9 Enthalpy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
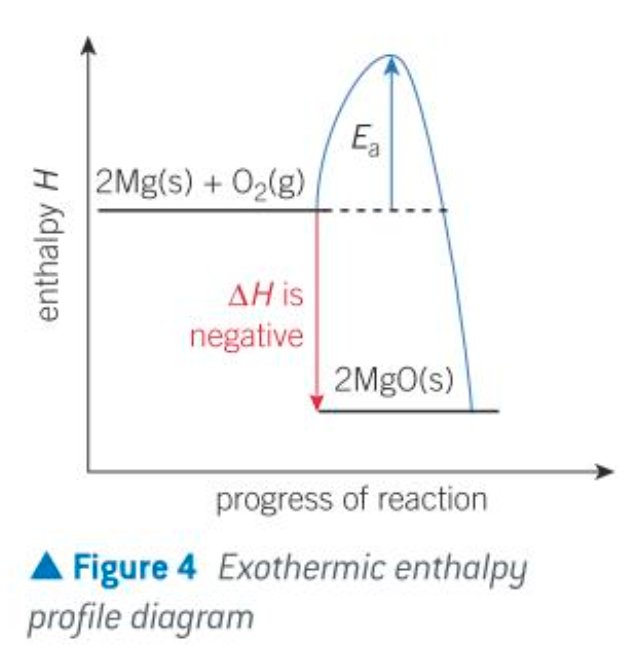
exothermic profile diagram
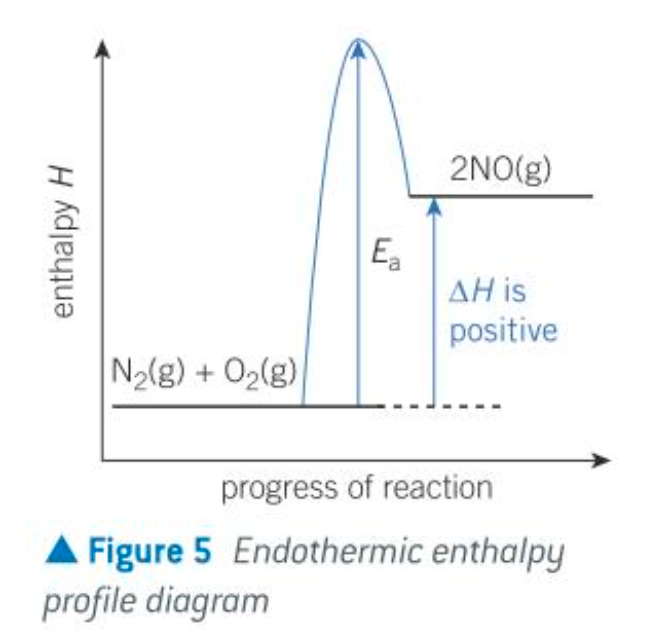
endothermic profile diagram
equation for energy change
Q = m x c x ΔT
C = 4.18
enthalpy def
Enthalpy, H: measure of heat energy in a chemical system.
Enthalpy is sometimes thought of as the energy stored within bonds. It can't be measured, but enthalpy changes can.
chemical system def
Chemical system: atoms, molecules, or ions making up chemicals
ΔH formula
ΔH = H(products) - H(reactants)
ΔH can be positive or negative depending on whether the products contain more or less energy than the reactants.
conservation of energy rule
energy can’t be created or destroyed
examples of conservation of energy
Heat energy is transferred between the system and the surroundings in a chemical reaction.
System: chemicals - the reactants and products
Surroundings: apparatus (e.g. thermometer), the laboratory, everything that isn't in the system
The universe is everything, including system and surroundings.
describe the energy transfer in exothermic reactions
Energy transfer from the system to the surroundings - exothermic, negative ΔH
Chemical system loses energy
describe the energy transfer in endothermic reactions
Energy transfer from the surroundings to the system - endothermic, positive ΔH
Chemical system gains energy
activation energy Ea
Energy input required to break bonds acts as an energy barrier to the reaction, activation energy Ea
why is Ea needed
Atoms and ions held together by chemical bonds
Bonds in reactants broken by input energy
New bonds in products from to complete the reaction
how does size of Ea affect a reaction
Generally, reactions with small Ea take place very rapidly as energy needed to break bonds is readily available from surroundings.
Very large Ea's may mean there is such a large energy barrier the reaction takes place extremely slowly or not at all.
standard conditions
100kPa
298K (25°C)
1moldm-3 for solutions
standard state
ΔrH
Enthalpy change that accompanies a reaction in the molar quantities shown in a chemical equation under standard conditions, with all reactants and products in their standard states.
ΔfH
Enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions, w all reactants and products in their standard states.
Forms 1 mole
ΔcH
Enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of a substance reacts completely with oxygen under standard conditions, w all reactants and products in their standard states.
When 1 mole of a substance completely reacts
ΔneutH
Energy change that accompanies the reaction of an acid by a base to form one mole of H2O(l), under standard conditions, with all reactants and products in their standard states.
1 mole of H2O formed
The value of ΔneutH is the same for all neut reactions.
average bond enthalpy
The energy required to break one mole of a specified type of bond in a gaseous molecule.
Energy is always required to break bonds
Bond enthalpies are always endothermic
Bond enthalpies always have a positive enthalpy value
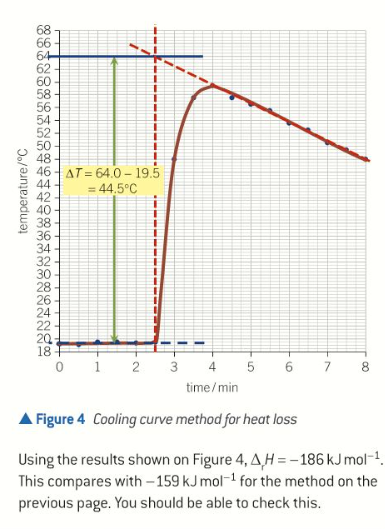
reasons why experimental values of combustion aren’t accurate
Heat loss to surroundings other than the water (beaker and air surrounding flame)
Incomplete combustion of alcohol (CO and C produced instead. C as a black layer of soot on beaker)
Evaporation of alcohol from wick (burner must be weighed as soon as possible after extinguishing flame)
Non-standard conditions (conditions are unlikely to be identical to standard conditions)
Therefore ΔcH is less exothermic than expected
how to make experimental value of combustion more accurate
Use of draught screens and an input of oxygen gas could minimise errors from heat loss and incomplete combustion.
cooling curve shape
limitations of average bond enthalpies
Actual bond enthalpy varies on chemical environment of bond.
An average bond enthalpy is calculated from the actual bond enthalpies in different chemical environments.
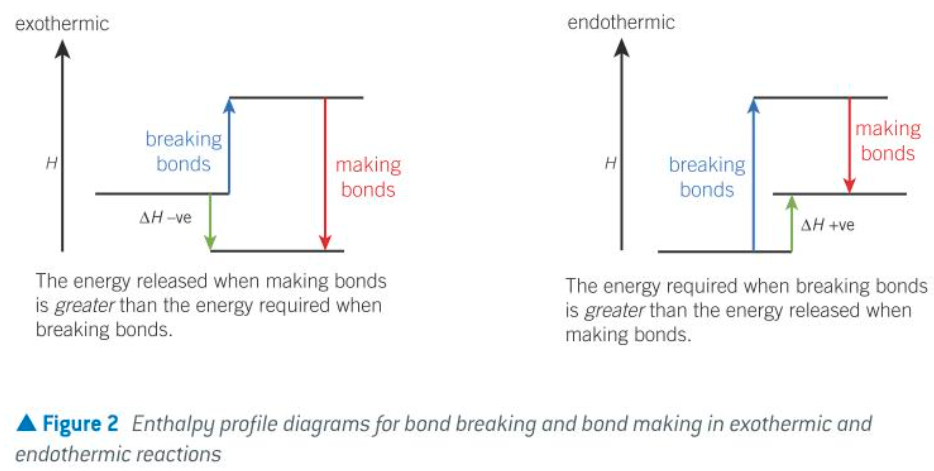
how is energy related to bond breaking/making
Energy is required to break bonds, endothermic
Energy is released when bonds form, exothermic
what does the difference between energy required for bond breaking and energy released by bond making determine
The difference between energy required for bond breaking and energy released by bond making determines whether overall reaction is exo or endothermic.
enthalpy profile diagrams for bond breaking and bond making in exo and endo reactions
enthalpy change from average bond enthalpies
ΔrH = ∑(bond enthalpies in reactants) - ∑(bond enthalpies in products)
what state do all species need to be in when doing calculations w avg bond enthalpies
When doing calculations using avg bond enthalpies all species need to be gaseous molecules.
Therefore calculated ΔrH is NOT a standard enthalpy change.
what does hess’ law state
if a reaction can take place by 2 routes, and the starting and finishing conditions are the same, the total enthalpy change is the same for each route