Glycogen Metabolism
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Energy is stored in mammals in three forms: ___________________
serum glucose, glycogen, and fat
________ is a polymer of glucose.
glycogen
_______________ are referred to as the "end of glycogen molecules" where hydroxyl (OH group) is _____________involved in a glycosidic linkage with another glucose molecule
Non-reducing ends, NOT
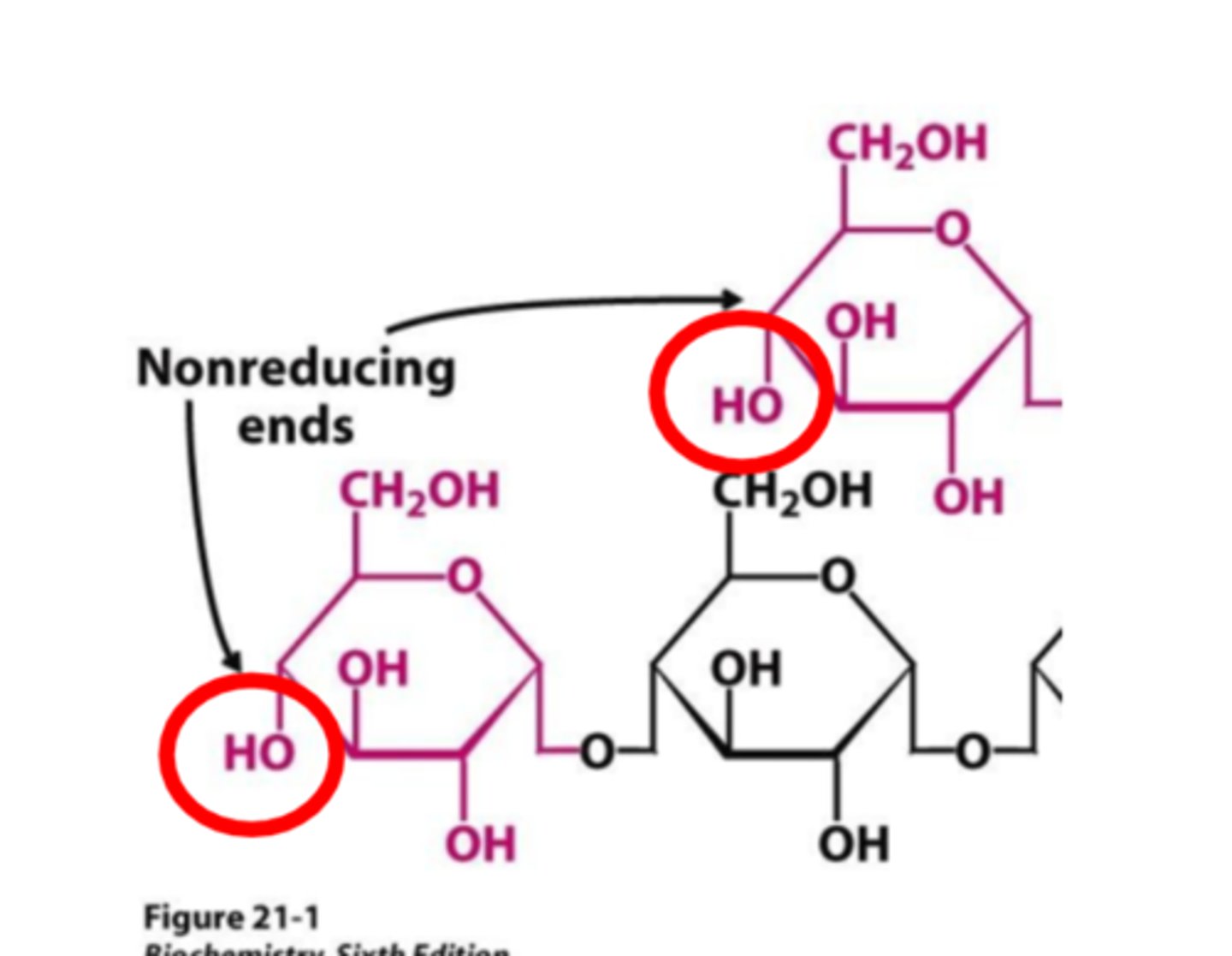
Glycogen is branched to increase the number of ___________________ so that much glucose can be added or removed simultaneously.
non-reducing ends
Glycogen is a highly branched homopolymer of glucose present in _________________ of all tissues.
the cytoplasm
The largest stores of glycogen are in ___________________
the liver and skeletal muscle.
The ________________ breaks down glycogen and releases glucose into the blood to provide energy for the brain and red blood cells.
liver
Muscle glycogen stores are mobilized to provide energy for _________________
muscle contraction.
_________________________, the key enzyme in glycogen breakdown, cleaves its substrate by the addition of Pi to yield glucose 1-phosphate, which is termed _________________
Glycogen phosphorylase, phosphorolysis
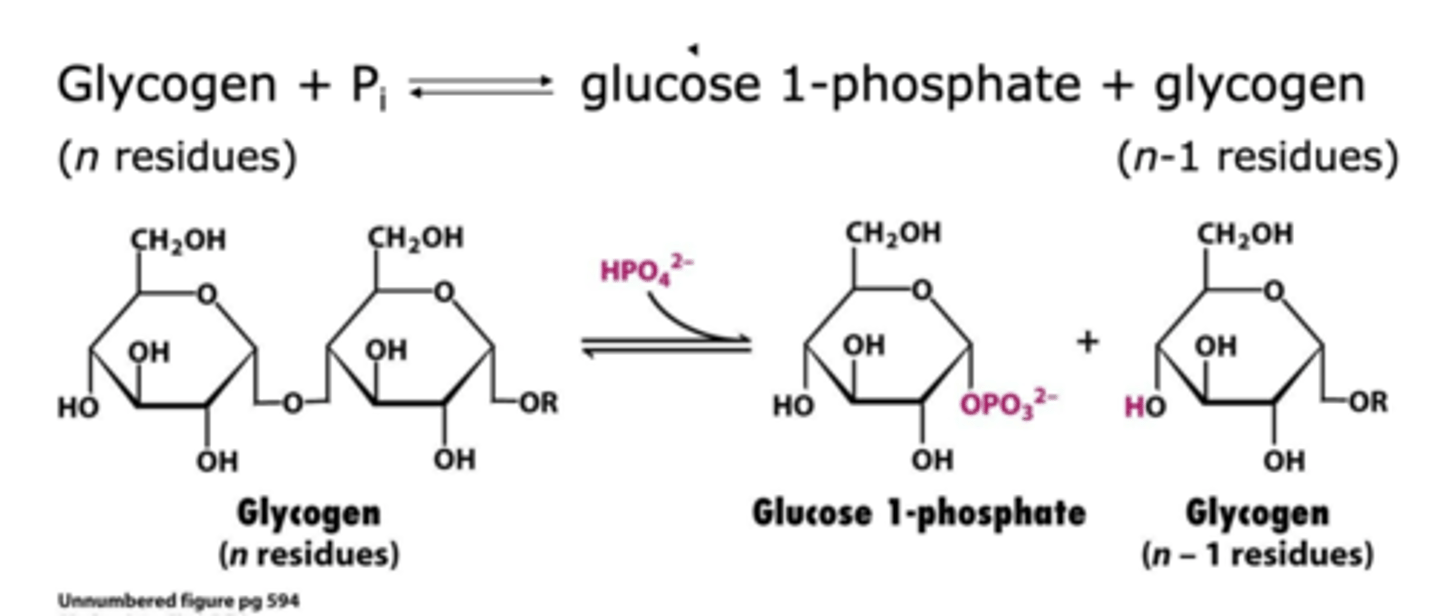
_________________ adds glucose to extend the glycogen polymer
Glycogen synthase
_________________ are active when energy or blood glucose is needed
kinases
__________________ are active when blood glucose is adequate and no energy is need
phosphatases
Glycogenesis Step 1
Hexokinase reaction
- Glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
Glycogenesis Step 2
Phosphoglucomutase reaction
- Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose-1-phosphate
Glycogenesis Step 3
UDP glucose pyrophosphorylase reaction
- Glucose-1-phosphate to UDP glucose
Glycogenesis Step 4
Glycogen synthase reaction
- UDP glucose + glycogen —>> glycogen +1
Glycogenolysis Step 1
Glycogen phosphorylase reaction
- Glycogen and Pi react to become glucose-1-phosphate
Glycogenolysis Step 2
Phosphoglucomutase reaction
- Glucose-1-phosphate becomes glucose-6-phosphate
Glycogenolysis Step 3
Glucose-6-phosphatase
- Glucose-6-phosphate becomes glucose
pentose-phosphate pathway step 1
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase reaction
- Glucose-6-phosphate and NADP+ are reactants, with NADPH and 6-phosphogluconolactone as products
- Irreversible transfer of hydride ion
pentose-phosphate pathway step 2
6-phosphogluconolactonase reaction
- 6-phosphogluconolactone becomes 6-phosphogluconate
pentose-phosphate pathway step 3
6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase reaction
- Oxidative decarboxylation
- 6-phosphogluconate and NADP+ are reactants, with NADPH, CO2, and ribulose-5-phosphate as products
pentose-phosphate pathway step 4
Ribulose-5-phosphate isomerase
- Ribulose-5-phosphate becomes ribose-5-phosphate