Lectures 24-25: Limbic System
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Overview of the Limbic System
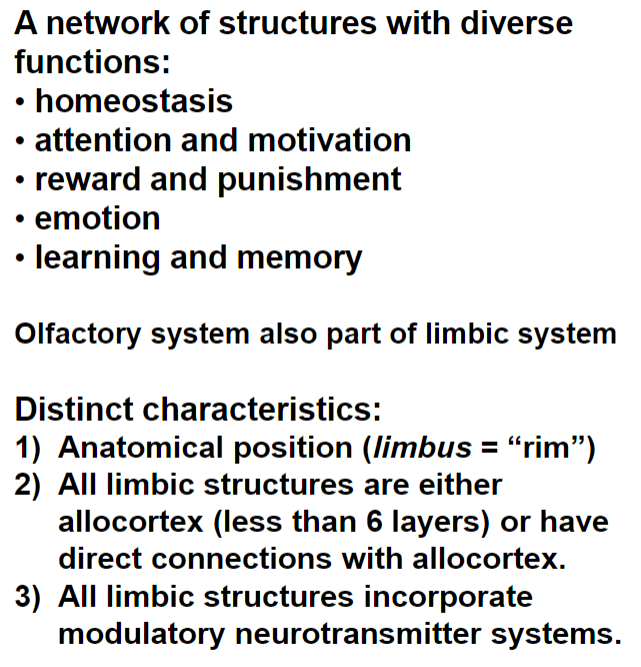
Limbic lobe
allocortex
Limbic system
limbic lobe plus subcortical nuclei &
pathways
Limbic Cortex

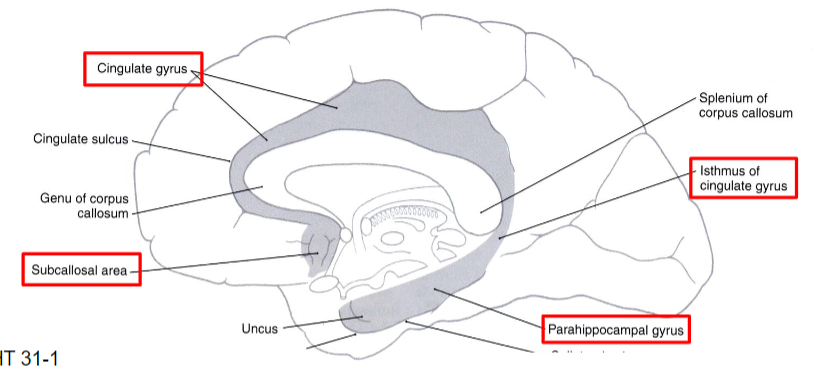
Parahippocampal gyrus
Piriform cortex (anterior)
Entorhinal cortex (posterior)
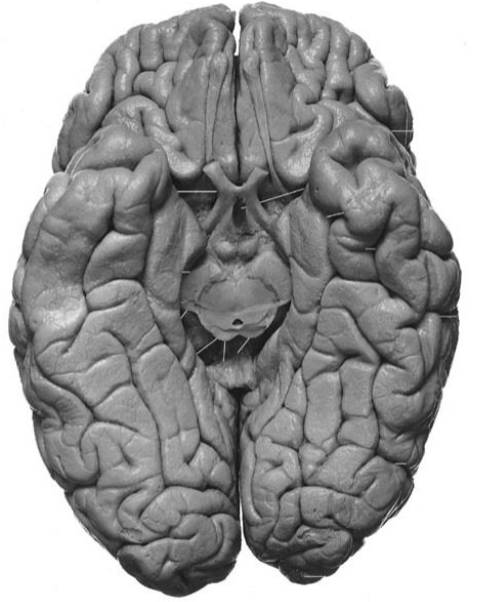
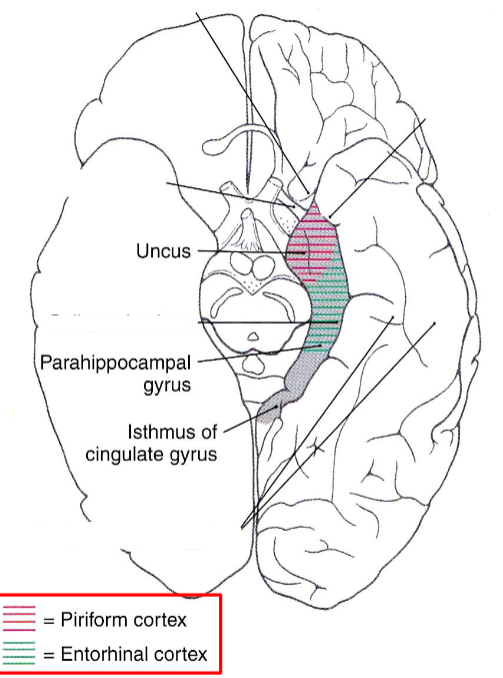
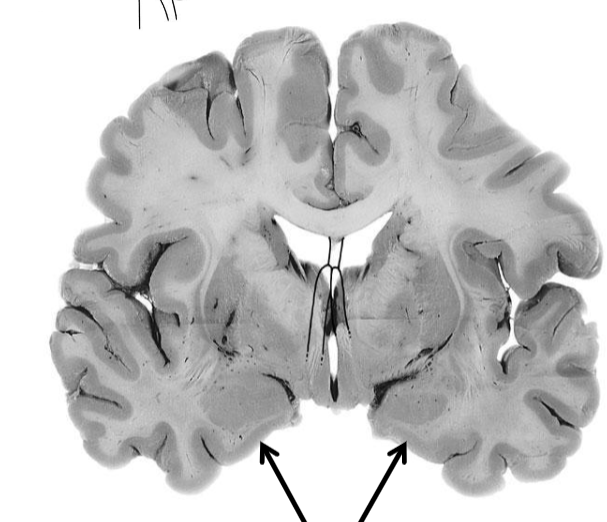
Piriform cortex covers amygdala
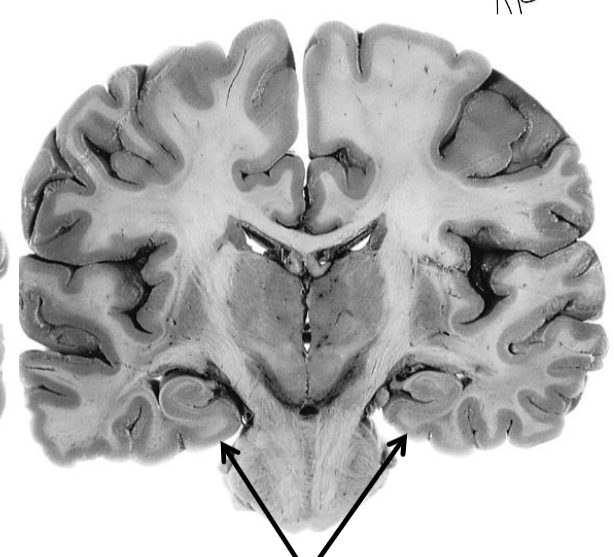
Entorhinal cortex covers hippocampal formation
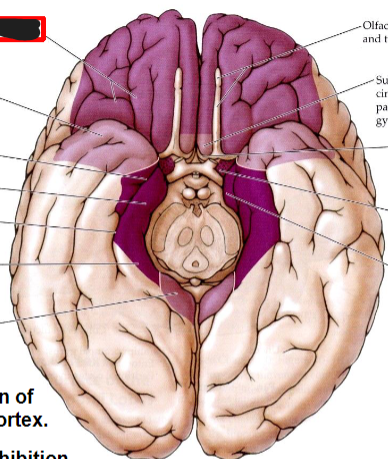
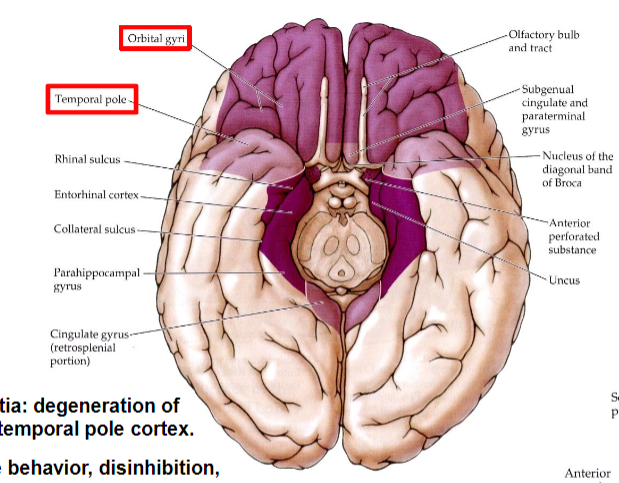
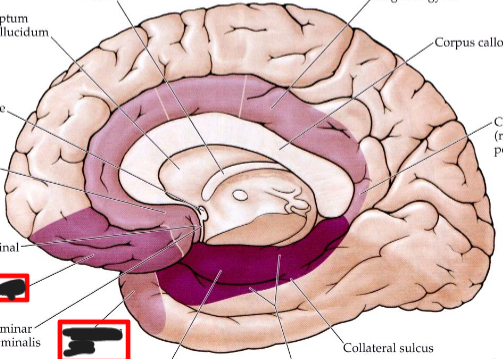
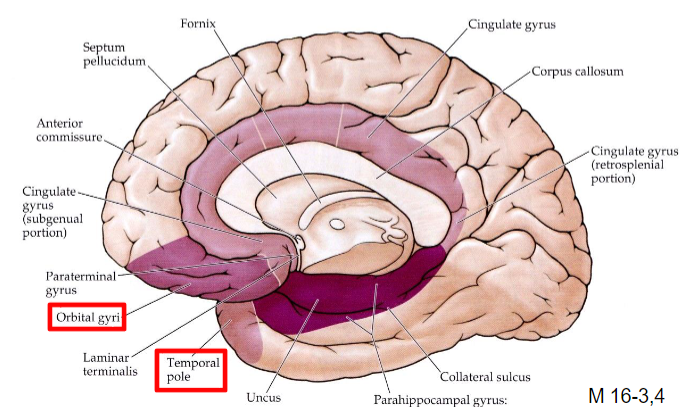
Limbic Association Cortex
Includes temporal pole and
orbitofrontal cortex
Receives inputs from association
areas of neocortex, and then exchanges that information with allocortex
Frontotemporal dementia
degeneration of orbitofrontal cortex and temporal pole cortex
Patients exhibit compulsive behavior, disinhibition, memory deficits, inability to control emotions
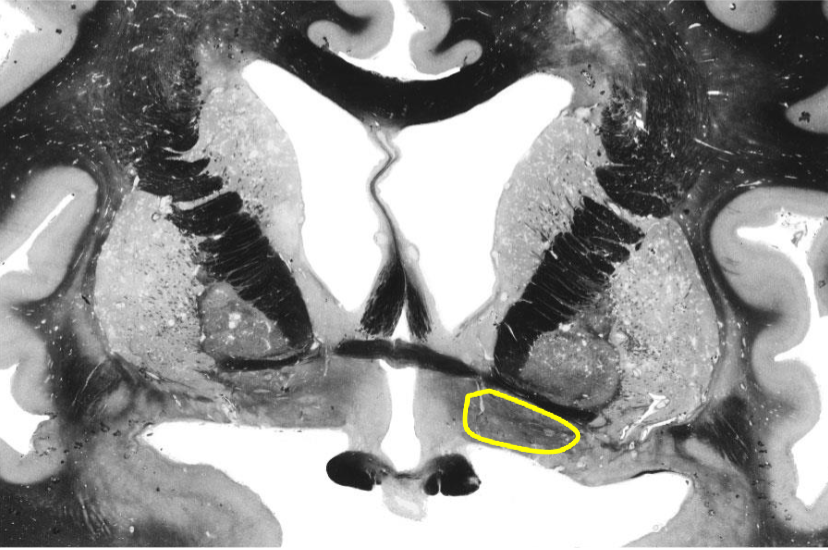
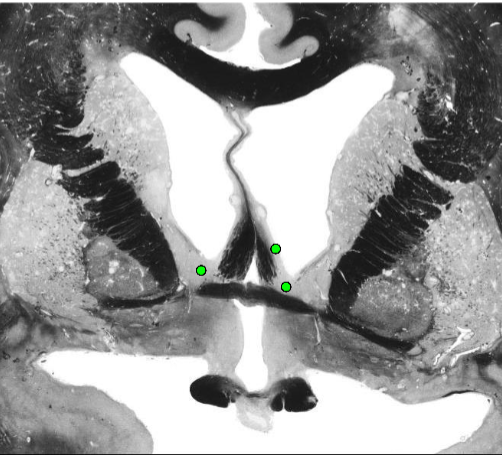
Basal Nucleus of Meynert
Basal Nucleus of Meynert
source of cholinergic projections (acetylcholine)
within substantia innominata
limbic projections to amygdala and hippocampal formation
influences arousal, attention, memory
part of etiology of Alzheimer disease
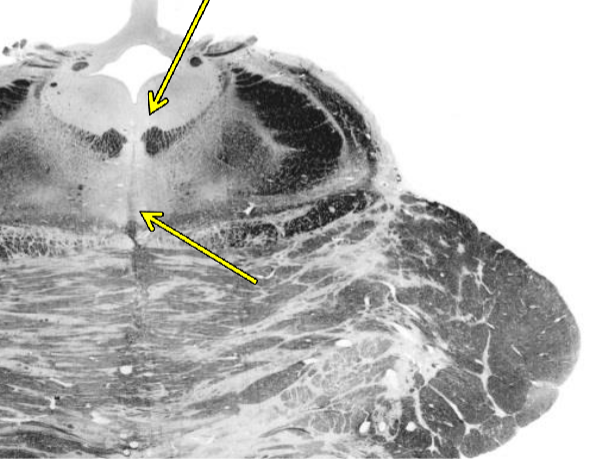
Dorsal & Median Raphe Nuclei
Dorsal & Median Raphe Nuclei
source of serotonergic projections (serotonin)
component of reticular formation
limbic projections to amygdala, hippocampal formation, hypothalamus
influences sleep and arousal, feeding/satiety, and mood
SSRIs demonstrate role in depression, anxiety, OCD, & other mood disorders
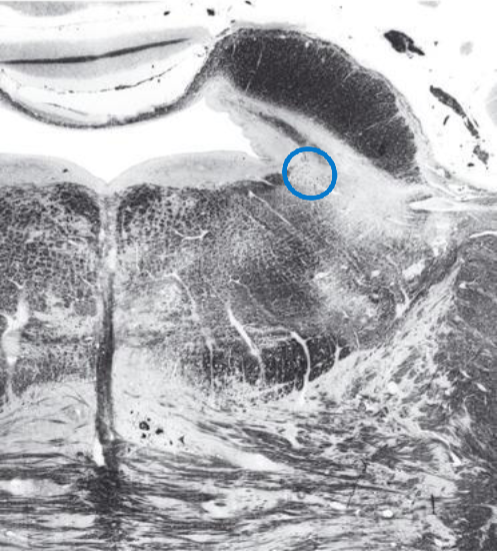
Locus Ceruleus
Locus Ceruleus
source of noradregenergic projections (norepinephrine)
diffuse projections to limbic system
influences sleep and arousal, autonomic functions
SNRIs demonstrate interaction with serotonergic system to affect mood
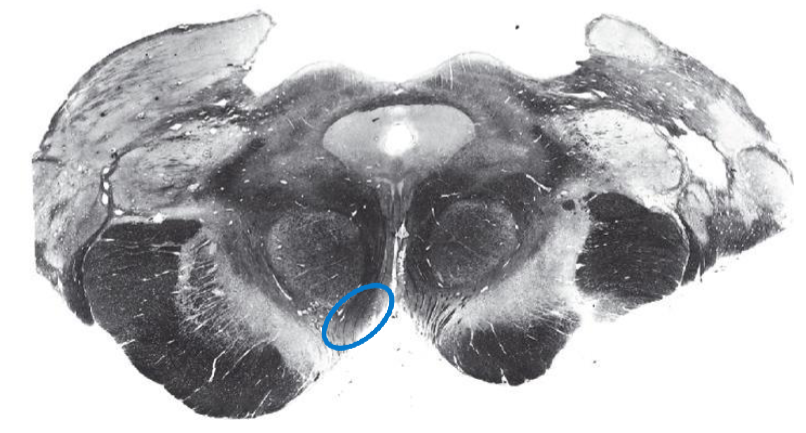
Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA)
Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA)
source of dopaminergic projections (dopamine)
limbic projections to hypothalamus, septal n., n. accumbens, & ventral pallidum
projection to nucleus accumbens (mesolimbic reward pathway)
influences motivation, reward, reinforcement
part of etiology of addiction, substance abuse
Septal Nuclei
Septal Nuclei
Receives dopaminergic input from VTA via the medial forebrain bundle
Connections with hippocampal formation, amygdala, and hypothalamus
Reward, pleasure, and reinforcement center
Lesion in humans may produce “sham rage”
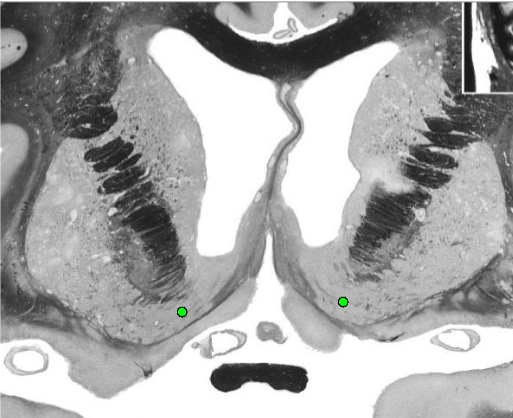
Nucleus Accumbens (Ventral Striatum)
Nucleus Accumbens (Ventral Striatum)
Receives dopaminergic input from VTA via the medial forebrain bundle
(mesolimbic reward pathway)
Expresses receptors for endogenous opiates
Connections with hippocampal formation, hypothalamus, amygdala, and basal nuclei (part of limbic loop)
Reward, pleasure, and reinforcement center
Involved in addiction pathologies
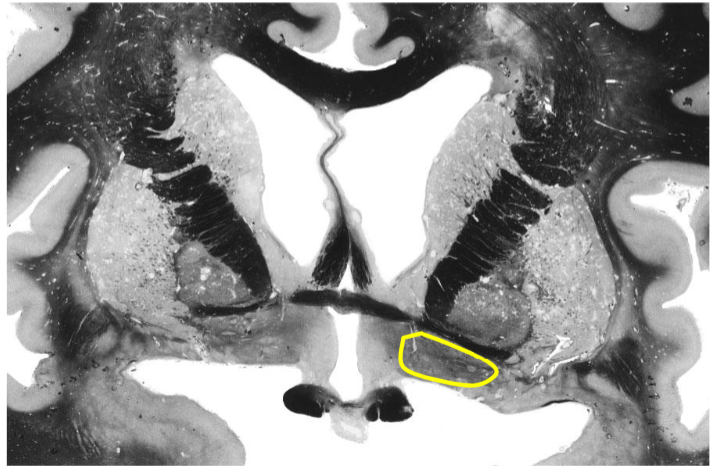
Ventral Pallidum
Ventral Pallidum
Located within substantia innominata
Relay from nucleus accumbens to dorsomedial n. of thalamus (part of limbic loop)
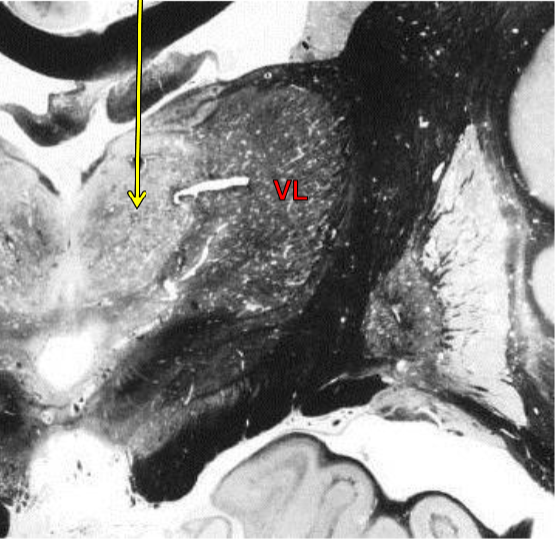
Dorsomedial nucleus of thalamus
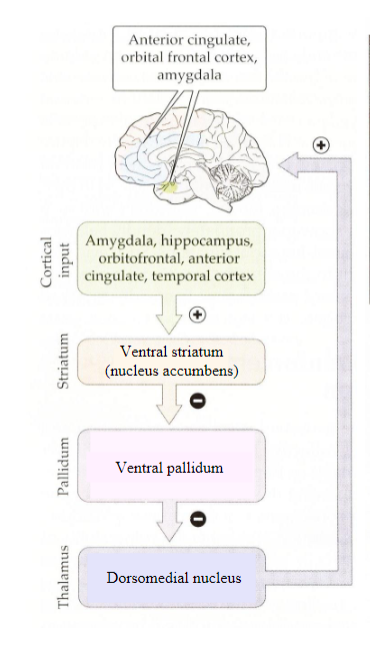
Limbic Loop Overview
limbic loop involves disinhibition
of the dorsomedial nucleus of the
thalamus, which projects to limbic,
prefrontal and orbitofrontal
association cortices
The limbic loop functions to regulate
emotional and motivational drives
Like the motor loop, the limbic loop is
facilitated by dopaminergic inputs
dopaminergic inputs to the limbic
loop originate in the VTA and project
to the nucleus accumbens
Dysfunction of the limbic loop
and/or VTA dopaminergic
modulation is implicated in
schizophrenia, depression, and
other disorders
Limbic Loop
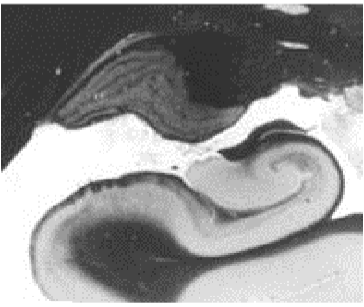
Hippocampal Formation
Hippocampal Formation Components
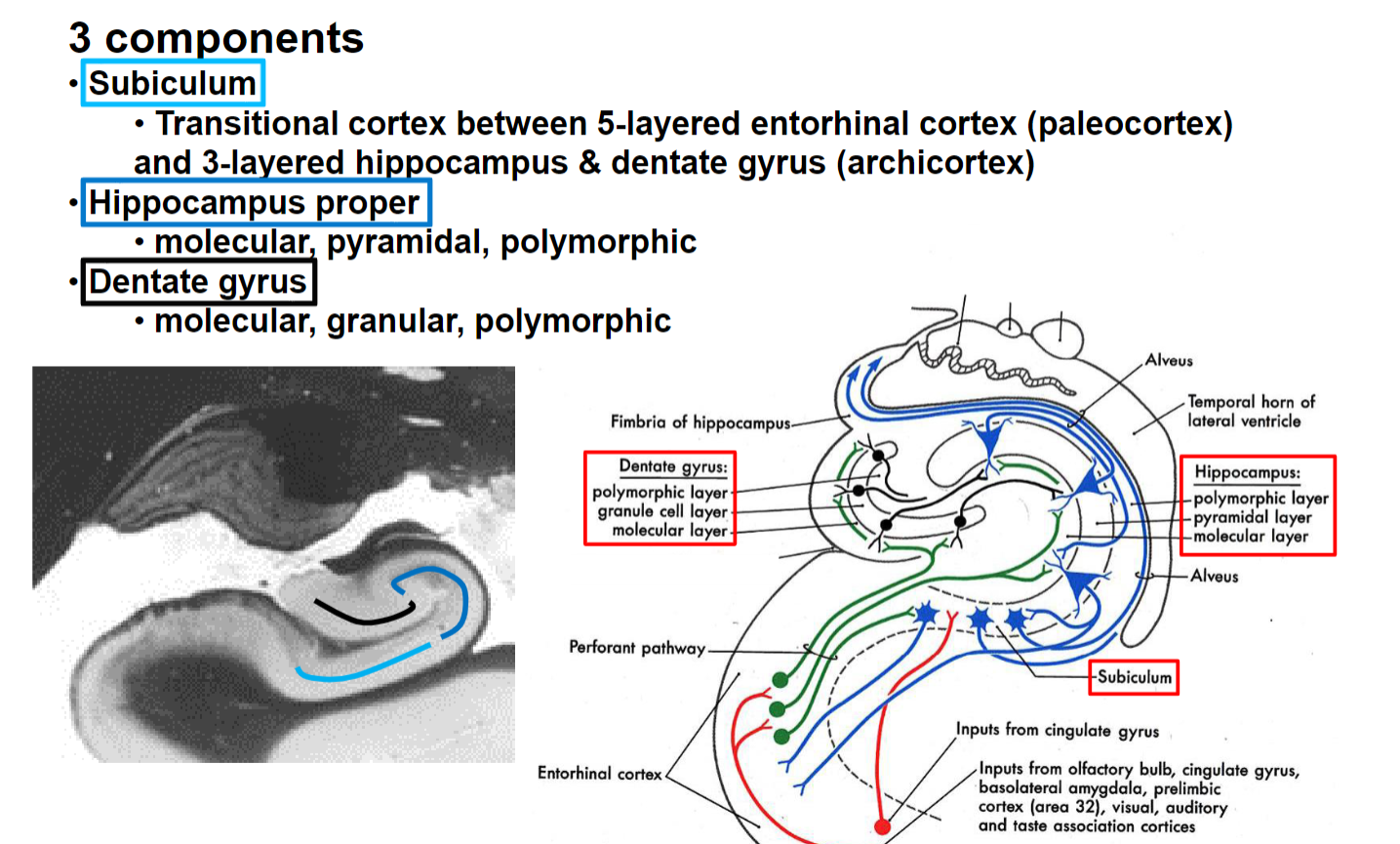
Hippocampal Formation Afferents and Efferents

Cornu Ammonis

Flow of signals through the hippocampal formation

Hippocampal Formation

H.M.
Resection included amygdala,
parahippocampal gyrus, and ant.
2/3 of hippocampal formation
profound anterograde amnesia
Normal immediate and short-term (working) memory of approx. 5 minutes
Retrieval of existing memory (explicit & implicit) largely unaffected (retrograde amnesia limited to about ~8 months)
Implicit (procedural) memory unaffected
Priming intact
Personality and general intelligence normal (IQ of 112, ~ pre-operative level)
Although bilateral hippocampal resections are no longer performed, the hippocampal formation is especially vulnerable to cerebral anoxia or severe
hypoglycemia
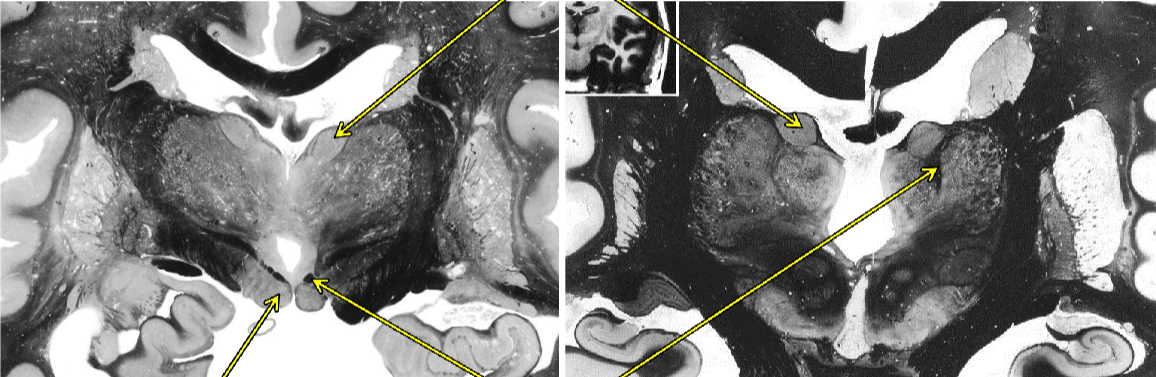
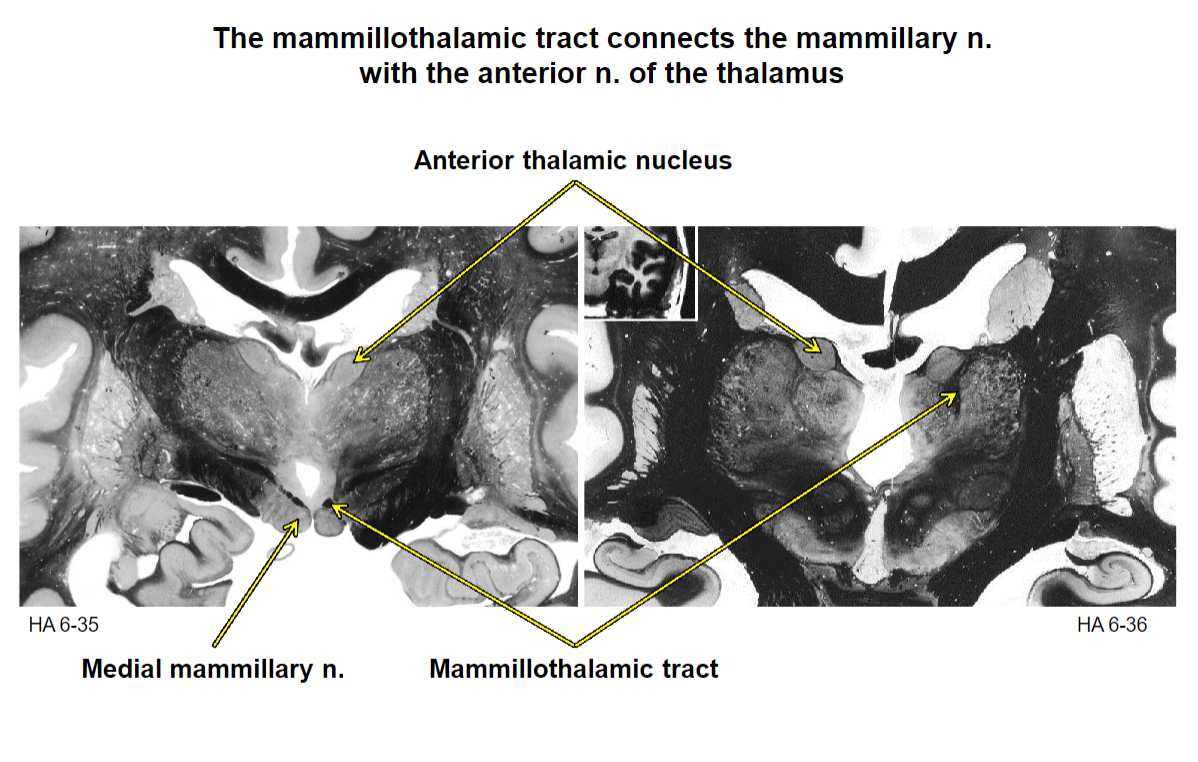
Fornix
connects the hippocampal formation
with the mammillary nuclei of the hypothalamus
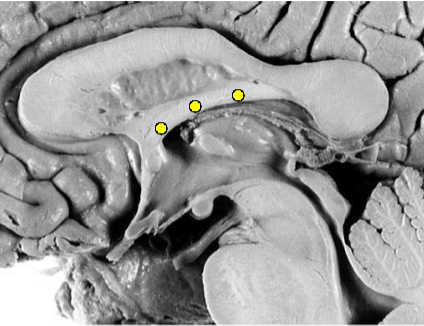
Fornix
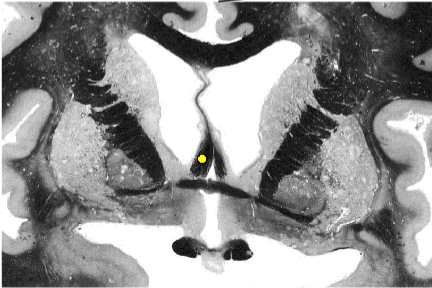
Fornix
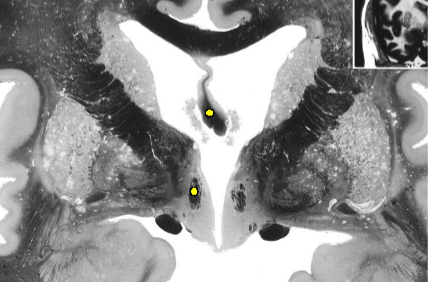
Fornix
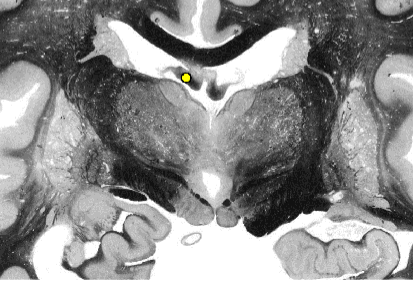
Fornix
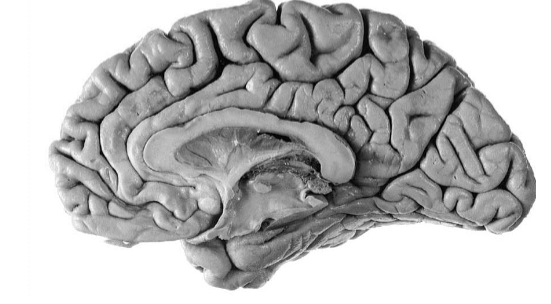
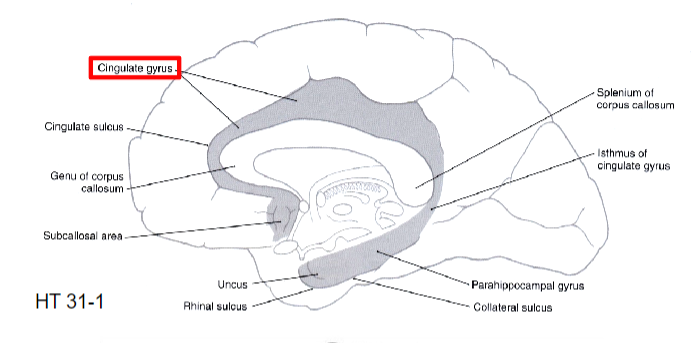
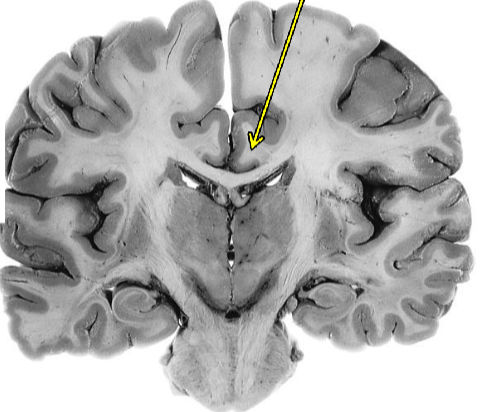
cingulum
Papez Circuit

Papez circuit overview
Structures of the Papez Circuit receive signals regarding sensation, memories, emotion, internal state, executive cognition, etc.
Structures of the Papez Circuit also send output signals, either via physiological expression
(autonomic/endocrine) or conscious experience
Memory
Korsakoff syndrome (alcoholic dementia)
Disorder of the Papez Circuit
thiamine deficiency often as a
result of chronic alcoholic
malnutrition
Degeneration of hippocampal
formation, fornix, mammillary
nuclei, or anterior thalamic nuc.
Dementia, as well as deficits in
short-term memory and memory
consolidation
Retrograde amnesia variable
Prone to confabulation
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome

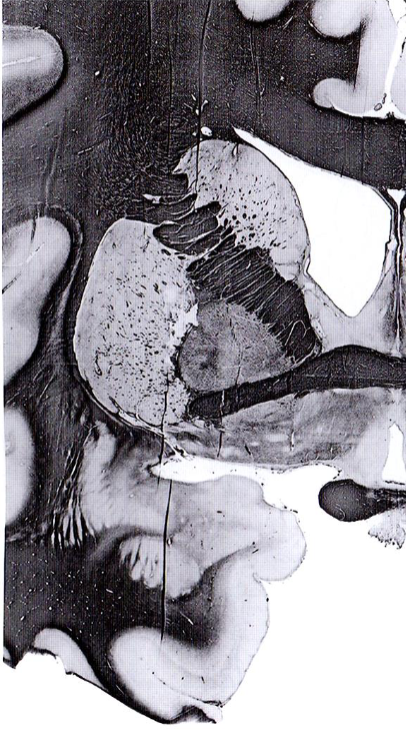
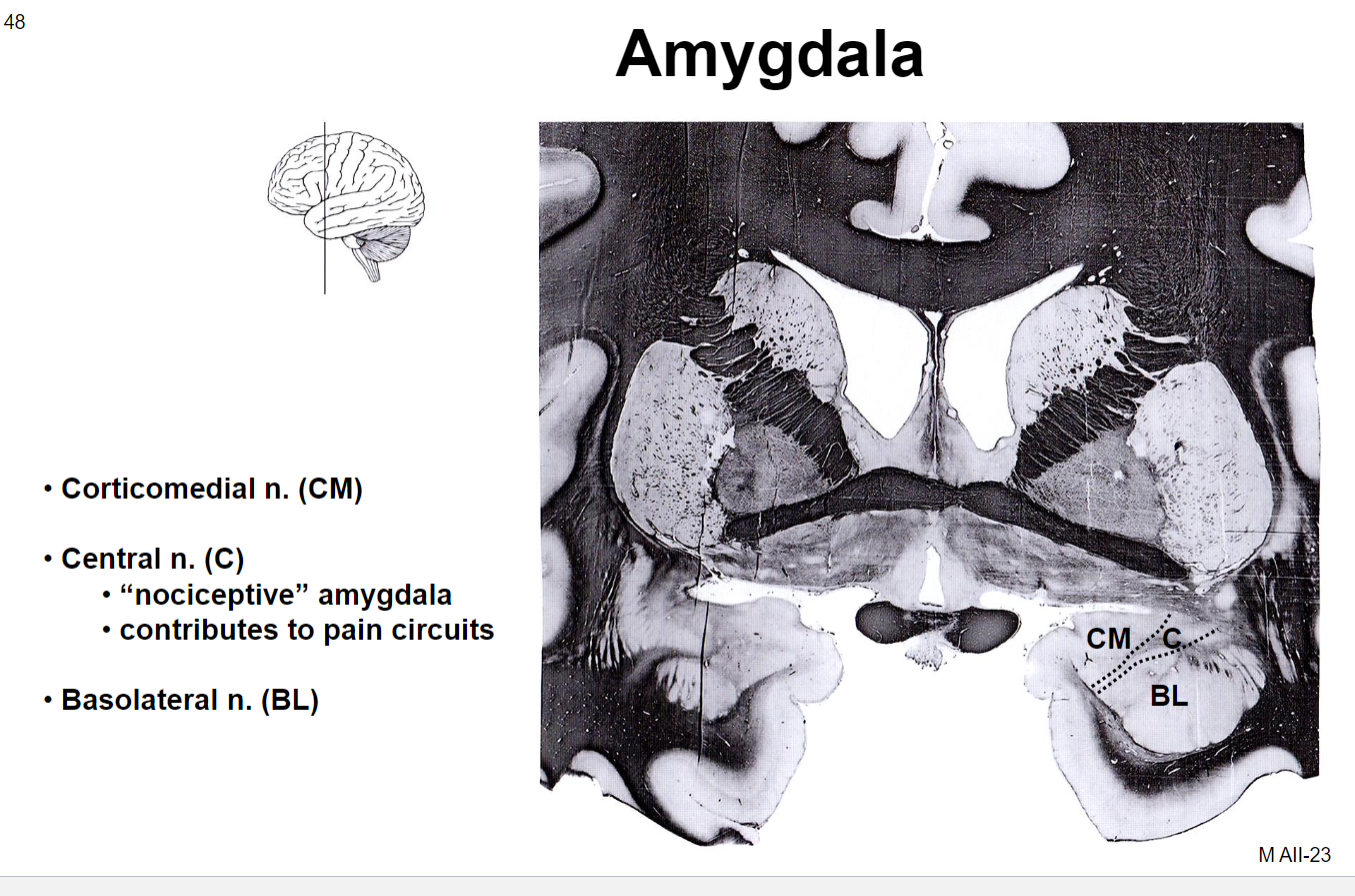
Amygdaloid Afferents
Corticomedial: Olfactory tract, hypothalamus (feeding centers), brainstem nuclei
Basolateral: Hippocampal formation (subiculum), dorsomedial n. of thalamus, diverse areas of cerebral cortex
Amygdaloid Efferents
Corticomedial: Stria terminalis to hypothalamus, septal nuclei, nucleus accumbens
Basolateral: Ventral amygdalofugal pathway ascending to hypothalamus, dorsomedial n. of thalamus, cerebral cortex; and descending to brainstem nuclei
Amygdala

Klüver-Bucy syndrome

S.M.
with rare autosomal recessive condition (Urbach-Wiethe disease)
Calcification and atrophy of the anterior medial temporal lobes
Bilateral extensive lesions of the amygdalae with no detectable damage to the hippocampal formation
No motor or sensory impairments; no deficits in intelligence or language
Profound inability to recognize and experience fear
Some deficits in consolidation of emotional memory
Normal abilities relative to other emotions (both positive and negative emotions)
S.M., and two other individuals with Urbach-Wiethe, experienced fear and panic in response to CO2 inhalation
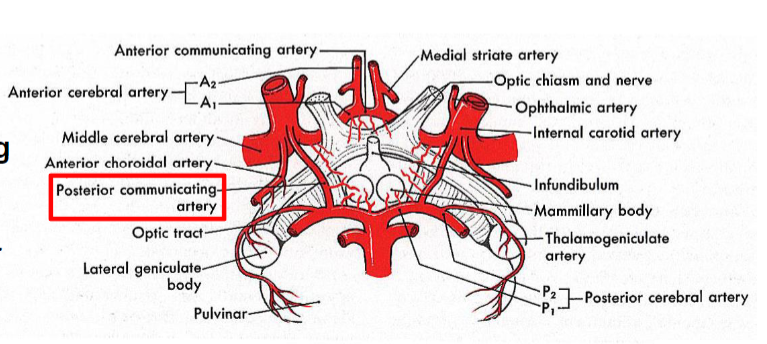
Anterior choroidal artery supplies
hippocampal formation and amygdala
Anterior choroidal a. occlusion
Contralateral homonymous hemianopia
Possible contralateral hemiparesis/hemiplegia
Transient anterograde amnesia
Transient emotional instability
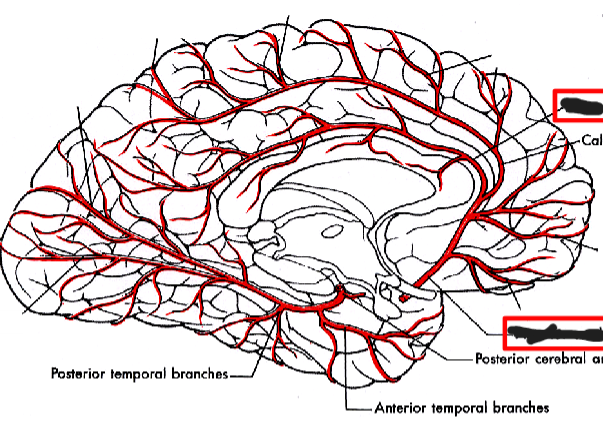
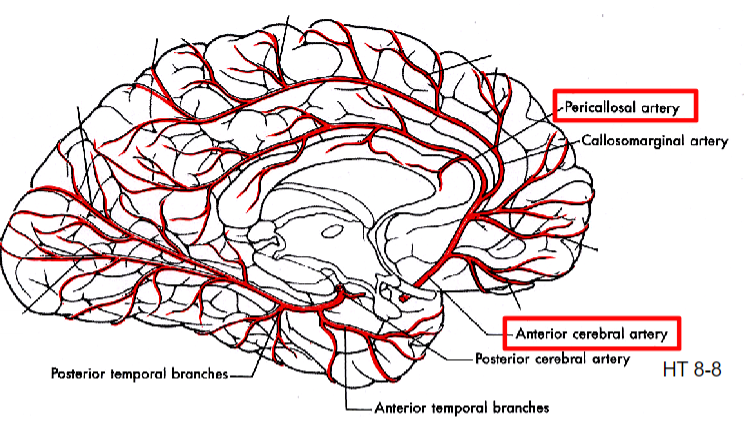
pericallosal branch of anterior cerebral artery supplies
Cingulate gyrus
posteromedial branches of posterior
communicating artery supplies
Mammillary nuclei
Focal occlusions affecting the cingulate gyrus or mammillary nuclei
can produce dementia and/or memory deficits (Papez Circuit)