Biology 1000 Exam #1 - Matthew Kearley
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
what is the organization of living organisms
atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ system
describe the characteristics of living organisms
have organization
acquire and use energy
maintain constant internal conditions
have inherited information that determines form and function
are composed of 1 or more cells
respond to their environment
all living organisms are going to reproduce
define science
a collection of unified insights about nature, the evidence for which is an array of facts
science does not deal with what kind of truth?
absolute truth
what are facts
explanations that are thought to be true
which scientific sources are considered to be the most reliable? the least?
most: peer reviewed journals
least: internet
list all of the scientific sources best to worst
peer reviewed journals
reviewed texts
science books
science magazines
newspapers/TV
internet
Explain the difference between a theory and a hypothesis
theory: generalization that explains many observations -- has been tested and researchers have yet to fond evidences that disprove it
hypothesis: tentative, testable explanation for an observed phenomenon
describe the steps of the scientific method and be able to apply the scientific method to a given problem
observation
hypothesis
experiment/test
conclusion
independent variables
factor of the experiment being tested
dependent variable
response of change that occurs due to the independent variable
control sample
a sample where the independent variables are omitted
what is the definition of an element
a substance that can't be reduced to a simpler substance (composed of atoms)
definition of an atom
basic unit of matter composed of protons, electrons and neutrons
describe the particles found in an atom
protons: positive, atomic number
neutrons: neutral, no charge
electrons: negative, more or less than protons
what is the definition of a nucleus
very little space, but contains nearly all the mass
given the atomic number, atomic mass, and charge of an atom, list the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in that atom
protons = atomic mass number
neutrons = mass # - protons
electrons = if negative - more than protons
if positive - less than protons
given the number of electrons, or the atomic # and charge of an atom, determine the # of electrons found in the outer shell of an atom
1) first shell will only have two
2) 8 to make a full shell
3) atomic # = number of shells on the circles
given the mass number and atomic number, determine the number of protons and neutrons
protons = atomic number
neutrons = mass # - protons
define the term isotope
forms of a single element that differs in the number of neutrons
definition of radioisotopes
an isotope that has an unstable nucleus - loss of neutrons from the nucleus
what makes a radioisotope radioactive
it has an unstable nucleus
electrons
very little mass, negative charge (if it's negative then it has one more than proton, if positive it has one less)
ions
atoms that differ in the number of protons and electrons = positive or negative charged atoms
atoms will form _______ to satisfy the requirements of their outer shells
bonds
molecule
number of atoms in a defined spatial relationship
Covalent bonding
bonds in which atoms share electrons positive charge - lower number of electrons than the atomic number
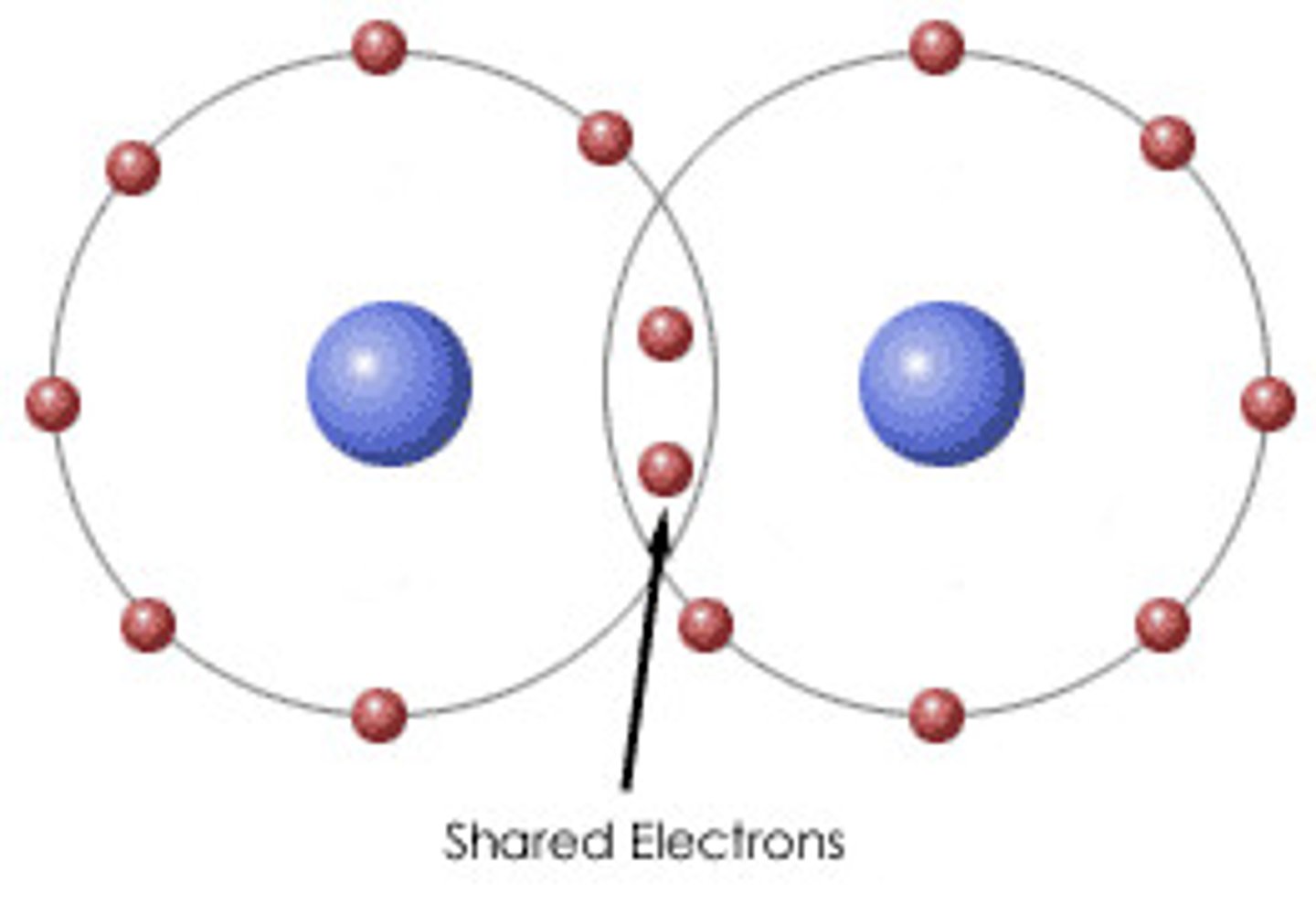
ionic bonding
atoms bonded through attraction of oppositely charged particles (ions) - exchange electrons
polar covalent bonding
shared electrons spend more time neat the larger nucleus, creates a negative charge on 1 end of the molecule
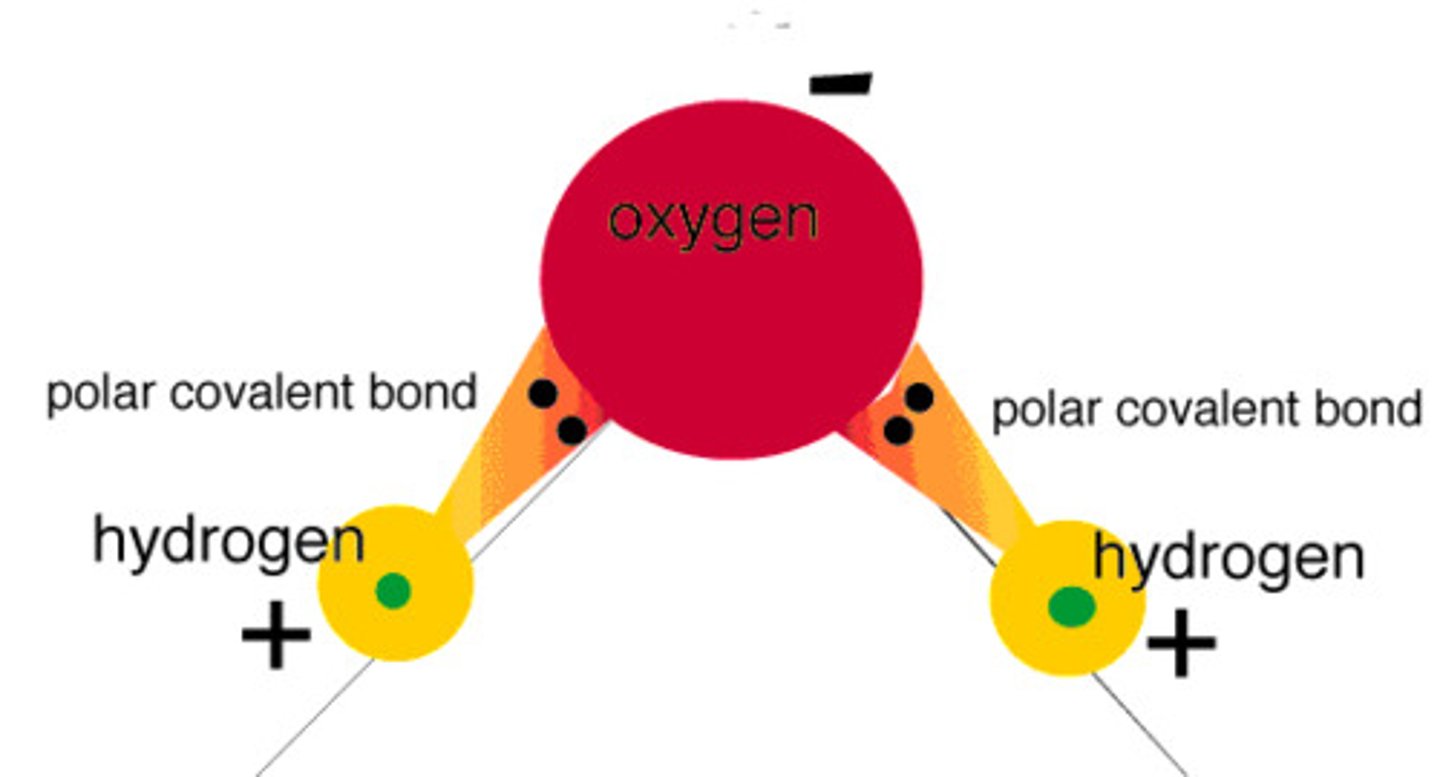
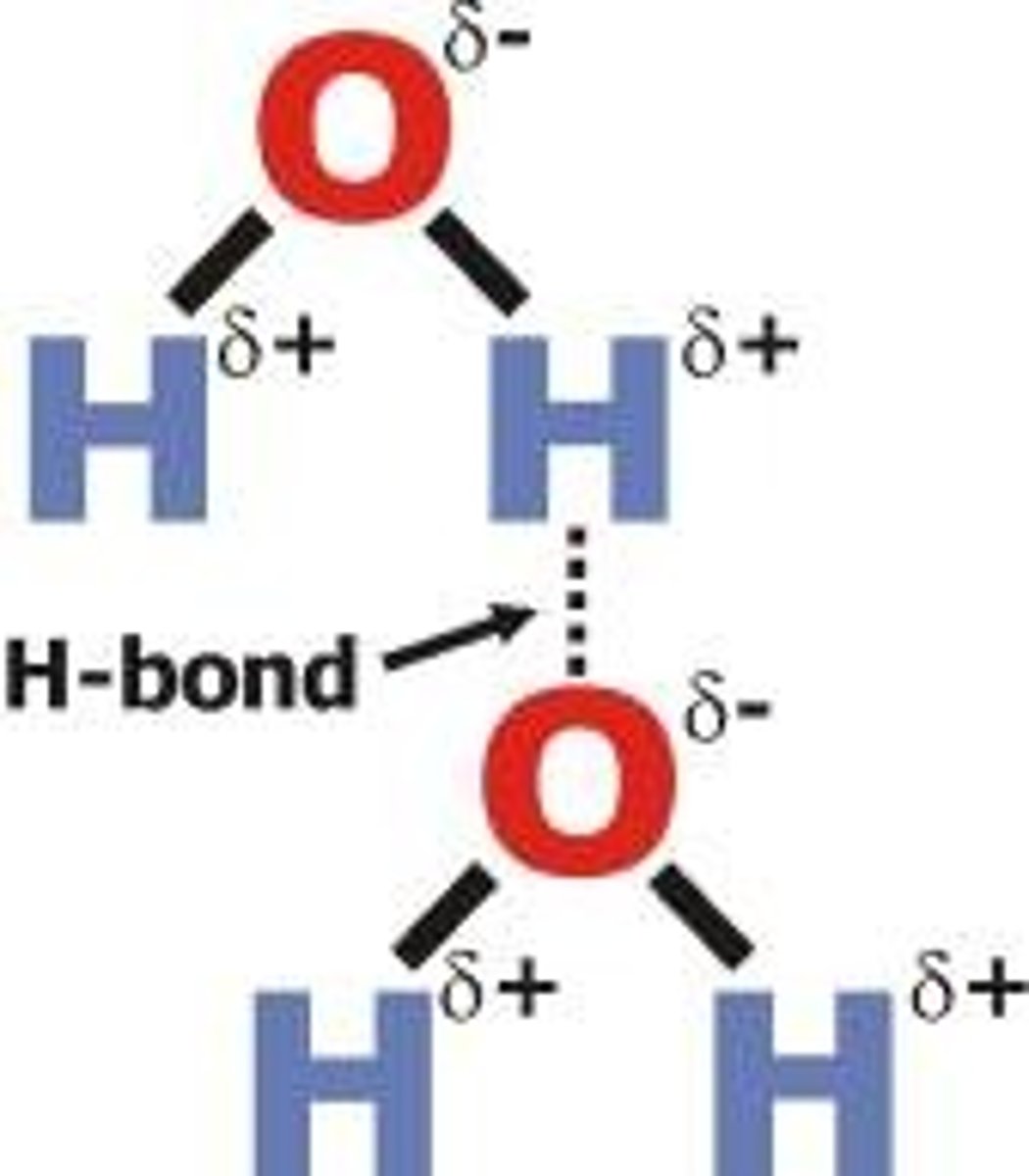
hydrogen bonding
formed when partially positive hydrogen atom in a polar cobalt bond is attracted to a partially negative atom in antlers polar covalent bond
How do solute, solution, and solvent relate to one another?
they all have to work together to figure out which substance is which.
Solution
mixture of two or more substances
solute
substance that is dissolved in a solvent
solvent
the substance in which a solute is dissolved
describe the properties of water
provides the basis for life
freezes at 0 degrees celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit): ice is less dense than water
has a high specific heat
buffers climates
within a water molecule it is __________ bonds that bond hydrogens to oxygen, and then within water itself _________ bonds water molecules to other water molecules
polar covalent; hydrogen
surface tension
water molecules bond to each other more strongly the to air (hydrogen bonds create surface tension)
hydrophilic molecules
interact with water (ex. salt)
hydrophobic molecules
do not interact with water (ex. lipid)
how are acids and bases defined. How do H+ and OH- ions determine pH? How is pH important to living organisms
acids lower pH and bases raise the pH living organisms usually thrive in a pH of 6-8
acids
lower pH
bases
raise pH
acidosis
lower pH levels in their blood, makes people sick
alkalosis
moved acid, higher pH levels
why is carbon so important in the molecules that make up living organisms?
it keeps things going
water intoxication
too much water can kill you and cause this
if lime (a base) is spread on a field with acidic soil, the the pH of the soil will....
increase
how many covalent bonds can carbon contain
4
if you add ammonia (base) to a neutral solution, the number of OH- ions will....
increase
what are hydrocarbons
a chain of carbons and hydrogens
what are functional groups
the groups of atoms in an organic molecule that usually participate in chemical reactions
how are functional groups important in chemical reactions? Diagram the following functional groups: Hydroxyl, Carboxyl, Amino, Phosphate
they participate in chemical reactions
most organic molecules are what type of units
repeated units
when molecules bond to one another and produce water what is it called
dehydration synthesis
when a more complex molecule is spilt into simpler molecules and water is required it is called what
hydrolysis
when you chew on bread for awhile what begins to happen
it begins to taste sweeter
what is a monomer
a single unit
what is a polymer
string of monomers
describe the characteristics or carbohydrates
contain C,H, and O
monosaccharide (monomer)
polysaccharides (polymer)
how are carbohydrates important to living organisms
they provide many important things
what are the differences between dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis?
dehydration synthesis: makes non water into water
hydrolysis: makes water into non water
what are the 4 main things in a polysaccharide
starch
glycogen
cellulose
chitin
what is a starch
carbohydrate storage in plants, digestible by animals
what is glycogen
how animals store carbohydrates
what is cellulose
primary structural component of plants (provides rigidity). Animals can't digest, only bacteria can
what is chitin
strengthens the exoskeleton of many organisms (ex. Insects and arthropods)
what are the characteristics of lipids?
composed of C,H, O
hydrophobic
energy storage, insulation
what is fat
a type of lipid (fatty acids + glycerol)
what is a fatty acid
a carboxyl and a long hydrocarbon chain
how are lipids important to living organisms?
the store energy
describe the different type of lipids
fat: saturated and unsaturated
steroids: 4 linked carbon rings
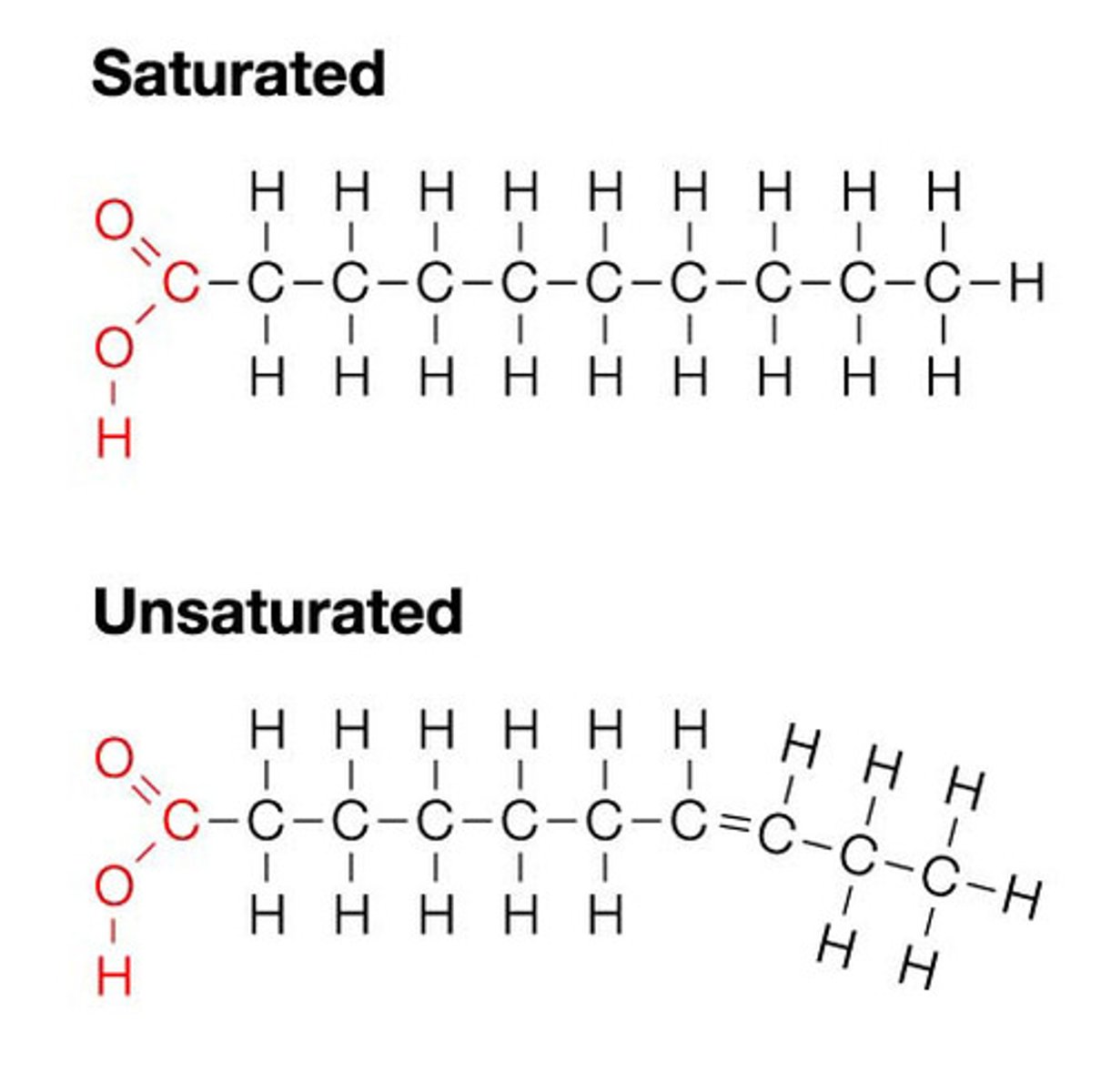
what are the differences between saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids?
saturated: all C-C bonds are single bonds (donuts, fries)
unsaturated: at least one C-C bond is a double bond (avocados, fish)
what is a phospholipid
a type pf lipid; makes up the outer membranes of cells
what are the characteristics of proteins?
they consists of polypeptide chains made up of amino acids
what is a protein
polymer commode of many amino acids
list 4 things about proteins
all amino acids have an amino group and a carboxyl group attached to a central carbon
proteins consist of polypeptide chains made up of amino acids
protein functions are numerous and depend on the proteins shape
change in the environment can change the shape of a protein = denature the protein
how are proteins important to living organisms?
they transport lipids in and out of the bloodstream
what is a lipoprotein
a capsule surrounded by a globule of lipid
why is a lipoprotein important
it transports lipids in and out of the bloodstream
LDL - low density lipoprotein ( carry cholesterol to coronary arteries of the heart)
HDL- high density lipoprotein ( carry cholesterol to liver - away from heart)
You want a high LDL and a low HDL
what are the functions of DNA and RNA?
RNA: takes DNA encoded instructions to the sites in cells where proteins are put together
DNA: contains the instructions to the sites in cells where proteins are put together
DNA and RNA are composed of _______
nucleotides
nucleotides are composed of what
a phosphate groups, a 5 carbon sugar, and a nitrogen base ( Guanine, Cytosine, thymine, and adenine)
what does a fatty acid look like
this-
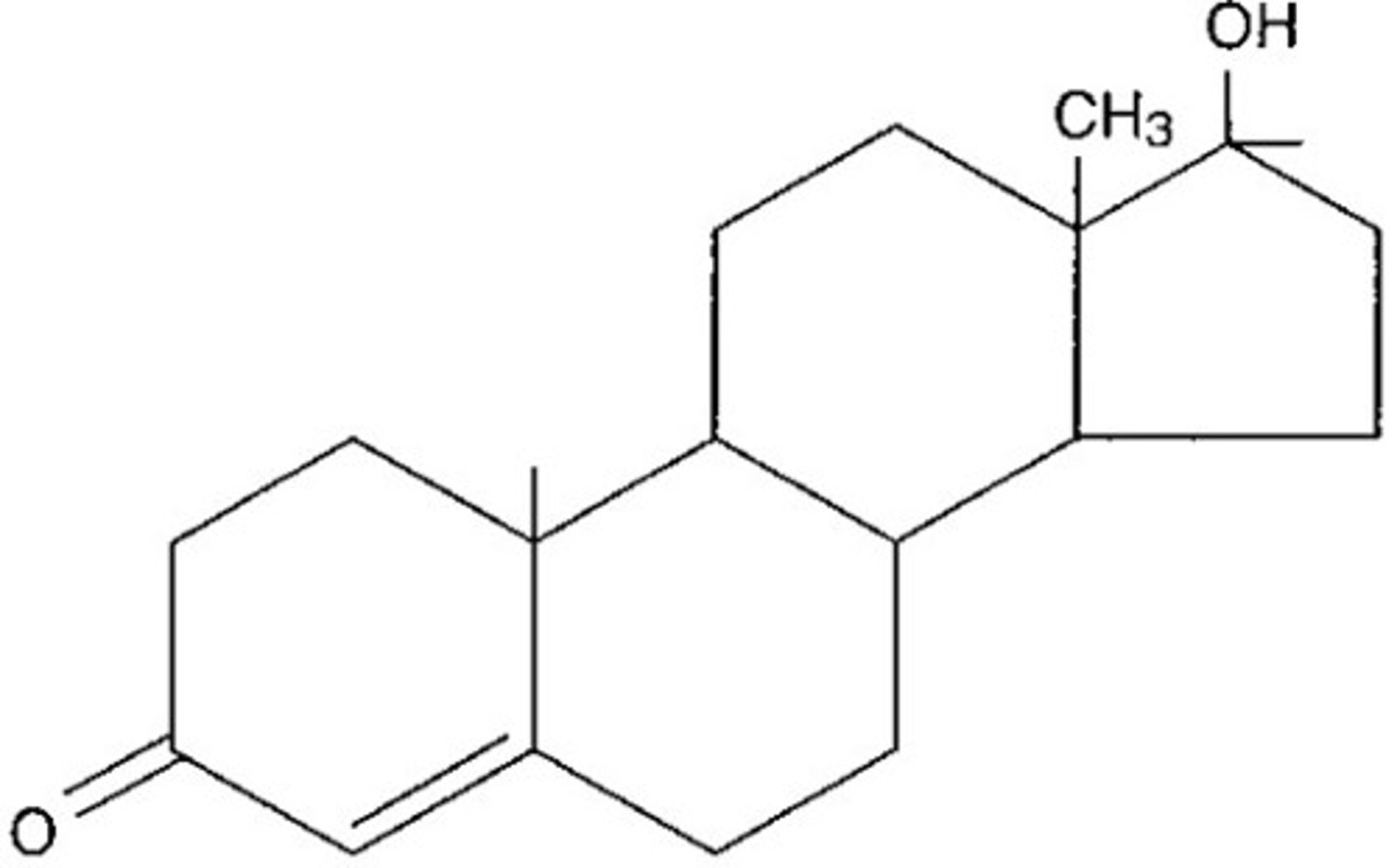
what does a steroid look like
this:
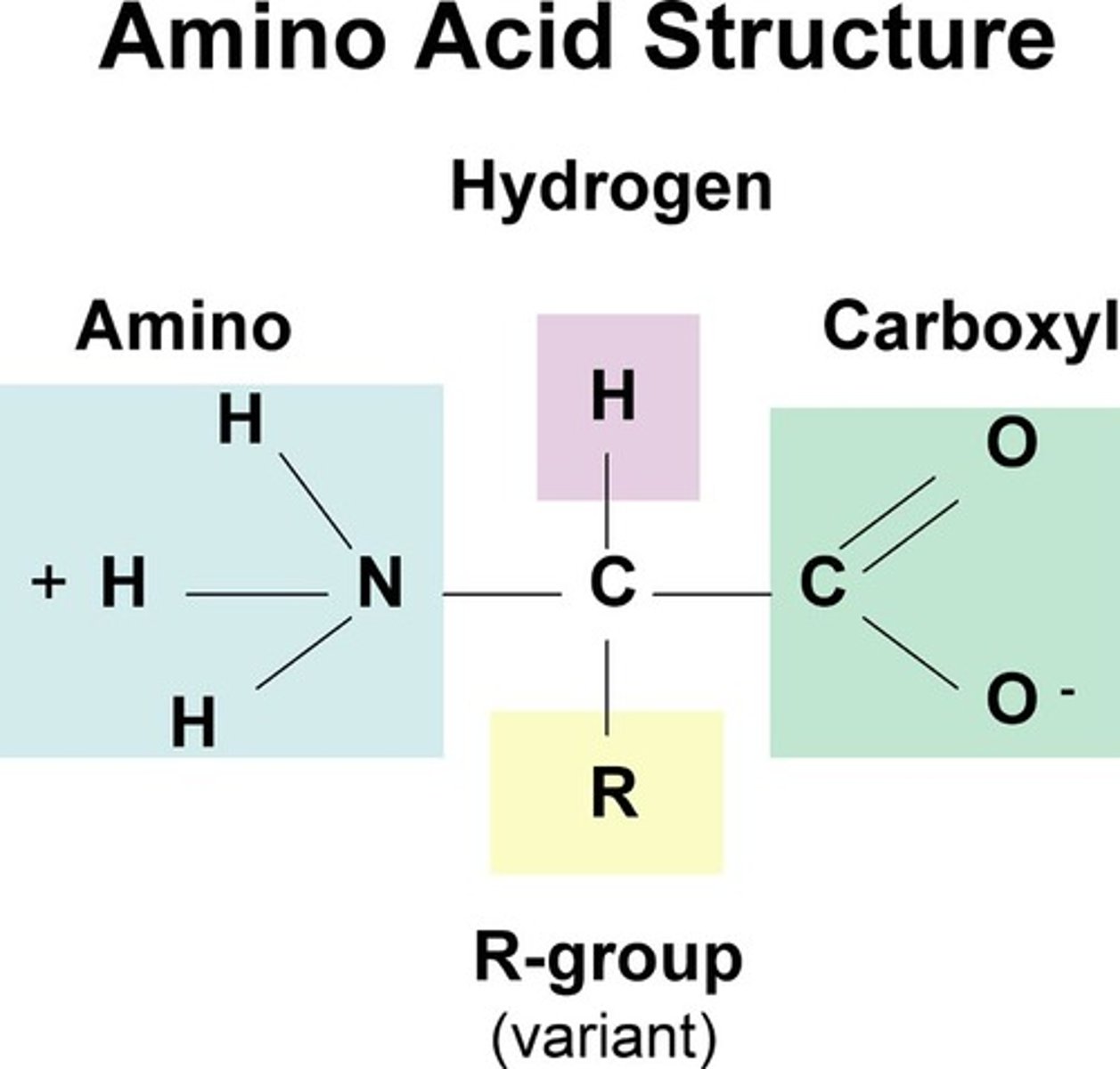
what does an amino acid look like
this
prokaryotic cells
bacteria, no nuclei, single celled, many don't use oxygen, no organelles
eukaryotic cells
everything else, nuclei, many are multicellular, most use oxygen, organelles
what is a plasma membrane
outer boundary of the cell
what is cytoplasm
region inside the plasma membrane and outside of the nucleus
what are organelles
structures within the cells which carry out specific functions
what is a nucleolus
it is within the nucleus - RNA and proteins combine to make ribosomal subunits
what is cytosol
fluid in which cell's organelles are immersed outside of the nucleus
what is a ribosome
a structure that translates RNA to proteins
list and describe the components of the cytoskeleton
internal scaffolding that maintains the shape of a cell
distinguish between plant and animal cells. What structures do they share, which are different?
plant cells: starch is a storage, cellulose is their primary structure, chitin strengthens the exoskeleton
animal cells: starch is digestible, animals can't digest cellulose
what is the Golgi complex
consists of membranous sacs. received proteins from the ER, modifies them and then ships them off to their final destination
what is a vesicle
tiny membrane sacs in the cytoplasm
what is a lysosome
organelles that contains enzymes that break down organelles and return them to the cytosol so they can be reused -- also digest nutrient
what is a peroxisome
vesicle containing enzymes which break down fatty and amino acids
what is a mitochondria
it converts energy found into a molecular form ATP that the cell can use