Topic 22 - The Geography and Importance of Soil
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
How do soils form?
Weathering - All rocks on Earth are exposed to natural processes that cause them to break down
What happens to this pile of mineral and rock fragments?
It gets carried or transported away and deposited elsewhere to become new sedimentary rocks; OR it accumulates and forms soils at Earth's surface
what is regolith?
loose inorganic material that accumulates as rocks and minerals break down
what is soil?
the accumulation of weathered rock material, plus organic material, water, and air.
What makes something a true soil?
It must be able to grow and support plant life
What is organic material? Where does it come from?
Dead leaves, twigs, branches, etc. from plants, plus dead insects and animals, sometimes feces
what is the best makeup for plant growth?
45% mineral matter, 5% organic matter, 50% pore spaces
Why do you need so much pore space for a plant to grow?
Think what happens when you put a plant into soil either in a container or in the ground. If you mush down the soil too much, no water or air can get into the soil. Pore space is absolutely needed
why do we describe soil as having a profile?
a distinct arrangement of layers that each represent a portion of the soil
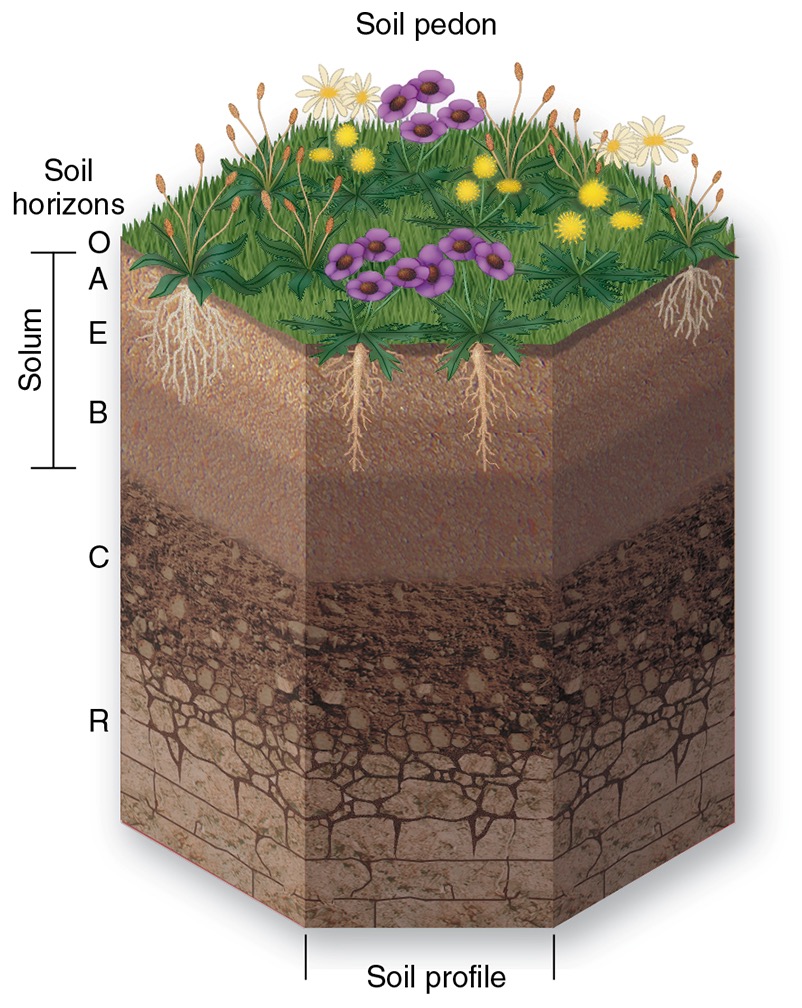
what is a soil profile?
A well-developed soil has a characteristic layering formed over a long period of time. Except for the bottom layer of material, all of the layers form at the same time
what are the three most important layers?
top two layers and the bottom layer
what is the top layer?
O-Horizon

what is the O-Horizon?
at the very top. Made of loosely compacted and partly decayed organic material (organics)
what does the O-Horizon provide?
This provides all of the elements and minerals needed for growth
what is the second layer?
A-Horizon

what is the A-Horizon?
this is the second layer but the true start to the soil profile. It is dark in color due to the organic content. Plants grow in this horizon.
what is the A-Horizon commonly called?
commonly called Topsoil, this is what you buy at the garden center.
what is the bottom layer?
R-Horizon

what is the R-Horizon?
the Parent Material - the rock layer (R) solid rock from which the soil began to develop. It is only present if the material has not been transported. Little to no weathering occurs here and there are no plant roots present.
Soils also develop from…?
material that has been transported into the area
what are residual soils?
formed from the material that was originally there – such as bedrock
what are transported soils?
formed from material that has been transported in to the region such as glacial material (till, and outwash, and loess)
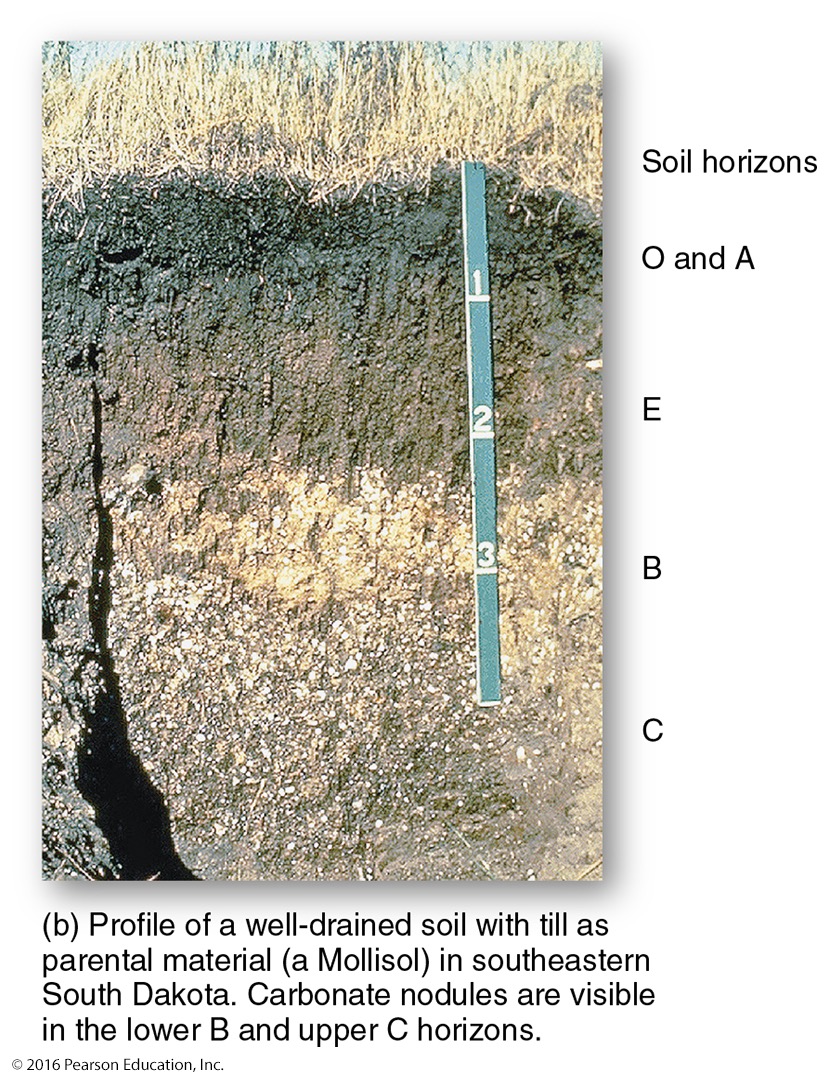
what kind of soil does Illinois have?
transported soils, and they are called mollisols