Stems & Transport
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Early & Late Wood
early: larger vessels; suggest warm moist growing conditions and more precipitation
late: smaller vessels; drier, cooler conditions; denser tissues
Vascular Plants
plants with true stems
include club mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, and flowering plants
Stems
organs for attachment of leaves, buds, cones, flowers, and fruits
indispensable to plants
Woody Plant Twigs
lateral (axillary) buds, leaf scars from previous year’s leaves, bud scales on terminal buds, bud scale scars marking position of previous years’ terminal buds
Horizontal Stems
stems that lie just above or below ground
Rhizomes
underground stem, usually horizontally oriented, may be superficially rootlike in appearance but that has definite nodes and internodes (the space between nodes)
Corms
vertically oriented (upright), thickened food-storage stem that is usually enveloped by a few papery, nonfunctional leaves; underground storage stem
ex: gladiolus and cyclamen
Tubers
swollen, fleshy underground stem
ex: potato
Runners
stem that grows horizontally along the surface of the ground; typically has long internodes
Stolons
stem that grows vertically below the surface of the ground; it typically has relatively long internodes
Tendrils
thin stems that coil around supporting structures upon contact with other surface that allow plants to grow tall without putting energy into secondary wood production
usually a modified leaf or leaflet and aids the plant in climbing
Thickened Stems
used for water storage in cactus and euphorbs
stems are often main photosynthetic organ
ex: barrel cactus
Programmed Cytoplasmic Death
xylem cells are dead empty pipe-like cells at maturity
tracheid and vessel elements both undergo programmed cytoplasmic death (cytoplasm is removed)
water flow facilitated through the dead, empty cells
Movement of Water & Minerals
move by cohesion-tension
Vascular Bundles
strand of tissue that develops from procambium composed mostly of xylem and phloem; usually enveloped by a bundle sheath
in monocots: scattered
in dicots: in a ring
Fascicular & Interfascicular Cambium
meristematic cells found in stems that differentiate into xylem (inside) or phloem (outside)
inside vascular bundle: fascicular
between vascular bundle: interfascicular
Xylem
narrow tracheids (tapered cell with thick walls containing pits) with wide vessel elements
reinforced with lignin
also has nonlignified areas called pits that allow flow
Phloem Sieve Elements
Individual cells are called sieve tubes; end walls are called sieve plates
sieve cells are ALIVE unlike in xylem: have cell membrane, mitochondria, plastids, and some ER
nucleus and some cell components absent, removal seems essential for flow of phloem sap
Companion Cells
provide materials for sieve elements via plasmodesmata
specialized cell derived from the same parent cell as the closely associated sieve tube member immediately adjacent to it
Sugar Flow in Phloem
from source cell to sink; i.e. from a place of high concentration of sugars to place where sugar will be used
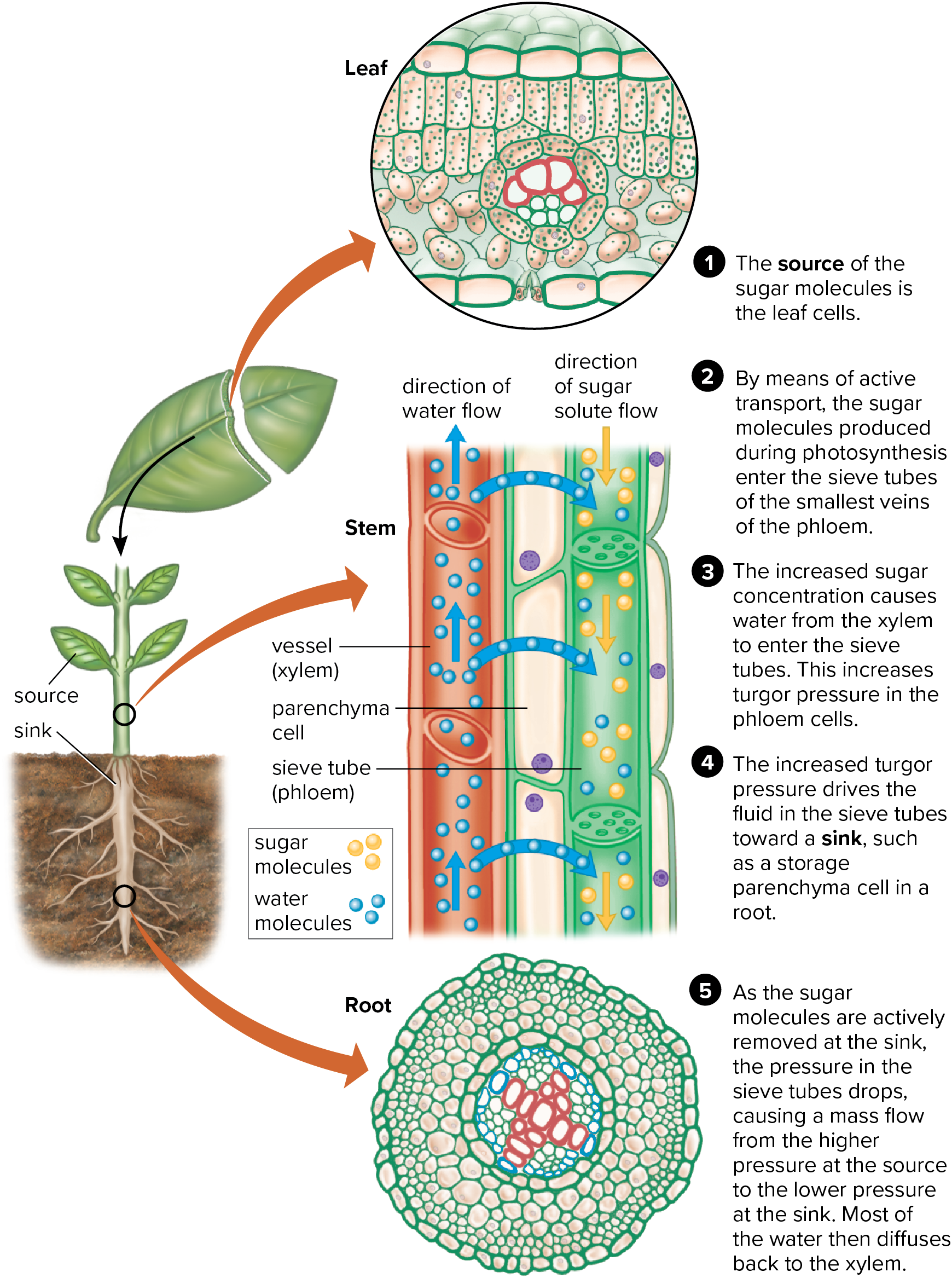
Symplast
the continuous network of the living cytoplasm within a plant that is interconnected by plasmodesmata
Symplastic Loading vs Apoplastic Loading
sym: does not require energy (simple diffusion); sugars loaded directly or via companion cells through plasmodesmata; symplast present
apo: requires some transport energy expense (in the form of ATP); no symplast- sugars loaded from intercellular spaces through the cell membrane
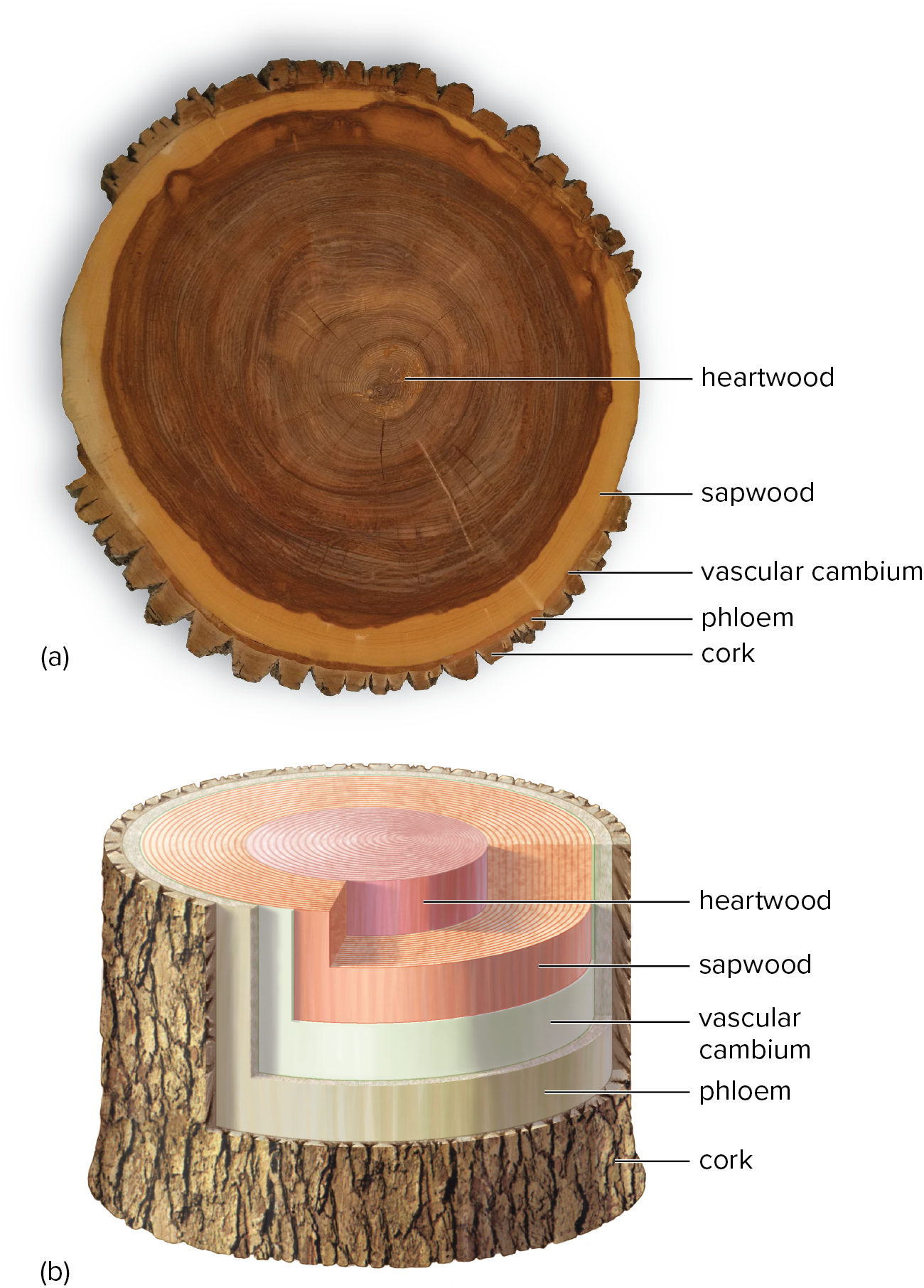
Wood Sections
tyloses: peel-like protusions that clog and prevent conduction of water- these clogs leads to materials accumulating, which darkens the heartwood
heartwood: nonliving, darker-colored wood whose cells have ceased to function in water conduction
sapwood: outer layers of wood that transport water and mineral in tree trunk; usually lighter than heartwood
bark: the outermost layer, also called the periderm
Ray Initials
responsible for transporting food, water, minerals
Cork Cambium
lenticels
periderms