Lesson 21: Cytoskeleton 4: Actin Motors and Regulators
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
light
Calmodulin (CaM) = myosin _______ chain - binds and stabilizes neck region
yes
did u look at it
bi
Non-muscle myosin II regulated by phosphorylation, forming ___polar filaments
-organizes actin cytoskeleton, roles in adhesion, cell migration, etc.
VI
Myosin ___ is the opposite and is MINUS end directed!
X
Myosin ___ moves cargo to the tips of filopodia
III, XV, VI
Myosin ___ and ___ transport cargo to the tips of stereocilia, Myosin ___ moves cargo OUT of stereocilia
size, directionality
myosin power stroke dictates step ____ and _________
II, thick
Muscle myosin is myosin ___ AKA ____ filaments
M, Z
myo II thick filaments are anchored at the __-line
thin filaments have plus ends anchored at the __-disc
ATP
the rigor state happens when no more ____ is generated
rigor
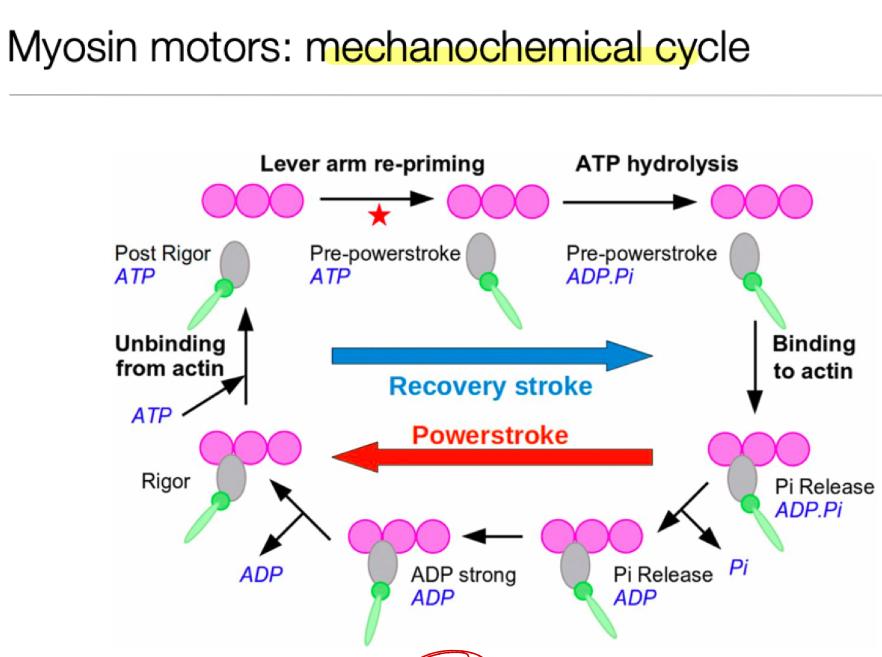
Myosin II/muscle mechanochemical cycle:
Attached (nothing bound, attached to actin filament in ______ configuration)
Released (molecule of ATP binds, lets go of actin filament)
Cocked (hydrolysis moves it back a bit)
Rebinding/Power Stroke (weak binding and ADP/P leave, causing large movement forward)
back to step 1
Calcium
What molecular signal triggers activation of actomyosin contraction?
acetylcholine
Striated Muscle contraction:
neuron releases __________
electrical impulse propagates through T-tubules
triggers saarcoplasmic release of Ca into sarcomeres
calcium binds to troponin so tropomyosin unblocks site on F-actin for myosin motor domain to bind and move
calcium pumps push Ca back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
phosphatase
Smooth Muscle contraction:
calcium-bound CaM activates myosin light chain kinase
phosphorylates myosin light chain
activates myosin motor
causes contraction
TURNED OFF BY A ______