Viruses, Viroids, and Prions: Key Features and Comparisons
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Obligatory intracellular parasites
Viruses that require living host cells to multiply.
Virion
Complete, fully developed viral particle.
Nucleic acid
Viral genome that is either DNA or RNA, never both.
Capsid
Protein coat made of capsomeres (subunits).
Envelope
Lipid, protein, and carbohydrate coating on some viruses.
Spikes
Projections from the outer surface of some viruses.
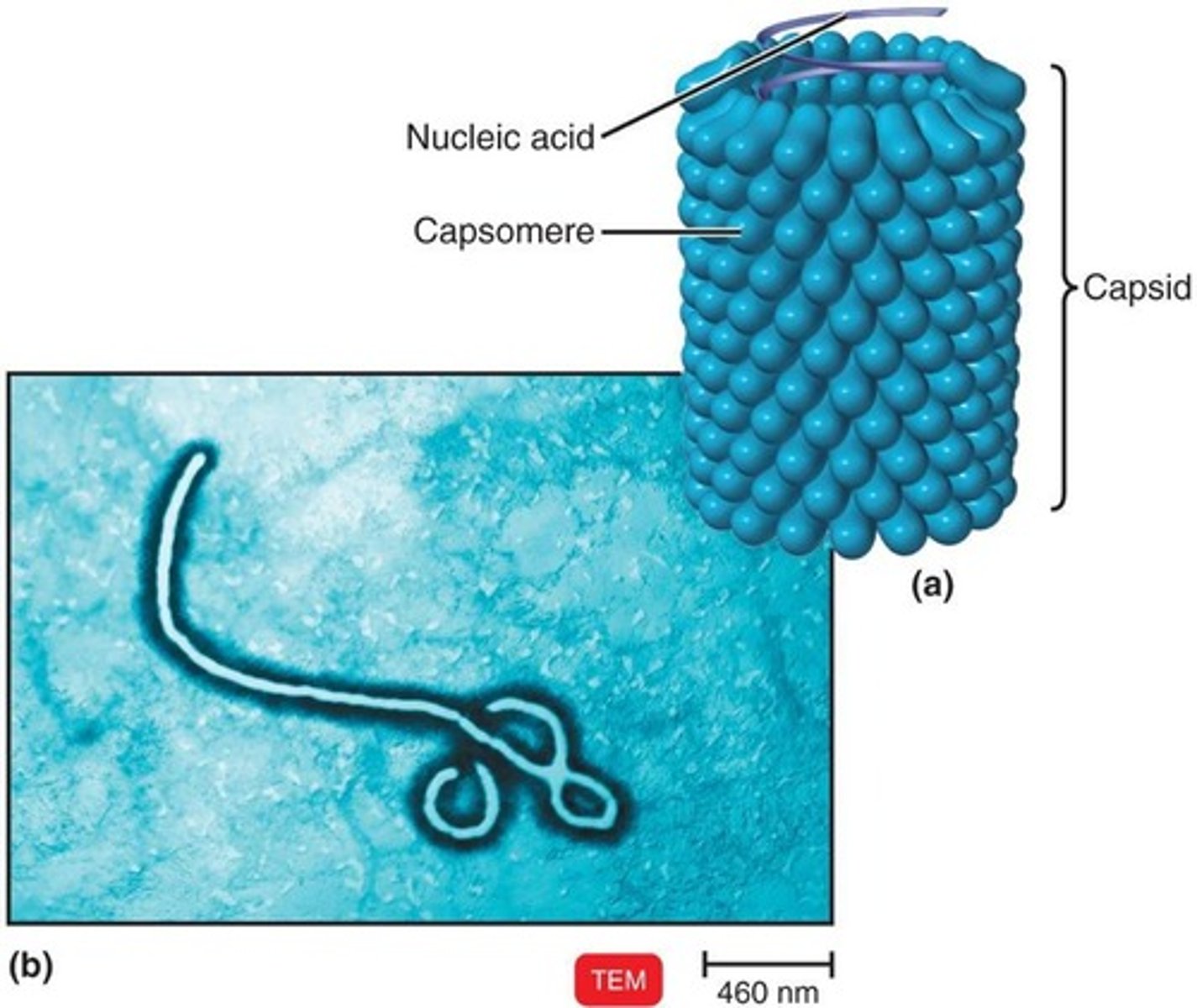
Helical Viruses
Viruses with a hollow, cylindrical capsid that is helical.
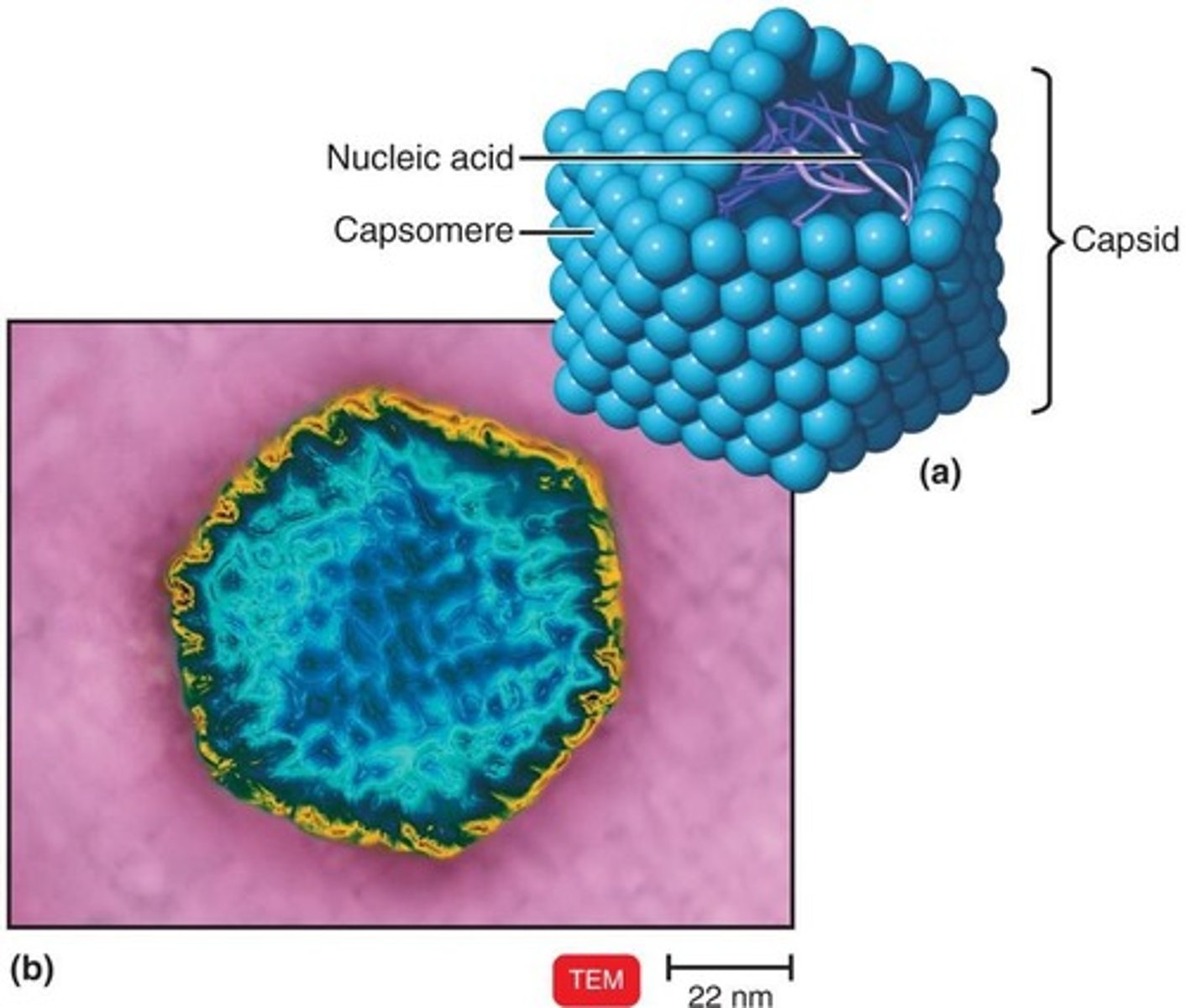
Polyhedral Viruses
Most are an icosahedron (20 triangular facets and 12 corners).
Enveloped Viruses
Viruses that are roughly spherical and have an envelope.
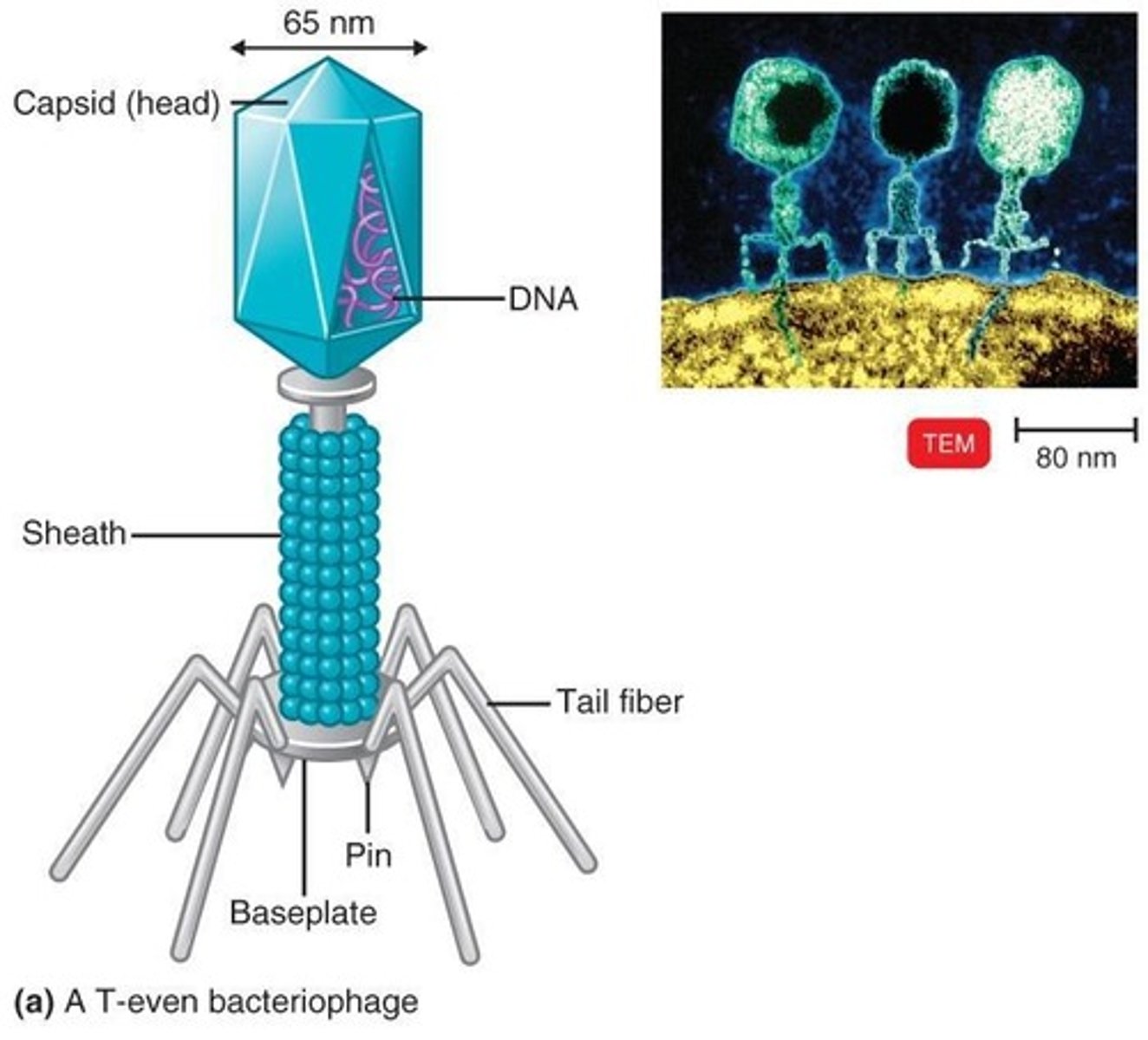
Complex Viruses
Viruses with complicated structures, such as bacteriophages.
Baltimore classification system
Classification based on virus's nucleic acid and how its mRNA is produced.
Group I
Double-stranded DNA viruses.
Group II
Single-stranded DNA viruses.
Group III
Double-stranded RNA viruses.
Group IV
(+) sense single-stranded RNA viruses.
Group V
(-) sense single-stranded RNA viruses.
Group VI
Retroviruses (RNA reverse-transcribing viruses).
Group VII
Pararetroviruses (DNA reverse-transcribing viruses).
Plaques
Clearings on a lawn of bacteria on the surface of agar formed by bacteriophages.
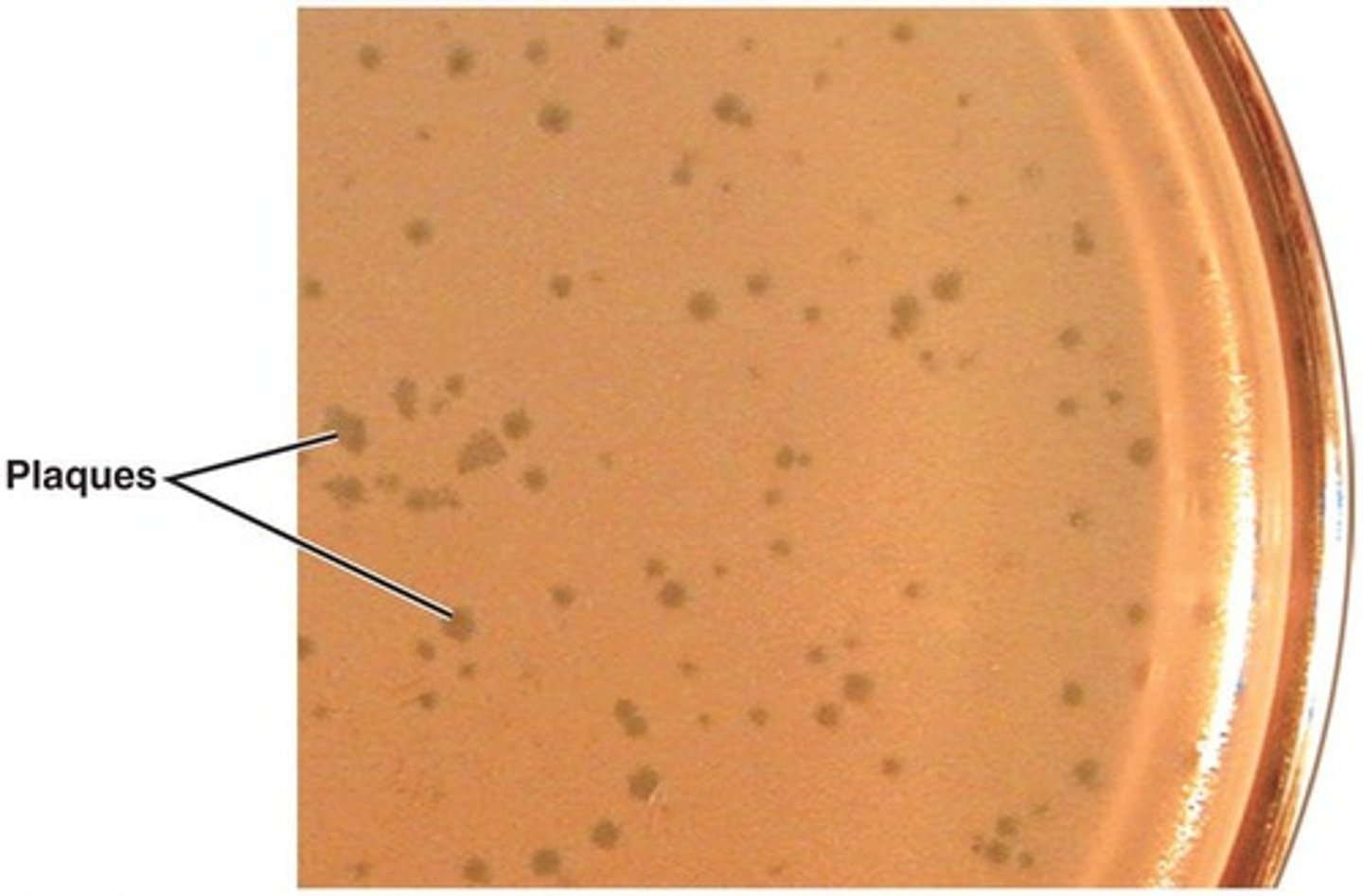
Plaque-forming units (PFU)
A measure of the number of infectious virus particles.
Cytopathic effect (CPE)
Changes or deterioration of cells in a cell culture due to viral infection.
Primary cell line
Cells suspended in a nutrient solution that reproduce to form a monolayer.
Diploid cell lines
Cell lines derived from human embryos maintained for about 100 generations.
Continuous Cell Lines
Cell lines derived from transformed (cancerous) cells that can be maintained indefinitely.
ELISA
A serological test to detect and identify viruses by their reaction with antibodies.
PCR
A method to identify viruses by detecting their nucleic acids.
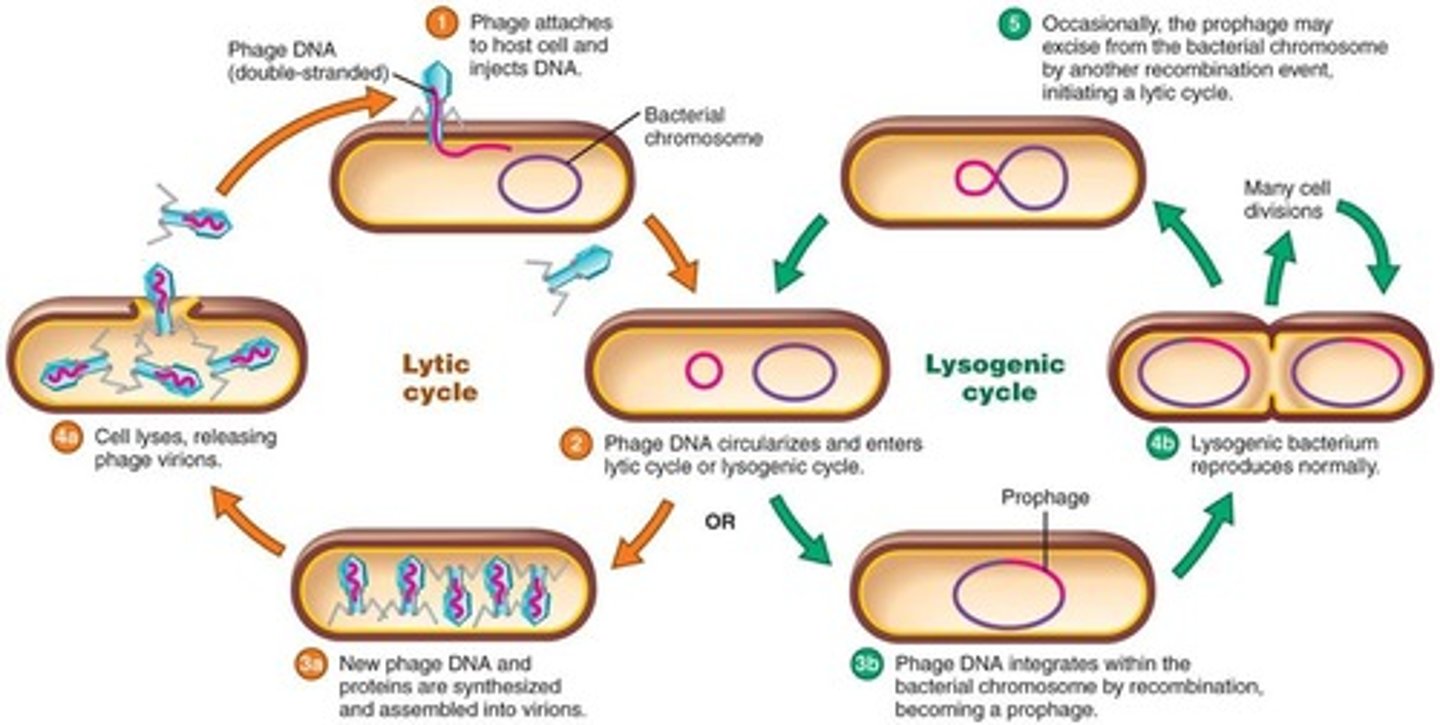
Lytic Cycle
A mechanism of multiplication where the phage causes lysis and death of the host cell.
Lysogenic Cycle Step
Phage DNA is incorporated in the host DNA.
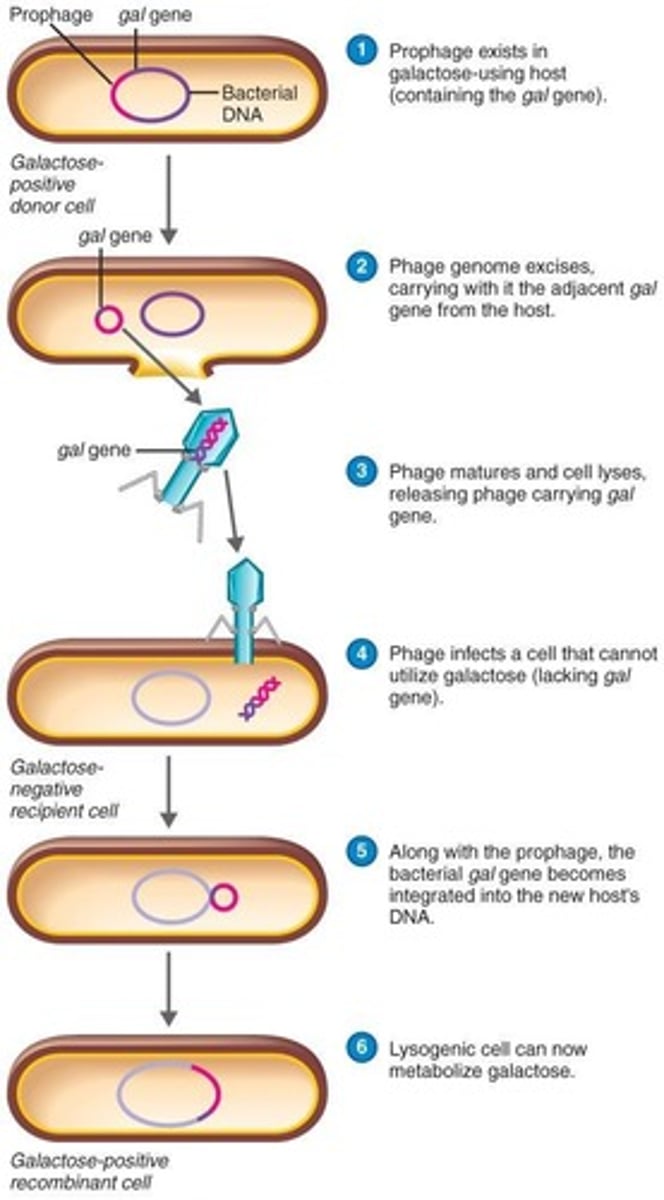
Phage conversion
A process where the host cell acquires new properties due to the presence of phage DNA.
Specialized transduction
A form of transduction where specific bacterial genes are transferred by a phage.
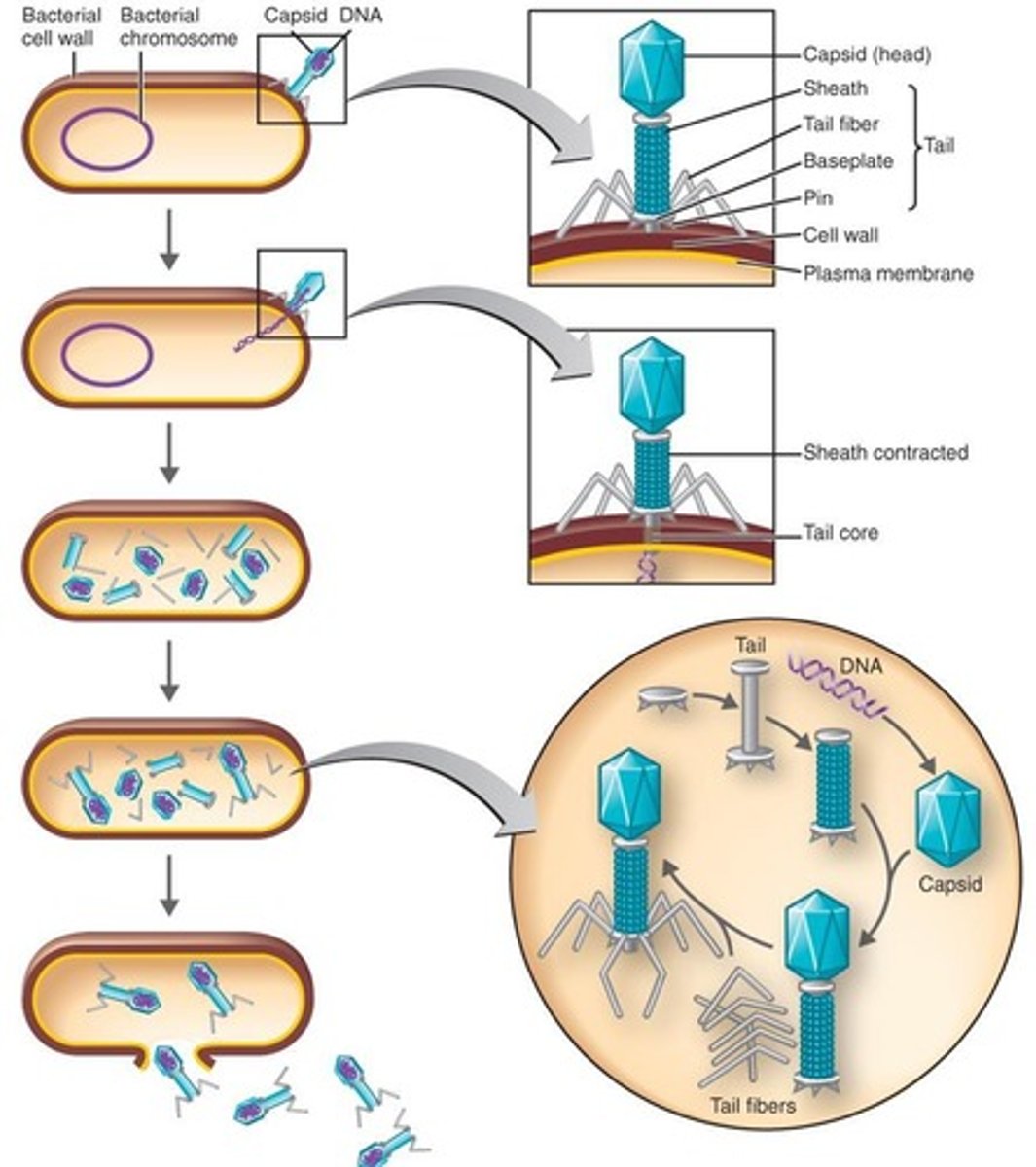
Attachment
Phage attaches by the tail fibers to the host cell.
Penetration
Phage lysozyme opens the cell wall and the tail sheath contracts to force tail core and DNA into the cell.
Biosynthesis
Production of phage DNA and proteins while host cell protein synthesis is halted.
Maturation/Assembly
Assembly of phage particles.
Release
Phage lysozyme breaks the cell wall.
Lambda Phage (𝜆)
Not all phages complete the lytic cycle; they can enter the lysogenic cycle.
Temperate Phages
Phages that can choose between the lytic and lysogenic cycles.
Lambda Phage
Adsorb and penetrate but not induce expression.
Prophage
The viral genome inserts into bacterial genome and becomes inactive; the cell is not lysed.
Induction
Can occur resulting in activation of lytic cycle, typically triggered by host cell stress.
Lysogenic Cycle
Lysogenic host cells are immune to reinfection by the same phage.
Phage Conversion
Host cell exhibits new properties encoded by the prophage DNA.
Specialized Transduction
Bacterial genes transferred to another bacterium via a phage, changing genetic properties of the recipient bacteria.
Attachment/Adsorption
Binding of virus to specific molecules on the host cell.
Genome Entry/Penetration
Viral genome enters the host cell, occasionally in an endosome.
Uncoating
Viral genome is released from the capsid.
Synthesis and Assembly
Viral components are produced and new viral particles are constructed.
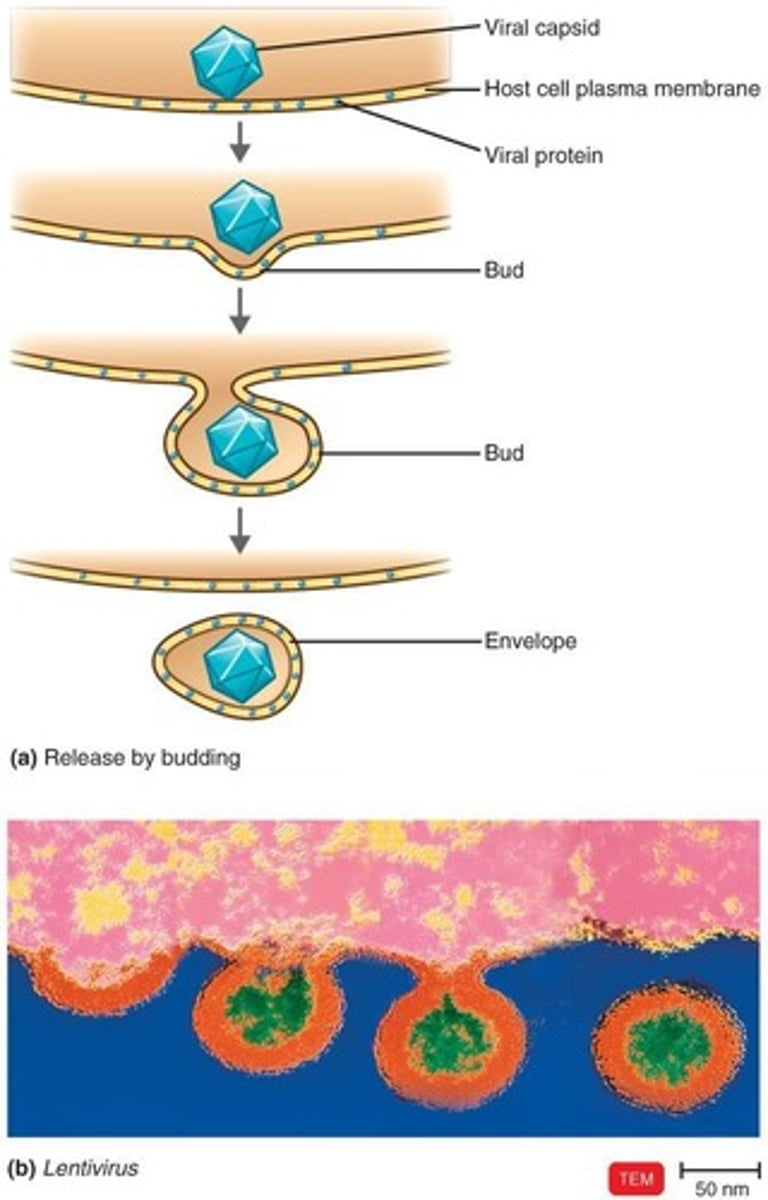
Exit and Transmission/Release
Assembled viruses are released by budding (enveloped viruses) or cell lysis (naked viruses).
Biosynthesis of DNA Viruses
Replicate their DNA in the host nucleus, using host enzymes.
Adenoviridae
Double-stranded DNA, nonenveloped; causes respiratory infections in humans and tumors in animals.
Poxviridae
Double-stranded DNA, enveloped; causes skin lesions including smallpox virus and MPOX virus.
Herpesviridae
Double-stranded DNA, enveloped; includes HHV-1 and HHV-2 causing cold sores, HHV-3 causing chickenpox.
Papovaviricetes
Double-stranded DNA, nonenveloped; includes Alphapapillomavirus causing warts and some species that can transform cells and cause cancer.
Hepadnaviridae
Double-stranded DNA, enveloped; includes Hepatitis B virus which uses reverse transcriptase to make DNA from RNA.
Biosynthesis of RNA Viruses
Virus multiplies in the host cell's cytoplasm using RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
Coronaviridae
Includes SARS-CoV-2 which causes COVID-19; single-stranded RNA, + strand, enveloped.
Togaviridae
Single-stranded RNA, + strand, enveloped; includes Alphavirus transmitted by arthropods.
Rhabdoviridae
- Strand Single-stranded RNA; includes Lyssavirus causing Rabies.
Picornaviridae
+ Strand Single-stranded RNA, nonenveloped; includes Enterovirus (Poliovirus) and Rhinovirus (Common cold).
Reoviridae
Double-stranded RNA, nonenveloped; includes Reovirus and Rotavirus.
Retroviruses
Single-stranded RNA, produce DNA using reverse transcriptase.
Oncogenic Viruses
Viruses that can cause cancer, such as Adenoviridae and Herpesviridae.
Latent Virus
Remains in asymptomatic host cell for long periods; all herpesviruses are capable of latency.
Persistent Viral Infection
Occurs gradually over a long period and is generally fatal.
Viroids
Short pieces of naked RNA that cause diseases in plants.
Prions
Proteinaceous infectious particles that cause neurodegenerative diseases.
PrPC
Normal cellular prion protein found on cell surfaces.
PrpSC
Scapie protein that accumulates in the brain, forming plaques.