Hypersensitivity and Precipitation / Agglutination
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Hypersensitivity
Adverse effects of immune system that can result in ilness
Type 1 hypersensitivity
IgE mediated hypersensitivity or immediate
Anaphylaxis - against protection
Local - hay fever or hives
IgE stimulates basophils and mast cells = degranulate
Systemic - contractions, decreased BP, organ failure
Type 1 examples
Insect stings - heymenopterae - ants, bees, wasp
Haptens - RXN when bound to protein
Type 1 treatment
Vasopressor
Bronchodilator - theophylline
Epi pens
Type 1 mediator release
Activation of platelets, neutrophils, and eosinophils release histamine
Type 1 atopy
hay fever or asthma; hypersensitivity reaction with genetic predisposition
Type 1 ImmunoCap
Measures total IgE against a specific allergen, skin test
Type II hypersensitivity
IgG or IgM mediated or cytotoxic response
Ig reacts with cell-associated antigen, causing complement to be activated
Immediate transfusion RXN
HDFN
Treatment of some drugs
AIHA (Autoimmune hemolytic anemia)
Type III hypersensitivty
Immune complex formation
Soluble antigen + soluble antibody (primarily IgG) form a precipitate
Complexes formed activating complement and causing inflammation
Immune complex glomerulonephritis, SLE, Rheumatoid arthritis
Type IV hypersensitivity
T cell mediated, Delayed T cell hypersensitivity, 48 - 72 hours after exposure
No antibodies involved
Prev exposed T cells come in contact with antigen
Type IV examples
Release of cytokines
Contact dermatitis = poison ivy
Tuberculin reaction = Patch test, skin test
Precipitation
Soluble antigen + soluble antibody joins to form an insoluble precipitate
Ouchterlony
Radial immunodiffusion
Aspergillus
Ouchterlony
Double diffusion of Antigen and Antibody, nothing in gel
Identity
Partial identity
Non-identity
Identity
Two antigens are immunologically identical
Partial identity
Determinants present in one antigen but lacking in the other, one “spur”
Non-identity
None of the antibodies in the serum react with antigenic determinants that may be present in both the antigens,
Two antigens are immunologically unrelated as far as that antiserum is concerned
Radial immunodiffusion
Quantitative, single diffusion
Ring is proportional to the concentration of the antigens
ANTIGEN in the well diffusing outward
GEL contains antibody conc.
Agglutination
Particulate antigen combining with antibody to form a particle clump
Particulate cary antigens 100-1000 times larger than antibody
IgM are best agglutinates, very sensitive
Precipitation
Soluble antigens + soluble antibodies = insoluble
IgG are best precipitators
More specific than agglutination
Direct agglutination
Cold agglutinins, Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Antigen ON the RBCs, at 0-20C (I blood group)
Single significant titer of 1:32 or fourfold rise in titer
Must keep warm
Indirect or Passive agglutination
Carrier for antigen on latex or manufactured RBCs, looking for antibodies
TPO antibodies
Rheumatoid factor = Usually IgM Ab to Fc portion of human IgG
CCP more useful than RF
Tanned RBCs
Hemagluttination
Indirect agglutination
Absorb antigens
Hashimotos
Indirect agglutination
TPO elevated with 90%
Thyroglobulin elevated with nearly all
Hypothyroidism,
stimulation of B cells—> plasma cells produce antibodies to destroy thymocytes + activate CD8 T cells
Graves
TPO elevated with 75%
Thyroglobulin elevated in 70%
Antibodies attach toTSH receptors = unlimited production = hyperthyroidism
Rheumatoid factor
Latex, Antibody against FC portion of IgG
Frequent in women 30-50 y/o
Latex particles are coated with human IgG antigen, 1:6 dilution
Rheumatoid factor increased in
Elderly, sarcoidosis, SLE, Sjogren’s syndrome, hepatitis, cancer, tuberculosis, syphilis
Rheumatoid factor confirmatory test
CCP (cyclic citrullinated protein) more specific for diagnosis of RA
Reverse passive agglutination
FC portion of antibody attached to carrier - latex
Detects soluble antigen
Cryptococcus neoformans
Looking for antigen
Agglutination inhibition
Inert hapten coated particles + specific antisera
Patient sera added to antisera then hapten added
Looking for antigen, presence of antigen prevents clumping
No agglutination = +ve
HIA Hemagglutination inhibition assay
Patient serum is mixed with a standardized amount of antigen.
The titer of the patient’s serum is the highest dilution that blocks agglutination

Syphilis
Treponema pallidum
Primary chancre - 1-5 weeks
Secondary - 6-8 weeks after chancre, swollen lymphs
Tertiary - 10-30 years = cardiac, CNS
Syphilis microscope
Darkfield microscope, spirochetes
Non treponemal testing
Looking for antibody to reagin
Byproduct of cell damaged and breakdown of lipids (cardiolipin) = body produces antibody (reagin)
VDRL = beef cardiolipin, cholesterol, and lecithin
Heat inactivated serum or CSF = destroy complement
Looking for flocculation
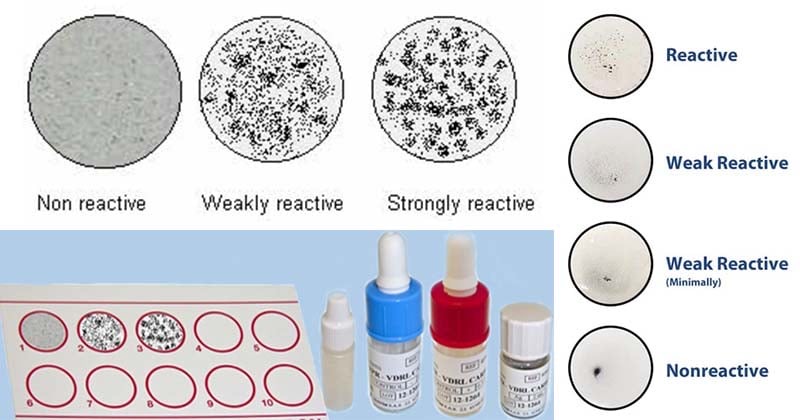
RPR Rapid plasma reagin
Non-treponemal testing
Cardiolipin, chlone chloride, EDTA, and charcoal
Swirl and look for tail
Plasma or serum no heat inactivation
CANNOT USE CSF
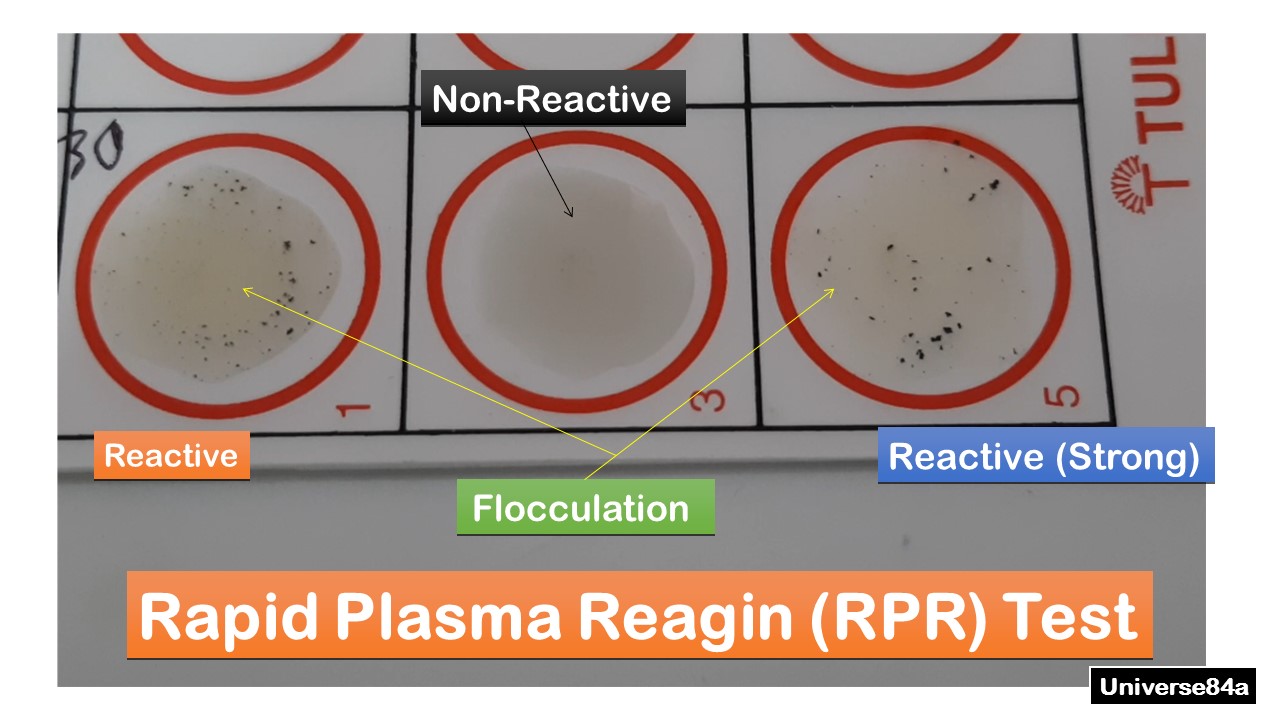
RPR false positive
Other treponemal infections, SLE, RA, acute viral disease, immunizations, pregnancy, old age
Treponemal testing
Detect direct antibodies to Treponema pallidum
FTA - ABS
TPPA
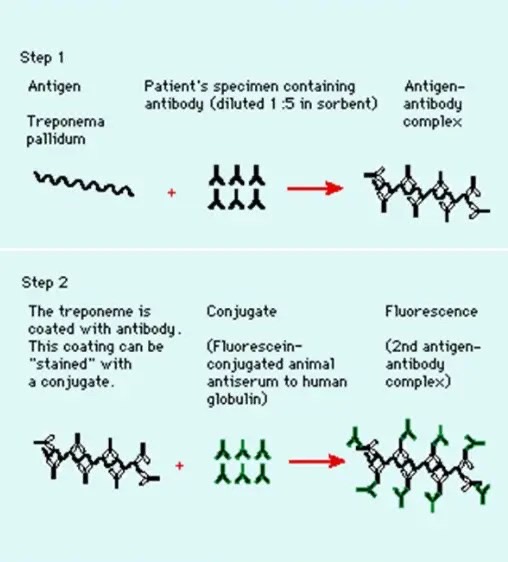
FTA-ABS Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption
Reiters strain removes non specific Ab (non pathogenic)
Nicholas strain - pathogenic, specific antibodies to syphillus
Antibody-Antigen complex = glow
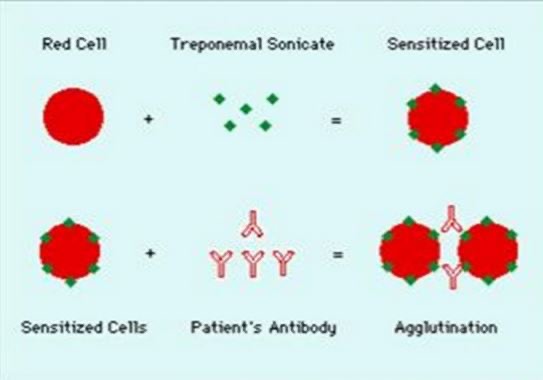
TPPA treponema pallidum particle agglutination
Antigen attached to stained gelatin particles
Reactive = +ve in TP well and negative in control = +ve antibody