechanism:
Ligand binds → receptor dimerizes.
Autophosphorylation of intracellular tyrosine residues.
Activates downstream signaling pathways:
RAS/MAPK → cell proliferation
PI3K/AKT → cell survival, metabolism
Clinical relevance:
Target for monoclonal antibodies
Insulin RTK → upregulates GLUT4 in skeletal muscle/adipose
Non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (Cytoplasmic Tyrosine Kinase)
Ligands:
Cytokines: IL-2, IL-6, IFN-α, IFN-γ
Hematopoietic factors: EPO, G-CSF, TPO
Hormones: GH, prolactin
Associated pathway: JAK-STAT
Mechanism:
Ligand binds membrane receptor (no intrinsic kinase activity).
JAK (Janus kinase) binds cytoplasmic domain.
JAK phosphorylates STAT proteins.
Phosphorylated STATs dimerize and enter nucleus → gene transcription.
Mnemonic: “JAK for cytokines & growth hormones”
Clinical correlation:
Ruxolitinib (JAK inhibitor) used for myeloproliferative disorders
G-Protein
Gs → ↑ cAMP → PKA activation
examples:
TSH → thyroid hormone synthesis
PTH → bone resorption & renal Ca²⁺ reabsorption
β₂ → bronchodilation:
Gi → ↓ cAMP → ↓ PKA
effects:
α₂ agonists (e.g., clonidine) → ↓ sympathetic outflow
D₂ antagonists (antipsychotics) → ↑ prolactin (via pituitary disinhibition)
Gq → ↑ IP₃/DAG → ↑ PKC + Ca²⁺
effects:
α₁: smooth muscle contraction → ↑ BP
M₃: glandular secretion
Angiotensin II: vasoconstriction + aldosterone release
Pathway | Mnemonic | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
Gs | “FLAT ChAMP” | FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, CRH, hCG, ADH (V2), MSH, PTH |
Gi | “MAD 2s” | M2, α2, D2 |
Gq | “HAVe 1 M&M” | H1, α1, V1, M1, M3 |