Veterinary Parasitology CH5 - Class Cestoda
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study material for Chapter 5 of Diagnostic Parasitology for Veterinary Technicians. For class BIO225 at MWCC.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Phylum Platyhelmenthes (flatworms) contains…
Trematodes and Cestodes
Trematodes and Cestodes are also called what?
Flukes and Tapeworms
True or false: Flatworms are dorsoventrally flattened?
True
What shape are flukes?
Leaf shaped
What shape are tapeworms?
Ribbon-like and segmented into proglottids
The two classes of cestodes are…
Eucestoda (true tapeworms) and Cotyloda (pseudotapeworms)
Anterior end of cestodes is called…
Scolex or head
The four suckers of cestodes are called…
Acetabula
What is the function of the acetabula?
Hold on to intestinal linging
True or false: Cestodes only attach, they do not take blood meals
True
Where do cestodes absorb nutrients from the host intestine?
Through their skin/tegument
Proglottids closted to the neck are sexually…
Immature
Proglottids intermediate distance away from the neck are sexually…
Mature
Gravid proglottids furthest away from the neck
Sex organs are old and “spent”, only remaining part is uterus filled with eggs
True or false: Cestodes are hermaphroditic
True
Each proglottid contains…
Both male and female reproductive organs
Cestodes’ sex organs are on what side of their proglottids?
Lateral sides
What is the difference between cross-fertilization and self-fertilization?
Cross-fertilization: Between two proglottids
Self-fertilization: Within one proglottid
Gravids contain what stage of egg? What is it called and why?
Larval stage - Hexacanth because it has 6 hooks
The four types of gravid eggs are…
Pyriform apparatus
Dipylidium
Taenia
Pseudophyllidium
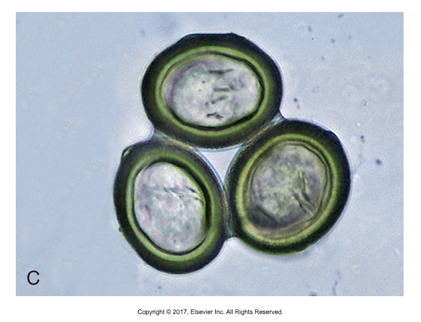
Pyriform egg type
Pear shape innermost layer of 3 egg coverings
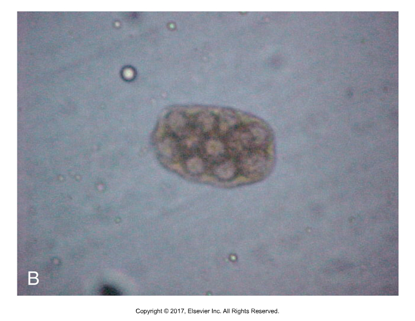
Dipylidium egg type
Multiple hexacanths in one egg
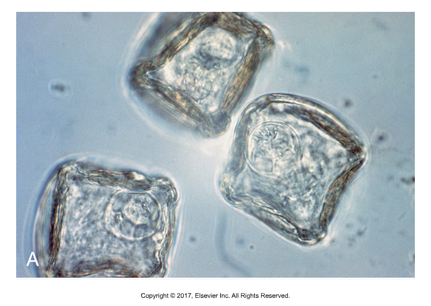
Taenia egg type
Thicker outer shell, hexacanth in egg
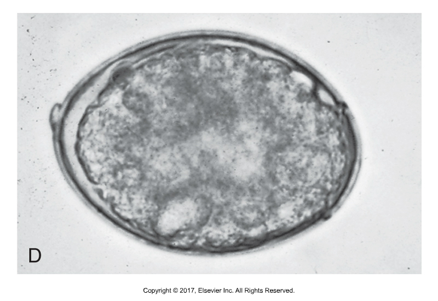
Pseudophyllidium egg type
Operculum at one end, hexacanth inside
Life cycle of tapeworms
Gravids pass in feces into environment
Rupture and release hexacanth embryos (eggs)
Eggs must be swallowed by intermediate host, depending on species can be vertebrate or invertebrate
Develop in intermediate host to larval metacestode stage
Definitive host ingests intermediate host
Juvenile emerges from metacestode state and attaches to intestine, begins to produce strobila
Proglottids have muscles and can move, can find in feces, hair coat or bedding of infected animal
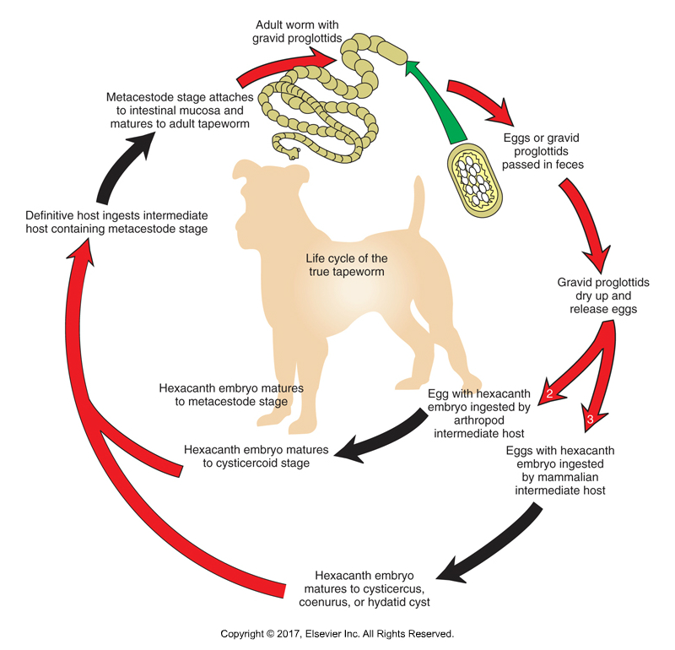
Metacestode forms
Hydatid cyst: A fluid-filled sac that forms in the body as a result of infection by the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus
Cysitcercus: If intermediate host is mammal (rabbit). Example: Taenia pisiformis (dog)
Coenurus: Multiceps multiceps
Tetrathyridia: Larval stage of certain tapeworms, resembling an elongated form with an invaginated scolex at one end
Cysticercoid: If intermediate host is arthropod (flea or mite). Examples: Dipyllidium caninum (dogs and cats), Thysanosoma actinoides (cattle)
Class Cotyloda, also know as…
Pseudotapeworms
What shape are pseudotapeworms?
Long, segmented, flattened, ribbon-like
True or false: Pseudotapeworms have an anterior scolex
True
Pseudotapeworms have 2 slit-like grooves along the length of the scolex called what?
Bothria
What is the function of the bothria?
Helps them attach to intestinal lining
Strobila are made of…
Immature, mature and gravid proglottids
True or false: Pseudotapeworms are hermaphroditic
True
Pseudotapeworms sex organs are located where in proglottids?
Centrally
Pseudotapeworm eggs are operculated, which means…
They have one flat end of the egg that acts as a lid
Where do their operculated eggs exit?
Through uterine pore
Pseudotapeworm gravids tend to…
Drop off in long chains
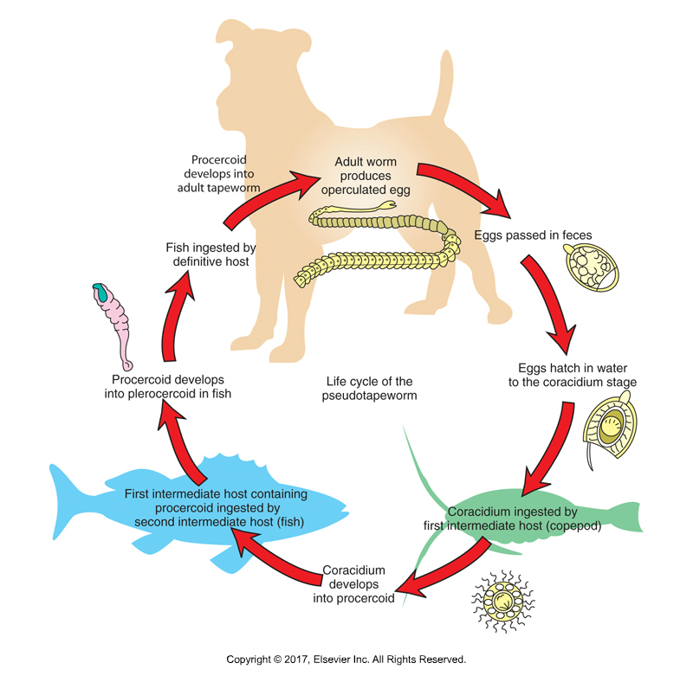
Lifecycle of pseudotapeworms
Operculated eggs pass into environment
If in water, eggs hatch, release ciliated hexacanth embryo—coracidium out of operculum
Must be ingested by first intermediate host, a tiny crustacean copepod
Inside copepod, coracidium becomes procercoid
When copepod is ingested by second intermediate host, a fish, develops into second infective plerocercoid stage
Definitive host is infected by ingesting fish, plerocercoid develops into juvenile worm and attaches to intestinal lining, builds strobili
The common name of Dipyllobothrium latum is what?
Broad fish tapeworm
The common name of Spirometra mansonoides is what?
Zipper tapeworm