BIO 233 UNIT 6 (Part 1) - Muscle Types, the Sarcomere, NMJ, Steps of Contraction
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Muscle Types, the Sarcomere, NMJ, Steps of Contraction
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
actin
thin filaments (red) get pulled towards middle
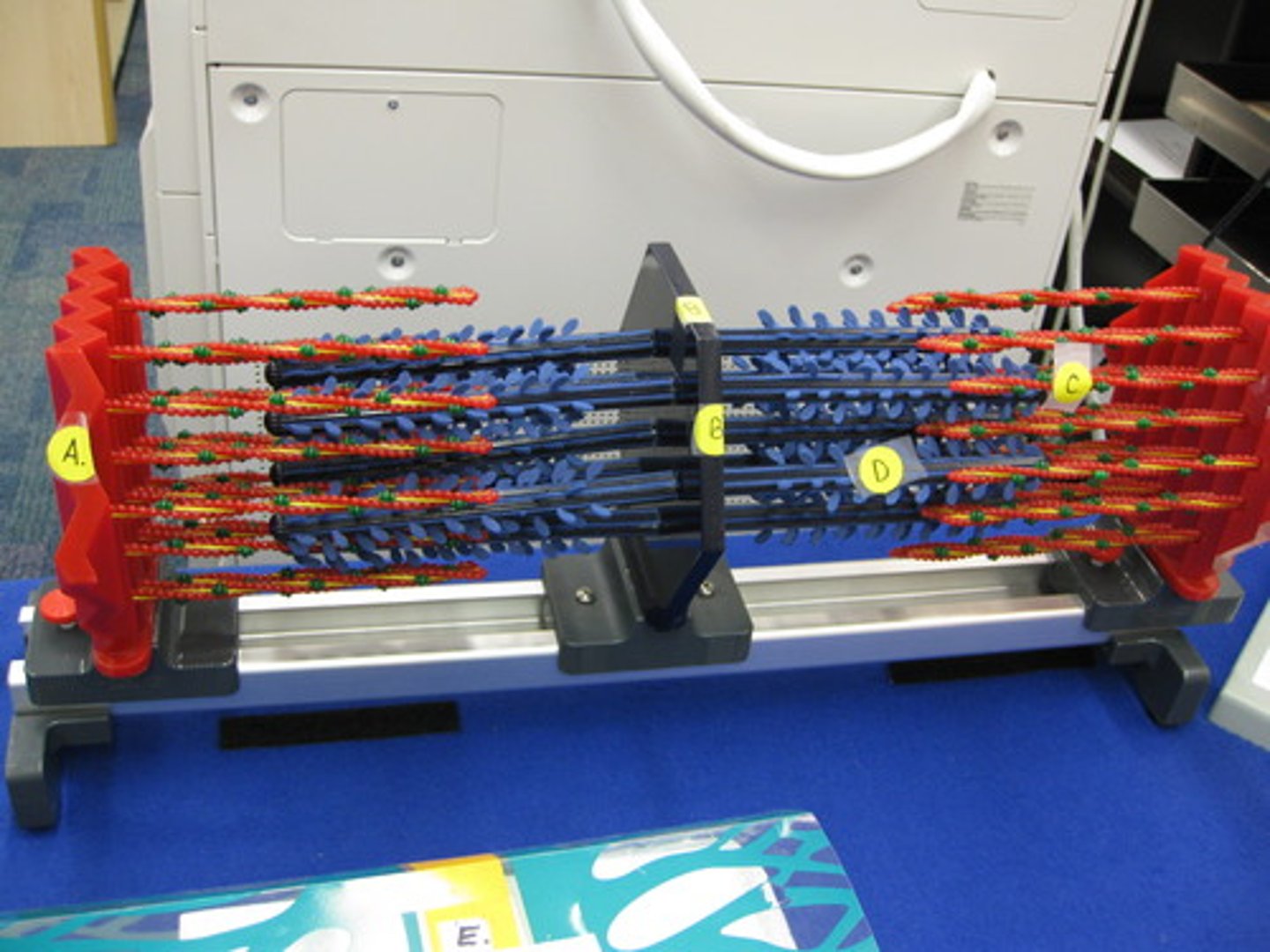
myosin
thick filaments (blue) - pulls actin in towards middle
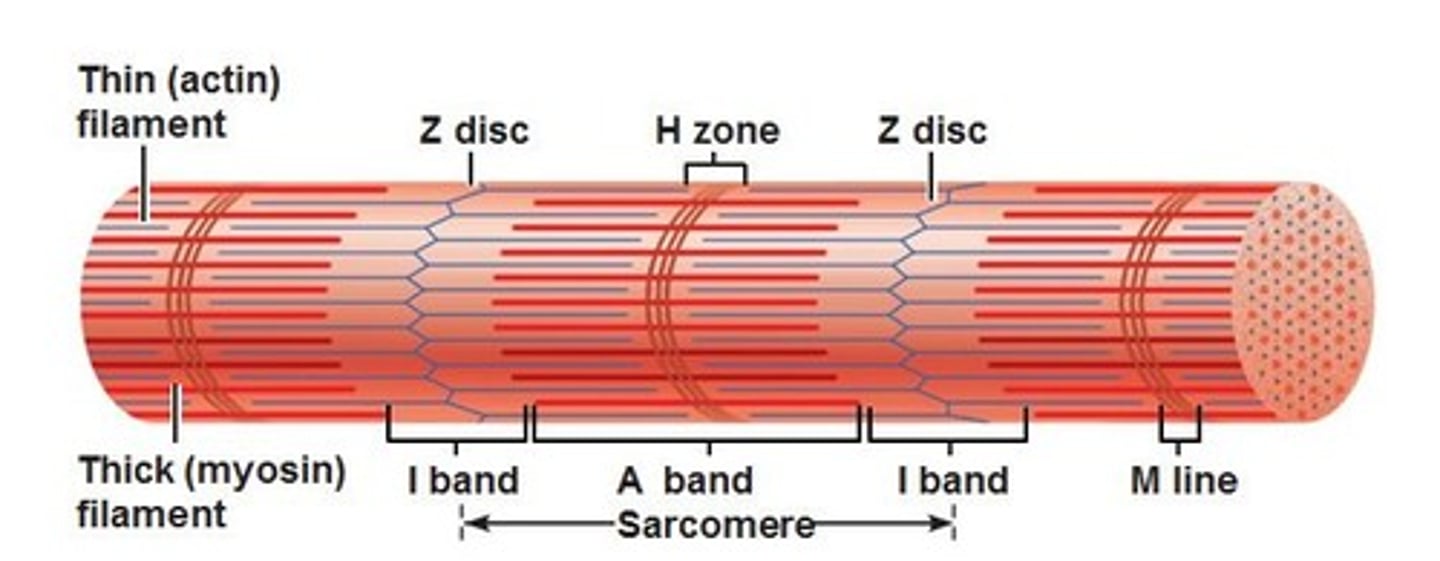
Z-disc
forms each end of the sarcomere
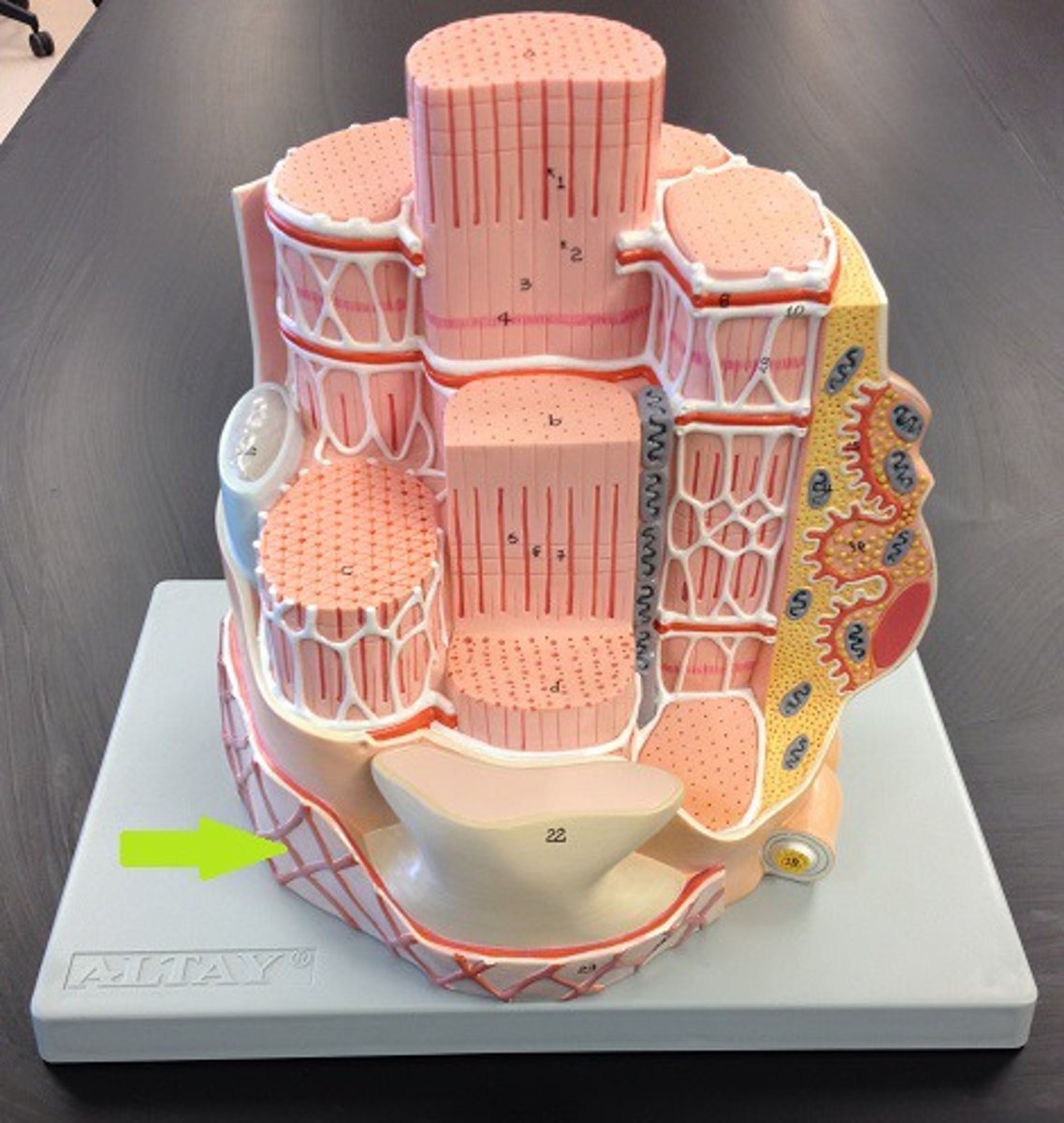
Schwann cell
cell that forms insulation and wraps itself around nerve axons (helps nerve signals travel faster)

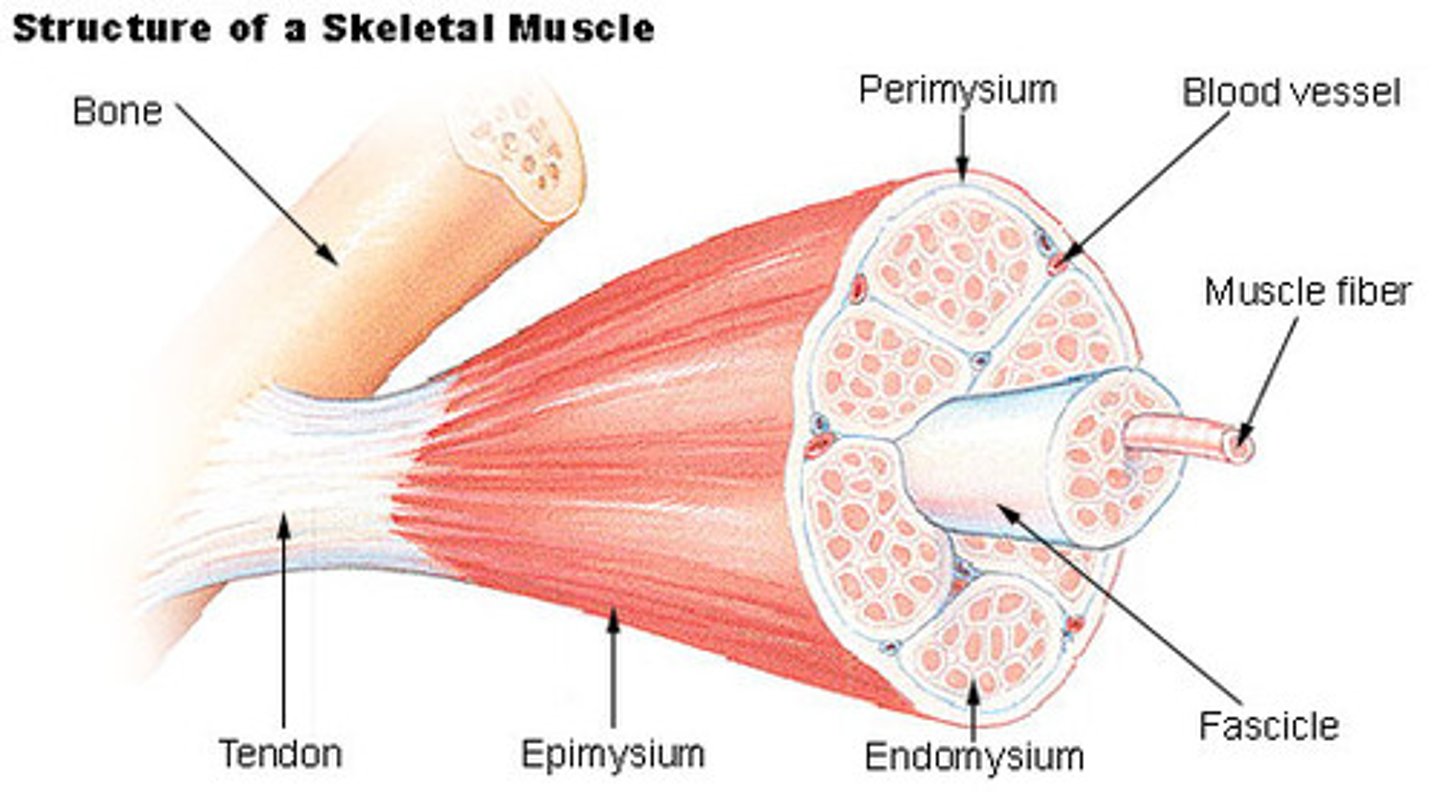
Endomysium
connective tissue layer -- Surrounds individual muscle fibers

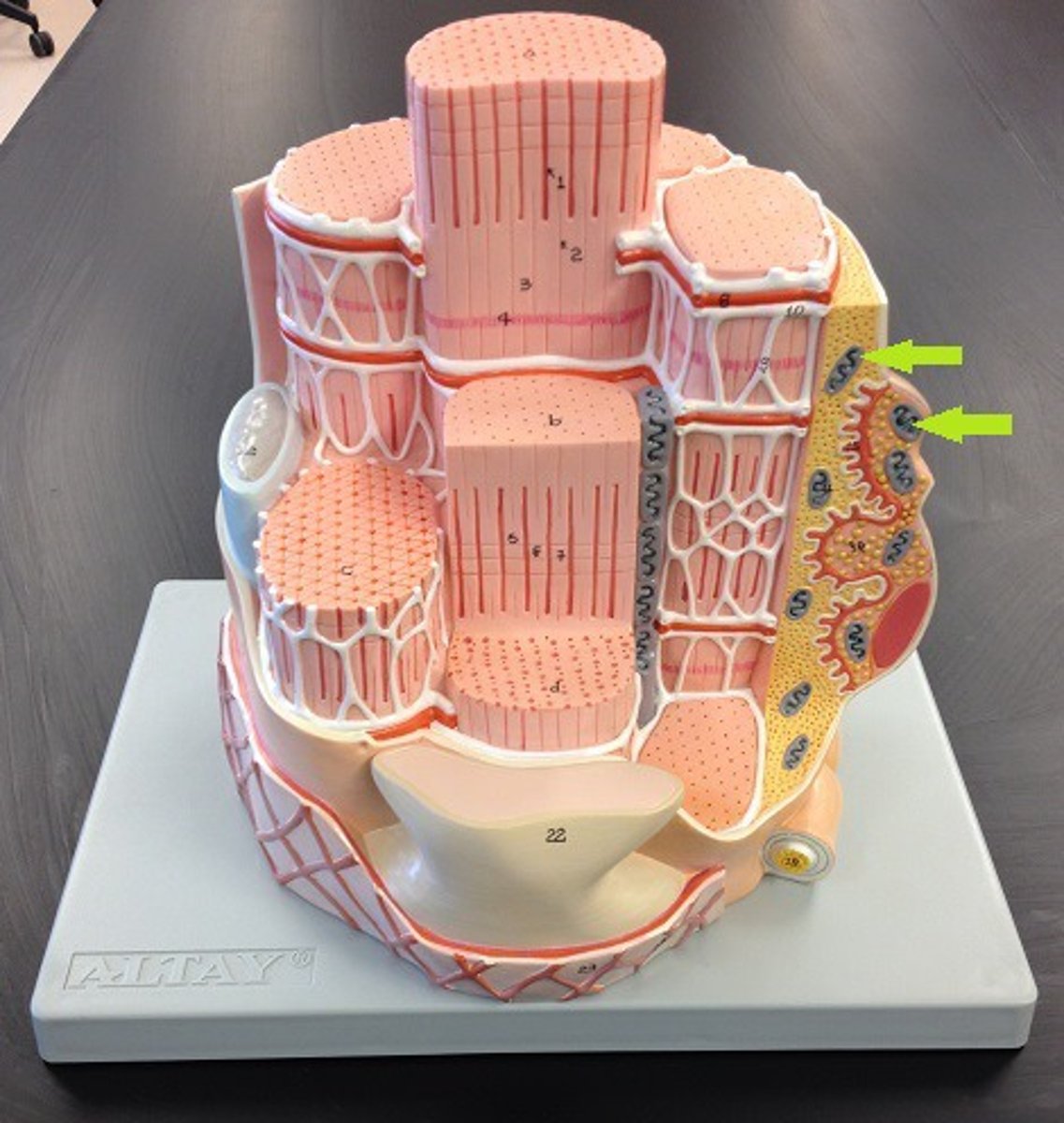
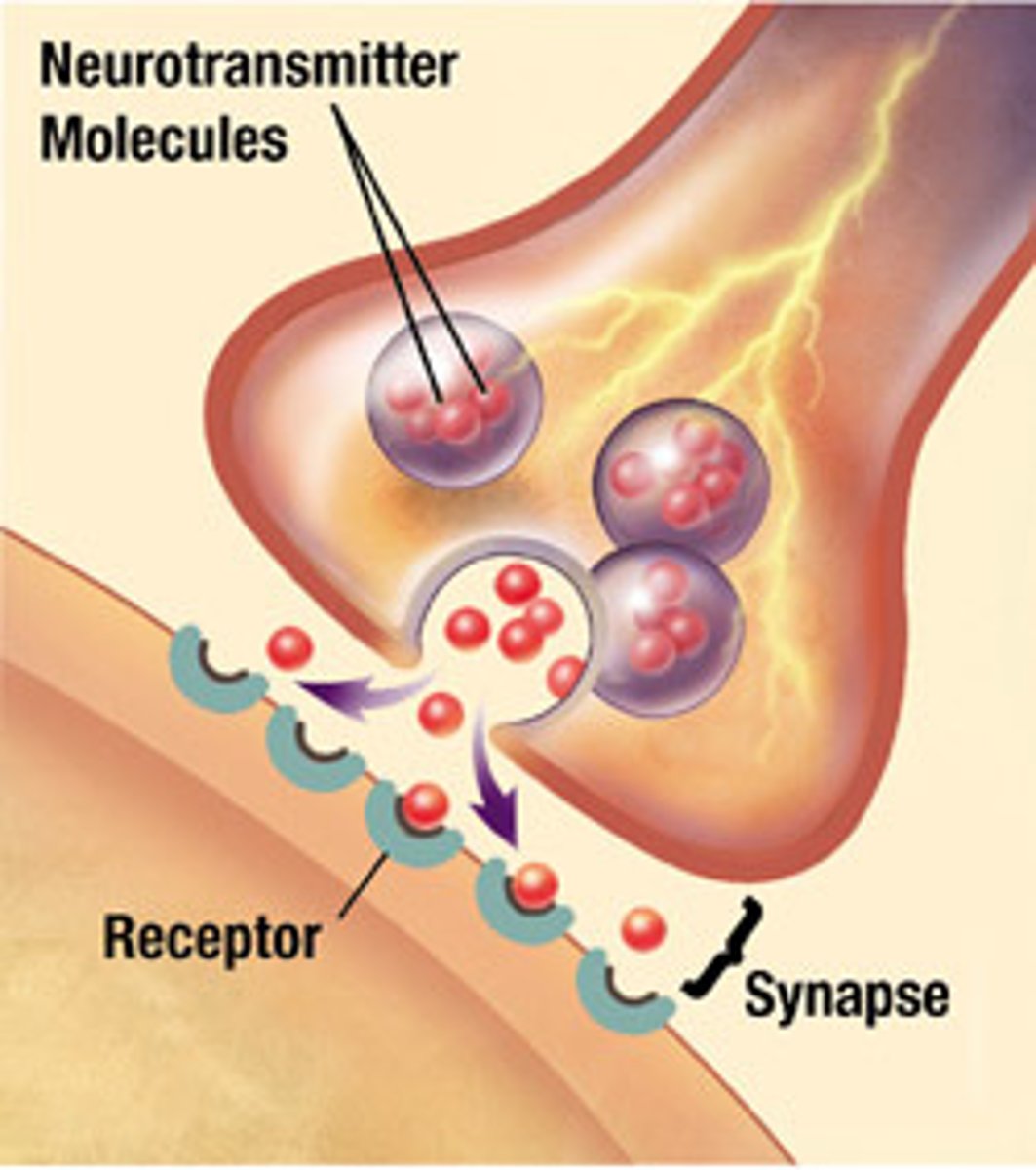
Sarcolemma
muscle cell membrane
T-tubules (transverse tubules)
spread the action potential into the interior of the muscle fiber
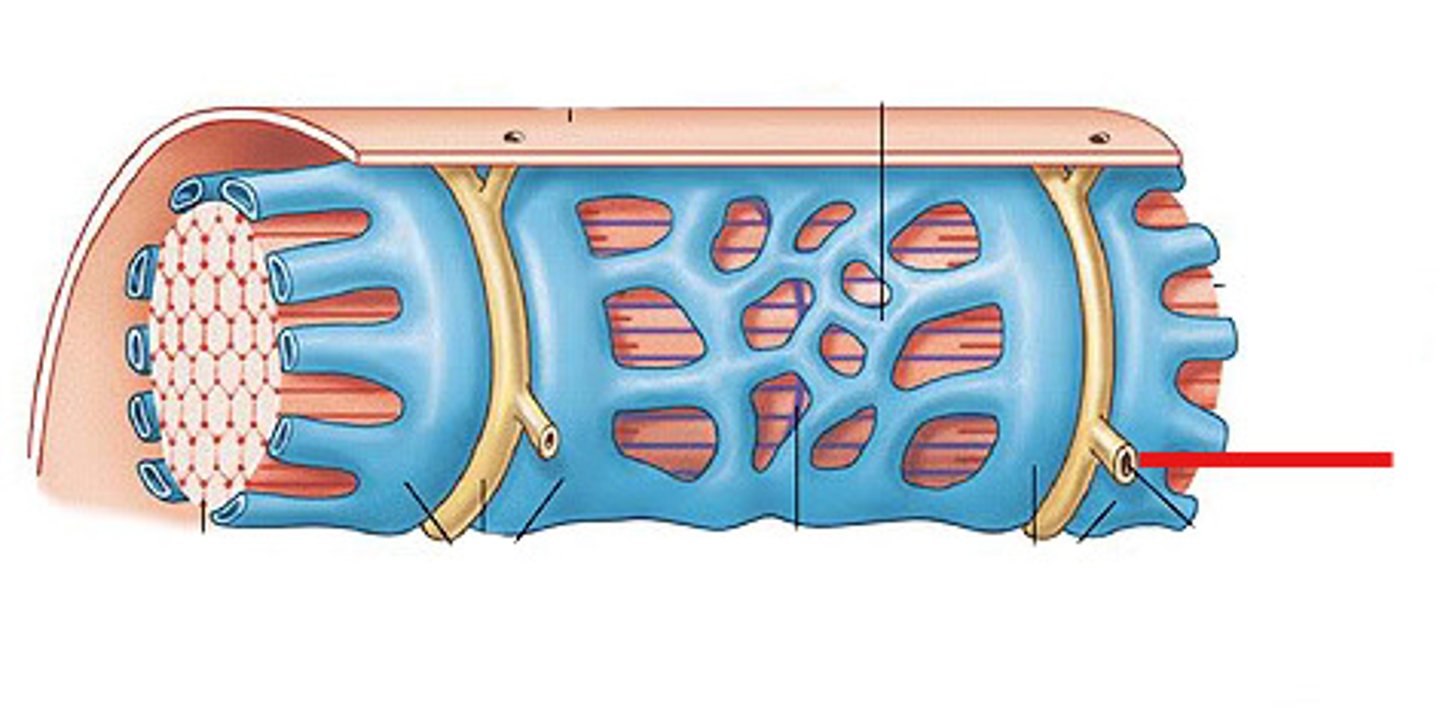
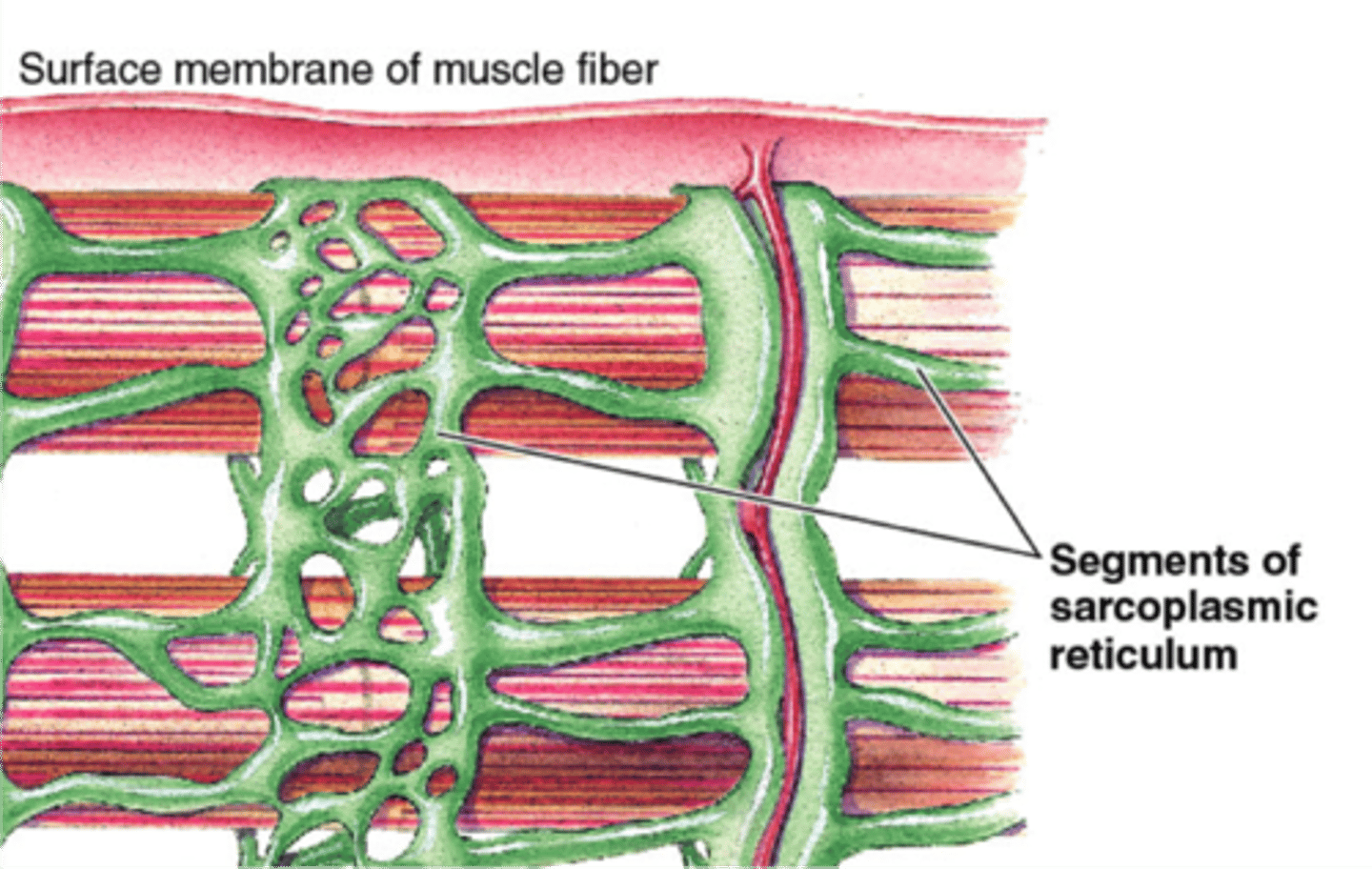
sarcoplasmic reticulum
specialized endoplasmic reticulum of muscle cells that stores calcium
mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production

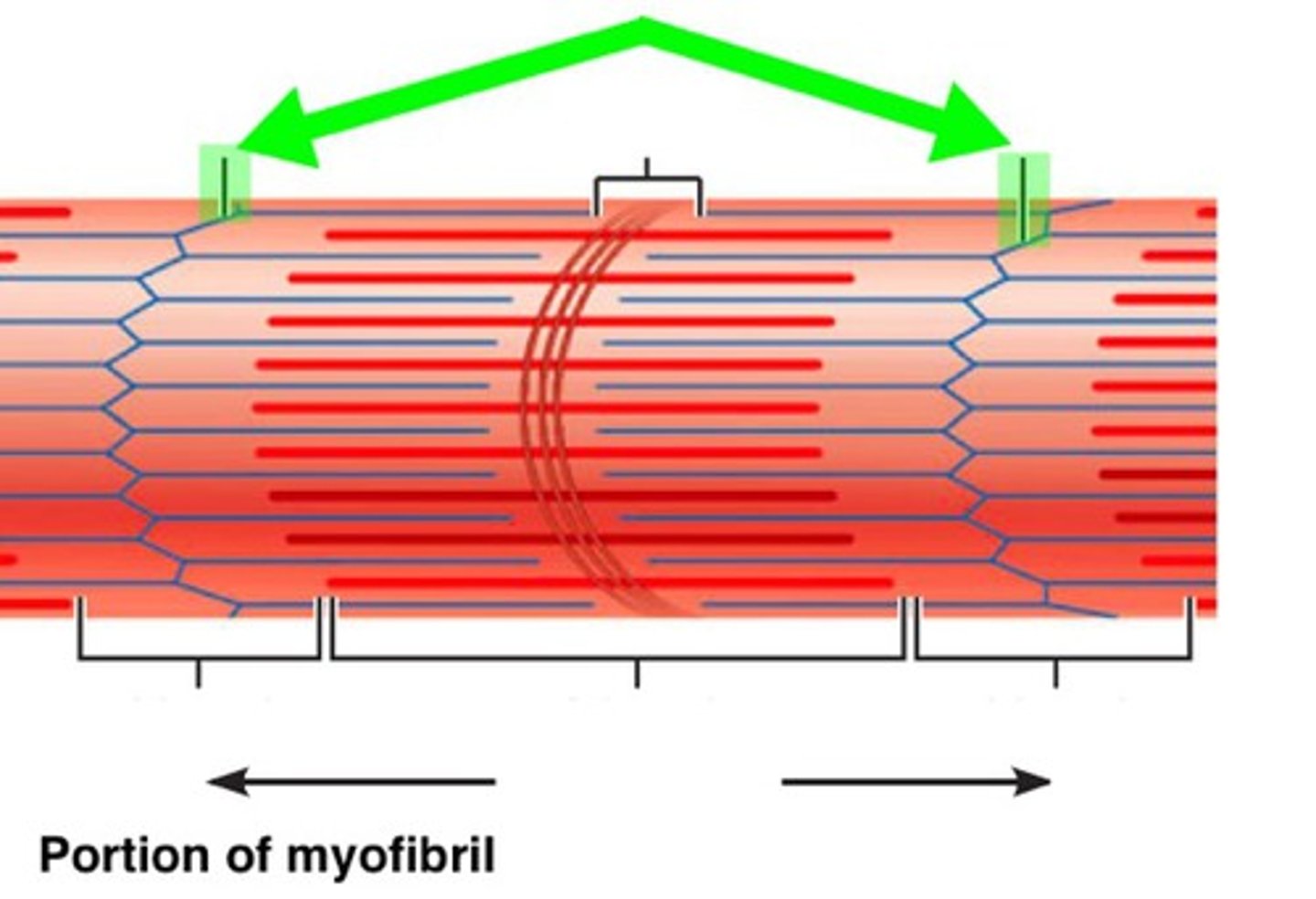
A-bands
dark bands on skeletal muscle formed mostly by myosin
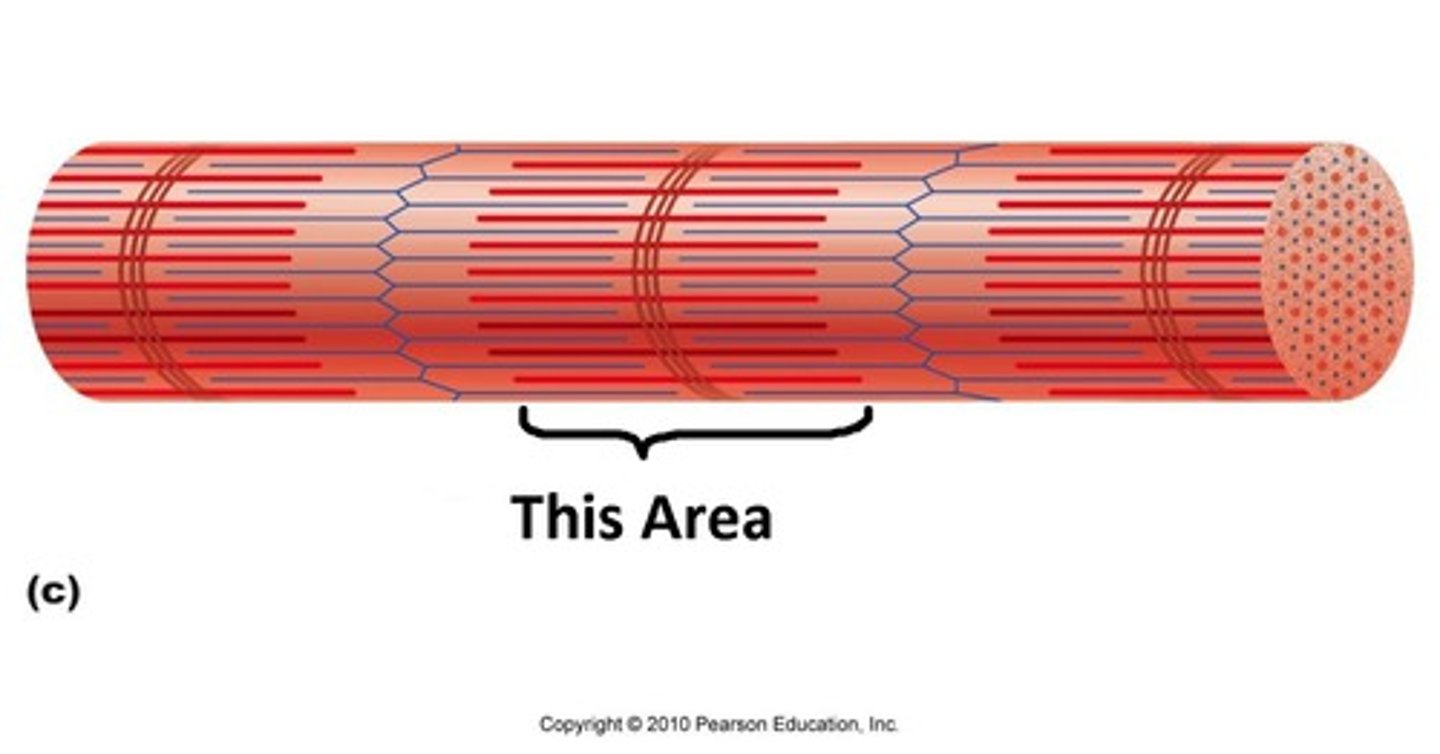
I-bands
light bands because they contain only thin filaments (actin)
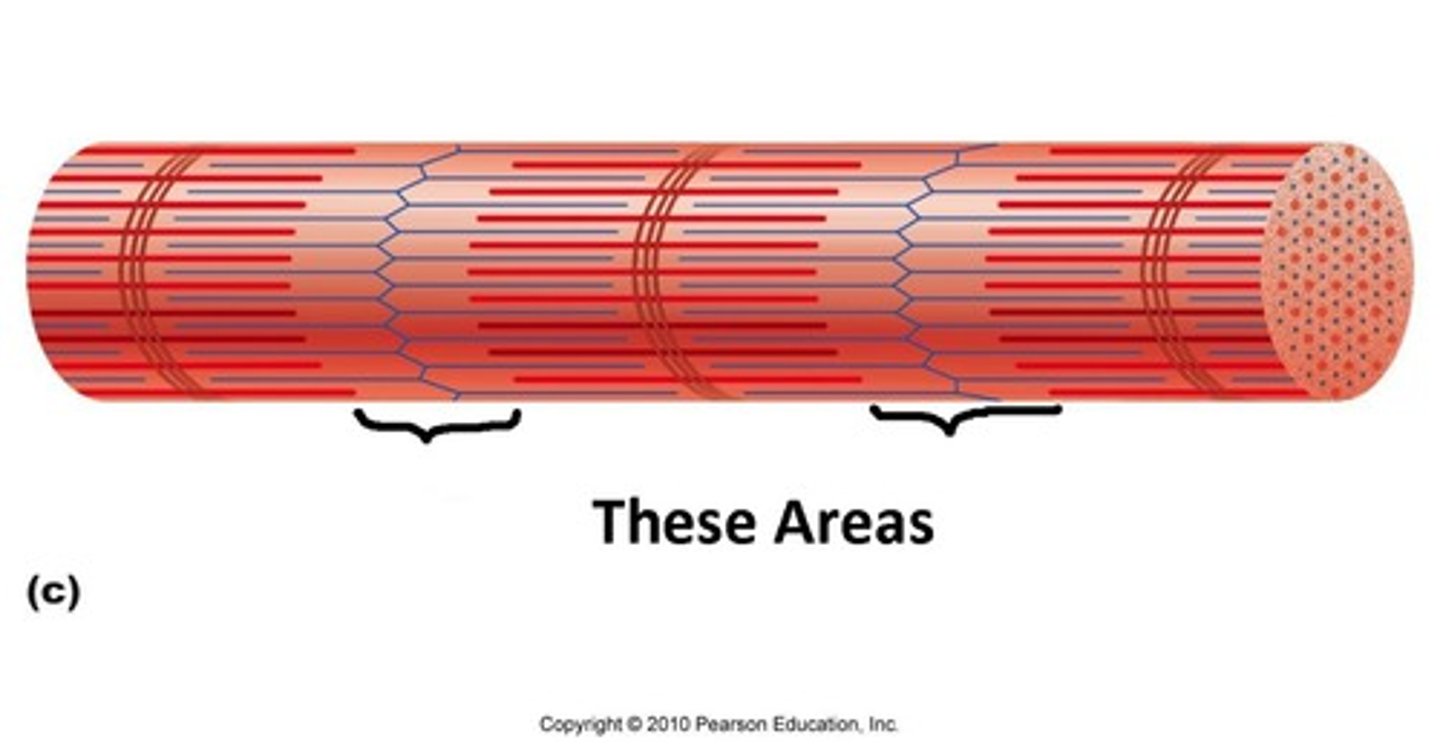
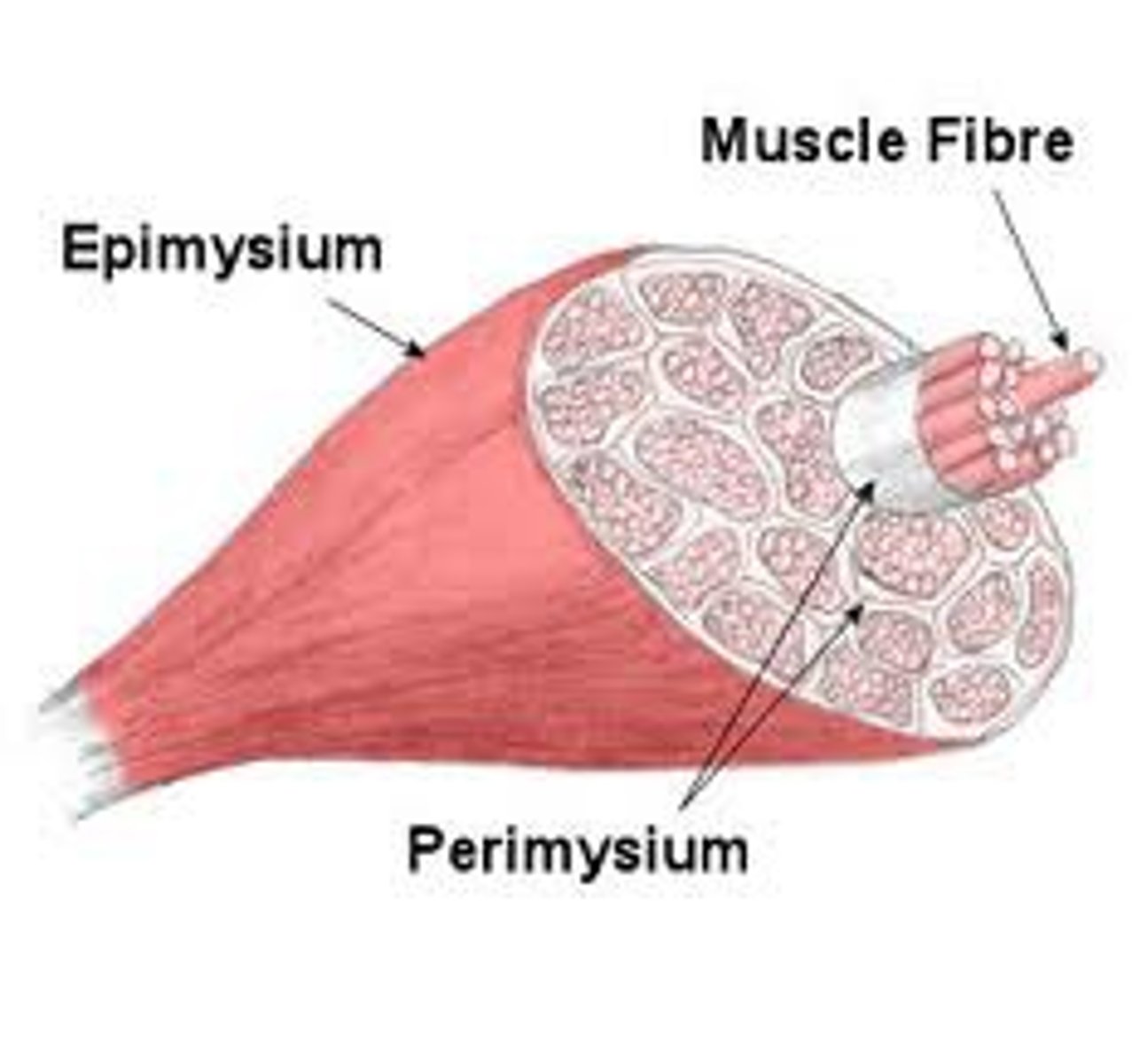
Epimyseum
connective tissue covering entire muscle
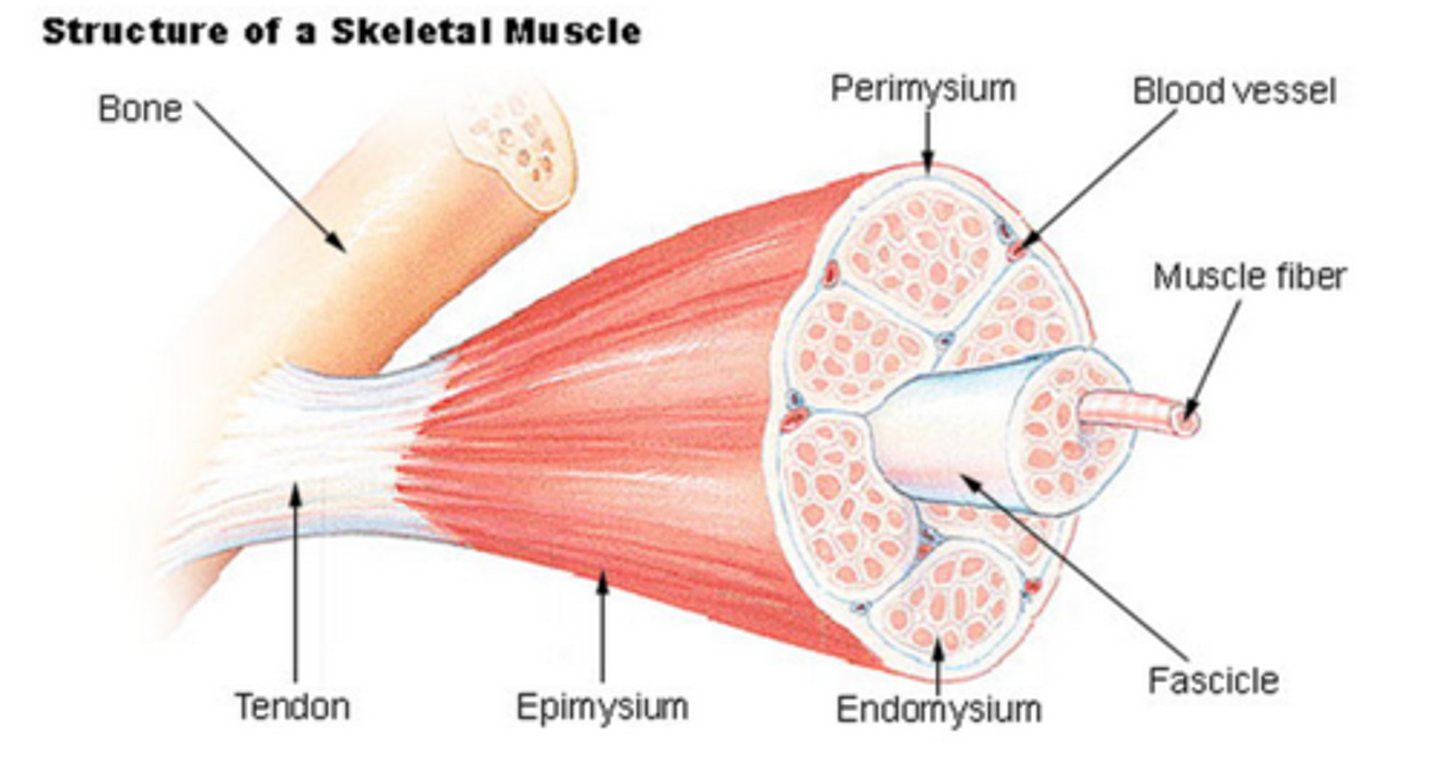
perimysium
connective tissue surrounding fascicule of muscle
skeletal muscle
striated, long and cylindrical, voluntary, multi-nucleated (more than 1 nucleus per cell)

smooth muscle
spindle--shaped, not striated, one nucleus, involuntary
cardiac muscle
striated, Y-shaped, involuntary, 1 or two nuclei, intercalated discs
muscle fiber
a single muscle cell
nerve fiber
axon of a neuron (the long process of a nerve cell)
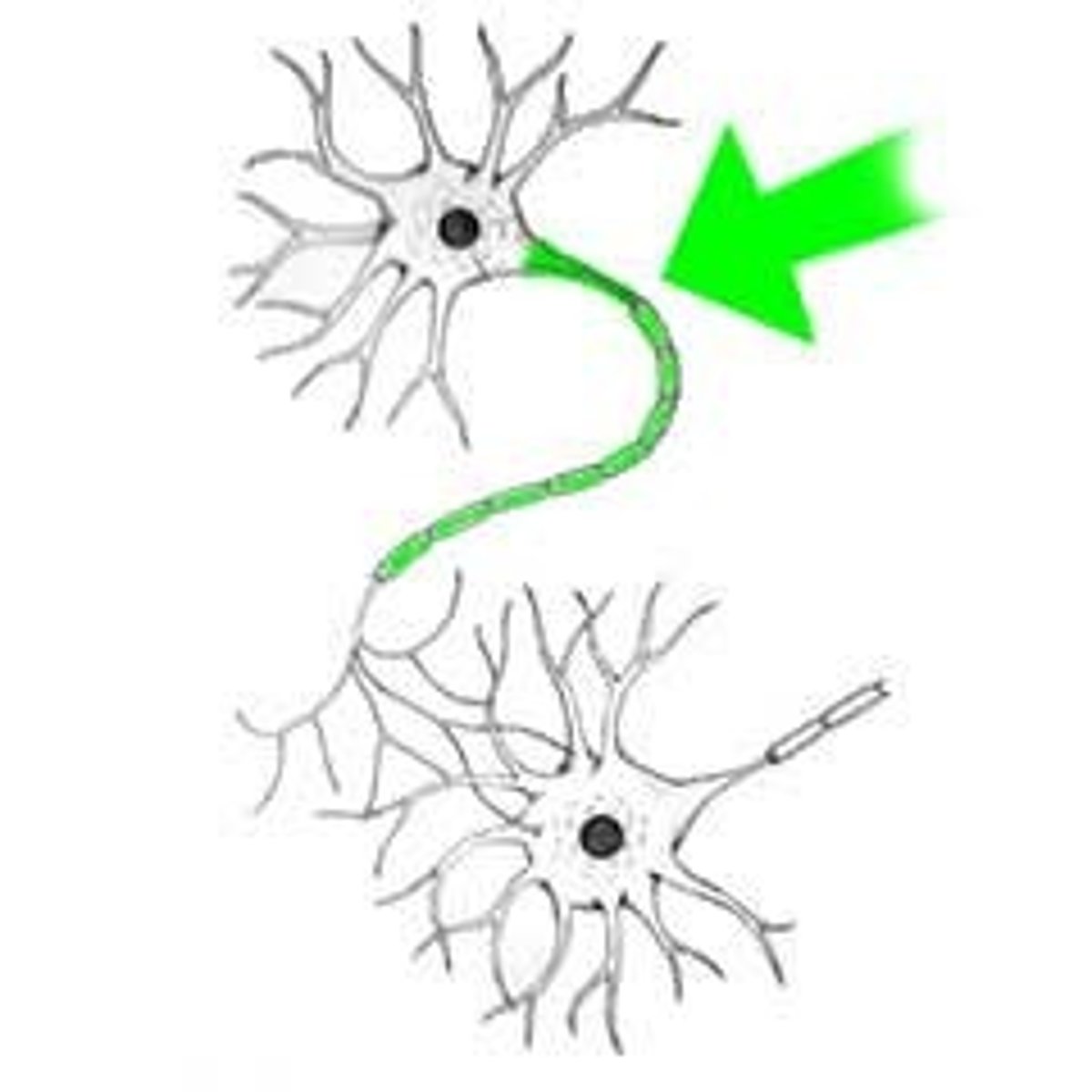
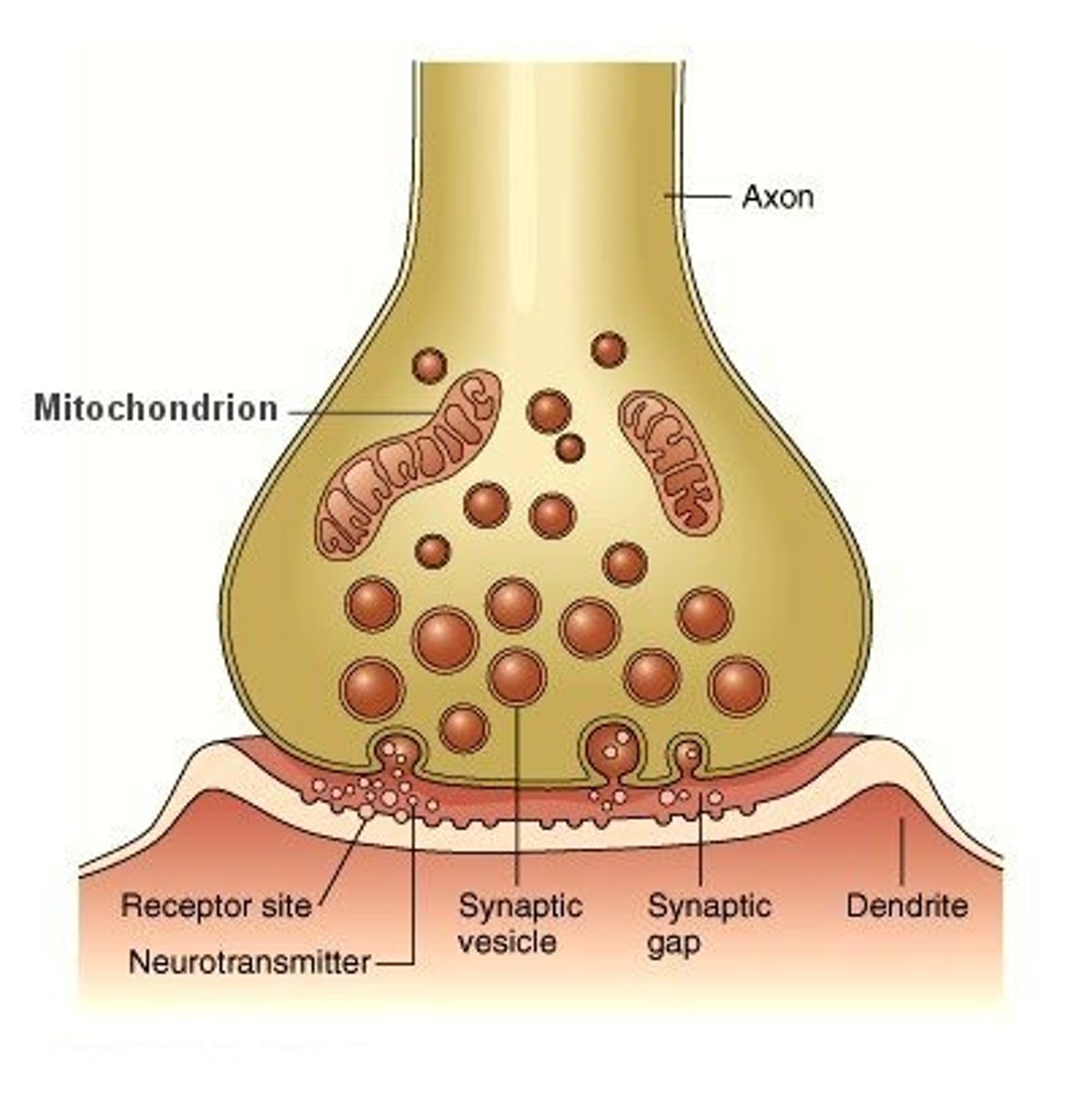
synaptic end bulb (terminal bouton)
A swollen area at the end of a nerve axon--it stores and releases neurotransmitter molecules onto a target cell across a synapse
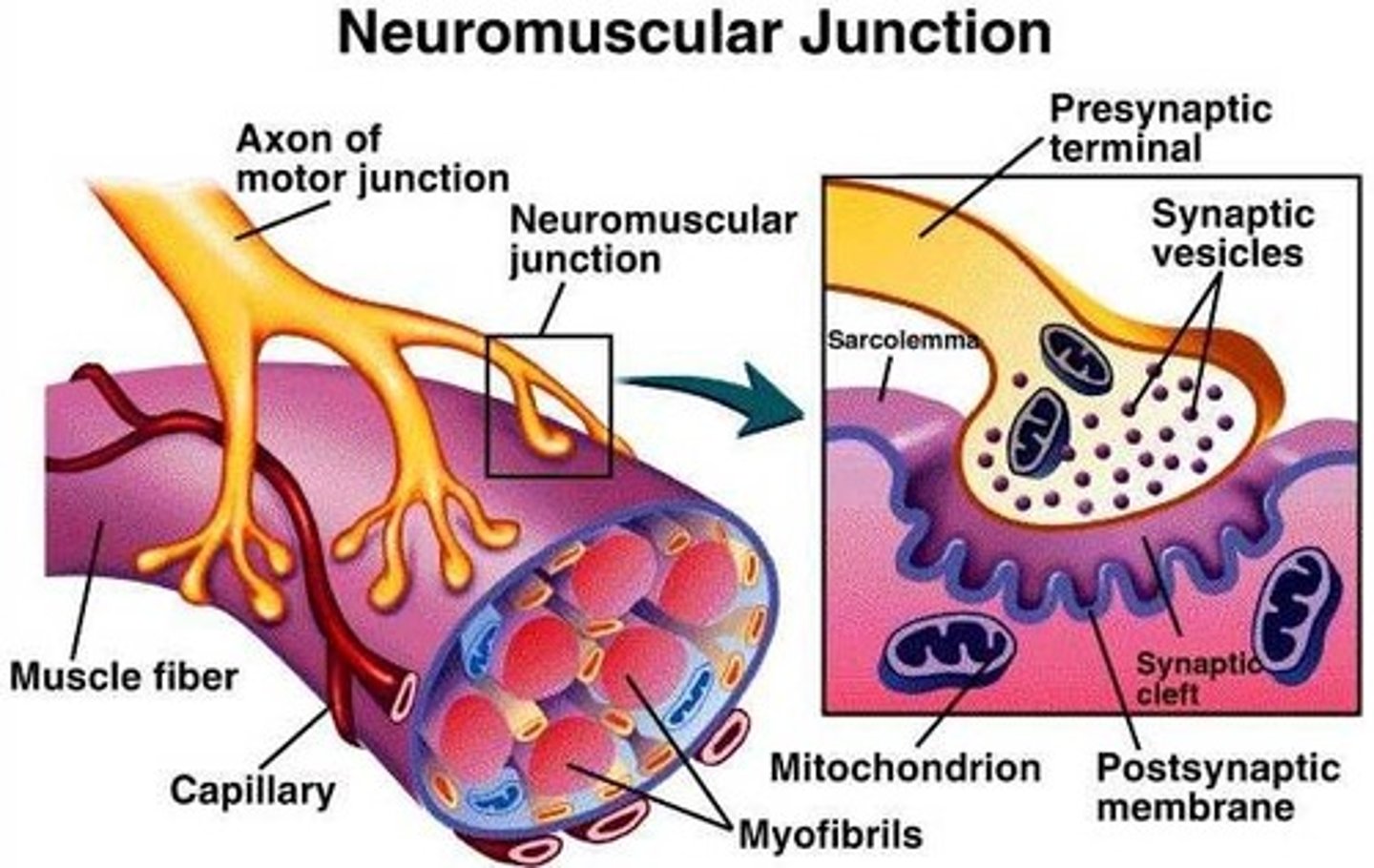
nueromuscular junction (NMJ)
a synapse between a motor neuron axon and a muscle cell (=muscle fiber)
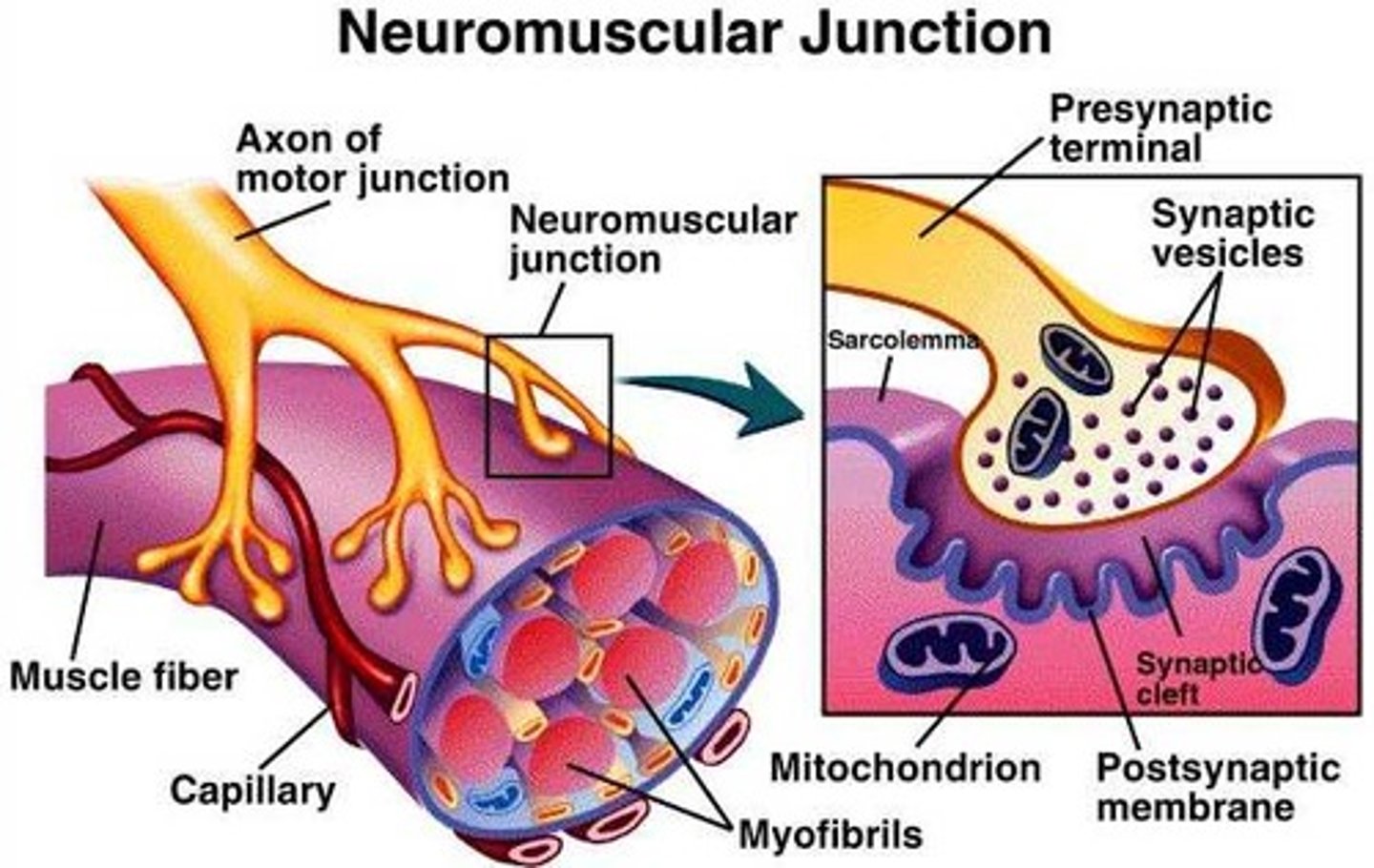
motor end plate
the flattened end under the synaptic bulb of a motor neuron that transmits neural impulses to a muscle, usually by releasing neurotransmitter molecules across the synaptic cleft

4 functions of the muscular system
movement, posture, joint stability, heat production
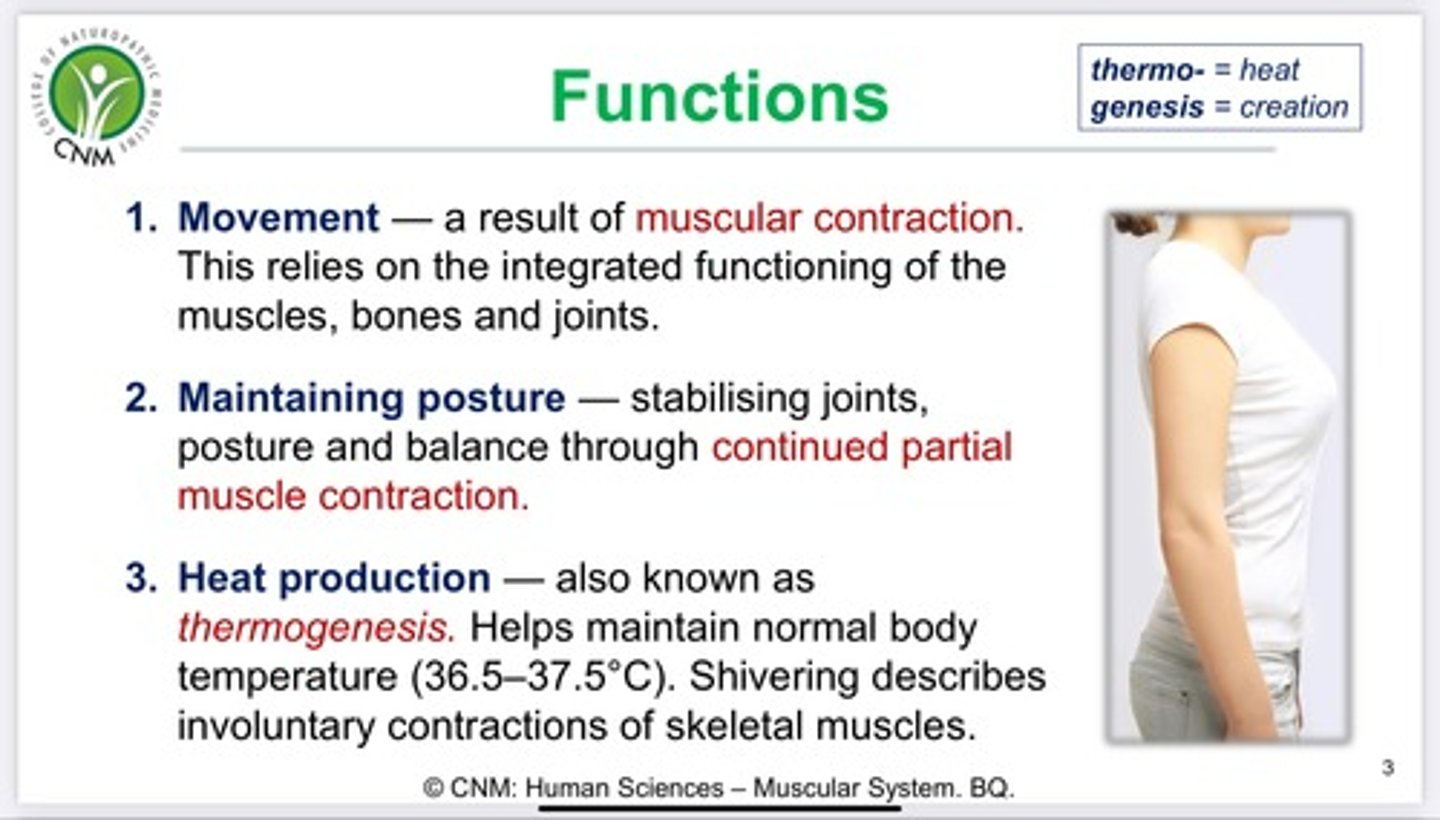
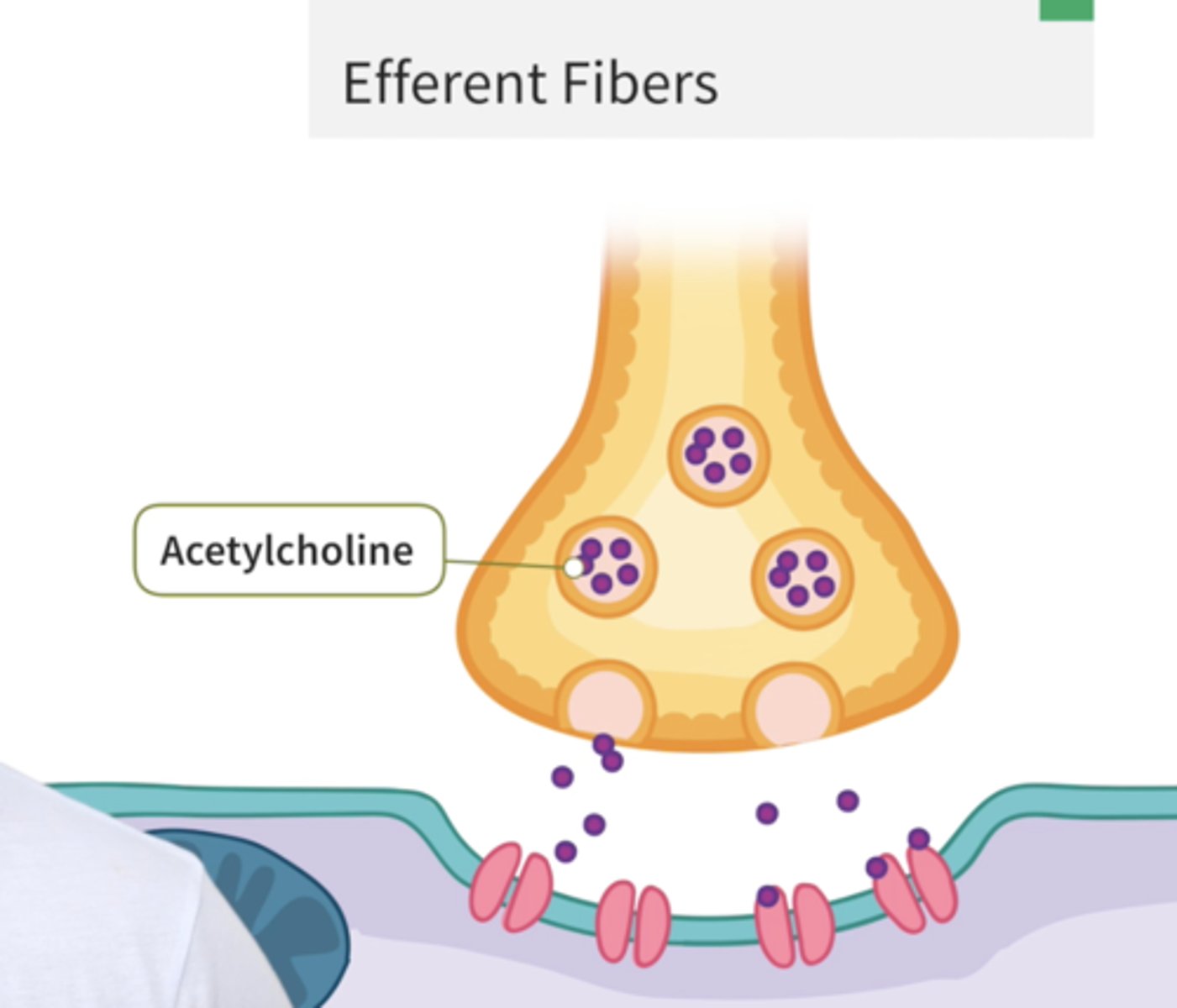
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that travel from the nerve cell synaptic bulb to receptors on the muscle cell membrane (sarcolemma). In muscular system, neurotransmitter = ACh (Acetylcholine)
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle cell
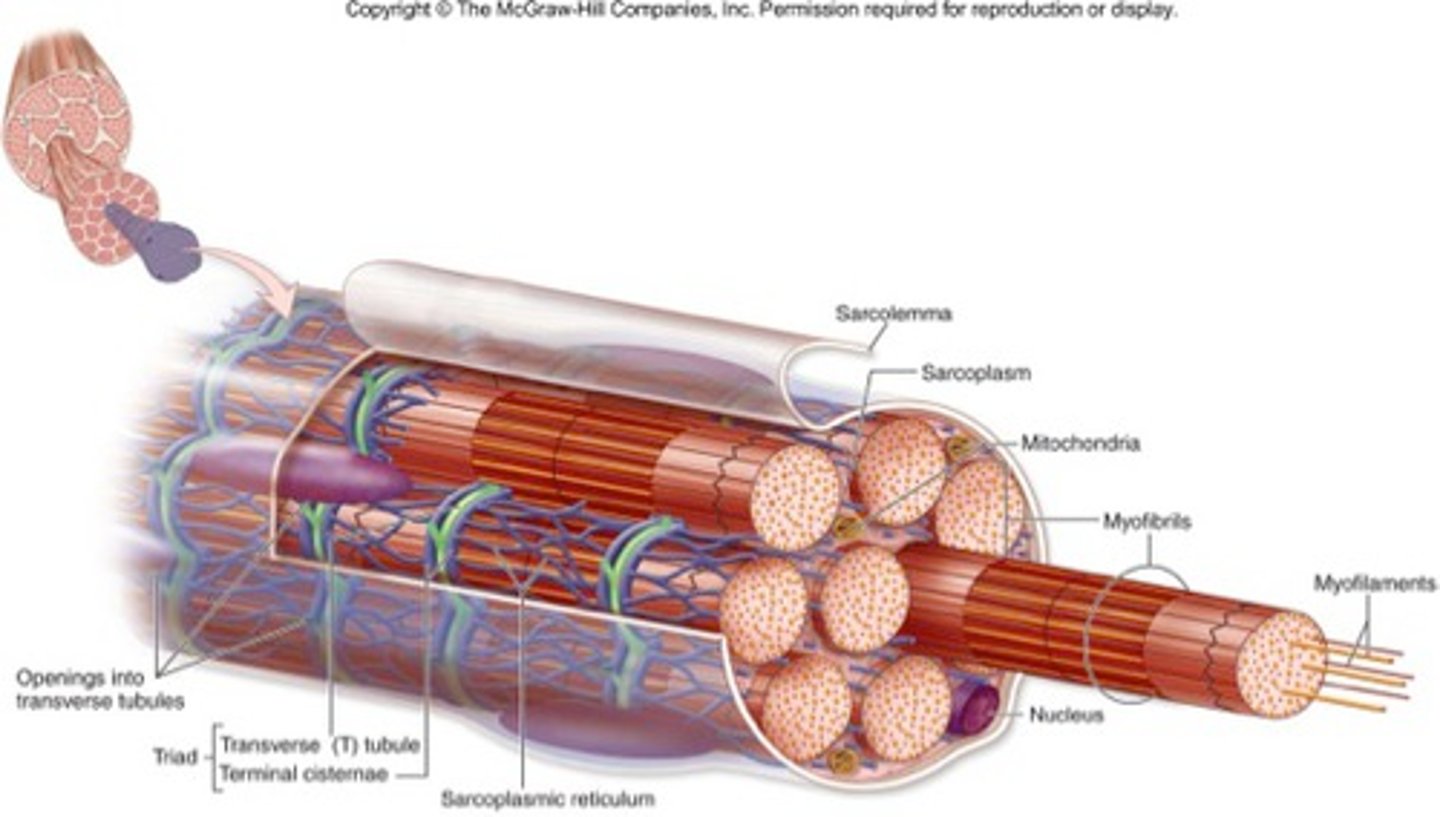
Glycogen crystals
stored in sarcoplasm as a source of energy for the muscle cell
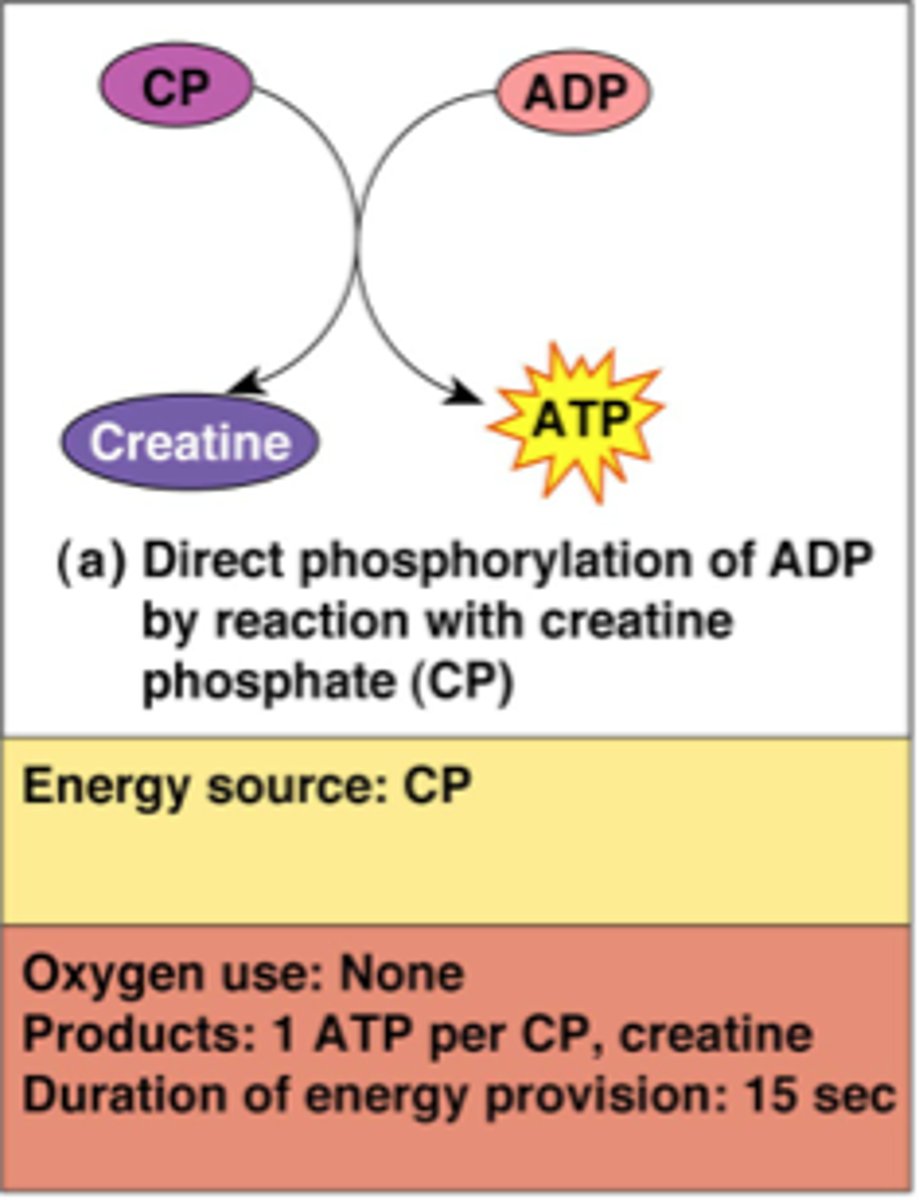
creatine phosphate
can transfer phosphate to form ATP--this form of energy can last around 15-30 sec
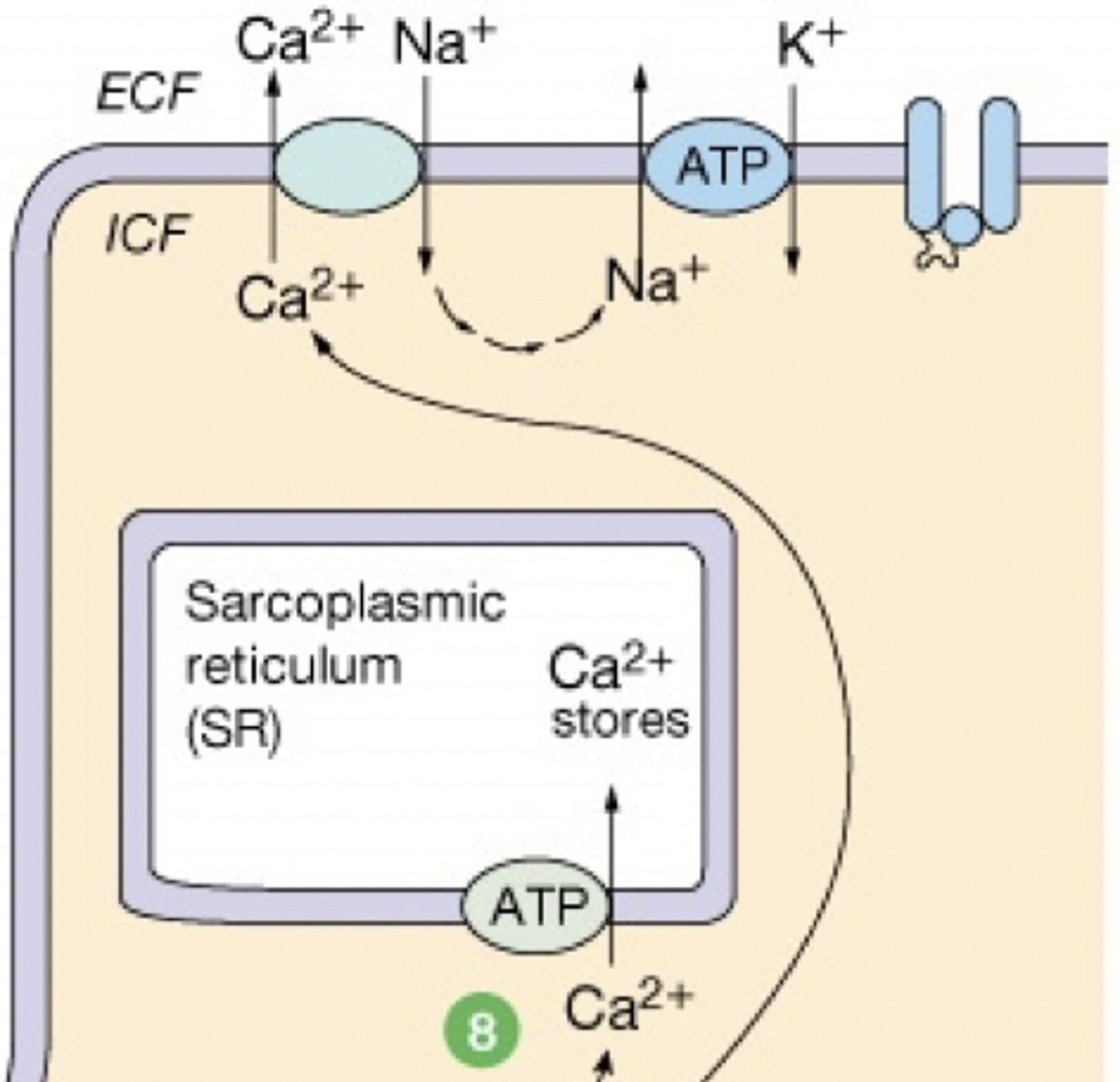
calcium ions are removed from the sarcoplasm by ______.
active transport (requires ATP)-- ATPase SERCA
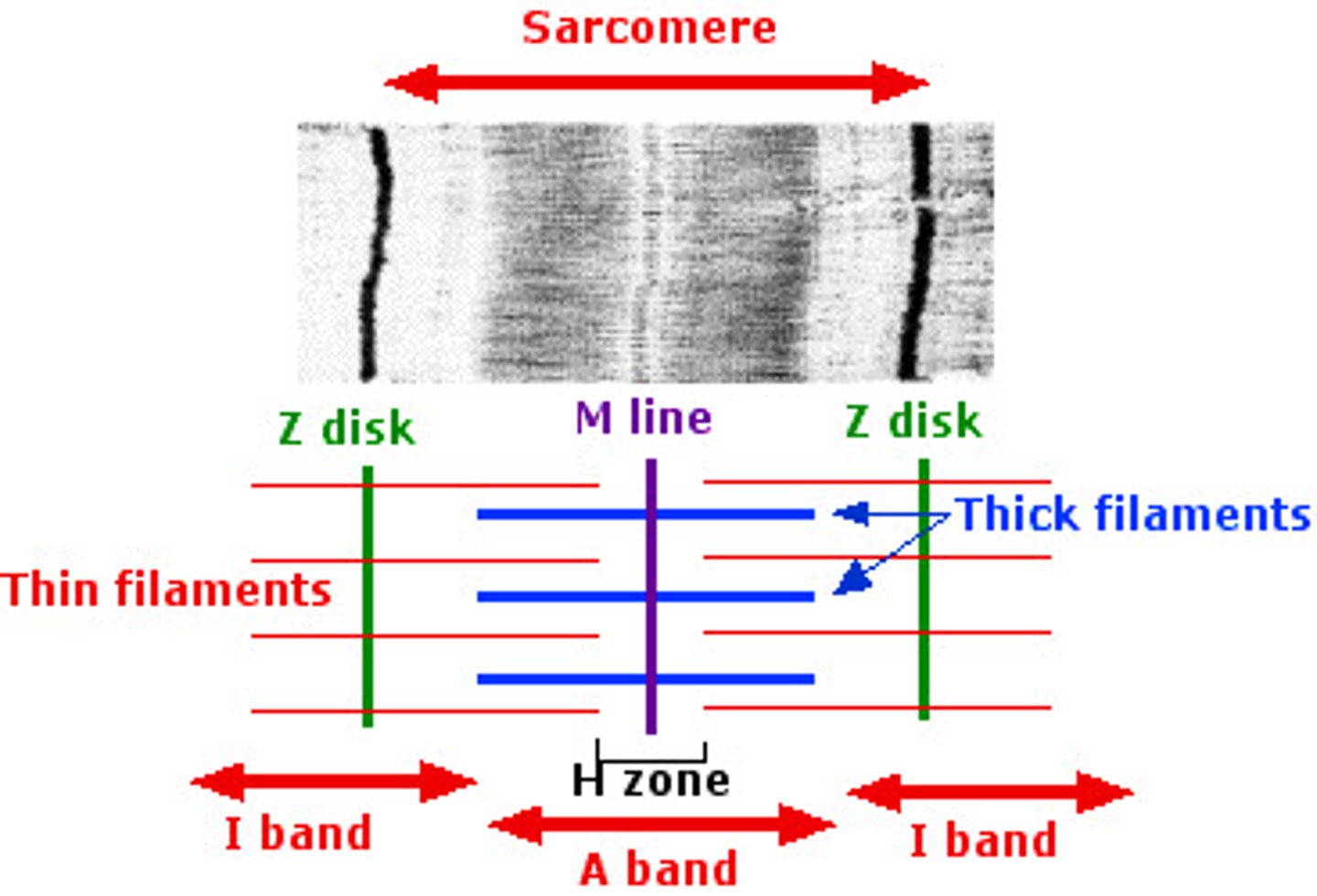
sarcomere
functional unit of skeletal muscle cells
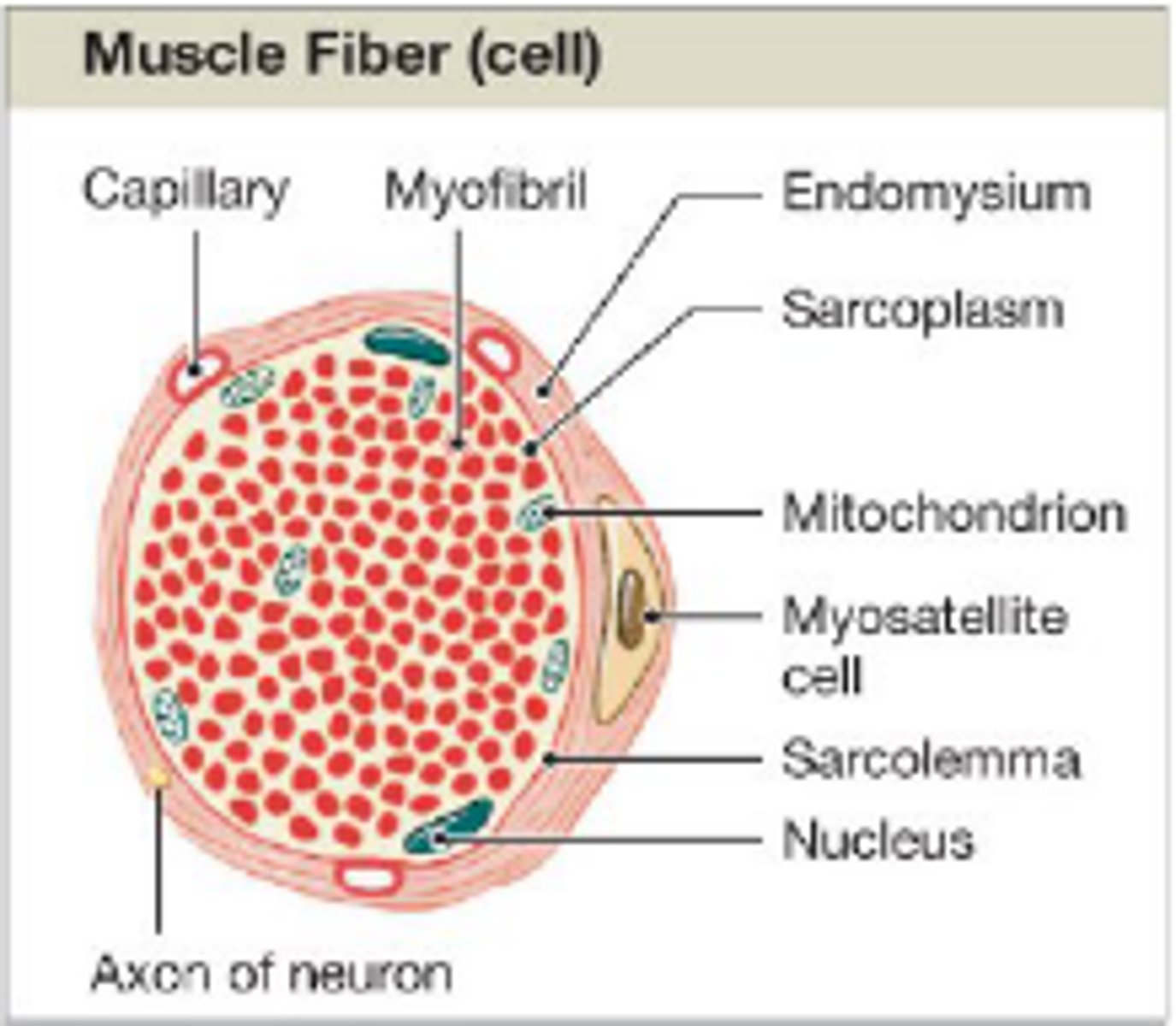
myosatellite cells
support and repair damaged muscle cells
Can you change the number of muscle cells in your body?
No, but they can increase diameter with exercise. They can not increase length!
synptic cleft
the space between the motor neuron and the sarcolemma (muscle cell membrane)
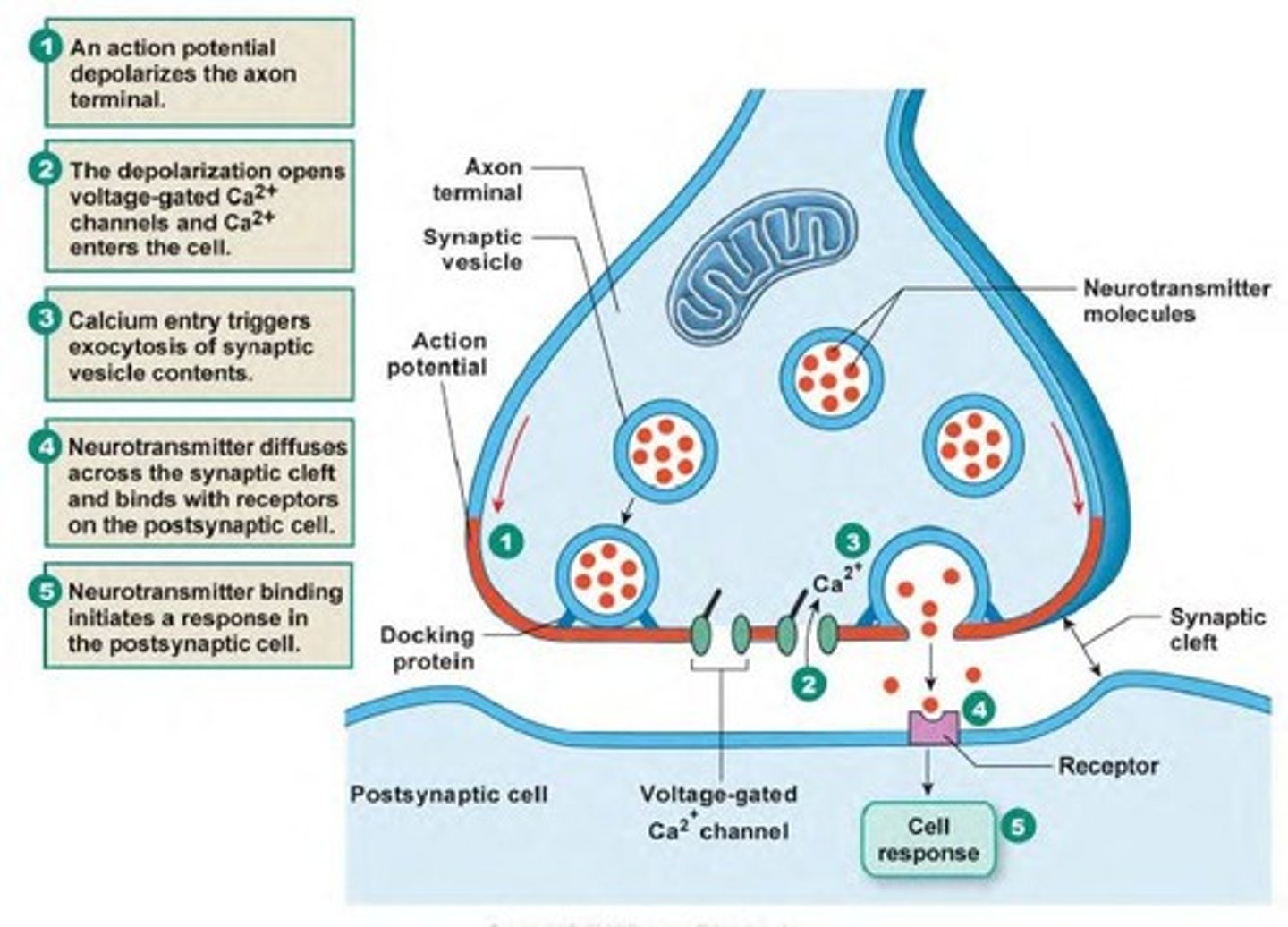
ACh receptors
Proteins receptors on the motor end plate of muscle cell that bind ACh
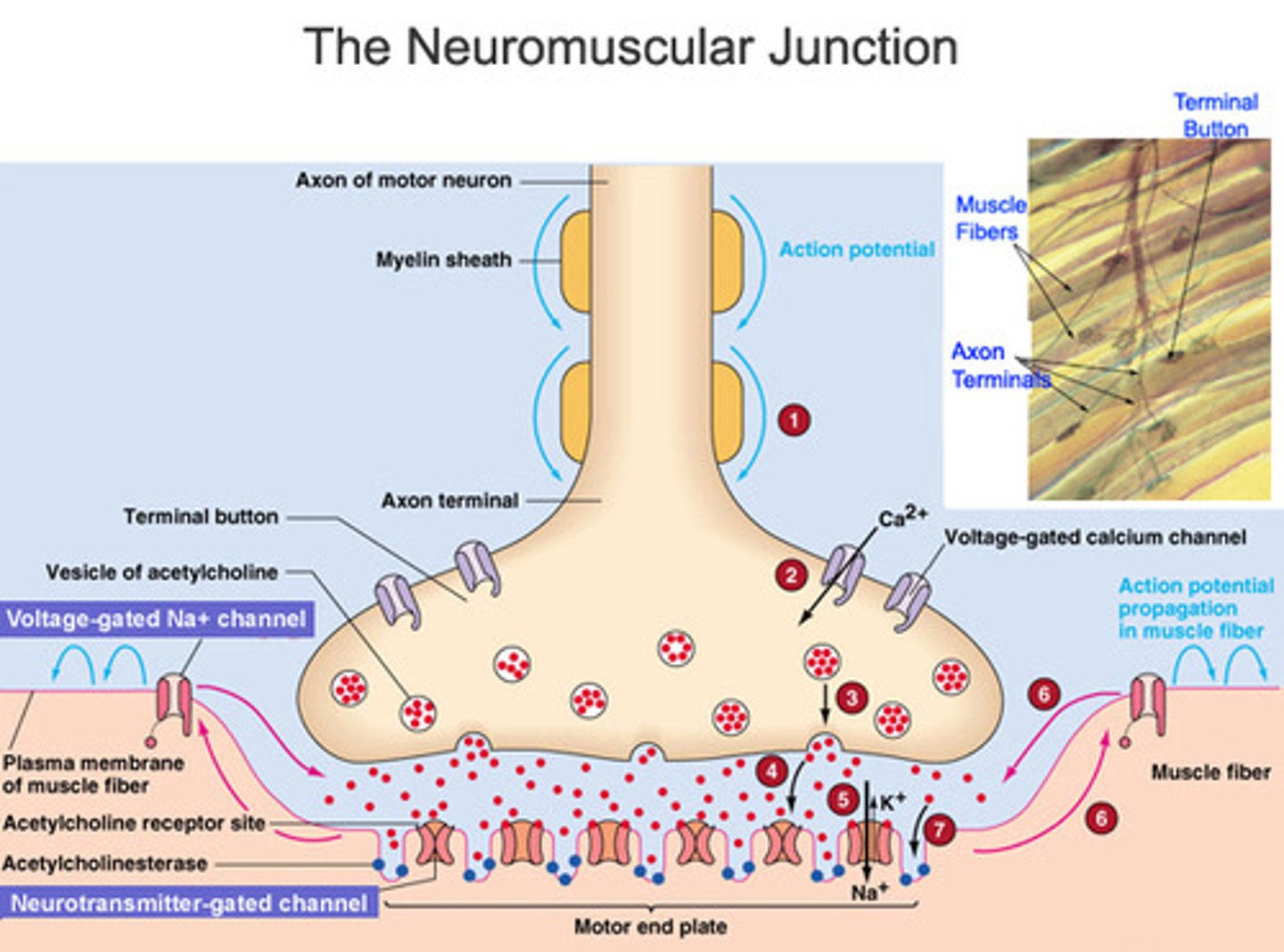
When ACh binds to receptors ______.
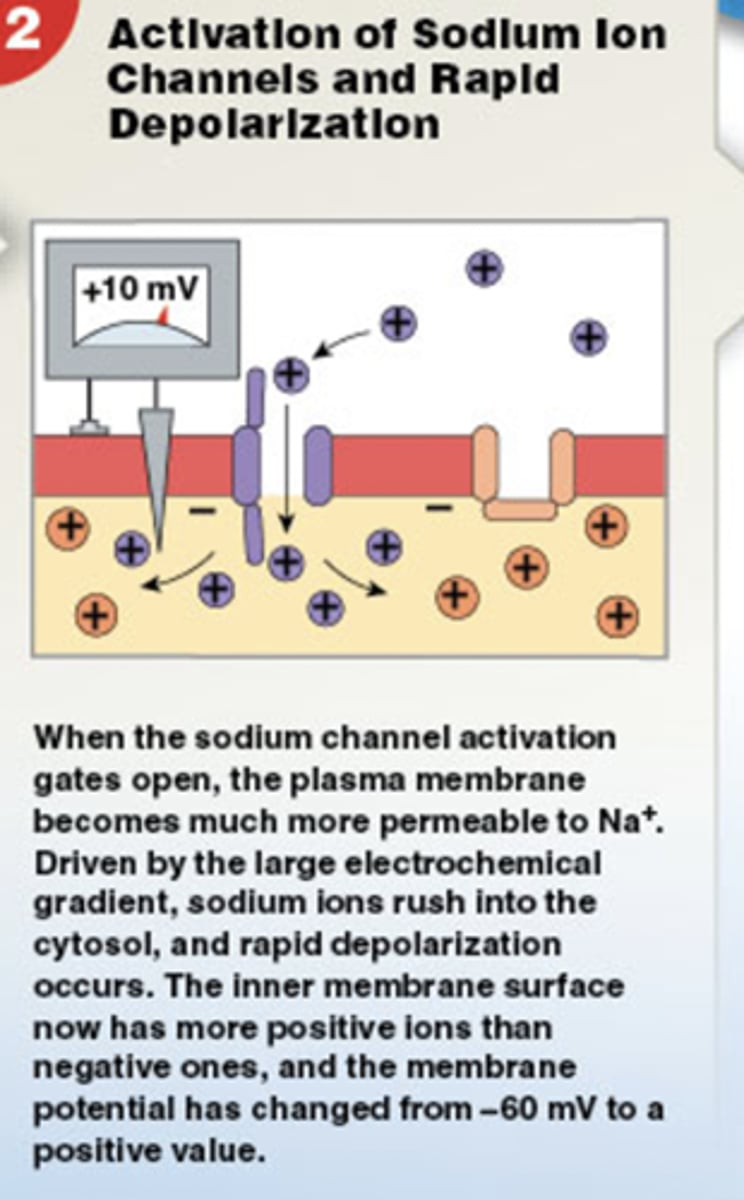
Sodium ions rush into the sarcoplasm
The first step in a muscle contraction is _________.
A nerve impulse enters the
presynaptic terminal (nerve) of the neuromuscular junction.
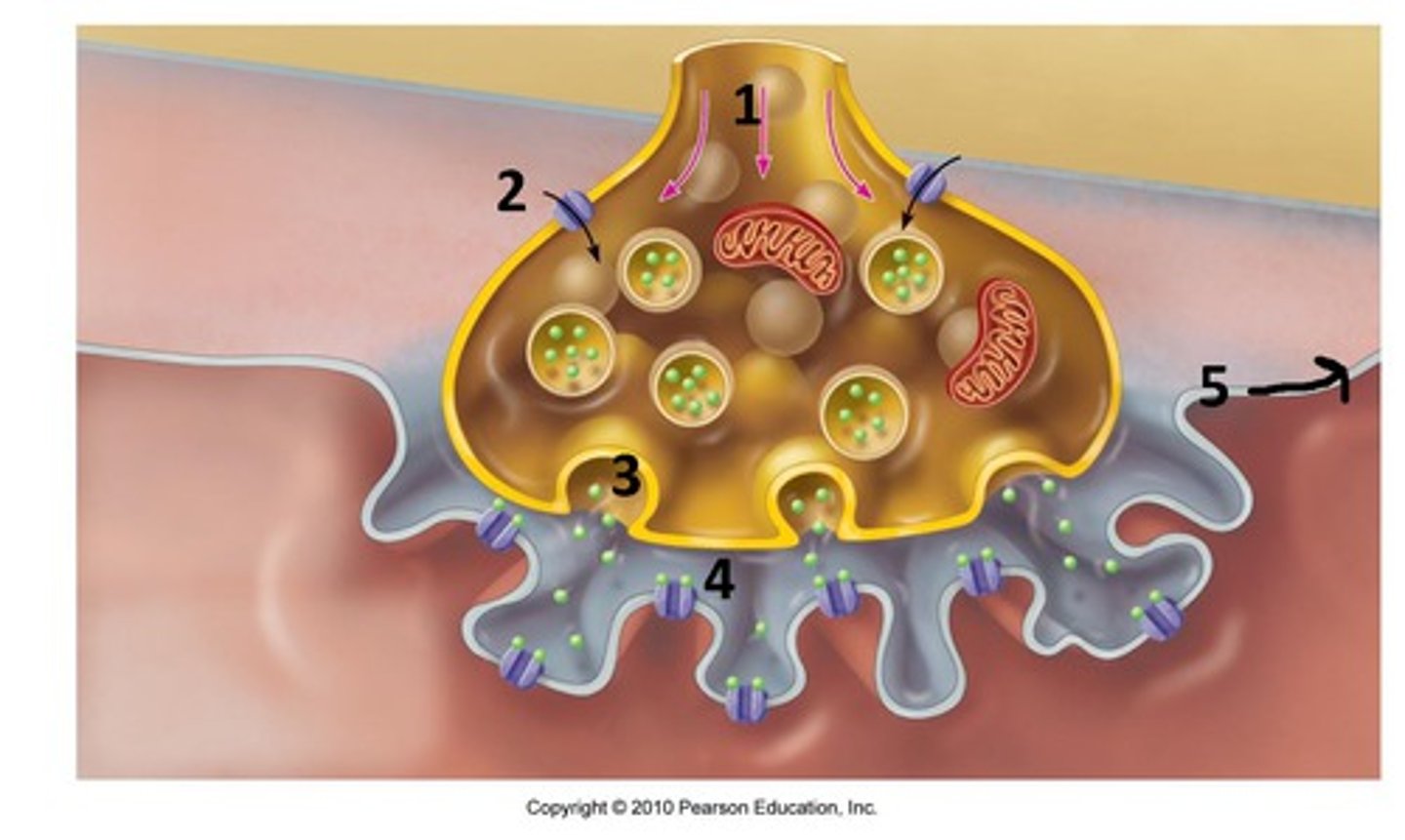
Synaptic vesicles in the terminal bulb of the motor neuron contain _________.
Acetylcholine
What happens after cross bridge breaks? What determines whether the contraction cycle continues?
10a. Cycle continues if Ca2+ is present -- if the nerve continues to fire, this cycle continues
10b. If no Ca2+ present, cycle stops and muscle relaxes -if nerve ceases to fire, Ca2+ is taken back up into terminal cisternae of the SR via ACTIVE TRANSPORT, and is ready for the next
time a nerve signal is received.
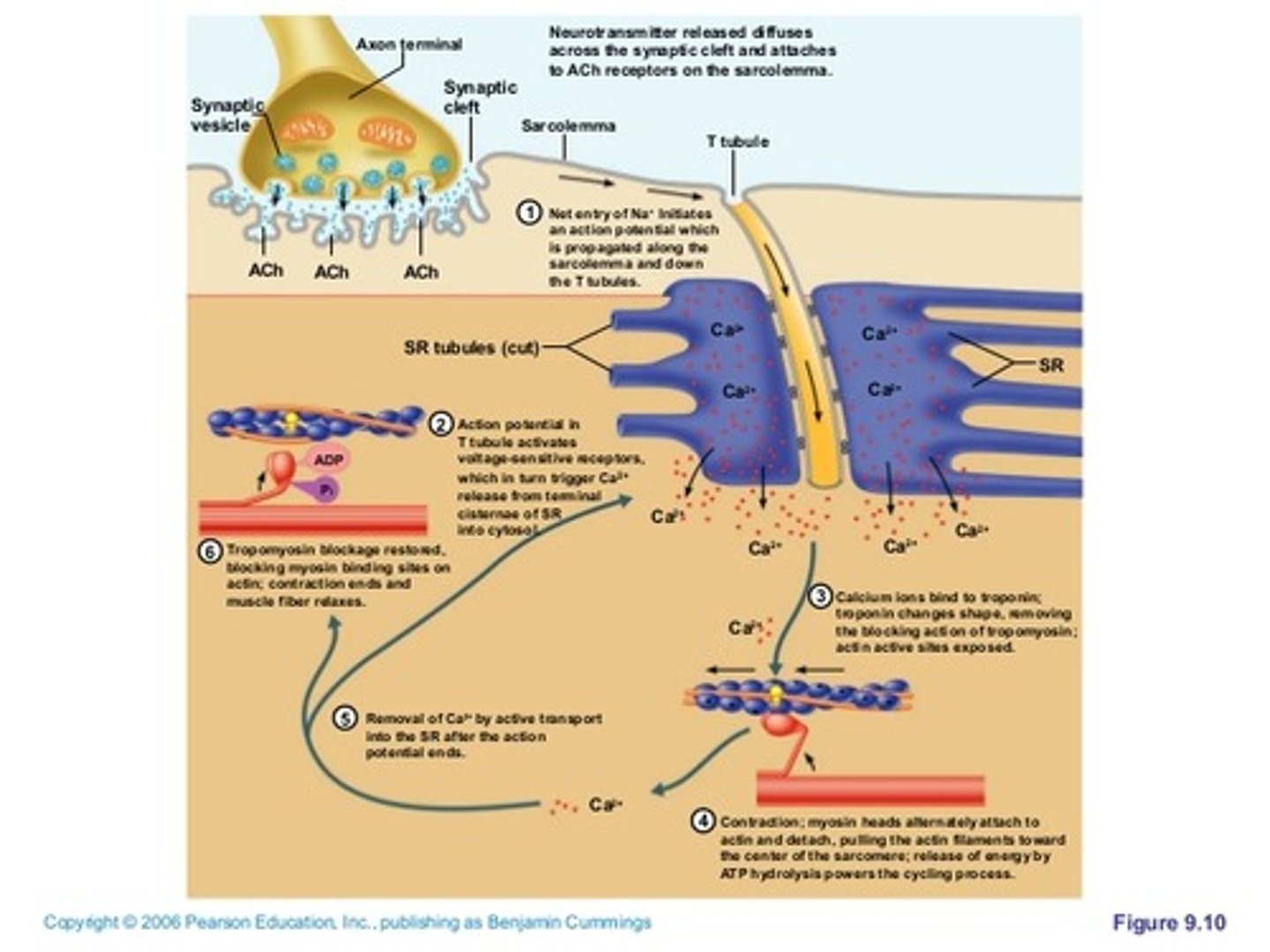
When the neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the muscle cell membrane, the muscle cell _______.
is stimulated to contract
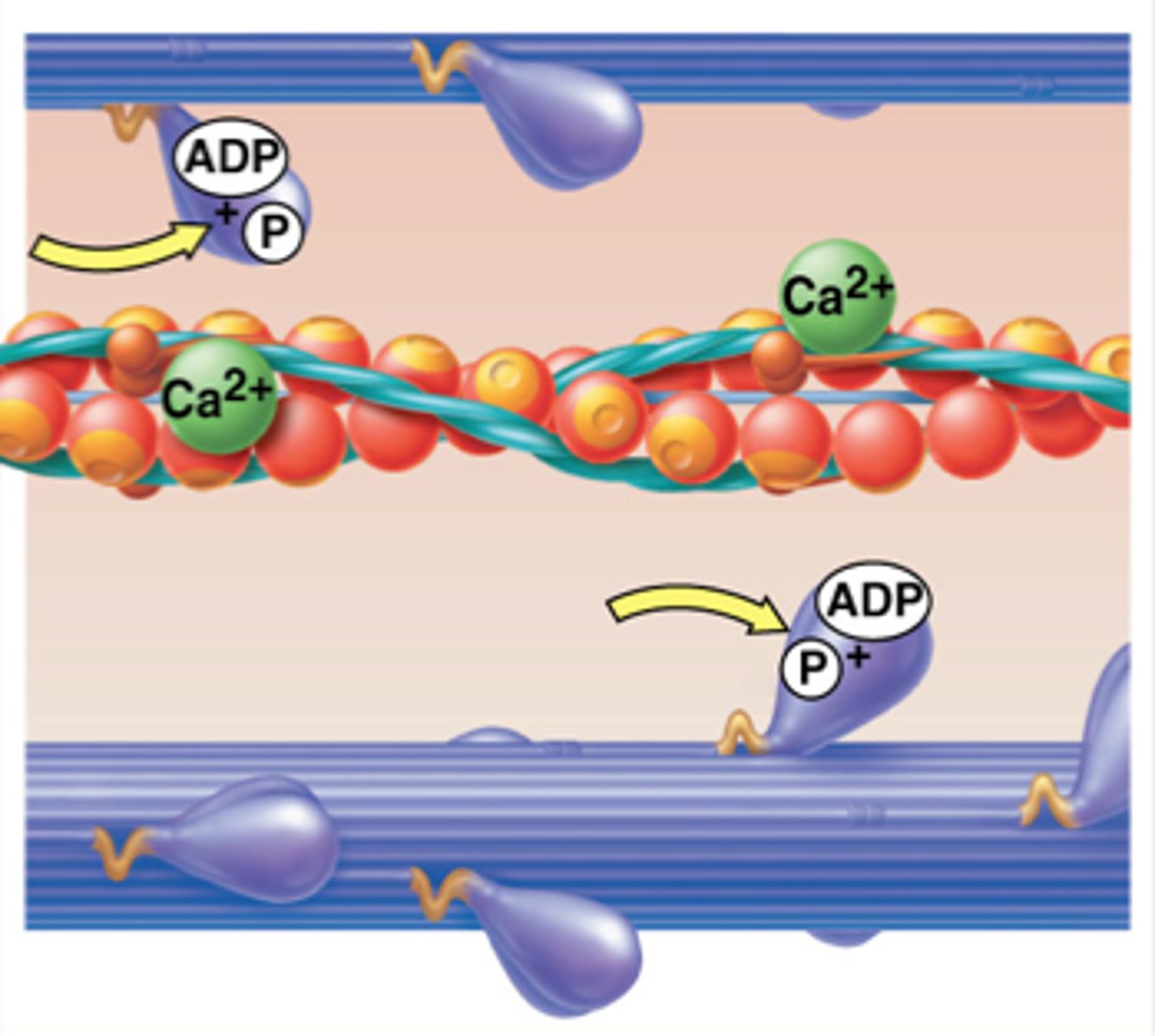
Calcium ions are released into the sarcoplasm and bind to ________.
TROPONIN on the troponin-tropomyosin complex (blocks the myosin binding sites)
As long as calcium is present in the muscle cell, the muscle will continue to _________.
contract
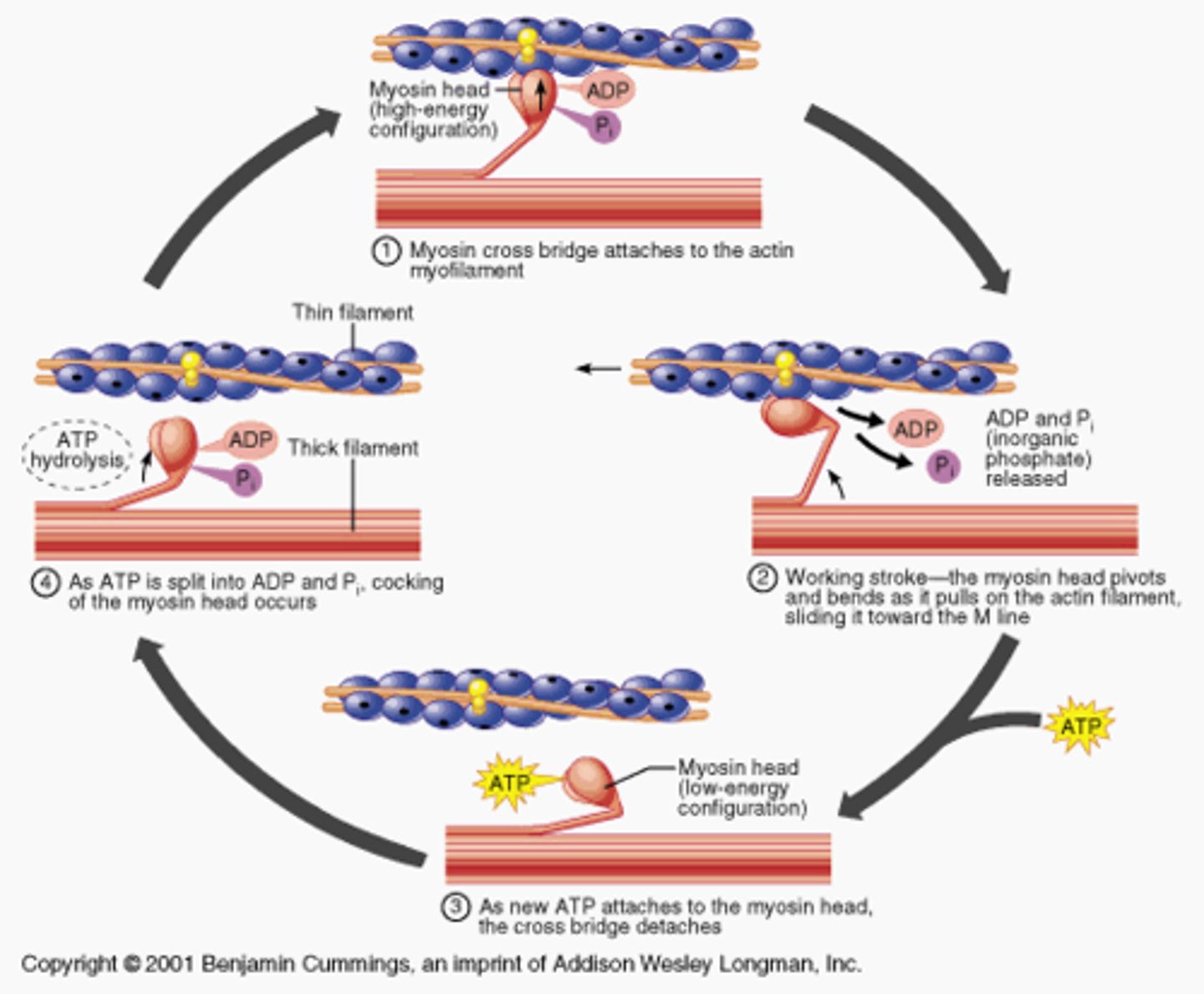
During skeletal muscle contraction, myosin heads bind actin filaments to form ________.
cross bridges
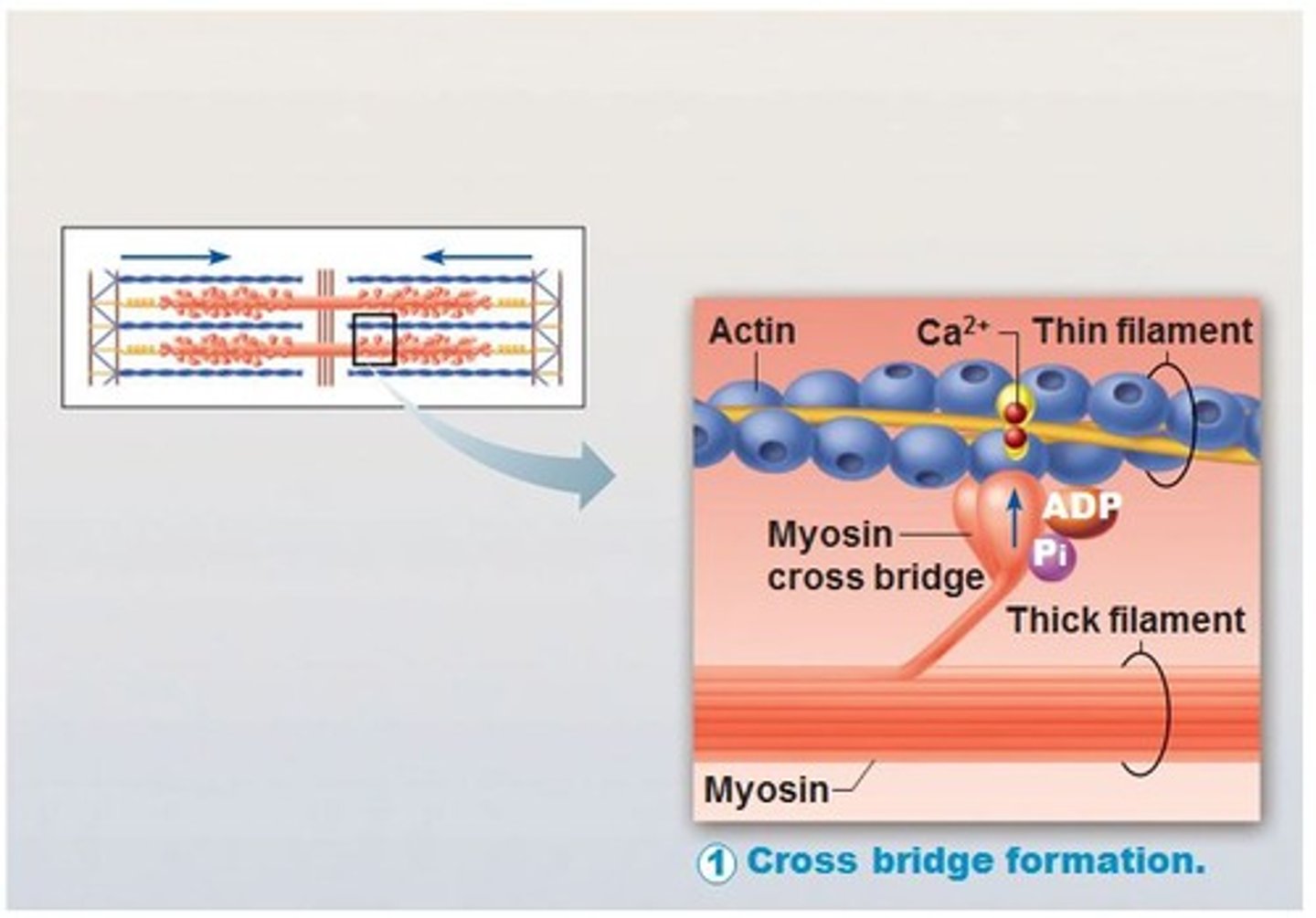
What causes myosin heads to release the cross bridge during muscle contraction?
ATP--the myosin releases actin because it preferentially binds to ATP
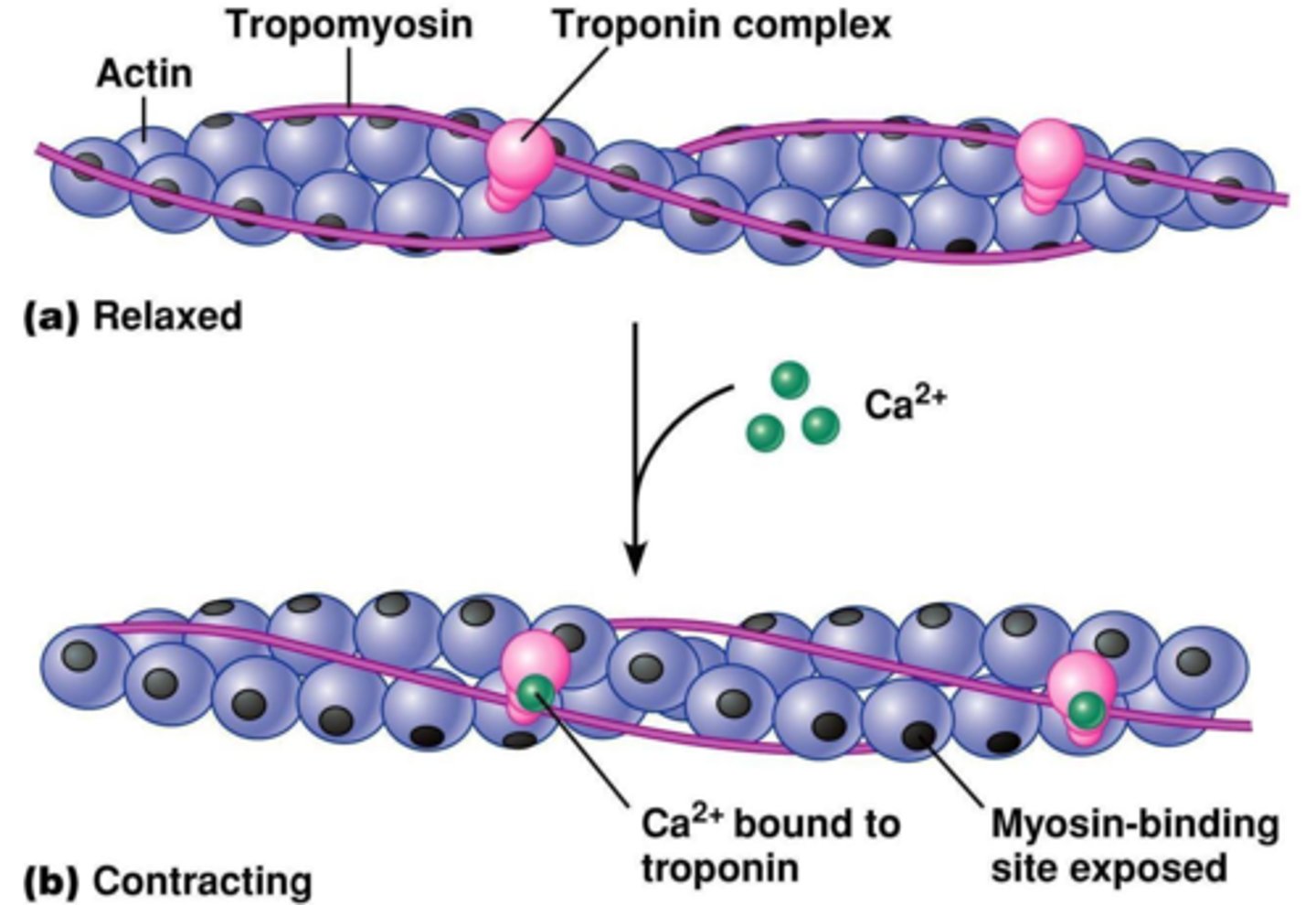
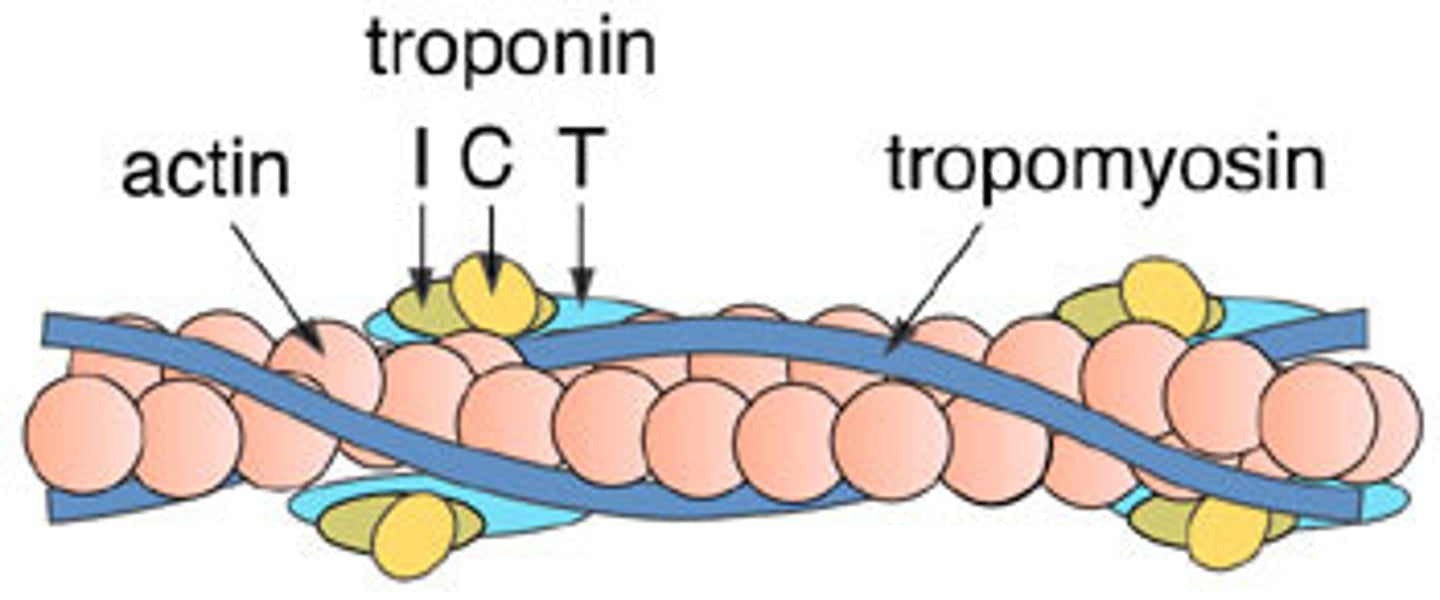
In a sarcomere, which structure is wrapped around the thin filaments like a rope?
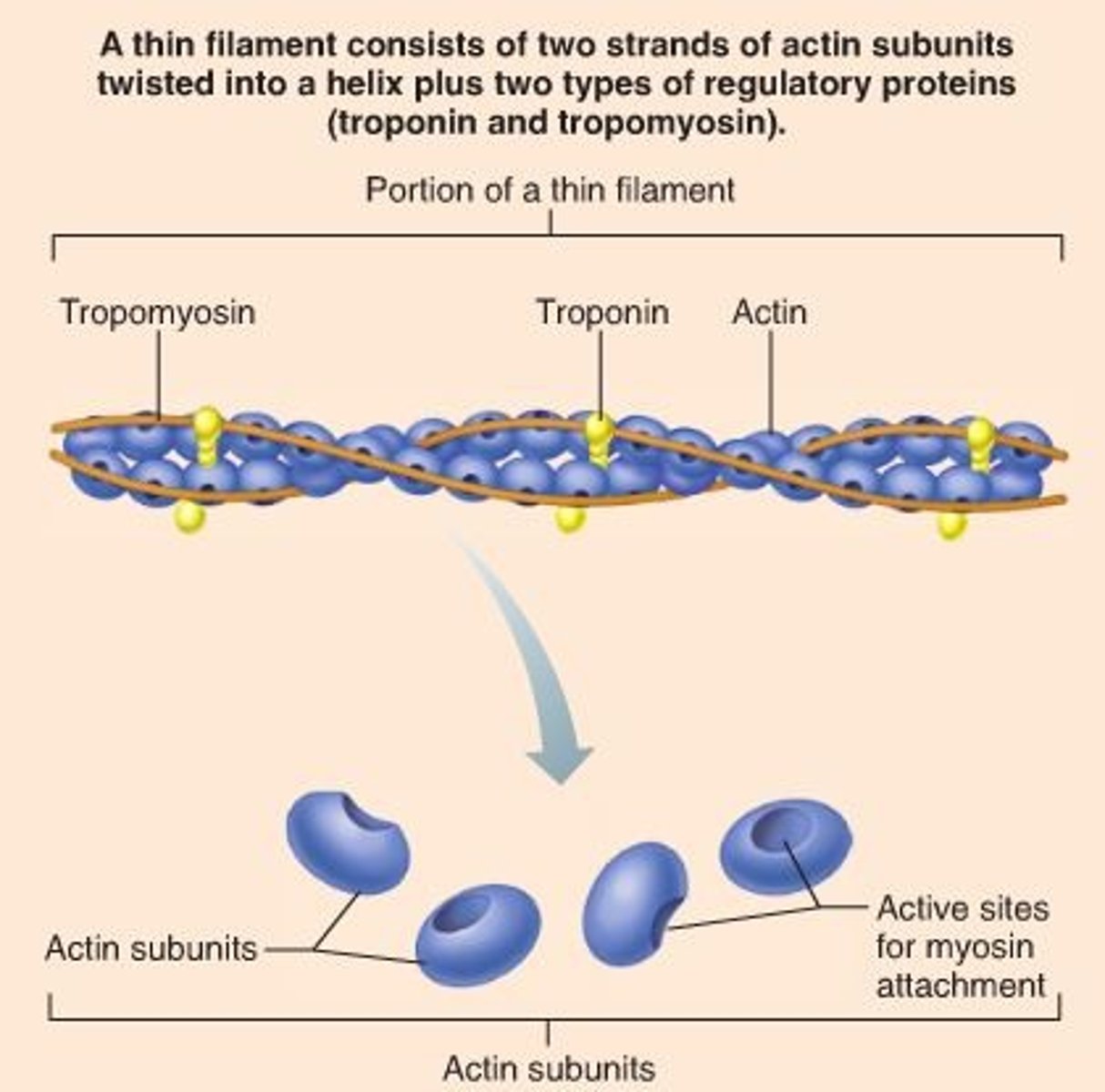
tropomyosin (shown in blue)
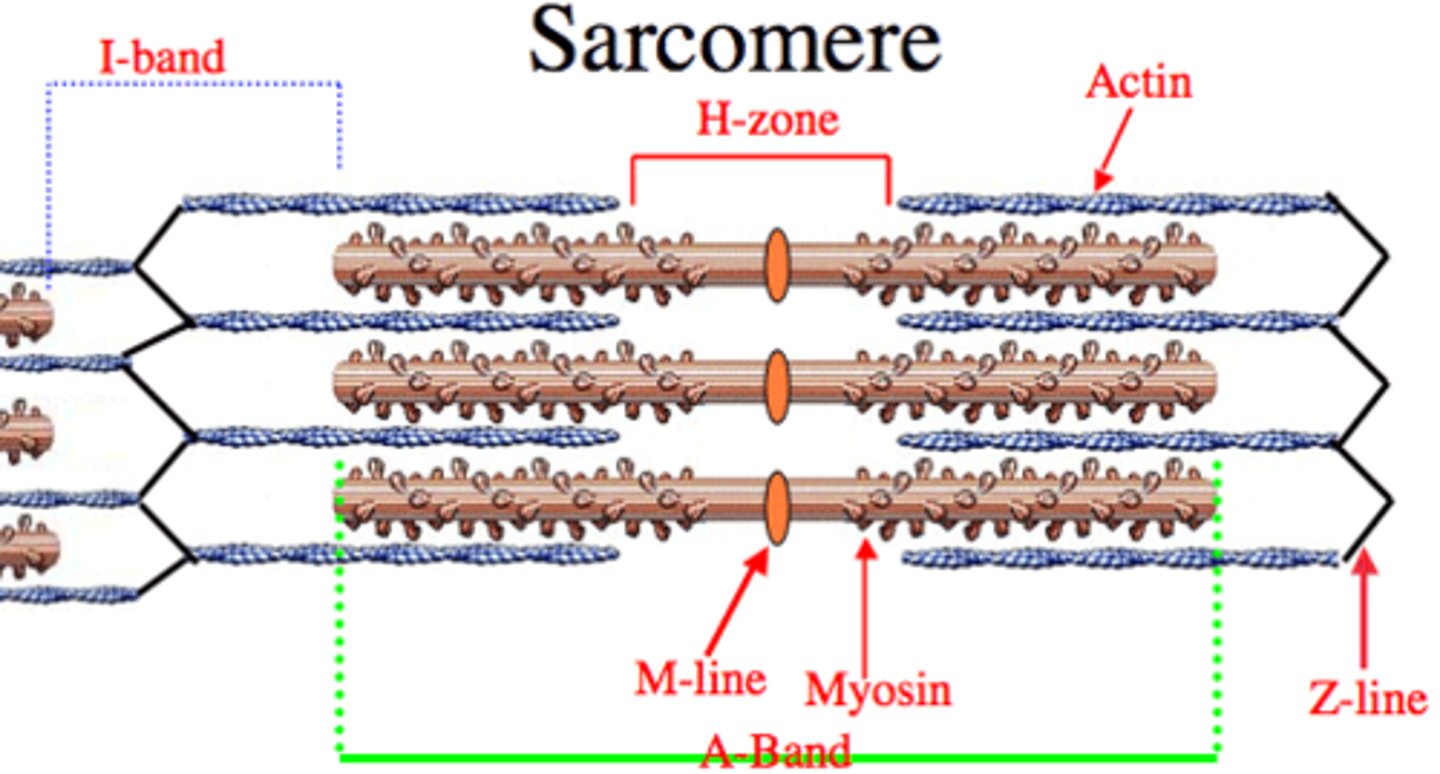
H zone
The region at the center of a sarcomere. Made up of myosin only. The H zone gets shorter (and may disappear) during muscle contraction.
Which property of muscle allows it to return to its original shape?
elasticity
Which neurotransmitter is released at the neuromuscular junction?
acetylcholine (ACh)
Troponin
Calcium binds to this--when calcium ions bind, the whole troponin-tropomyosin complex swivels and uncovers myosin binding sites
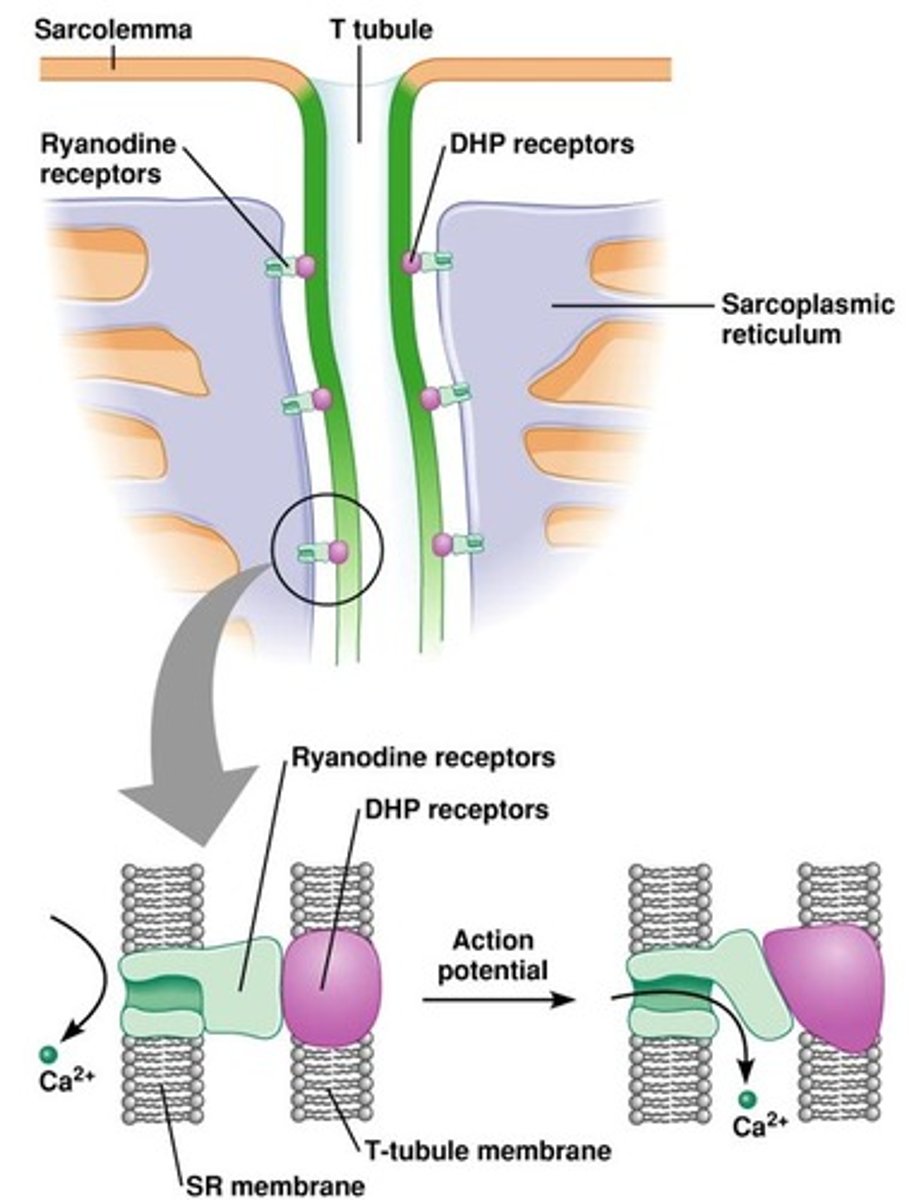
When a muscle fiber experiences an action potential, _______ channels on the membrane of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane open.
voltage-gated calcium ion channels
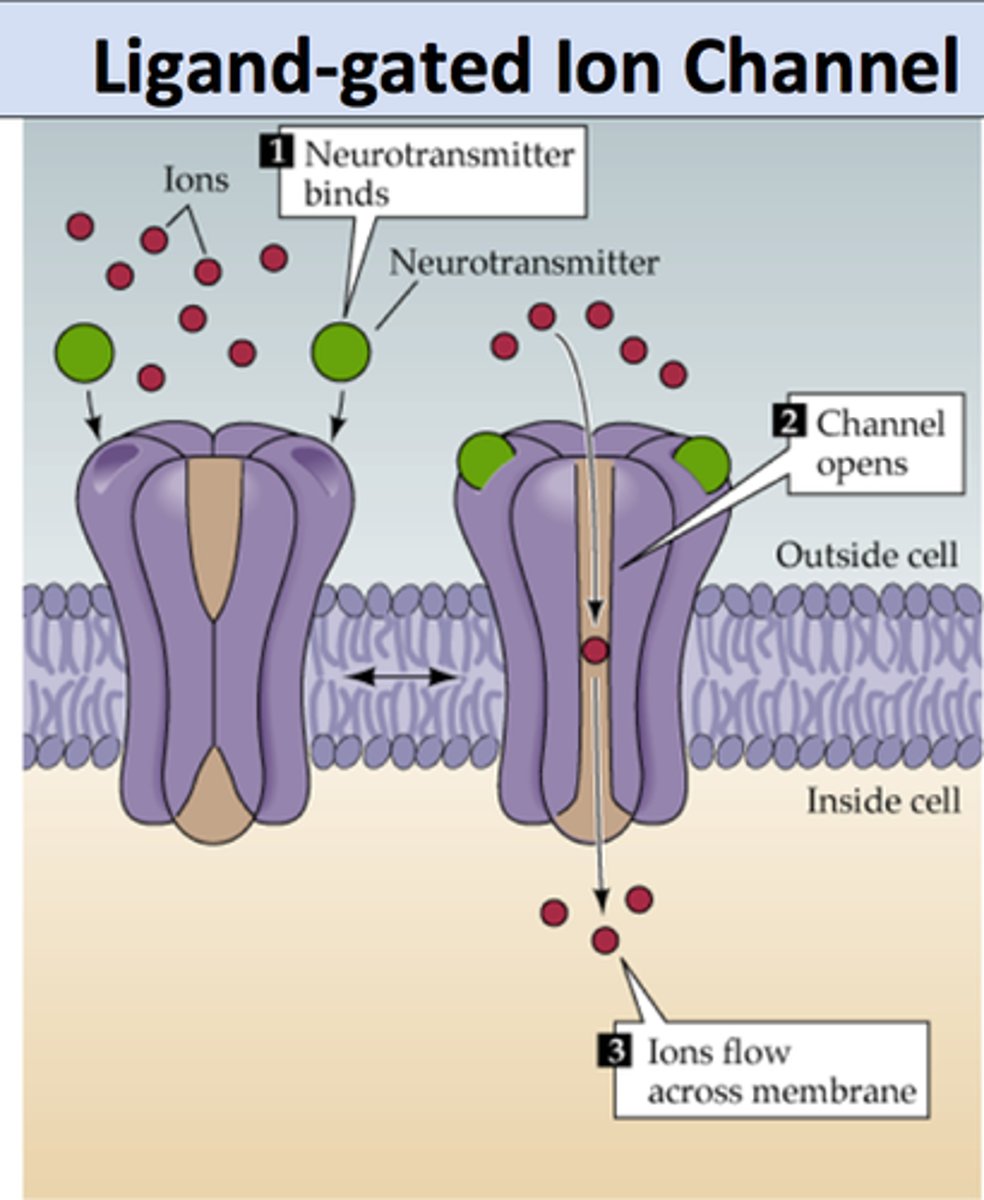
The neurotransmitters that diffuse across the synaptic cleft in a neuromuscular junction bind to _______.
ligand-gated sodium channels (ligand-gated means a chemical must bind to open the channel)
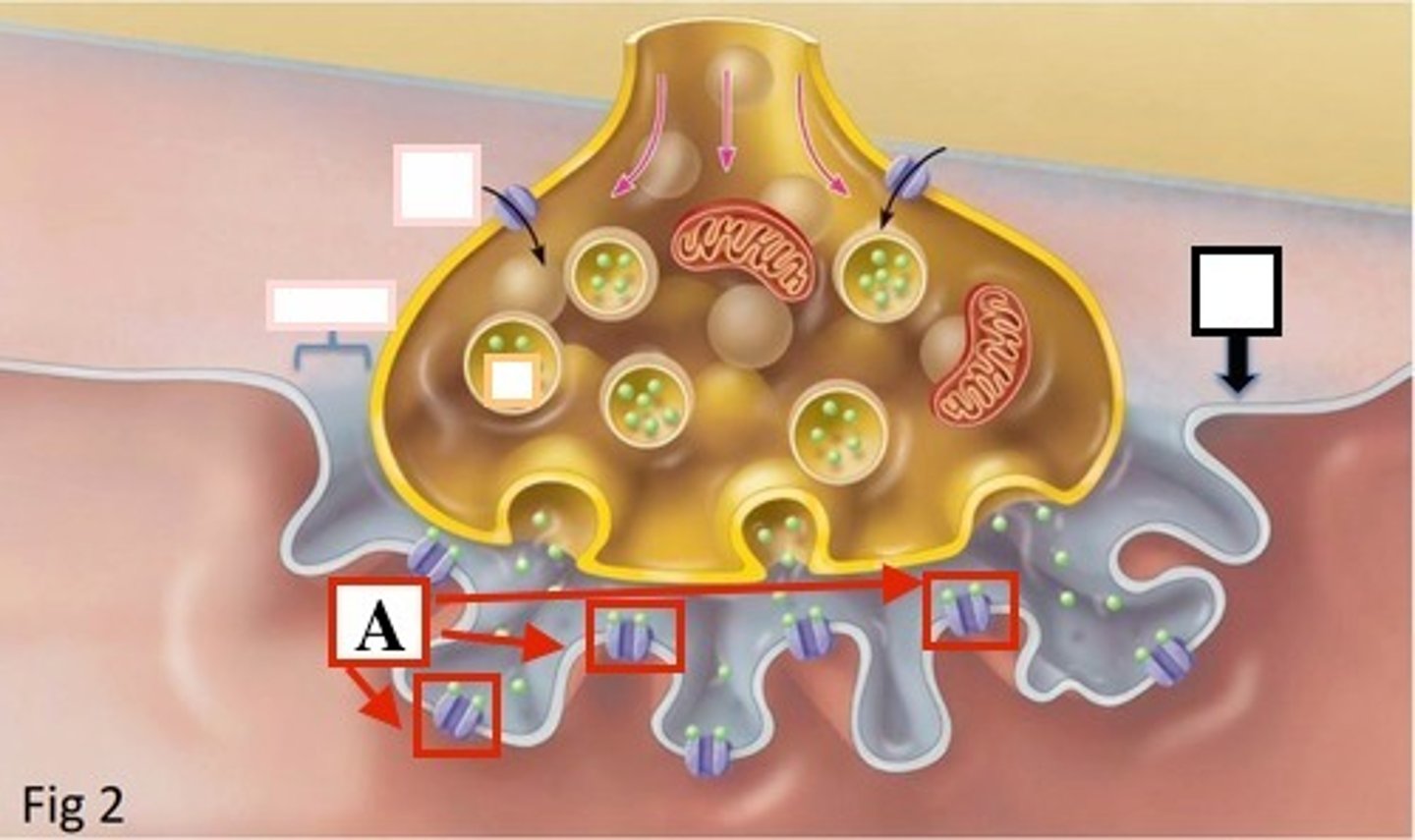
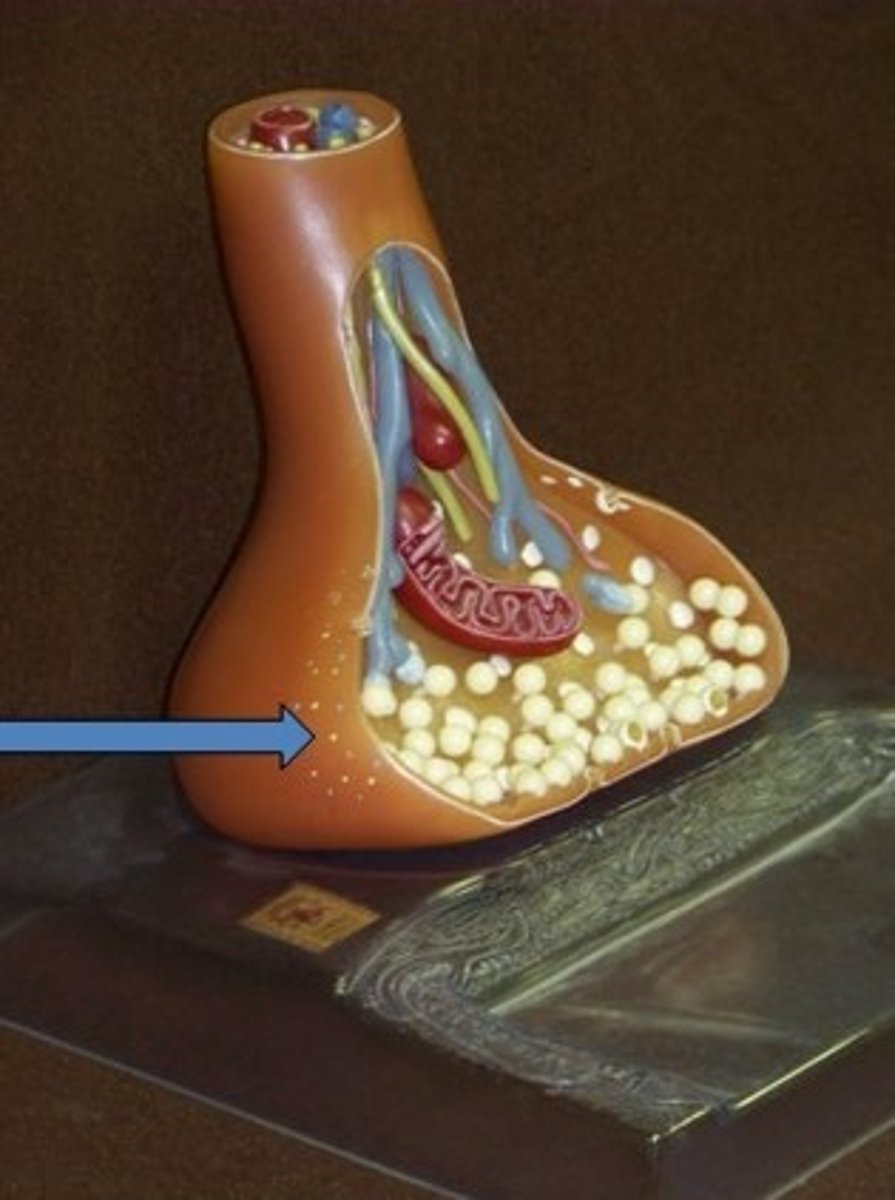
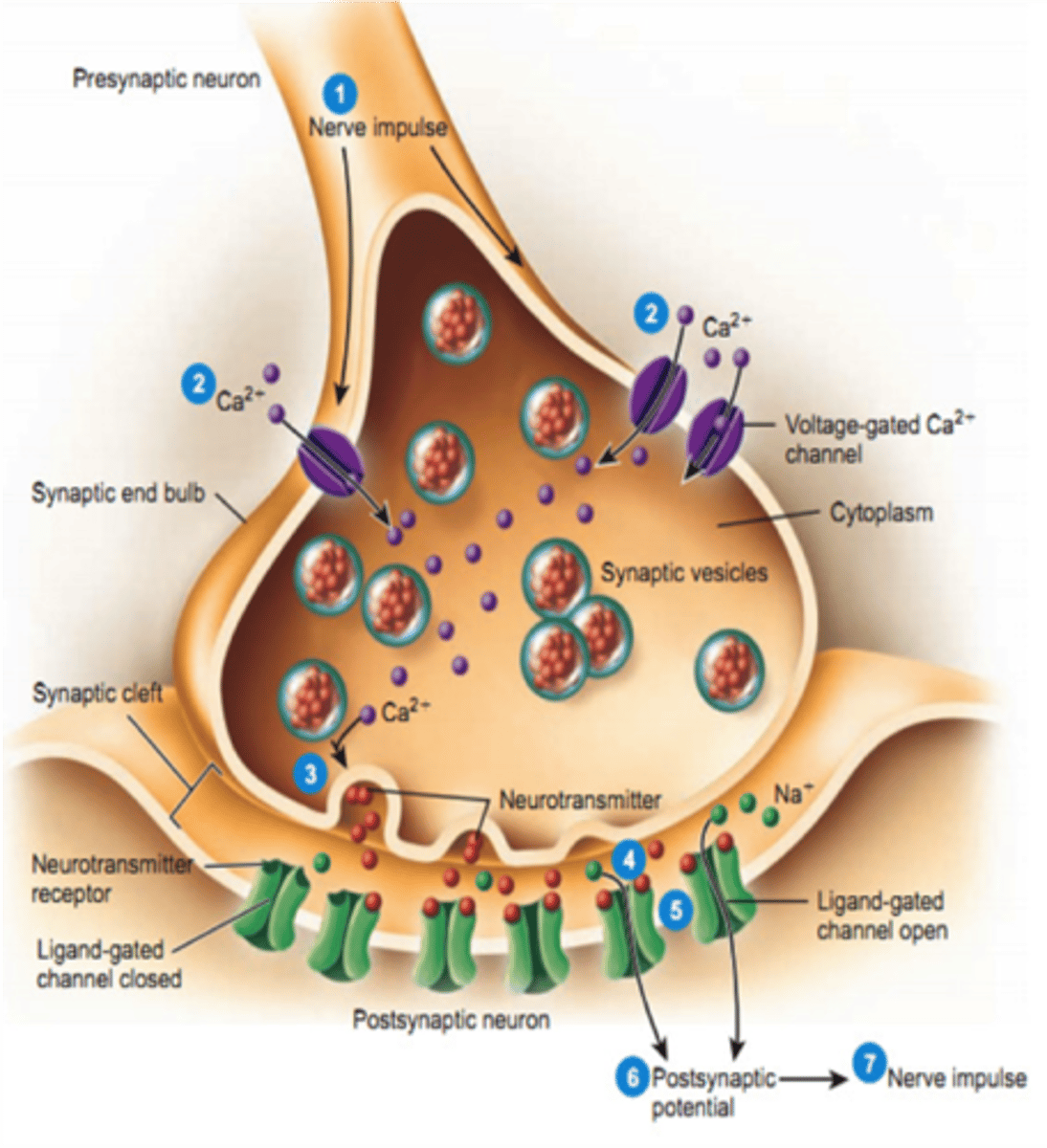
Identify calcium
Be able to identify 1) calcium 2) ACh receptors 3) synapyic vessicles in an image like this
flaccid
a state in which the muscles are limp and cannot contract (this can happen when no neurotransmitter is released from synaptic vesicles)
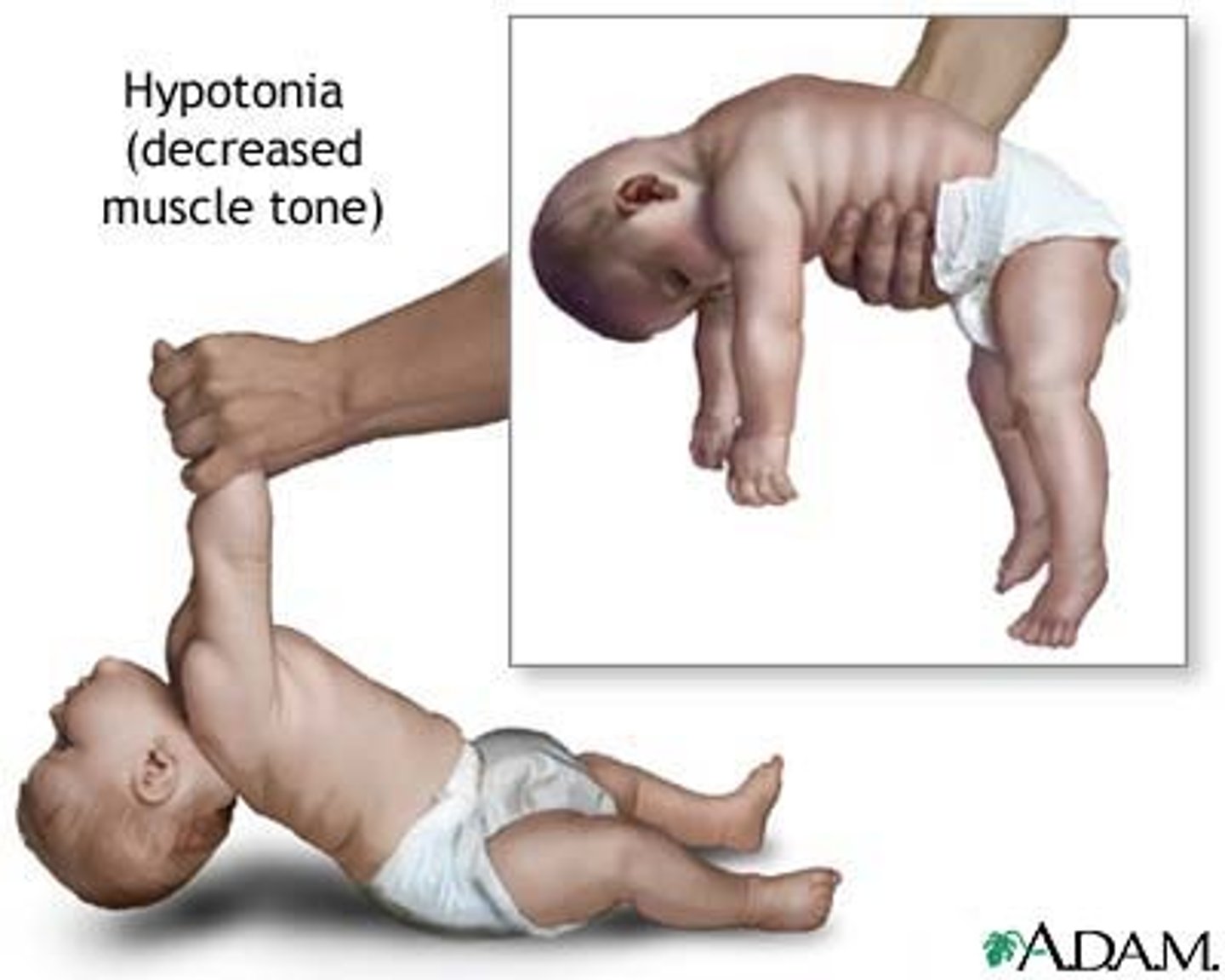
spastic paralysis
a state of continual contraction of the muscles; possible suffocation (this can happen if neurotransmitter is not removed from synaptic cleft)

H-zone
The region at the center of an A band of a sarcomere that is made up of myosin only. The H zone gets shorter (and may disappear) during muscle contraction.
Specialized synapses between neuron axons and muscle cells are called _________.
neuromuscular junctions
What can cause flaccid paralysis?
Anything that prevents binding of ACh to receptors: 1) Botox prevents release of ACh 2) Any toxin that prevents binding of ACh t receptors
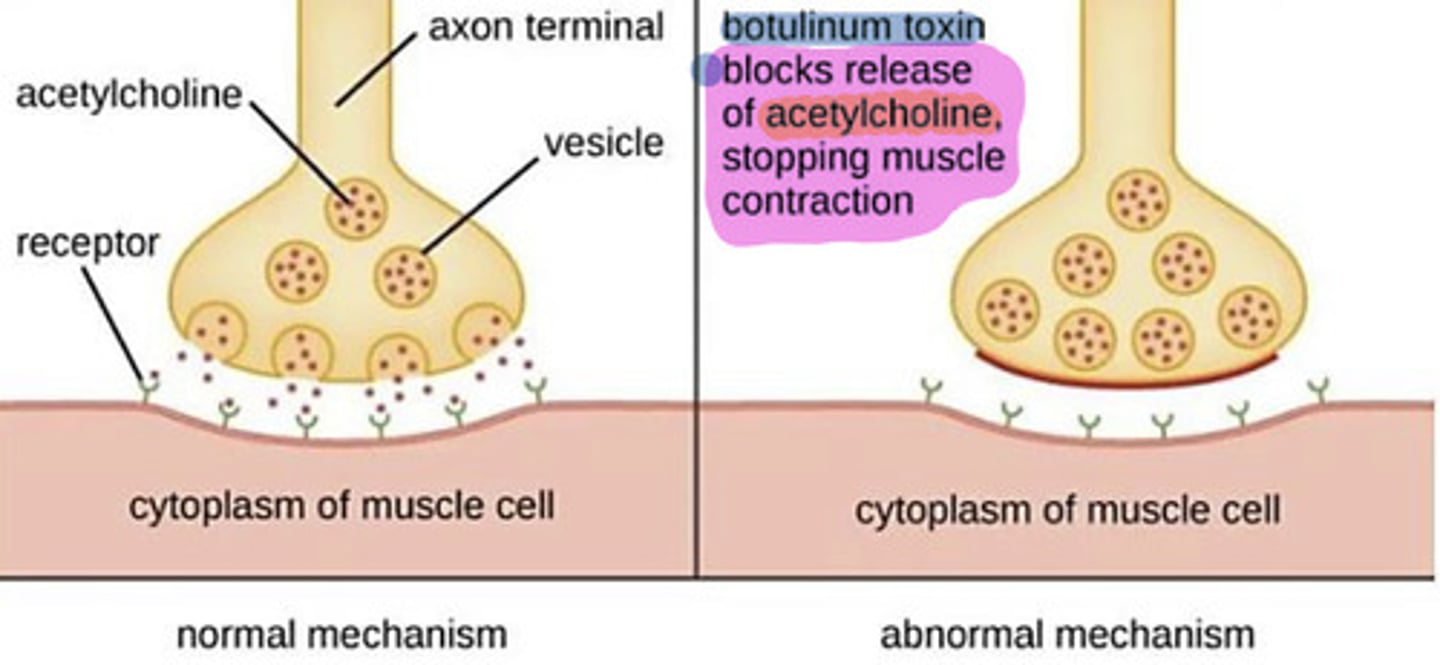
What can cause spastic paralysis?
Anything that 1) prevents breakdown of ACh by enzyme acetylcholinesterase 2) Anything that prevents sodium (Na+) channels from closing after depolarization
