Midterm 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:35 PM on 3/12/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
Bud scales protect ___________ plant’s dormant shoot apical meristems.
perennials
2
New cards
Bracts are associated with ___________ and inflorescences.
flowers
3
New cards
Tendrils are ___________ modifications used for climbing.
climbing
4
New cards
A spine is a pointed modified ___________.
leaf
5
New cards
A thorn is a pointed modified ___________.
stem
6
New cards
A modified leaf that stores starch and sugar underground is referred to as a ___________.
bulb
7
New cards
Asexual reproduction results in genetically ___________ plants produced via mitosis.
identical
8
New cards
Meiosis reduces chromosomes by ________ and creates gametes.
half
9
New cards
During fertilization, haploid cells recombine to form a ___________ zygote.
diploid
10
New cards
Gene variations can occur through ___________ which mixes up alleles.
crossing over
11
New cards
The process of crossing over occurs during ___________ I of meiosis.
prophase
12
New cards
The plant structure that supports the flower head is called the ___________.
pedicel
13
New cards
The stigma is a part of the ___________ reproductive organ.
female
14
New cards
The ___________ life cycle alternates between diploid and haploid generations.
alterations of generations
15
New cards
Pollen grains land on the ___________ during pollination.
stigma
16
New cards
The process whereby the egg plus sperm forms a ___________ zygote.
diploid
17
New cards
Imperfect flowers can be classified as ___________ or monoecious.
dioecious
18
New cards
Outcrossing increases genetic ___________ by increasing the number of alleles present.
variation
19
New cards
Seeds that remain in the pericarp after maturity are classified as ___________.
indehiscent
20
New cards
The first root that emerges during seed germination is called the ___________.
taproot
21
New cards
Seeds will not germinate in favorable conditions to prevent ___________.
vivipary
22
New cards
Light is required for seed germination in a process called ___________ promotion.
light
23
New cards
Primary growth occurs at the ___________ of roots and shoots.
meristems
24
New cards
Respiration is only __________% effective in capturing energy stored in glucose.
34
25
New cards
In the absence of oxygen, the electron transport chain will __________ completely.
stop
26
New cards
Fermentation converts NADH to NAD+ to produce ___________.
ethanol
27
New cards
Phospholipids are key components of ___________ membranes.
cell
28
New cards
oldest flowers are at the bottom of the plant and youngest flowers continue to grow vertically
racemose inflorescense
29
New cards
oldest flowers are at the top and younger flowers grow beneath them
cymose inflorescense
30
New cards
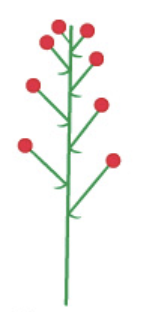
raceme
31
New cards
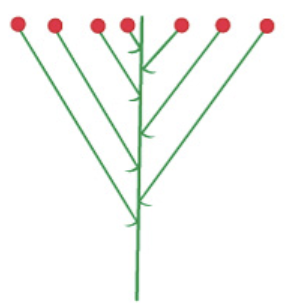
corymb
32
New cards
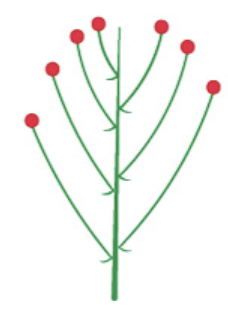
corymbose raceme
33
New cards
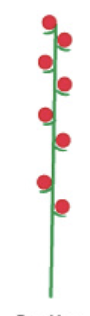
spike
34
New cards

catkin
35
New cards

spadix
36
New cards
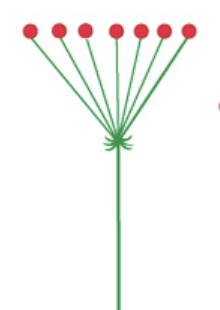
simple umbel
37
New cards
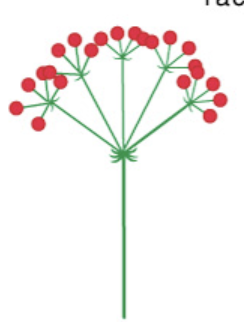
compound umbel
38
New cards
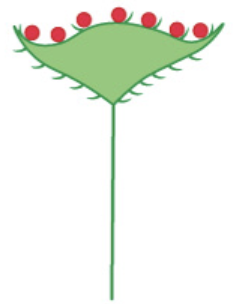
capitulum
39
New cards
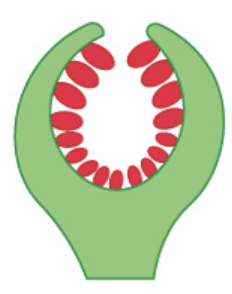
hypanthodium
40
New cards
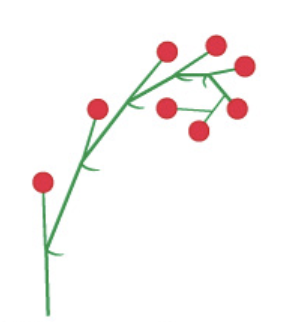
umparouse cyme
41
New cards
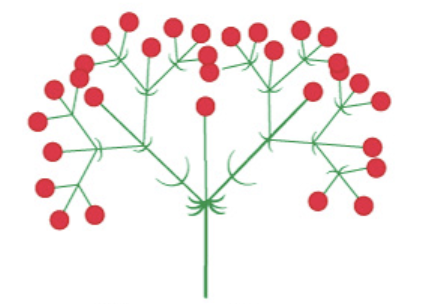
biparous cyme
42
New cards
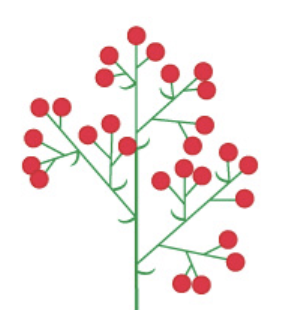
multiparous cyme